Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Binomial Theorem: All 2023 PYQ in CBT and PDF Format
Uploaded by
bhadusagar50 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesBinomialtherorem maths
Original Title
bin
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBinomialtherorem maths
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesBinomial Theorem: All 2023 PYQ in CBT and PDF Format
Uploaded by
bhadusagar5Binomialtherorem maths
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Binomial Theorem
All 2023 PYQ in CBT and PDF Format
https://t.me/vedantumath1/3938
Click on the above Link
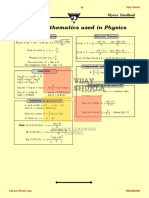
Definition
If a, b ∈ R and n ∈ N, then
(a + b)n = nC0anb0 + nC1an-1b1 + nC2an-2b2+.......+ nCn a0bn
• Remarks: If the index of the binomial is n then the
expansion contains n + 1 terms. Binomial Theorem
• in each term, the sum of indices of a and b is always n.
• Coefficients of the terms in binomial expansion equidistant
from both the ends are equal.
(a - b)n = nC0anb0 - nC1an-1b1 + nC2an-2b2+.......+ (-1)n nCn
a0bn
General and middle terms in the expansion of
(a+b)ⁿ
The general term of an expansion (a+b)n is Binomial Theorem for any index
Tr+1 = nCr a n-rbr, 0 ≤ r ≤ n, r ∈ N If n is negative integer, then n! Is not defined. We state
Middle Terms: binomial theorem in another form
1. In(a + b)n, if n is even, then the no. of terms in the
expansion is odd.
Therefore, there is only one middle term and it is
(n+2/2)th term.
2. In (a + b)n, if n is odd then the no. of terms in the
expansion is even. Therefore, there are two middle
terms and those are (n+1/2)th and (n+3/2)th terms.
Binomial Coefficients
The coefficient nC0, nC1, nC2, ……… nCn, in the expansion of
(a + b)n are called binomial coefficients and denoted by C0,
C1, C2 ……………. Cx, respectively.
Properties of binomial coefficients: Binomial Theorem
Some special cases of (a+b)ⁿ
In the expansion of (a + b)n,
(i) Taking a = x and b = -y, we obtain
(x - y)n = nC0xn - nC1xn-1 y + nC2 xn-2 y2 + …… + (-1)n nCn
n
y
(ii) Taking a = 1, b = x, we obtain
(1 + x)n = nC0 + nC1x + nC2x2 + nC3x3 + ……… + nCnxn
(iii) Taking a = 1, b = -x, we obtain
(1 - x)n = nC0 - nC1x + nC2x2 + ……… + (-1)n nCnxn
You might also like
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem PDFDocument46 pagesBinomial Theorem PDFXyzzNo ratings yet
- BinomialDocument3 pagesBinomialNeha NehaNo ratings yet
- BIN - 11th (2019C) - EmbhbjkhjDocument28 pagesBIN - 11th (2019C) - Embhbjkhjroving9fantasyNo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem - Short Notes - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024Document1 pageBinomial Theorem - Short Notes - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024dushyantsiwach3263No ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem: (A) General Term: (B) For Greatest TermDocument1 pageBinomial Theorem: (A) General Term: (B) For Greatest Termvidyakumari808940No ratings yet
- Binomial TheoremDocument2 pagesBinomial TheoremM MeganathanNo ratings yet
- Binomial Expression: y X X Q X P y X B ADocument3 pagesBinomial Expression: y X X Q X P y X B AAnirudh karanamNo ratings yet
- Statement of Binomial TheoremDocument2 pagesStatement of Binomial TheoremA ListerNo ratings yet
- Statement of Binomial TheoremDocument1 pageStatement of Binomial TheoremArya NairNo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem PDFDocument18 pagesBinomial Theorem PDFparita adhiaNo ratings yet
- Binomial TheoremDocument43 pagesBinomial TheoremSiddhi AroraNo ratings yet
- BT Theory PDFDocument18 pagesBT Theory PDFEndla KishanNo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem Sheet PDFDocument12 pagesBinomial Theorem Sheet PDFprateek amrawanshiNo ratings yet
- BinomialDocument8 pagesBinomialr.n.mishra18505No ratings yet
- Binomial: MathematicsDocument4 pagesBinomial: MathematicsTanishq PancholiNo ratings yet
- Binomial UpdatedDocument22 pagesBinomial UpdatedvinayakkanchalNo ratings yet
- 1.basic Maths For PhysicsDocument4 pages1.basic Maths For Physicsupanshupandit3No ratings yet
- Theory EnglishDocument11 pagesTheory EnglishwanderedNo ratings yet
- Best Approach: Binomial TheoremDocument33 pagesBest Approach: Binomial TheoremShreyas Mishra100% (1)
- BinomialDocument8 pagesBinomialavni agarwalNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics: Formula That Are Within The Syllabus and Which Need To Be LearntDocument2 pagesAdditional Mathematics: Formula That Are Within The Syllabus and Which Need To Be LearntJames SimNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics (Formulas)Document2 pagesAdditional Mathematics (Formulas)Yousuf MemonNo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem Complete Chapter Notes For Iit Jee @iit Jee RankersDocument5 pagesBinomial Theorem Complete Chapter Notes For Iit Jee @iit Jee RankersganeshNo ratings yet
- Binomial TheoremDocument36 pagesBinomial TheoremAvishkar Jaiswal100% (1)
- Kerala HSE 12th Maths Model Question Paper 5Document8 pagesKerala HSE 12th Maths Model Question Paper 5TANEESH VARMMA SNo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem PDFDocument20 pagesBinomial Theorem PDFCybeRaviNo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem - SheetDocument33 pagesBinomial Theorem - SheettanmayNo ratings yet
- 3.binomial Theorem Theory Module-1Document13 pages3.binomial Theorem Theory Module-1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem: Chapter HighlightsDocument45 pagesBinomial Theorem: Chapter HighlightsAditya WanwadeNo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem, Exponential & Logarithmic Series-249 PDFDocument8 pagesBinomial Theorem, Exponential & Logarithmic Series-249 PDFSuravi Kusuma PradhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 - Binomial TheoremDocument3 pagesChapter 05 - Binomial TheoremaccesshanifNo ratings yet
- Class Note-M101 Module-II PDFDocument24 pagesClass Note-M101 Module-II PDFprince KumarNo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorum Question Bank PDFDocument17 pagesBinomial Theorum Question Bank PDFKAPIL SHARMANo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 1 - Mathematics For Physics PDFDocument50 pagesPhysics Chapter 1 - Mathematics For Physics PDFShweta JainNo ratings yet
- BinomialDocument8 pagesBinomialAkshatNo ratings yet
- BinomialDocument12 pagesBinomialRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Binomial TheoremDocument1 pageBinomial TheoremAditya NandaNo ratings yet
- Iia-5. Binomial TheoremDocument3 pagesIia-5. Binomial Theoremmonu991No ratings yet
- Class 11 Maths Revision Notes Binomial TheoremDocument8 pagesClass 11 Maths Revision Notes Binomial TheoremSharayu SunilNo ratings yet
- Complete Binomial TheoremDocument163 pagesComplete Binomial TheoremSiddhant YadavNo ratings yet
- Binomial Theorem PDFDocument3 pagesBinomial Theorem PDFRaju Sharma0% (1)
- Binomial 11th 2018K EDocument24 pagesBinomial 11th 2018K Erobin bhandariNo ratings yet
- Definite Integral and Its Application: First Year of Engineering Program Department of Foundation YearDocument38 pagesDefinite Integral and Its Application: First Year of Engineering Program Department of Foundation YearChhin HoutNo ratings yet
- Problem Set (Headstart AY2022)Document7 pagesProblem Set (Headstart AY2022)Wei Ting ChuiNo ratings yet
- Vector and Calculus: Sin Sin SinDocument2 pagesVector and Calculus: Sin Sin SinAyush TiwariNo ratings yet
- Iia-5. Binomial TheoremDocument3 pagesIia-5. Binomial TheorempjaindakNo ratings yet
- Calculus:Nth Differential Coefficient of Standard FunctionsDocument14 pagesCalculus:Nth Differential Coefficient of Standard Functionsap021100% (5)
- Binomial Theorem-Jee (Main)Document19 pagesBinomial Theorem-Jee (Main)Resonance Dlpd76% (76)
- Binomial Theorem+ P& C BOOKLET Final - 08.10.20 Without AnsDocument96 pagesBinomial Theorem+ P& C BOOKLET Final - 08.10.20 Without AnsShibhaditya DohareNo ratings yet
- Classwork-15 1 Solution To The HomeworksDocument6 pagesClasswork-15 1 Solution To The HomeworksSeekerNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Induction and Binomial TheoremDocument28 pagesMathematical Induction and Binomial TheoremNIGHT THINKERNo ratings yet
- Y X C y X CDocument12 pagesY X C y X CK.Prasanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Formula: Topic Phase-3Document12 pagesMathematics Formula: Topic Phase-3testerNo ratings yet
- Notes On Succesive DifferntiationDocument14 pagesNotes On Succesive Differntiationloveshot844No ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Productivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionFrom EverandProductivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 2Document8 pagesCbse Class 2Amitoj SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Special Products & FactoringDocument17 pagesChapter 2 Special Products & FactoringMichael Racelis78% (9)
- HL MathsDocument425 pagesHL MathsBalageeon100% (1)
- Algebra (Refresher)Document46 pagesAlgebra (Refresher)Felix Violeta100% (1)
- Assignment-3: Sol Private Sub Command1 - Click Dim I As Integer For I 1 To 50 Print I Next I End SubDocument24 pagesAssignment-3: Sol Private Sub Command1 - Click Dim I As Integer For I 1 To 50 Print I Next I End SubNitin GroverNo ratings yet
- Gr6 Revision Answer Key Worksheet - PT1-June 2020Document5 pagesGr6 Revision Answer Key Worksheet - PT1-June 2020Umer FarooqNo ratings yet
- 10 Maths Test Paper ch1 1Document8 pages10 Maths Test Paper ch1 1aruba ansari0% (1)
- Definition of Perfect Number or What Is Perfect NumberDocument11 pagesDefinition of Perfect Number or What Is Perfect NumberRajjak SayedNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1-HandoutsDocument3 pagesAlgebra 1-HandoutsBarb BarianNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Modular ArithmeticDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Modular ArithmeticKiesha SantosNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Schools Division of Quirino Maddela District IiDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Schools Division of Quirino Maddela District Iianon_774161618No ratings yet
- Infinite SeriesDocument30 pagesInfinite SeriesBasu BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- RD SharmaDocument1,000 pagesRD SharmaBhargavi Patil100% (2)
- Integral of Jinc SquaredDocument4 pagesIntegral of Jinc Squaredkris7o2No ratings yet
- Grade 7/8 Math Circles Continued Fractions A Fraction of Our HistoryDocument23 pagesGrade 7/8 Math Circles Continued Fractions A Fraction of Our HistoryJaydeep GhoshNo ratings yet
- Pre RMO Previous Year Question Paper 2019 (11th Aug)Document9 pagesPre RMO Previous Year Question Paper 2019 (11th Aug)Siddharth SinghNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Numbers and Algebraic IntegersDocument16 pagesAlgebraic Numbers and Algebraic IntegersEhab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Rmo-2009 Previous Year Question Papers of Regional Mathematical Olympiad With SolutionsDocument4 pagesRmo-2009 Previous Year Question Papers of Regional Mathematical Olympiad With SolutionsAkshay PandeyNo ratings yet
- Olimpiade Rangsangan PendekDocument2 pagesOlimpiade Rangsangan PendekMom's PrincessaNo ratings yet
- Articles For Quant: Handa KA FundaDocument55 pagesArticles For Quant: Handa KA FundaSparsh ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument6 pagesFormulasram poisonNo ratings yet
- Binary To Dec2Document2 pagesBinary To Dec2Rishu Singh100% (1)
- China Western Mathematical Olympiad 2010 63Document2 pagesChina Western Mathematical Olympiad 2010 63Nitin JainNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Inequalities, Modulus and LogarithmDocument3 pagesClass 11 Inequalities, Modulus and LogarithmkwonswaraNo ratings yet
- Which of The Following Are Sets? Justify Your AnswerDocument4 pagesWhich of The Following Are Sets? Justify Your AnswerSamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Lec07 LinearDiophEqnsDocument3 pagesLec07 LinearDiophEqnsJames MlotshwaNo ratings yet
- Mba Strategy Quant AdvancedDocument196 pagesMba Strategy Quant Advanced1111111111111-859751No ratings yet
- Number Theory Part TwoDocument3 pagesNumber Theory Part TwosanjivsingNo ratings yet
- Purple Comet Math Meet Look InsideDocument8 pagesPurple Comet Math Meet Look InsideShanmuga SundaramNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Terms in Two or More UnknownsDocument3 pagesAlgebraic Terms in Two or More UnknownsaefielNo ratings yet