Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Page Notes Current Electricity
Uploaded by
12th.topper.pcmOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Page Notes Current Electricity
Uploaded by
12th.topper.pcmCopyright:
Available Formats
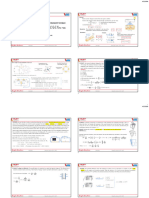
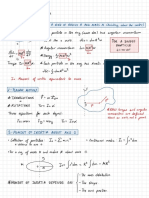
CURRENT ELECTRICITY Mobility : It is defined as the
magnitude of drift
velocity
per unit electric field It is denoted by U .
.
Electric Current :It is defined as the rate of flow of electric u =
(d) SI unit = m2V's-1
of the conductor E
charge through a cross-section .
if the current is flowing through
#charge
Ohm's Law :Et states that the current (i)
steady
a
i conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference (1)
a
=
across the ends of the conductor provided , physical conditions
Current is scalar
⑭ a
quantity o the conductor such as temperature ,
mechanical strain
Si unit is IA 6 23x10'8 electrons
⑪
ampere (A) 1 etc are kept constant.
.
= = .
- -
direction of current
D
# Vai = V = RI
the
charge
A
, 8 R =
constant of proportionality R is
Y
V
O
direction of called resistance of the conductors
-
ve
charge current
↑
Note : The current is same for all cross section of a conductor R =
=
um
of non uniform cross section . o(Slope of I-Y)
#Itr 4 Ltr 4 Ltr 4 Ltr
slope-tano
la Y 51 unit is ohm (-)
#Current in different situation is due to motion of different
charge carriers. # The resistance of a conductor is
Conductors/vacuum Electrolyte Semiconductor discharge tube R m1
Pe where = sunit
= =
due to motion of to due to the due to motion due to tre ions net A net
8-ve ions of 200 Holes o
negative e . P =
Specific resistance or resistivity of the conductor .
Ate: Discharge tube--
containing atomic gases
.
↳ depends upon material of the conductor .
# Current density at a point inside the conductor is defined if length of a given metallic wire of resistance R is stretched
as the amount of current flowing per unit area around that to n times , its resistance becomes neR but its
resistivity remains
point of the conductor , unchanged
.
R
ie R = =
en) =
n =
⑪ Note : Mass of the material
#n
remain constant.
thenSunil Jangra Physics
if area A is not normal to the current but makes an angle Conductivity reciprocal : The of resistivity is known as
O with the direction of current , conductivity specific or conductance It is denoted ·
by
J =
or i =
JACOSO =
J A o
u =
1 = nett siunit-a'm
coso P
#Current density is M
a vector
quantity
↳ SI unit =
Am ? O Relationship between 5, E-FrE
or i =
55.s Eas is small area of given surface areay .
↳ Ohmic Conductors : Those conductors which Obey Ohm's law
velocity with which free
# Drift
average velocity
: The are known as ohmic conductors ·
Cog metals· For ohmic conductors,
electron drifted towards the positive end of the
get the graph between current and potential difference is a
straight
conductor under the influence of an external electric line passing through the origin .
Field
. E
CE-
+
byTj
* O
⑭
= -E
-
Given = -
t *
↳ Non-ohmic Conductors : Those conductors which do not
D
·
In
8
+ -
Obey Ohm's law are known as non-ohmic conductors
·
T time of relaxation +
junction
g diode value
=
e .
diode .
Fondu
,
e =
charge of electron
I A A xi(mA) 1
I
m mass of electron cor
1
=
-
-
E =
applied Electric field .
Y V
Relation
8 ·
between i & Vd
⑭
S
⑭
* ⑪
8 y Y
i An eva Y
there is than
↳Without electric field (eA) more
=
=>
=
The relation between
V and I depends one value of V for
·
I'moving randomly V8 i is non-linear.
the same current :
· i =
0 ; i= 0
on the of v.
sign
Sunil Jangra Physics
You might also like
- Current Electricity 1 PageDocument2 pagesCurrent Electricity 1 PagewytaziNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 Current Resistance and Electricmotive ForceDocument4 pagesChapter 25 Current Resistance and Electricmotive Forcehieuvuong647No ratings yet
- KMC EE 2022 JuneDocument10 pagesKMC EE 2022 JuneDIPNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual For Grade 12Document21 pagesLab Manual For Grade 12Anvi MantriNo ratings yet
- DC Machine - 2 MOTORSDocument25 pagesDC Machine - 2 MOTORSSanyaNo ratings yet
- E M Waves New Notes 2024Document9 pagesE M Waves New Notes 2024pingjin010No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves 2022Document12 pagesElectromagnetic Waves 2022ADITYA MAHECHANo ratings yet
- EMI and ACDocument26 pagesEMI and ACdjrhgvjdNo ratings yet
- Physics PracticalsDocument31 pagesPhysics PracticalsAdhityaNo ratings yet
- Eee130 - Exam ReviewerDocument10 pagesEee130 - Exam ReviewerABRIELLE LANCE CANIANo ratings yet
- Electric: 3.1 Current and Potential DifferenceDocument6 pagesElectric: 3.1 Current and Potential DifferenceEv LamNo ratings yet
- Circuits: BEE ElectricalDocument20 pagesCircuits: BEE ElectricalShivaram kumar V.RNo ratings yet
- Report Electric FluxDocument6 pagesReport Electric FluxDhan Lee MostarNo ratings yet
- Physics Mind MapDocument14 pagesPhysics Mind Mapyour momNo ratings yet
- 17 Current Electricity Formula SheetsDocument16 pages17 Current Electricity Formula Sheetsrithikesh sathishNo ratings yet
- T.284xlobmaxwell-Slots - In: Direct GeneratorDocument7 pagesT.284xlobmaxwell-Slots - In: Direct GeneratorFelix Mar Colipano EspejoNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Field 2022Document24 pagesElectric Charges and Field 2022Raghav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 17 Current Electricity Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument18 pages17 Current Electricity Formula Sheets Quizrrsiddharth shastriNo ratings yet
- AQA Trilogy Unit 6.6: Waves and Electromagnetic Waves - Foundation A 1 F I CDocument8 pagesAQA Trilogy Unit 6.6: Waves and Electromagnetic Waves - Foundation A 1 F I CStudent TrialNo ratings yet
- Aakash 02 - Current ElectricityDocument14 pagesAakash 02 - Current ElectricityAshish RanjanNo ratings yet
- Unit1 - Ac FundamentalDocument18 pagesUnit1 - Ac FundamentalBlack spidey GamingNo ratings yet
- Chapter14 Electric CurrentDocument11 pagesChapter14 Electric CurrenteltytanNo ratings yet
- 01 Theory CEDocument20 pages01 Theory CESridhar NNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 17 Oct 2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 17 Oct 2023harinijeyasri7No ratings yet
- Current Electricity Edited 1Document18 pagesCurrent Electricity Edited 1midhunesh41No ratings yet
- Physics 212Document2 pagesPhysics 212maria.rangwala54No ratings yet
- Applied Physics: Instructor: Ayesha SiddiqueDocument53 pagesApplied Physics: Instructor: Ayesha SiddiqueUsama ThakurNo ratings yet
- Electromagnatic InductionDocument1 pageElectromagnatic InductionMahes JeyNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument50 pagesCurrent ElectricityAqeel HanifNo ratings yet
- STPM PHYSICS Definition and Formulae For Semester 2Document4 pagesSTPM PHYSICS Definition and Formulae For Semester 2ONG YU TING MoeNo ratings yet
- 2 Current ElectricityDocument17 pages2 Current ElectricityHimanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Electricity + Integrated PYQsDocument31 pagesPadhle 10th - Electricity + Integrated PYQsHarshit NegiNo ratings yet
- Design of Magnetic Circuits: Magneto Motive Force (MMF) : Magnetic Flux: Magnetic Field IntensityDocument69 pagesDesign of Magnetic Circuits: Magneto Motive Force (MMF) : Magnetic Flux: Magnetic Field IntensitySouparna SahaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics + Magnetostatic + CurrentDocument1 pageElectrostatics + Magnetostatic + Currentrudraveer2805No ratings yet
- Romeo Jose C. Purificando PT in Electronics Week 5 ND 6Document3 pagesRomeo Jose C. Purificando PT in Electronics Week 5 ND 6aeronh john PurificandoNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity NCERT Notes + PYQ'sDocument21 pagesCurrent Electricity NCERT Notes + PYQ'sAnil UniyalNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument39 pagesCurrent ElectricitySUBHRANIL CHOWDHURYNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics 2023-24 Chapter - 3 Current ElectricityDocument31 pagesClass 12 Physics 2023-24 Chapter - 3 Current Electricity10 B 13 Pratheep . SNo ratings yet
- Hsslive - Plus Two Chapter 3 - 2024Document11 pagesHsslive - Plus Two Chapter 3 - 2024dshaji078No ratings yet
- Emf MCQDocument4 pagesEmf MCQVaniprabha ANo ratings yet
- APC CircuitsDocument6 pagesAPC CircuitsRana MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Circuit of Of: Systems Electrical Power Type Circuits Speed Light DelaysDocument6 pagesCircuit of Of: Systems Electrical Power Type Circuits Speed Light DelaysDenizNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument93 pagesCurrent ElectricitySurya SNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Teaching Notes PDFDocument39 pagesCurrent Electricity - Teaching Notes PDFParas Singh RajpurohitNo ratings yet
- 8 - Alternating Current 8.1 Alternating Voltage and Alternating Current (A. C.)Document17 pages8 - Alternating Current 8.1 Alternating Voltage and Alternating Current (A. C.)padma princessNo ratings yet
- Current and ResistanceDocument1 pageCurrent and Resistanceusman_sahibzadaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 JumawidDocument4 pagesActivity 1 JumawidKai JumawidNo ratings yet
- CHP 8Document1 pageCHP 8south8943No ratings yet
- CHP 8Document1 pageCHP 8south8943No ratings yet
- Circular Motion and Gravitational ForcesDocument3 pagesCircular Motion and Gravitational ForcesAntony MwangiNo ratings yet
- Curre NT An D Vol Tage: Form of Energy Can Be Changed Into Other FormsDocument1 pageCurre NT An D Vol Tage: Form of Energy Can Be Changed Into Other FormsMadeleine Agius CarbonaroNo ratings yet
- Tarea 9 - Fernando CamposDocument1 pageTarea 9 - Fernando CamposFernando Campos JuárezNo ratings yet
- Mind Maps EMI & Alternating CurrentDocument2 pagesMind Maps EMI & Alternating CurrentAyush KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism 3Document1 pageElectricity and Magnetism 3Julia KarakiNo ratings yet
- Current and ElectricityDocument10 pagesCurrent and ElectricitySiddanta PoudelNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Current ElectricityDocument14 pagesChapter - 3 Current ElectricitySHRIRAM JOSHINo ratings yet
- Rigid Body NotesDocument5 pagesRigid Body NotesGemaNo ratings yet
- PS2 Equation Sheet ExamsDocument4 pagesPS2 Equation Sheet ExamsWilliam ShenNo ratings yet
- Heaswring Points and Instruments: U-V, V-W W-U I WZZDocument1 pageHeaswring Points and Instruments: U-V, V-W W-U I WZZWilliam moreNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- SLS Ginopol L24 151-21-3-MSDS US-GHSDocument8 pagesSLS Ginopol L24 151-21-3-MSDS US-GHSRG TNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction Aviation Industry: Mini Project On Vistara AirlinesDocument84 pagesChapter 1: Introduction Aviation Industry: Mini Project On Vistara Airlinesselvaraj rapakaNo ratings yet
- Factor Affecting Child Dental Behaviour PedoDocument19 pagesFactor Affecting Child Dental Behaviour PedoFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- Masters Thesis Oral Reading For Masters in Education ST Xavier ED386687Document238 pagesMasters Thesis Oral Reading For Masters in Education ST Xavier ED386687Bruce SpielbauerNo ratings yet
- Paul's Defence of His Apostleship - Gal 1 - 2Document13 pagesPaul's Defence of His Apostleship - Gal 1 - 231songofjoyNo ratings yet
- CAPEX Acquisition ProcessDocument5 pagesCAPEX Acquisition ProcessRajaIshfaqHussainNo ratings yet
- Datasheet lcd03 20x4 B PDFDocument8 pagesDatasheet lcd03 20x4 B PDFFrancis100% (1)
- DS ClozapineDocument3 pagesDS ClozapineMiggsNo ratings yet
- Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited: Prepared For: Prepared By: MavericksDocument18 pagesAl-Arafah Islami Bank Limited: Prepared For: Prepared By: MavericksToabur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Orthodox Pebbles Raising of LazarusDocument29 pagesOrthodox Pebbles Raising of LazarusMonica DavidNo ratings yet
- Coles Stategic AssessmentDocument10 pagesColes Stategic AssessmentRichardNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Soal UPDocument16 pagesKumpulan Soal UPTriono SusantoNo ratings yet
- Cases Torts 7-29-17 DigestDocument1 pageCases Torts 7-29-17 Digestczabina fatima delicaNo ratings yet
- Math - Gr6 - Q2 - Week-08 - Comparing and Arranging Integers On The Number LineDocument37 pagesMath - Gr6 - Q2 - Week-08 - Comparing and Arranging Integers On The Number LineDiana TubigNo ratings yet
- 12-List of U.C. Booked in NGZ Upto 31032017Document588 pages12-List of U.C. Booked in NGZ Upto 31032017avi67% (3)
- 2.peace Treaties With Defeated PowersDocument13 pages2.peace Treaties With Defeated PowersTENDAI MAVHIZANo ratings yet
- Fish Immune System and Vaccines-Springer (2022) - 1Document293 pagesFish Immune System and Vaccines-Springer (2022) - 1Rodolfo Velazco100% (1)
- Fourth Wall ViolationsDocument7 pagesFourth Wall ViolationsDanomaly100% (1)
- ECB Priority III: Deutz - Starter MotorDocument7 pagesECB Priority III: Deutz - Starter MotorMarcelo OlivaresNo ratings yet
- PI SQC 2015 R3 User GuideDocument50 pagesPI SQC 2015 R3 User Guideislam ahmedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Presented By: Mrs. Marie Nella T. VictoriaDocument75 pagesChemistry: Presented By: Mrs. Marie Nella T. VictoriaJESPHER GARCIANo ratings yet
- How To Perform A Financial Institution Risk Assessment: Quick Reference GuideDocument15 pagesHow To Perform A Financial Institution Risk Assessment: Quick Reference GuideYasmeen AbdelAleemNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Building: Submitted By-Naitik JaiswalDocument17 pagesSustainable Building: Submitted By-Naitik JaiswalNaitik JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Small Scale Business ReportDocument28 pagesSmall Scale Business ReportJatin PahujaNo ratings yet
- Definition of CultureDocument14 pagesDefinition of CultureRenee Louise CoNo ratings yet
- RJSC - Form VII PDFDocument4 pagesRJSC - Form VII PDFKamruzzaman SheikhNo ratings yet
- Policing System Indonesia PolicingDocument5 pagesPolicing System Indonesia Policingdanilo bituin jrNo ratings yet
- Essay 1 John WatsonDocument4 pagesEssay 1 John Watsonapi-259502356No ratings yet
- STGS7115-B3 Mini Esmeriladoramanualusuario-29505070 PDFDocument14 pagesSTGS7115-B3 Mini Esmeriladoramanualusuario-29505070 PDFHydro Energy GroupNo ratings yet
- Mouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsDocument52 pagesMouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsIrfan FalahNo ratings yet