Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Terminology of Coordination Compounds CARCELLAR
Terminology of Coordination Compounds CARCELLAR
Uploaded by
JOHNERROL CARCELLAROriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Terminology of Coordination Compounds CARCELLAR
Terminology of Coordination Compounds CARCELLAR
Uploaded by
JOHNERROL CARCELLARCopyright:
Available Formats
I.
OBJECTIVES
A. Content Standard Terminology of Coordination Compound
B. Performance
Standard
C. Learning Students will be able to define and apply key terminology related to
Competencies coordination compounds.
D. Instructional
Objectives
Values Integration: Creativity, Critical Thinking Skill and Cooperation
II.CONTENT Balancing Redox Equation Using Oxidation Number and Half Reaction
method.
III.LEARNING
RESOURCES
A. References
1. Teacher’s Guide
pages
2. Learners’ Materials
pages
3. Textbook pages
4. Additional materials
from learning
resource (LR) portal
B. Other Learning
Laptop, projector, board marker
Resources/Materials
IV.PROCEDURES
ELICIT
Objective: Stimulate prior knowledge and capture students interests by
prompting them to share their existing understanding of the topic.
Teacher: Good day, class! Let’s start by discussing what comes in to your
mind when you hear the term “coordination compound”, what do you
already know about them? Feel free to share your thoughts, or you can
write down key terms on the board.
ENGAGE
Objective: Foster curiosity and create an emotional connection to the subject
matter. Present content in a way that captivates student, making them eager
to explore and learn more.
Teacher: Imagine you’re a scientist studying the human body. How do
coordination compounds play role in transporting oxygen through our
bloodstream? Let’s discuss the significance of coordination compound in
real-world scenarios.
EXPLORE
Objective: Encourage hands-on experiences or activities that allow students
to directly interact with the concept. This promotes active learning and
deeper understanding of the material.
Teacher: I’ve handed out a list of common coordination compound terms –
ligands, coordination number, central atoms, coordination sphere, etc. In
your houses, go through these terms, discuss their meanings, and use any
available resources to deepen your understanding.
EXPLAIN
Objectives: Provide clear and concise explanation of key concepts.
Teacher: Let’s delve into the core of coordination compounds. I’ll provide a
brief lecture explaining each term. Pay close attention, and don’t hesitate to
ask question. We’ll use visuals and examples to make these concepts more
tangible.
ELABORATE
Objectives: Facilitate higher-order thinking by challenging students to apply
their knowledge in different context. Group discussion, case studies or
problem-solving activities help reinforce and extend their understanding.
Teacher: Time to apply what we’ve learned! I have a few scenarios and case
studies for you. Work in your group to analyze how different ligands and
coordination numbers impact the properties of coordination complexes.
Discuss and share your findings with the class.
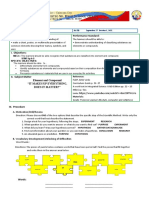
Quiz:
EVALUATE
Test I. Matching type
A B
1. A chemical compound in which the central A. Central atoms/ions
ion or atom is bound to a set number of atom is
called
2. The atoms, molecules or ions that are bound B. Coordination Entity
to the coordination center are referred to as
3. Refers to the total sigma bond through which C. Coordination
the ligands are bound to the coordination Numbers
center
4. Atoms and ions to which a number of atoms, D. Ligands
molecules, are bound are refers to as
5. The non-ionizable part of complex E. Coordination Sphere
compound.
Test II. Modified True or False
Direction: Write TRUE if the underlined word is correct and FALSE if its
incorrect and change it the correct answer.
1. Coordination compounds are chemical compounds that consists of an
array or anions or neutral molecules that are bound to a central atom via
ionic bond.
Answer: FALSE / Coordinate covalent bonds
2. The geometric shape formed by the attachment of the ligands to the
coordination center is called “Lewis structure”
Answer: FALSE / Coordination polyhedron
3. When the coordination center is bound to only one type of electron
pair donating ligand group, the coordination complex is called a
heteroleptic complex.
Answer: FALSE / homoleptic complex
4. When the central atom is bound to many different types of ligands,
the coordination compound in question is called heteroleptic complex.
Answer: TRUE
5. In coordination compounds, the central atoms or ion are typically
Lewis Base
Answer: FALSE / Lewis Acid
EXTEND Objectives: encourage continued exploration and application of the topic
beyond the classroom.
Teacher: For homework, I want you to explore, real-life application of one
or more coordination compound term. Write short paragraph explaining
their significance in practical solution.
V.REMARKS
VI.REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who
earned 80% in the
evaluation
B. No. of learners who
require additional
activities for remediation
C. Did the remedial work?
No. of learners who have
caught up with the lesson
D. No. of learners who
continue to require
remediation
E. Which of my teaching
strategies worked well?
Why did this work?
F. What difficulties did I
encounter which my
principal or supervisor can
help me solve?
G. What innovation or
localized materials did
you used /discover which
I wish to share with other
teachers?
Prepared by: Checked by: Reviewed:
NOTED:
____________________
Observer
You might also like
- ReSA B44 FAR First PB Exam Questions Answers SolutionsDocument17 pagesReSA B44 FAR First PB Exam Questions Answers SolutionsWesNo ratings yet
- Topic Sentence and Supporting DetailsDocument3 pagesTopic Sentence and Supporting DetailsAlfeo OriginalNo ratings yet
- Daedalus and IcarusDocument5 pagesDaedalus and IcarusMichael GreenNo ratings yet
- Paul Foster Case - 32 Paths Lessons 1-17 - 1950 PDFDocument316 pagesPaul Foster Case - 32 Paths Lessons 1-17 - 1950 PDFGracchus Dionysus100% (20)
- Le 1Document5 pagesLe 1jingvillaruelNo ratings yet
- Learner's Activity Sheet Assessment ChecklistDocument12 pagesLearner's Activity Sheet Assessment ChecklistracmaNo ratings yet
- RW Co3Document5 pagesRW Co3Wawa ManNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesLesson PlanAdisti FernandaNo ratings yet
- COT 1 - ConjunctionsDocument3 pagesCOT 1 - ConjunctionsEnglish Department100% (1)
- SCIENCE 7 DLP For Class Observation (1st Quarter)Document3 pagesSCIENCE 7 DLP For Class Observation (1st Quarter)Malixi Integrated School (CARAGA - Surigao del Sur)No ratings yet
- Activity 1: Finding An ExampleDocument4 pagesActivity 1: Finding An ExampleMemai L100% (4)
- Eng.5 Second CODocument5 pagesEng.5 Second COMarie Cleofe EmbalzadoNo ratings yet
- LP Coherence and CohesionDocument7 pagesLP Coherence and CohesionHazel Mae DoydoraNo ratings yet
- Le 1Document5 pagesLe 1jingvillaruelNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Assessment of Grammar Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan I. ObjectivesDocument7 pagesTeaching and Assessment of Grammar Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan I. ObjectivesSavar GrayNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Co 2Document6 pagesLesson Plan - Co 2JaysonNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Conjunctions in Spoken Texts LPDocument4 pagesGrade 10 Conjunctions in Spoken Texts LPJoshua Lander Soquita CadayonaNo ratings yet
- CONJUNCTIONDocument9 pagesCONJUNCTIONsoumick bhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Science 4th QTR CotDocument4 pagesScience 4th QTR Cotsofia gamer girlNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Example (BRAIN-BASED)Document4 pagesLesson Plan Example (BRAIN-BASED)Fermin Fedillaga Celada Jr.100% (1)
- Q2w4-Dll-Maricel GonzalesDocument4 pagesQ2w4-Dll-Maricel GonzalesMaricel Ceyh GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Philo Week 2Document3 pagesPhilo Week 2Abe King PedronanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English 12: Pre-Test in English For Academic and Professional PurposesDocument9 pagesLesson Plan in English 12: Pre-Test in English For Academic and Professional PurposesAngeline Limbaga TrayfalgarNo ratings yet
- Edoc - Pub Grade 10 Science DLL q3 Week 3Document5 pagesEdoc - Pub Grade 10 Science DLL q3 Week 3Geraldine Pascua CardenasNo ratings yet
- The Teacher and The School CurriculumDocument13 pagesThe Teacher and The School CurriculumGiane Gayle CadionNo ratings yet
- September 4-8 2-2023 Tr. Delaila Medina 1Document16 pagesSeptember 4-8 2-2023 Tr. Delaila Medina 1Delaila MedinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document7 pagesLesson 2J Rymnd Oayalos100% (1)
- LP CombinationDocument7 pagesLP CombinationSandy Manligro NaingueNo ratings yet
- March 13Document3 pagesMarch 13Queenvierlyn RupidoNo ratings yet
- A. Content Standards: I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesA. Content Standards: I. ObjectivesGladys Jane OlanonNo ratings yet
- DLP 3RDDocument6 pagesDLP 3RDnyxsursheeyaNo ratings yet
- Cot 2 English 6 ConjunctionsDocument6 pagesCot 2 English 6 ConjunctionsMaryjane Tolero100% (1)
- I. Objectives: Grade 8 Daily Lesson LOG Region Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDocument3 pagesI. Objectives: Grade 8 Daily Lesson LOG Region Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterBongskie escalonaNo ratings yet
- Demo DLL-Q1-WEEK-7-ENGLISH-4Document5 pagesDemo DLL-Q1-WEEK-7-ENGLISH-4ELAINE ARCANGELNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 6 Week1Document7 pagesSCIENCE 6 Week1ellen joy gulamNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Eapp Academic Reading StrategiesDocument8 pagesWeek 2 Eapp Academic Reading StrategiesMA. luisa ECHANONo ratings yet
- Philo Week 1Document3 pagesPhilo Week 1Abe King PedronanNo ratings yet
- DLP in Compound SentencesDocument4 pagesDLP in Compound SentencesLorna Caronan Caylaluad100% (2)
- 4as Detailed Lesson Plan Final FormatDocument3 pages4as Detailed Lesson Plan Final FormatAllen BianzonNo ratings yet
- Science 5 - Chemistry Unit PlanDocument23 pagesScience 5 - Chemistry Unit Planapi-484413318No ratings yet
- DLL SynthesizingDocument8 pagesDLL SynthesizingErlene CardonaNo ratings yet
- English 6-Q4-L5 ModuleDocument14 pagesEnglish 6-Q4-L5 ModuleAngelo Jude CobachaNo ratings yet
- DLP - 9Document3 pagesDLP - 9Hezl Valerie Arzadon100% (1)
- Biñan Secondary School of Applied Academics 10 Patrick James R. Pelicano January 24, 2019/ 11:30 - 12:30 4thDocument4 pagesBiñan Secondary School of Applied Academics 10 Patrick James R. Pelicano January 24, 2019/ 11:30 - 12:30 4thPatrick Pelicano100% (1)
- Learning Guide Ep 2Document34 pagesLearning Guide Ep 2Ged RocamoraNo ratings yet
- 4as Q1 English 5 Using Compound SentenceDocument10 pages4as Q1 English 5 Using Compound SentenceMei MCNo ratings yet
- Efap w4Document3 pagesEfap w4Jane Daming AlcazarenNo ratings yet
- GENCHEM1-12-Q1-WEEK2-MELC08-Oaquera-Jessie - Marissa AreolaDocument17 pagesGENCHEM1-12-Q1-WEEK2-MELC08-Oaquera-Jessie - Marissa AreolaYer Bal80% (5)
- Field Study 1 Learning EpisodeDocument90 pagesField Study 1 Learning EpisodeRoxanne DelezNo ratings yet
- Q4 Feb14wk5EngDocument4 pagesQ4 Feb14wk5EngCher ChaNo ratings yet
- DLL Co 1 English 8Document6 pagesDLL Co 1 English 8Jean Olbes ChavezNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document4 pagesModule 4Rosalie A. GuiananNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - DLL For July 16 2019Document2 pagesMicrosoft Word - DLL For July 16 2019Marilyn LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document6 pagesChapter 2Martimonica SolivenNo ratings yet
- Cooperative Learning Lesson Plan 542Document6 pagesCooperative Learning Lesson Plan 542api-347023972No ratings yet
- R. Nadao DLP-Science 7 Module 3 Week 3Document4 pagesR. Nadao DLP-Science 7 Module 3 Week 3ROWENA NADAONo ratings yet
- DLP - Classification of MatterDocument6 pagesDLP - Classification of MatterInah Cunanan-BaleteNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English 8Document4 pagesLesson Plan in English 8rozzeille jyne geraldez0% (1)
- DLL Per - Dev.Document2 pagesDLL Per - Dev.Yasu HamNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument258 pagesUntitledPrince Joshua BumanglagNo ratings yet
- Tingog Smart 2024Document156 pagesTingog Smart 2024JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
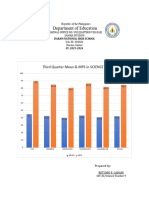
- Third Mean and Mps Word GraphDocument2 pagesThird Mean and Mps Word GraphJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q4 Mod8.2Document7 pagesSci9 Q4 Mod8.2JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Secondary Student Teachers Internship AssignmentDocument4 pagesSecondary Student Teachers Internship AssignmentJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument11 pagesProjectile MotionJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- SSU OVPAA FR 018 Course Syllabus Sci6Document11 pagesSSU OVPAA FR 018 Course Syllabus Sci6JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- PP John ObjectiveDocument1 pagePP John ObjectiveJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument13 pagesAssessmentJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Questions For ExaminationDocument4 pagesQuestions For ExaminationJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument6 pagesQuizJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Carcellar PictoDocument15 pagesCarcellar PictoJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Arrangement of Star in Group-1Document11 pagesArrangement of Star in Group-1JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- LP 4 Sci 6 Inorganic ChemistryDocument11 pagesLP 4 Sci 6 Inorganic ChemistryJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Rationalization of The 1st Pretest in CE1Document51 pagesRationalization of The 1st Pretest in CE1JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- DLP CarcellarDocument8 pagesDLP CarcellarJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- DLP Carcellar 1Document14 pagesDLP Carcellar 1JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- In Campus Fs 2 Summary of RatingsDocument2 pagesIn Campus Fs 2 Summary of RatingsJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- PROF ED 9 UNIT 4 5 StudentsDocument18 pagesPROF ED 9 UNIT 4 5 StudentsJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 8 LP4 2Document13 pagesProf Ed 8 LP4 2JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Science 7Document2 pagesScience 7JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis North Korea Jessa AngelicaDocument6 pagesComparative Analysis North Korea Jessa AngelicaJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Development Models and Designs AutosavedDocument45 pagesCurriculum Development Models and Designs AutosavedJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Organizational LeadershipDocument26 pagesOrganizational LeadershipJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- PBL InstrumentDocument1 pagePBL InstrumentJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- REFLECTIONDocument2 pagesREFLECTIONJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Great Books 1001Document7 pagesGreat Books 1001JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- LP 4 FINAL Waves and OpticsAutosaved Copy 1Document15 pagesLP 4 FINAL Waves and OpticsAutosaved Copy 1JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Enzyme MechanismDocument3 pagesEnzyme MechanismJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- LP2 SCI-12 MICROBIO LABORATORY-fINALDocument21 pagesLP2 SCI-12 MICROBIO LABORATORY-fINALJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Learning Packet 1 Unit 1 Prof - Ed.7Document15 pagesLearning Packet 1 Unit 1 Prof - Ed.7JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Syah SemangkaDocument9 pagesJurnal Syah SemangkaDian PuspitaNo ratings yet
- 400 Bad Request 400 Bad Request Nginx/1.2.9Document4 pages400 Bad Request 400 Bad Request Nginx/1.2.9muthuswamy77No ratings yet
- October Sky ThesisDocument8 pagesOctober Sky Thesisfc4zcrkj100% (2)
- For mRNA Vaccines, COVID-19 Is Just The BeginningDocument3 pagesFor mRNA Vaccines, COVID-19 Is Just The BeginningMike ReyesNo ratings yet
- 1 GENERAL NOTES MergedDocument23 pages1 GENERAL NOTES MergedLaedyn Faye IsipNo ratings yet
- View ItineraryDocument1 pageView ItineraryAbhishek NareshNo ratings yet
- IBM Blockchain Hands-On Hyperledger Composer PlaygroundDocument32 pagesIBM Blockchain Hands-On Hyperledger Composer PlaygroundPushpamNo ratings yet
- Rules For Reading The Dasamsa ChartDocument7 pagesRules For Reading The Dasamsa ChartV Narayan Rao60% (5)
- SCDD RTIManualDocument187 pagesSCDD RTIManualMohd Sohail AliNo ratings yet
- Resolute Electronics: Quotation Quotation No: Quotation DateDocument1 pageResolute Electronics: Quotation Quotation No: Quotation DatePANCHATCHARAM SNo ratings yet
- Etsi DMR ProtocoloDocument177 pagesEtsi DMR ProtocoloIvan Flores MelchorNo ratings yet
- Amity School of BusinessDocument34 pagesAmity School of BusinessYash MittalNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 2nd Quarter Module 6 Mole Concept FinalizedDocument24 pagesGrade 9 2nd Quarter Module 6 Mole Concept FinalizedAkisha Jen Calicdan100% (2)
- Victor Kilui Wabwile Final ThesisDocument76 pagesVictor Kilui Wabwile Final ThesisarzaianNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1Document4 pagesWorksheet 1KouNo ratings yet
- Pengetahuan Wirausaha Dan Minat Berwirausaha Pada Siswa SMK: Sahade Dan M. Yusuf A. NgampoDocument6 pagesPengetahuan Wirausaha Dan Minat Berwirausaha Pada Siswa SMK: Sahade Dan M. Yusuf A. NgampoFani Rachmawaty Putri, S.Pd (Guru)No ratings yet
- Theo 141 Final PDFDocument8 pagesTheo 141 Final PDFlrpongNo ratings yet
- A - Topic - Divide and Conquer - GeeksforGeeksDocument7 pagesA - Topic - Divide and Conquer - GeeksforGeeksNiraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical SpillDocument33 pagesChemical SpillKodeChandrshaekharNo ratings yet
- Cornell University, School of Industrial & Labor RelationsDocument3 pagesCornell University, School of Industrial & Labor RelationsZana S. NajmaddinNo ratings yet
- INSOFE-Comprehensive Curriculum On Big Data AnalyticsDocument11 pagesINSOFE-Comprehensive Curriculum On Big Data AnalyticslokssaNo ratings yet
- 3.2.4 Thin Converging LensDocument5 pages3.2.4 Thin Converging LensPeterMwagweNo ratings yet
- What Is Narrative ParagraphDocument3 pagesWhat Is Narrative ParagraphAnderson LeonNo ratings yet
- Authentic Assessment OverviewDocument5 pagesAuthentic Assessment Overviewdzakwan13No ratings yet
- ProvisionsDocument5 pagesProvisionsAngelshine LacanlaleNo ratings yet
- 06 TheCPUAndMemoryDocument34 pages06 TheCPUAndMemoryAkbar BadhushaNo ratings yet
- FDocument36 pagesFBrezeanu CatalinaNo ratings yet
- Fm1 Funktion eDocument67 pagesFm1 Funktion eRafaelNo ratings yet