Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sensory System-Glosary
Sensory System-Glosary
Uploaded by
Jennevi Bruno0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesThe document provides definitions for 35 common medical terms related to the sensory system in both English and Spanish. Some key terms defined include: aphasia (inability to understand or use language), astigmatism (distorted vision due to irregular lens shape), cataract (clouding of the eye lens), cleft lip (split in upper lip), cochlea (snail-shaped structure in inner ear responsible for hearing), and conjunctiva (mucous membrane lining eyelids). The glossary covers terms pertaining to vision, hearing, speech, smell, and other sensory functions and disorders.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides definitions for 35 common medical terms related to the sensory system in both English and Spanish. Some key terms defined include: aphasia (inability to understand or use language), astigmatism (distorted vision due to irregular lens shape), cataract (clouding of the eye lens), cleft lip (split in upper lip), cochlea (snail-shaped structure in inner ear responsible for hearing), and conjunctiva (mucous membrane lining eyelids). The glossary covers terms pertaining to vision, hearing, speech, smell, and other sensory functions and disorders.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesSensory System-Glosary
Sensory System-Glosary
Uploaded by
Jennevi BrunoThe document provides definitions for 35 common medical terms related to the sensory system in both English and Spanish. Some key terms defined include: aphasia (inability to understand or use language), astigmatism (distorted vision due to irregular lens shape), cataract (clouding of the eye lens), cleft lip (split in upper lip), cochlea (snail-shaped structure in inner ear responsible for hearing), and conjunctiva (mucous membrane lining eyelids). The glossary covers terms pertaining to vision, hearing, speech, smell, and other sensory functions and disorders.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
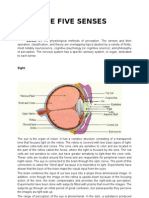
The Sensory System
Basic Glossary of Terms for Healthcare Interpreters
English Definition Spanish
1. Aphasia Partial or total inability to understand or use language. Afasia
Spherical deviation in the lens of the eye, leading to
2. Astigmatism Astigmatismo
distorted images.
3. Cataract Opacification of the eye lens, leading to blurred vision. Catarata
A split or opening in the upper part of the mouth caused
by failure of lip to close together during fetal
4. Cleft lip Labio leporino
development. Babies with this condition may also
suffer from a cleft in the palate.
Inner ear structure that is shaped like a snail and is the
5. Cochlea Cóclea
organ responsible for hearing.
An infection characterized by the formation of a cluster
6. Cold sore of tiny blisters on or around the mouth caused by the Herpes labial
herpes simplex virus. Also called fever blister.
It refers to a person who has a vision deficiency in which
7. Colorblind Daltónico
the ability to see certain colors is decreased.
The mucous membrane that lines the inside of the
8. Conjunctiva Conjuntiva
eyelids to protect the white of the eye.
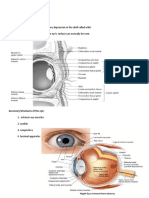
9. Cornea The transparent layer covering the front part of the eye. Córnea
10. Dysphonia Difficulty speaking, or a vocalization impairment. Disfonía
The translucent fibrous structure separating the
external ear from the middle ear and attached to the
11. Eardrum Tímpano
ear bones; it vibrates with sound and sends the waves
to the inner ear.
The tube that leads from the throat to the middle ear,
12. Eustachian tube Trompa de Eustaquio
and is responsible for pressure equalization in the ears.
A physician that specializes in disorders of the ear,
13. ENT Otorrino
nose, and throat. Also called otolaryngologist.
Eye floaters are black or gray spots in one’s vision; they
14. Floaters may also look like a spider’s web or strings that drift Flotadores del ojo
with eye or head movement.
A condition marked by several eye disorders that affect
15. Glaucoma the optic nerve. Damage to this nerve leads to Glaucoma
irreversible loss of vision.
16. Halitosis Commonly known as bad breath. Halitosis
17. Hearing impairment Partial or complete loss of the ability to detect sounds. Discapacidad auditiva
Harsh-sounding voice caused by vocal cord overuse or
18. Hoarseness Ronquera
other condition.
Commonly known as farsightedness, this is a condition
19. Hyperopia where people can see distant objects more clearly than Hipermetropía
those nearby.
The bone in the middle ear between the stapes and
20. Incus Yunque
malleus; also known as the anvil because of its shape.
Medical Interpreting Training School | MITS © all rights reserved 1
The part of the ear that contains the hearing organ
21. Inner ear called the cochlea and the balance organ called the Oído interno
labyrinth.
The colored part of the eye behind the cornea,
22. Iris Iris
containing the adjustable opening called the pupil.
Part of the inner ear that holds the sensory organs for
23. Labyrinth
hearing and equilibrium.
Laberinto
It is a laser eye procedure that uses a device called a
24. LASIK microkeratome to change the shape of the cornea to Cirugía LASIK
correct myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism.
Commonly referred to as the hammer because of its
25. Malleus shape, it is the first ear bone that connects to the Martillo
eardrum.
A condition of the inner ear marked by hearing and
Enfermedad de
26. Meniere’s disease balance disorders, leading to tinnitus, vertigo, hearing
Meniere
loss, and fullness in the ear.
Includes the eardrum and the three middle ear bones
27. Middle Ear Oído medio
that end at the round window leading to the inner ear.
Commonly known as nearsightedness, this is a
28. Myopia condition marked by the ability to see objects up close Miopía
more clearly than objects farther away.
A surgical incision of the eardrum to relieve pressure,
29. Myringotomy Miringotomía
drain fluid, or place ear tubes.
The external openings in the face leading to the nasal
30. Nostrils cavities, which connect to the throat and airways to Fosas nasales
allow the passage of air into the lungs.
Very small bones, especially when referring to the
31. Ossicles Osículos
bones in the ear.
Inflammation of either the external, middle or inner
32. Otitis ear, which will be defined by the terms otitis externa, Otitis
otitis media, or otitis interna.
There is a soft and hard palate. The soft palate is the
fleshy portion towards the back of the roof of the
33. Palate Paladar
mouth. The hard palate is the bony front part of the
roof of the mouth.
Another term for farsightedness, it is marked by the
34. Presbyopia ability to see things farther away more clearly than Presbicia
objects up close.
A growth of tissue in the conjunctiva of the eye,
35. Pterygium originating on the nasal side and gravitates to the Pterigión
cornea.
The adjustable opening in the middle of the iris, which
36. Pupil Pupila
is where light passes to the retina.
The innermost part of the eye that receives images
37. Retina from the outside world; these images are then sent to Retina
the brain through the optic nerve.
Inflammation in the nasal structures or lining causing a
38. Rhinitis Rinitis
runny or stuffy nose.
A membrane that separates the middle ear from the Membrana timpánica
39. Round window
inner ear. secundaria
40. Sclera The white part of the eye. Esclerótica
Medical Interpreting Training School | MITS © all rights reserved 2
Smallest of the three ear bones that connect the
41. Stapes eardrum to the inner ear; commonly referred to as the Estribo
stirrup because of its shape.
Also called cross-eyed, this is the inward turning of the
42. Strabismus Estrabismo
iris and cornea as if looking at the nose.
An infection of the throat and tonsils caused by group Faringitis por
43. Strep throat
A streptococcus bacteria. estreptococos
Inflammation or narrowing of the voice box, leading to
44. Stridor Estridor
noisy breathing.
Complete or partial word repetition, which disrupts the
45. Stuttering Tartamudeo
smooth flow of speech.
An abscess in or around the eye caused by bacteria in
46. Sty Orzuelo
the eyelid glands.
Hearing a roaring, ringing, or buzzing sound in the head
47. Tinnitus Zumbido
or ears.
The illusion of movement, leading to a whirling
48. Vertigo Vértigo
sensation and loss of balance.
The system responsible for maintaining one’s
perception of the body’s place in space, posture, and
49. Vestibular system Sistema vestibular
balance. Regulates movements and locomotion to help
with visual focus on objects during movement.
50. Vestibule A bony channel or cavity within the inner ear. Vestíbulo
Notes: Key Word Parts:
6. Colloquially known in Latin America as fuego kerat/o cornea
13. Also known as otorhinolaryngologist. In Spanish: myring/o eardrum
otorrinolaringólogo or otolaringólogo. dilat/o widening
16. It is also acceptable to interpret as mal aliento. -otomy cutting into
34. In Spanish, a farsighted person is: hipermétrope, a
nearsighted person is: míope, and a person with
astigmatism is: astigmático.
35. Commonly called: carnocidad en los ojos.
42. Cross-eyed: bizco in Spanish.
43. Also correct: faringitis or amigdalitis estreptocócica.
47. Also correct: tinnitus (pronounced as spelled)
Medical Interpreting Training School | MITS © all rights reserved 3
You might also like
- Brain Hemisphere HatDocument1 pageBrain Hemisphere Hatkleberttoscano100% (1)
- DLL (Science 9, Module 1, Unit 1, Week 1)Document4 pagesDLL (Science 9, Module 1, Unit 1, Week 1)liberty100% (2)
- Kenneth J. Koval, Joseph D. Zuckerman Auth. Hip Fractures A Practical Guide To ManagementDocument340 pagesKenneth J. Koval, Joseph D. Zuckerman Auth. Hip Fractures A Practical Guide To ManagementWisnu Surya Wardhana100% (2)
- How To Draw Manga Sketching (Manga-Style) - Vol. 3 - Unforgettable CharactersDocument184 pagesHow To Draw Manga Sketching (Manga-Style) - Vol. 3 - Unforgettable Charactersmahoutsukai_monika85% (34)
- Psych101-Midterms-Chapter 3 (Mechanisms of Human Behavior-Receiving Mechanism)Document3 pagesPsych101-Midterms-Chapter 3 (Mechanisms of Human Behavior-Receiving Mechanism)Archaios DrakosNo ratings yet
- Special Senses: Presented by Group 5Document65 pagesSpecial Senses: Presented by Group 5Marianne HeramilNo ratings yet
- 002 ARA CCHI Mini - Glossary ENT EarDocument5 pages002 ARA CCHI Mini - Glossary ENT Eartarboosh20146No ratings yet
- Surface Anatomy (Part 2) : Oral Exam VideoDocument63 pagesSurface Anatomy (Part 2) : Oral Exam VideoAna UsharidzeNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class X Sense Organs NotesDocument26 pagesICSE Class X Sense Organs Notesprogrammer.ron.akNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Term 2Document11 pagesReviewer Term 2zabalaiiirogeliopaclibarNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Sensitive OrgansDocument4 pages2.1 Sensitive OrgansSOFI ULLISKYNo ratings yet
- Ha NotesDocument12 pagesHa NotessrslytrdNo ratings yet
- Report (Chap 10)Document81 pagesReport (Chap 10)Field StudyNo ratings yet
- Sense OrgansDocument12 pagesSense Organsriwisi2139No ratings yet
- Nur 097 Ha Lec TransesDocument9 pagesNur 097 Ha Lec TransesmiloubandoNo ratings yet
- Activity 11 The Tongue and The SkinDocument7 pagesActivity 11 The Tongue and The SkinRoi Vincent VillaraizNo ratings yet
- The Senses: Eugene Flor Lindawan Ulpindo, MSNDocument67 pagesThe Senses: Eugene Flor Lindawan Ulpindo, MSNayoNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody Human Eye Ebook 2017Document15 pagesVisibleBody Human Eye Ebook 2017Sandra RubianoNo ratings yet
- The Eye: (We'll Leave The Lord Sauron Jokes To You.)Document15 pagesThe Eye: (We'll Leave The Lord Sauron Jokes To You.)ناديه المعمريNo ratings yet
- Bell's PalsyDocument5 pagesBell's PalsyFD PCP Cueto, Marc Anthony P.No ratings yet
- Special Senses WSDocument6 pagesSpecial Senses WSJamaica LunaNo ratings yet
- University of Hargeisa: Faculty Veterinary MedicineDocument5 pagesUniversity of Hargeisa: Faculty Veterinary MedicineCabdale Binu YahyeNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument7 pagesAssignmentLABSA PLANTNo ratings yet
- ICSE-X Biology Chap-10 (Sense Organs)Document11 pagesICSE-X Biology Chap-10 (Sense Organs)TAHMEENA ZAFARNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 2nd Quarter Unit 3 Lesson 1 Sense Organs and How To Care For ThemDocument89 pagesGrade 3 2nd Quarter Unit 3 Lesson 1 Sense Organs and How To Care For ThemRaul Rivera SantosNo ratings yet
- Biology Class IX J Unior H Igh S Chool: 5 Senses in OurbodiesDocument22 pagesBiology Class IX J Unior H Igh S Chool: 5 Senses in OurbodiesRuth May Roselin TobingNo ratings yet
- Special Organ: DR - Abdul Rashad Isra Institute of Rehabilitation SciencesDocument37 pagesSpecial Organ: DR - Abdul Rashad Isra Institute of Rehabilitation SciencespashaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 SensationDocument4 pagesChapter 4 SensationPAULINA GABRIELLE H. GAMIDONo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 11 Eyes: Eye Part FunctionDocument6 pagesLaboratory Activity 11 Eyes: Eye Part FunctionCrystal Jade RetuyaNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise - Special SensesDocument8 pagesLab Exercise - Special SensesDOSALLA PRINCESS ALLYSSANo ratings yet
- Lab 22 The Eye VisionDocument12 pagesLab 22 The Eye Visionrhycelayon304100% (1)
- Unit 12,13 Eye and EarDocument51 pagesUnit 12,13 Eye and EarlauraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology SensesDocument19 pagesAnatomy Physiology SensesMika Ela EismaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Mechanism of Human BehaviorDocument46 pagesChapter 4 Mechanism of Human BehaviorIsmaela BawicaNo ratings yet
- UNIT3 ArticulatoryPathophysiology (StudyGuide)Document9 pagesUNIT3 ArticulatoryPathophysiology (StudyGuide)leiannbellecorrecheNo ratings yet
- Tonsils-Are-Located-Between-Which-Two-Structures - HTML: D. Vestibular ApparatusDocument17 pagesTonsils-Are-Located-Between-Which-Two-Structures - HTML: D. Vestibular Apparatusmcycy miNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Answers: RememberingDocument24 pages4.1 Answers: RememberingDanny TNo ratings yet
- 1.14 - Special SensesDocument5 pages1.14 - Special SensesUwen NalpNo ratings yet
- Activity (Laboratory) No. 6 Special Senses: Fill in The Correct Terms Missing On Each StatementDocument9 pagesActivity (Laboratory) No. 6 Special Senses: Fill in The Correct Terms Missing On Each StatementPaulynne PaulynneNo ratings yet
- A. Eye Balls D. Lacrimal Glands: 1. External Structures of The EyeDocument7 pagesA. Eye Balls D. Lacrimal Glands: 1. External Structures of The EyebeayapNo ratings yet
- Auditory DefectsDocument6 pagesAuditory DefectsKivumbi EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Health AssessmentDocument3 pagesHealth AssessmentonlyellaNo ratings yet
- The Five SensesDocument8 pagesThe Five Sensesr.g100% (3)
- Vocabulary Special SensesDocument3 pagesVocabulary Special SensesJoshua FloresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 10Document5 pagesChapter 9 10Norman TorregosaNo ratings yet
- 002 SPA CCHI Mini - Glossary ENT EarDocument5 pages002 SPA CCHI Mini - Glossary ENT EarfrangomezchirinoNo ratings yet
- CRANIAL NERVES and SPECIAL SENSESDocument8 pagesCRANIAL NERVES and SPECIAL SENSESanyaNo ratings yet
- Health 6Document4 pagesHealth 6Karen RayosNo ratings yet
- Minimalist Pastel Cream Waves Education Center by SlidesgoDocument15 pagesMinimalist Pastel Cream Waves Education Center by SlidesgoEslam EltayebNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire NCM101 LP4Document3 pagesQuestionnaire NCM101 LP4Rhoma Mae IsoNo ratings yet
- Eye and Ears AssessmentDocument17 pagesEye and Ears AssessmentPrincess Añabeza100% (1)
- Eye & Ear Stations ONLYDocument6 pagesEye & Ear Stations ONLYVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Siti Nur Haliza - Farmasi 1B - Task 1Document6 pagesSiti Nur Haliza - Farmasi 1B - Task 1Gio ArgyandraNo ratings yet
- Each Eyeball Is Positioned in A Bony Depression in The Skull Called Orbit. - Only The Anterior One-Sixth of The Eye's Surface Can Normally Be SeenDocument14 pagesEach Eyeball Is Positioned in A Bony Depression in The Skull Called Orbit. - Only The Anterior One-Sixth of The Eye's Surface Can Normally Be SeenMark AngeloNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument8 pagesSpecial SensesdjiamaeduremdezNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER5 Form2Document14 pagesCHAPTER5 Form2basraawi379No ratings yet
- Unit 4/5 Pronunciation Focus Anatomy of The EyeDocument7 pagesUnit 4/5 Pronunciation Focus Anatomy of The EyeIon NagomirNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Activities Science 3Document2 pagesLesson 2 Activities Science 3rhykaserolfNo ratings yet
- ATENGCO - Activity11 The Sense OrgansDocument8 pagesATENGCO - Activity11 The Sense OrgansJoann Mae PudaderaNo ratings yet
- Foutsizoglou 2017 LipDocument3 pagesFoutsizoglou 2017 LippsdsportsdocNo ratings yet
- LEARNERS With PHYSICAL DISABILITIESDocument26 pagesLEARNERS With PHYSICAL DISABILITIESJoshua SevillanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - BIO310Document2 pagesChapter 9 - BIO310Ilham Amni AmaninaNo ratings yet
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsFrom EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNo ratings yet
- Snoring, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSnoring, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Assignment Structure of Oral CavityDocument4 pagesAssignment Structure of Oral CavityNarjis BatoolNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and Coordination (Edustudy Point) - UnlockedDocument8 pagesNeural Control and Coordination (Edustudy Point) - Unlockedkushwahvivek1028No ratings yet
- Chapter 38 Endocrine System FunctionDocument2 pagesChapter 38 Endocrine System FunctionPaige Nicole GauthreauxNo ratings yet
- Technique, Variation, and Progression of The Rear-Foot-Elevated Split SquatDocument5 pagesTechnique, Variation, and Progression of The Rear-Foot-Elevated Split SquatSheril MarekNo ratings yet
- 181 Anatomy Eyes and EarsDocument23 pages181 Anatomy Eyes and EarsAnita YadavNo ratings yet
- Module - Wk5&6 - The Biological Foundation of BehaviorDocument11 pagesModule - Wk5&6 - The Biological Foundation of Behavioraudree d. aldayNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody - Respiratory System EBook - 2017Document11 pagesVisibleBody - Respiratory System EBook - 2017sylNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument23 pagesCirculatory Systemhellwakeisbored12No ratings yet
- The Ear, Nose, and Throat Exam: Jeffrey Texiera, MD and Joshua Jabaut, MD CPT, MC, Usa LT, MC, UsnDocument37 pagesThe Ear, Nose, and Throat Exam: Jeffrey Texiera, MD and Joshua Jabaut, MD CPT, MC, Usa LT, MC, Usnsaraswati SabatNo ratings yet
- Craniofacial MicrosomiaDocument21 pagesCraniofacial MicrosomiaMarcela Cano Ricardo100% (1)
- LUNGSDocument1 pageLUNGSVergel Jigs EnriquezNo ratings yet
- 2008-2016 Anatomy 2Document20 pages2008-2016 Anatomy 2sayed aashiqNo ratings yet
- MR Rabu 22 May 2019 Fix 2Document25 pagesMR Rabu 22 May 2019 Fix 2Ayu SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- Simplifying Anatomy Printable Worksheet PDFDocument21 pagesSimplifying Anatomy Printable Worksheet PDFAarushi NairNo ratings yet
- Bodyweight Strength Training ManualDocument43 pagesBodyweight Strength Training ManualRonalth PerezNo ratings yet
- Pons Anatomy - Medicosis Perfectionalis NotesDocument3 pagesPons Anatomy - Medicosis Perfectionalis Noteshiba jasimNo ratings yet
- Pig DissectionDocument8 pagesPig DissectiondvinalNo ratings yet
- Cardiovasular System (Dentistry)Document34 pagesCardiovasular System (Dentistry)amroayman21890No ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism: Annals of Internal Medicine July 2012Document17 pagesHyperthyroidism: Annals of Internal Medicine July 2012Deepa RajNo ratings yet
- Oral Mucosa Presentation 1 1Document38 pagesOral Mucosa Presentation 1 1SibatNo ratings yet
- The Shut Up Program - T NationDocument18 pagesThe Shut Up Program - T NationJon shieldNo ratings yet
- Skin Histology 1Document72 pagesSkin Histology 1ace danielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesChapter 9-Nervous SystemLynNo ratings yet
- 0 - Tugas MR Syafik ML B. InggrisDocument9 pages0 - Tugas MR Syafik ML B. InggrisBandar LampungNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Regional Biomechanics 2Document12 pagesIntroduction To Regional Biomechanics 2Rokia AlmazNo ratings yet
- Newborn AssessmentDocument15 pagesNewborn Assessmentmarie97% (35)