Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gen Biology 2ND Monthly
Uploaded by
pearl japson0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pages1) This document provides a review of key concepts in general biology for a 2nd monthly examination, including macromolecules like carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.
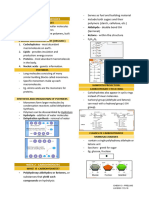
2) It defines enzymes as catalytic proteins that speed up reactions by lowering activation energy barriers through substrate binding and an induced fit mechanism in their active sites.
3) The review covers factors that affect enzyme function like temperature and pH, as well as types of enzyme inhibitors like competitive and noncompetitive inhibitors.
Original Description:
Gen Biology
Original Title
GEN-BIOLOGY-2ND-MONTHLY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) This document provides a review of key concepts in general biology for a 2nd monthly examination, including macromolecules like carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.
2) It defines enzymes as catalytic proteins that speed up reactions by lowering activation energy barriers through substrate binding and an induced fit mechanism in their active sites.
3) The review covers factors that affect enzyme function like temperature and pH, as well as types of enzyme inhibitors like competitive and noncompetitive inhibitors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesGen Biology 2ND Monthly
Uploaded by
pearl japson1) This document provides a review of key concepts in general biology for a 2nd monthly examination, including macromolecules like carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.
2) It defines enzymes as catalytic proteins that speed up reactions by lowering activation energy barriers through substrate binding and an induced fit mechanism in their active sites.
3) The review covers factors that affect enzyme function like temperature and pH, as well as types of enzyme inhibitors like competitive and noncompetitive inhibitors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
GENERAL BIOLOGY Ü
2ND MONTHLY EXAMINATIONS REVIEWER Goodluck!
b) Unsaturated Fatty Acids – contains
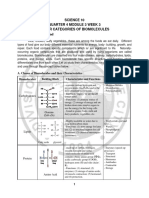
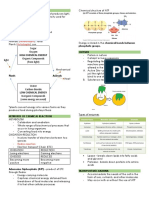
Carbon Compounds at least one carbon-carbon double
Macromolecules – giant molecules bond
c) Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids –
- Made up of thousands or hundreds
contain more than one double bond
of thousands of smaller molecules
of carbon-carbon
- Polymerization: a process in which
4) Nucleic Acids – contains carbon,
large compounds are built by joining
hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus
smaller ones together (monomers)
(CHONP)
to form polymers
- Nucleotides: polymers assembled
1) Carbohydrates – made of carbon,
from individual monomers
hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of 1:2:1
o Consists of three parts
- Used by living organisms as their
▪ 5-carbon sugar
main source of energy
▪ Phosphate group
- Also used by some animals or plants
▪ Nitrogenous base
for structural purposes
- Stores and transmits hereditary or
- Starches: extra sugar that is stored
genetic information
(complex carbohydrates)
- RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) and DNA
a) Monosaccharide – single sugar
(Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
a. Galactose – milk sugar
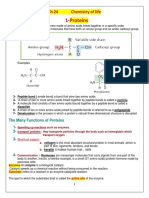
5) Proteins – contains carbon, hydrogen,
b. Fructose – fruit sugar
oxygen, and nitrogen (CHON)
c. Glucose – plant sugar
- Amino Acids: polymers of
b) Disaccharide – two
molecules. Compounds with an
monosaccharides
amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl
a. Sucrose (table sugar) –
group (-COOH)
glucose + fructose
- R-Group: side chain of amino acid
b. Lactose – glucose +
o Can be acidic or basic
galactose
o Polar or nonpolar
c) Polysaccharide – large molecules
o Can contain carbon rings
formed from monosaccharides
- DNA is responsible in giving
- Glycogen (Animal starch): a
instructions on arranging amino
polysaccharide where animals store
acids
excess sugar
- Can control the rate of reactions and
- Cellulose: plant starch that gives
regulate cell processes
plants’ strength and rigidity
2) Lipids – aren’t soluble in water and Enzymes
made of mostly carbon and hydrogen
Catalysts – chemical agent that speeds up
(sometimes there is oxygen)
a reaction without being consumed by the
3) reaction
- Fats, oils, and waxes are common
categories of lipids Enzyme – a catalytic protein
- Can be used to store energy
- (-ase) to determine an enzyme
- They are formed when glycerol
- Enzymes speed up the reaction by
combines with fatty acids
lowering energy barriers
a) Saturated Fatty Acids – maximum
possible number of hydrogen atoms
- Single bonded carbon
GENERAL BIOLOGY Ü
2ND MONTHLY EXAMINATIONS REVIEWER Goodluck!
o Orienting substrates correctly
o Staining substrate bonds
o Providing a favorable
microenvironment
o Covalently bonding to the
The Activation Energy Barrier – initial substrate
energy needed to start a chemical reaction
- Supplied in the form of thermal
energy that the reactant molecules
absorb from their surroundings
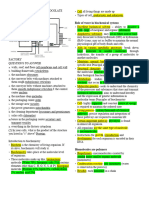
Factors that Affect Enzyme Function
1) Effects of Temperature and pH – each
enzyme has an optimal temperature and
pH level in which it can function
How Enzymes Lower the EA Barrier
- Enzymes catalyze reactions by
lowering the EA barrier
- They do not affect the change in free
energy, they hasten reactions
Substrate Specificity of Enzymes
- Substrate – reactant that an
enzyme act on
- Enzyme-subtrate complex –
enzyme binds to substrate
- Active site – region on the enzyme
where the substrate binds
- Induced fit – enzyme will always
cater a substrate
Catalysis in the Enzyme’s Active Site
Metabolism = Catabolism + Anabolism
- Substrate binds to the active site of
the enzyme a) Catabolism – breaking down of
- The active site can lower an EA substances; produce energy
barrier by:
GENERAL BIOLOGY Ü
2ND MONTHLY EXAMINATIONS REVIEWER Goodluck!
b) Anabolism – form substances;
requires energy
Cofactors
- nonprotein enzyme helpers
- cofactors may be inorganic or
organic
- Coenzyme – organic cofactor
Enzyme Inhibitors
a) Competitive Inhibitors – bind to
the active site of an enzyme,
competing with a substrate
b) Noncompetitive Inhibitors –
binds to another part of an
enzyme causing the enzyme to
change shape and making the
active site less effective
- Examples of Inhibitors: toxins,
poisons, pesicides, antibiotics
You might also like
- A-level Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- CellDocument4 pagesCellanmbeltran31No ratings yet
- STUDY GUIDE For GENERAL BIOLOGY Finals Google DocsDocument3 pagesSTUDY GUIDE For GENERAL BIOLOGY Finals Google DocsTisha ArtagameNo ratings yet
- Biochem Transes 1st TermDocument18 pagesBiochem Transes 1st TermFaye Hashly AfunggolNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersJojo LouNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry ReviewerDocument20 pagesBiochemistry ReviewerabcdeniselimNo ratings yet
- Nucleotide - Monomer of Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesNucleotide - Monomer of Nucleic AcidsMika Sophia GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Foundations of BiochemistryDocument5 pagesChemical Foundations of BiochemistryrxpturousNo ratings yet
- Biochem PDFDocument7 pagesBiochem PDFNhư NguyễnNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Reviewer For SHS 1Document1 pageBIOLOGY Reviewer For SHS 1Johnloyd ParNo ratings yet
- General Biology Reviewer 2Document4 pagesGeneral Biology Reviewer 2nd555No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument6 pagesCarbohydrate MetabolismmygarcianoNo ratings yet
- Bacillus SPP Dormant: Clinical Bacteriology LecDocument5 pagesBacillus SPP Dormant: Clinical Bacteriology LecJamie BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Working Mechanism of EnzymesDocument4 pagesWorking Mechanism of EnzymesfintastellaNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument6 pagesPhysical ScienceCAYABAN, RISHA MARIE DV.No ratings yet
- Introduction To Biological Sciences MidtermsDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Biological Sciences MidtermsMatthew SantiagoNo ratings yet
- JLSRGDNDocument12 pagesJLSRGDNjamiegayleditaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Prelim CompilationDocument22 pagesBiochem Prelim CompilationKezia MadeloNo ratings yet
- DrMinaSamuel-BioEST-ACT-AP-Notes-3&4-Biochemistry & Enzymes-2022Document17 pagesDrMinaSamuel-BioEST-ACT-AP-Notes-3&4-Biochemistry & Enzymes-2022Nour ShahdNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY - The Study of The Chemistry of Living: LinkagesDocument2 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY - The Study of The Chemistry of Living: LinkagesOdessa KwonNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Lecture Term01: Introduction To Metabolism Metabolism Metabolism and Cell StructureDocument4 pagesBiochemistry - Lecture Term01: Introduction To Metabolism Metabolism Metabolism and Cell StructureJohn Daniel AriasNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesBiomoleculesgeecyjane YguintoNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Systems of The Cell PDFDocument6 pagesBiochemical Systems of The Cell PDFCzerinne AlarillaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument38 pagesUnit 2 NotesElen Mae PadugaNo ratings yet
- Chem of LifeDocument1 pageChem of LifeAllen ChristianNo ratings yet
- Science Quiz Bee Reviewer - High School LevelDocument6 pagesScience Quiz Bee Reviewer - High School LevelFamella GalmakNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Reviewer in ScienceDocument3 pagesQuarter 4 Reviewer in ScienceHanna Samantha LisingNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Reviewer Final 1Document5 pagesGen Bio Reviewer Final 1Emmanuelle CalleNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 ReviewDocument18 pagesExam 1 ReviewHannah ThorntonNo ratings yet
- Bmed 105 (Lec) Lecture 2a and 2b (Notes)Document5 pagesBmed 105 (Lec) Lecture 2a and 2b (Notes)Jobelle MalihanNo ratings yet
- Biological ElementsDocument16 pagesBiological Elementsmarwaaishah01No ratings yet
- Biology Exam Notes by ConstantinDocument120 pagesBiology Exam Notes by ConstantinbnvjNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in General Biology 1Document2 pagesReviewer in General Biology 1Moy ReyesNo ratings yet
- Enzymology To Kreb's CycleDocument34 pagesEnzymology To Kreb's Cycleferdinand padillaNo ratings yet
- What Are Enzymes?: EnzymeDocument4 pagesWhat Are Enzymes?: EnzymeMark Jayson ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism Metabolism - The Sum of All Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesMicrobial Metabolism Metabolism - The Sum of All Chemical ReactionsAGENT M.DNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Energy ProductionDocument5 pagesBiochemical Energy ProductionMaria Cyril BaldovinoNo ratings yet
- 1020 NotesDocument17 pages1020 NotesAfnan MNo ratings yet
- Ajssnansnwnnsn Modyol 1Document5 pagesAjssnansnwnnsn Modyol 1Snow Cordelia ThundilliorNo ratings yet
- 1-Proteins: CH 24 Chemistry of LifeDocument6 pages1-Proteins: CH 24 Chemistry of LifeXIBG21SANIANo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - EnzymesDocument19 pagesLecture 3 - EnzymesEiad SamyNo ratings yet
- 6 EnzymesDocument3 pages6 EnzymesIYA LABAONo ratings yet
- Amino Acids are linked by peptide bonds to form formed by linking the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid to the α-amino group of another amino acid with a peptide bond (also called an amide bond)Document2 pagesAmino Acids are linked by peptide bonds to form formed by linking the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid to the α-amino group of another amino acid with a peptide bond (also called an amide bond)Noviemae TuandaNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument6 pagesBiology NoteselviiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocument7 pagesIntroduction To BiochemistryClarence MallariNo ratings yet
- 2-1 Molecules To MetabolismDocument21 pages2-1 Molecules To MetabolismEdward YaoNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes SLDocument69 pagesBiology Notes SLIker GNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Energy ProductionDocument5 pagesBiochemical Energy ProductionAlexandria StylesNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 - REVIEWERDocument5 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 - REVIEWEREunice GarciaNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules - Chapter 4Document9 pagesBiological Molecules - Chapter 4Bimbo, Arabela June G.No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document3 pagesUnit 2Kyla Marie PacubasNo ratings yet
- 06-08 - Carbohydrates - Complex Carbohydrates (1) - 1Document31 pages06-08 - Carbohydrates - Complex Carbohydrates (1) - 1Frankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates in GeneralDocument6 pagesCarbohydrates in GeneralnnnnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Levels of Organization of The Human BodyDocument9 pagesChapter 2 - Levels of Organization of The Human BodyFrancine Danielle TiponesNo ratings yet
- Biochem Midterm ReviewerDocument22 pagesBiochem Midterm Reviewerrentachin18No ratings yet
- Biomolecules - Terms and ProcessesDocument3 pagesBiomolecules - Terms and ProcessesVivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- Webcontent 146 513 1 Biomolecules 20190926165314Document2 pagesWebcontent 146 513 1 Biomolecules 20190926165314Abhishek Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- High Chemical Energy: Sugar Oxygen Organic Compounds (From Light) LightDocument3 pagesHigh Chemical Energy: Sugar Oxygen Organic Compounds (From Light) LightKenneth Rodriguez HerminadoNo ratings yet
- Energy Utilization-1Document4 pagesEnergy Utilization-1Henu AryudaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes 1Document2 pagesBiology Notes 1Paulo AloroNo ratings yet
- Produk OGB DexaDocument4 pagesProduk OGB DexaBrigita AnugrahNo ratings yet
- Addition Polymers (4.8.1)Document4 pagesAddition Polymers (4.8.1)KeerthikaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 7+8+9 B-II)Document2 pagesChemistry-FUNGAT/ECAT: (Chapter 7+8+9 B-II)XXXNo ratings yet
- F.31 01 02 2021Document48 pagesF.31 01 02 2021archit rockzNo ratings yet
- BIS 102 MT 1 Hilt F10 BlankDocument6 pagesBIS 102 MT 1 Hilt F10 BlankKimNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Total Lipids From Chicken Egg Yolk and Qualitative Test For LipidsDocument4 pagesExtraction of Total Lipids From Chicken Egg Yolk and Qualitative Test For LipidsKizer Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Food Packaging Technology: BS-Final Year 18-March-2020Document15 pagesFood Packaging Technology: BS-Final Year 18-March-2020SONIA NABINo ratings yet
- Aaj Ki Chemistry Ki Class..Document9 pagesAaj Ki Chemistry Ki Class..prashant panwarNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2Document2 pagesGen Chem 2Ream MairNo ratings yet
- The RSPO Certified Sustainable Palm Oil Supply Chain - How To Take Part-EnglishDocument11 pagesThe RSPO Certified Sustainable Palm Oil Supply Chain - How To Take Part-Englishsowmya.mas1542No ratings yet
- MODULE 7 Lesson1 - General Biology IDocument32 pagesMODULE 7 Lesson1 - General Biology IAlvin PaboresNo ratings yet
- (Tannin Extract Potential of Surian Leaf and Bark as α-Glucosidase Inhibitor)Document9 pages(Tannin Extract Potential of Surian Leaf and Bark as α-Glucosidase Inhibitor)dimas rizqiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report Experiment No. 2 Title: Isolation and Qualitative TestsDocument12 pagesLaboratory Report Experiment No. 2 Title: Isolation and Qualitative TestsMaria Angelika Bughao100% (1)
- DNA DR In-Class ActivitiesDocument15 pagesDNA DR In-Class ActivitiesCéline Engels100% (1)
- Nucleic AcidsDocument56 pagesNucleic AcidsShane G.No ratings yet
- Urea CycleDocument13 pagesUrea CycleShampa SenNo ratings yet
- Product Information Product Data Sheet: DescriptionDocument4 pagesProduct Information Product Data Sheet: DescriptionIRENENo ratings yet
- CHEM 2324 SPRING 2012 EXAM 1 W AnswersDocument8 pagesCHEM 2324 SPRING 2012 EXAM 1 W AnswersSusana PortilloNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 Protein Biosynthesis: StructureDocument19 pagesUnit 14 Protein Biosynthesis: StructureAD-MQNo ratings yet
- Registered Medicine List 07-04-2014 Sse Frequently UpdatedDocument116 pagesRegistered Medicine List 07-04-2014 Sse Frequently Updatedjema; belihuNo ratings yet
- What Are Allosteric Enzymes?Document2 pagesWhat Are Allosteric Enzymes?Anila zafarNo ratings yet
- Nama Obat Puskes CisadeaDocument5 pagesNama Obat Puskes Cisadeahadira naNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Drag & Drop Activity 2021Document6 pagesProtein Synthesis Drag & Drop Activity 2021Gloria LaneNo ratings yet
- 6/27/2019 NO NAMA BARANG QTY UOM Batch EDDocument8 pages6/27/2019 NO NAMA BARANG QTY UOM Batch EDRedCazorlaNo ratings yet
- PiroxicamDocument10 pagesPiroxicamPapaindoNo ratings yet
- Nutrients of Bitter GourdDocument2 pagesNutrients of Bitter GourdEva Arian JoyNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Organic Basics + IUPAC Notes PDFDocument37 pagesClass 11 Organic Basics + IUPAC Notes PDFproud vedan laxmiNo ratings yet
- 404 - Lipid - ZC# 25-30Document47 pages404 - Lipid - ZC# 25-30fatehatun noorNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B (Pyridoxine) : FunctionDocument5 pagesVitamin B (Pyridoxine) : FunctionWill TohallinoNo ratings yet
- Siklus KalvinDocument5 pagesSiklus Kalvinnovani florensiaNo ratings yet
- ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideFrom EverandICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideAndrew TeasdaleNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingFrom EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeFrom EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsFrom EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesFrom EverandThe Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodFrom EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (20)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Billion-Dollar Molecule: The Quest for the Perfect DrugFrom EverandThe Billion-Dollar Molecule: The Quest for the Perfect DrugRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Essential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesFrom EverandEssential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)