Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bernoulli's Energy Equation
Bernoulli's Energy Equation
Uploaded by
ALDRIN JUSTADO0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views7 pagesThe Bernoulli equation describes the conservation of energy in fluid flow, relating pressure, velocity, and elevation, and states that the total energy per unit mass remains constant along a streamline for incompressible flow with negligible friction; it consists of kinetic energy from fluid motion, potential energy from gravitational position, and pressure energy associated with fluid pressure. The equation is valid for steady, incompressible flow with negligible net frictional forces.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Bernoulli equation describes the conservation of energy in fluid flow, relating pressure, velocity, and elevation, and states that the total energy per unit mass remains constant along a streamline for incompressible flow with negligible friction; it consists of kinetic energy from fluid motion, potential energy from gravitational position, and pressure energy associated with fluid pressure. The equation is valid for steady, incompressible flow with negligible net frictional forces.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views7 pagesBernoulli's Energy Equation
Bernoulli's Energy Equation
Uploaded by
ALDRIN JUSTADOThe Bernoulli equation describes the conservation of energy in fluid flow, relating pressure, velocity, and elevation, and states that the total energy per unit mass remains constant along a streamline for incompressible flow with negligible friction; it consists of kinetic energy from fluid motion, potential energy from gravitational position, and pressure energy associated with fluid pressure. The equation is valid for steady, incompressible flow with negligible net frictional forces.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
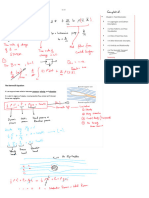
The Bernoulli equation is an approximate relation between
BERNOULLI’s pressure, velocity and elevation. It is a fundamental
principle in fluid mechanics that describes the
conservation of energy in a flowing fluid.
ENERGY The equation states that for an incompressible fluid (a fluid
EQUATION
whose density remains constant), the total energy per unit
mass at any point along a streamline is constant.
It is valid in regions of steady, incompressible flow where
net frictional forces are negligible.
COMPONENTS This Bernoulli’s total energy are consists
of three components:
OF Kinetic Energy (KE): The energy
associated with the motion of the fluid.
BERNOULLI’s Potential Energy (PE): The energy
ENERGY
associated with the position of the fluid
element in a gravitational field.
EQUATION Pressure Energy (PE): The energy
associated with the pressure of the fluid.
Problem 1
In the given figure, water flows from A where the diameter is 12in to B where the diameter
24in, at the rate 13.2cfs. The pressure head at A is 22.1ft. Considering no loss of energy from A to
B
a. Find the pressure head at B.
b. Find the pressure at B.
Problem 2
The head loss from section 1 to section 2 in the pipe system shown is 2.1m and the head loss
from section 2 to 3 is 4.9m. If the velocity of flow at 1 is 1.8m/s and the pressure is 180kPa.
a. What is the discharge?
b. Find the velocity at point 3?
c. Find the pressure at point 3?
Problem 3
A 50mm diameter siphon is drawing oil (sg = 0.82) from an oil reservoir as shown. The headloss
from point 1 to point 2 is 1.50m and from point 2 to point 3 is 2.40m.
a. What is the exit velocity?
b. Find the discharge.
c. Find the pressure at point 2
You might also like
- Hydraulics 1Document82 pagesHydraulics 1Vincent Louie Escover Foronda75% (16)
- Bernoulli's Equation PDFDocument9 pagesBernoulli's Equation PDFjagdeep_sekhonNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Class 11Document18 pagesPhysics Project Class 11Aarya Rajesh71% (55)
- Physics Investigatory Project: Bernoulli'S TheoremDocument18 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: Bernoulli'S TheoremSriram JNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Inviscid Flow and Bernoulli Equation - StudentsDocument35 pagesChapter 2 Inviscid Flow and Bernoulli Equation - StudentsMERSYA NABILA100% (1)
- T7 - Fluid Mechanics - CH4Document15 pagesT7 - Fluid Mechanics - CH4roi constantineNo ratings yet
- Bernouli's Equation and Its ApplicationDocument20 pagesBernouli's Equation and Its ApplicationBenjamin AsiriNo ratings yet
- Chapter4,5 and 6 PDFDocument118 pagesChapter4,5 and 6 PDFVarshaNo ratings yet
- Mass, Momentum and Energy EquationsDocument25 pagesMass, Momentum and Energy Equationslassi19a100% (1)
- Unit 5: ObjectivesDocument42 pagesUnit 5: ObjectivesNina MazuinNo ratings yet
- FMM OBE 2nd UnitDocument17 pagesFMM OBE 2nd UnitVignesh VickyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - The Bernoulli EquationDocument53 pagesLecture 6 - The Bernoulli EquationThatayamodimo KebueNo ratings yet
- City and Guilds 9210 UNIT 103 Hydraulics and Hydrology Level 6 Tutorial 1 - Pipe FlowDocument36 pagesCity and Guilds 9210 UNIT 103 Hydraulics and Hydrology Level 6 Tutorial 1 - Pipe Flowdipesh100% (1)
- BernoullisDocument19 pagesBernoullisSelwah Hj AkipNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Equation - MechanicsTipsDocument2 pagesBernoulli Equation - MechanicsTipsJosé Adalberto Caraballo LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Lec - Flow in Motion, BE, EG, HGL, EGL, Viscous Flow and LossesDocument67 pagesLec - Flow in Motion, BE, EG, HGL, EGL, Viscous Flow and Lossesalimajeg2No ratings yet
- Chapter 05 CengelDocument40 pagesChapter 05 CengelmariathesupergirlNo ratings yet
- Conservation LawsDocument33 pagesConservation Lawsafaq ahmad khanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document23 pagesChapter 1sgrsthNo ratings yet
- Ideal FlowDocument30 pagesIdeal FlowCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's Equation Redirects Here See: For An Unrelated Topic inDocument5 pagesBernoulli's Equation Redirects Here See: For An Unrelated Topic inshibu danielNo ratings yet
- 03-MEC441-Finite Control Volume Analysis-Part 2Document53 pages03-MEC441-Finite Control Volume Analysis-Part 2belNo ratings yet
- Cve 305 - 5,6Document22 pagesCve 305 - 5,6mohammed adoNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Flow of Fluids and BernoulliDocument21 pagesUnit 6 Flow of Fluids and BernoulliMOJALEFA JACOB MOLEFINo ratings yet
- Physics Project Class 11Document18 pagesPhysics Project Class 11NhjghkkkNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli ModuleDocument12 pagesBernoulli ModuleIamswellynkate SerranoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lect 5 Fall 2023Document27 pagesFluid Mechanics Lect 5 Fall 2023Dr.Ebrahim AboueleynanNo ratings yet
- EEEQ 221 Fluid Mechanics 3B - Notes For 12th January 2018Document37 pagesEEEQ 221 Fluid Mechanics 3B - Notes For 12th January 2018Ellie AwiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow TheoryDocument15 pagesFluid Flow TheorySamiksha ShivaniNo ratings yet
- EX5 - Bernoulli's EquationDocument7 pagesEX5 - Bernoulli's EquationBashar IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Research No 2Document14 pagesResearch No 2Mahmudul HasanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Fluid Dynamic: Mass, Bernoulli and Energy EquationsDocument41 pagesFluid Mechanics: Fluid Dynamic: Mass, Bernoulli and Energy EquationsJohnnie ChewNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - 2Document35 pagesLecture 1 - 2Professor GobozaNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's Energy TheoremDocument26 pagesBernoulli's Energy TheoremjaerzedNo ratings yet
- Demonstration of Bernoulli's EquationDocument27 pagesDemonstration of Bernoulli's Equationmahbub1332100% (5)
- 4.3-Euler's Equation PDFDocument6 pages4.3-Euler's Equation PDFRonald Cario SeguinNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Experiment PDFDocument4 pagesBernoulli Experiment PDFHazem JameelNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's Equation PNDocument4 pagesBernoulli's Equation PNafifa100% (1)
- CHAPTER 5 Dynamics of Fluid FlowDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 5 Dynamics of Fluid FlowMuluken MelesseNo ratings yet
- Engineering Fluid MechanicsDocument45 pagesEngineering Fluid MechanicsabsinitNo ratings yet
- Project Festus 2Document17 pagesProject Festus 2samuelhmar170No ratings yet
- Bernaulli's Theorem FullDocument17 pagesBernaulli's Theorem FullBart KwanNo ratings yet
- Giambattista Real FluidsDocument20 pagesGiambattista Real FluidscalmyourmindwithmusicNo ratings yet
- Fluid DyanamicsDocument19 pagesFluid DyanamicsSanthoshMBSanthuNo ratings yet
- Fluid Lab:) The Second PhaseDocument17 pagesFluid Lab:) The Second Phaseمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Equation PDFDocument10 pagesBernoulli Equation PDFaniefiok edetNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Finite Control Volume Analysis 3.1 Introduction To Fluid FlowDocument21 pages3.0 Finite Control Volume Analysis 3.1 Introduction To Fluid FlowJack SantosNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Mechanical Energy EquationDocument30 pages1.1 The Mechanical Energy EquationDante ZayasNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Lab ReportDocument17 pagesBernoulli Lab ReportJoshua Emmanuel PagulongNo ratings yet
- FM EXPERIMENT NODocument6 pagesFM EXPERIMENT NOpurushottam prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Fluid DynamicDocument81 pagesFluid Dynamicannysophillea19No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Fluid FlowDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Fluid Flowmark galangNo ratings yet
- Notes Part A - Pipes and Pipe SystemsDocument44 pagesNotes Part A - Pipes and Pipe SystemsProfessor GobozaNo ratings yet
- Continuity and Energy EquationsDocument53 pagesContinuity and Energy Equationssushil.vgiNo ratings yet
- Week7 Ch5Document10 pagesWeek7 Ch5bestniazNo ratings yet
- Lab Iii Report Hydraulic Group Flexi 03Document51 pagesLab Iii Report Hydraulic Group Flexi 03FAAI8007MUHAMAD ZUHAIRI SULAIMANNo ratings yet
- Fluid DynamicsDocument20 pagesFluid DynamicsMohammad Zunaied Bin Harun, Lecturer , CEENo ratings yet
- Print 10Document20 pagesPrint 10ALDRIN JUSTADONo ratings yet
- Print 2Document10 pagesPrint 2ALDRIN JUSTADONo ratings yet
- Print 2Document10 pagesPrint 2ALDRIN JUSTADONo ratings yet
- Print 4Document21 pagesPrint 4ALDRIN JUSTADONo ratings yet
- AsdasdDocument1 pageAsdasdALDRIN JUSTADONo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Fluid FlowDocument7 pagesFundamentals of Fluid FlowALDRIN JUSTADONo ratings yet
- Print 1Document7 pagesPrint 1ALDRIN JUSTADONo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 - Innovation and PathwaysDocument10 pagesWEEK 4 - Innovation and PathwaysALDRIN JUSTADONo ratings yet
- Group A1 - Ce304 - Prelim Problem SetDocument24 pagesGroup A1 - Ce304 - Prelim Problem SetALDRIN JUSTADONo ratings yet
- 100 Problems in GeotechDocument5 pages100 Problems in GeotechALDRIN JUSTADONo ratings yet
- CE013 - CE31S5 - Plate 9 - SILONGAN Andrea Mae E 1 Model4Document1 pageCE013 - CE31S5 - Plate 9 - SILONGAN Andrea Mae E 1 Model4ALDRIN JUSTADONo ratings yet
- Tos FormatDocument2 pagesTos FormatALDRIN JUSTADONo ratings yet
- Ce023-Ce31s2a Binasoy Van PrelimexamDocument3 pagesCe023-Ce31s2a Binasoy Van PrelimexamALDRIN JUSTADONo ratings yet
- Exercise Set 4.1 - Angular Displacement, Angular Velocity and Angular AccelerationDocument6 pagesExercise Set 4.1 - Angular Displacement, Angular Velocity and Angular AccelerationALDRIN JUSTADONo ratings yet