Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PDF 27feb24 0942 Splitted
PDF 27feb24 0942 Splitted
Uploaded by
ks7580713Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PDF 27feb24 0942 Splitted
PDF 27feb24 0942 Splitted
Uploaded by
ks7580713Copyright:
Available Formats
30025 ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY – II
DETAILED SYLLABUS
Contents: Theory
Unit Name of the Topic Hours
ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY
I
1.1 Air Pollution 5 Hrs
Pollution and Air pollution – Definition – Air pollutants (SO2, H2S, HF, CO
and Dust) – Sources and Harmful effects – Formation of Acid Rain –
Harmful effects – Green House Effect – Causes – Global warming –
Harmful effects – Ozone Layer – Importance – Causes for Depletion of
Ozone Layer (No equations) – Harmful effects of Ozone Layer Depletion
– Control of Air Pollution.
4 Hrs
1.2 Water Pollution
Causes of Water Pollution – Sewage, Effluents, Algae and
Microorganisms – Harmful effects –Sewerage – Definition – Sewage
Disposal – Industrial Effluents – Harmful effects of Effluents – Harmful
effects of Heavy Metal Ions – Lead, Cadmium, Zinc and Copper –
Treatment of Effluents – Eutrophication – Definition and harmful effects.
2 Hrs
1.3 Solid Waste Management
Solid Waste – Definition – Problems – Types of Solid Waste – Methods of
disposal – Land fill and Incineration. 2 Hrs
1.4 Green Chemistry
Definition – Goals of Green Chemistry (Basic ideas) – Recycling –
Definition – Examples – Advantages of Recycling (Basic ideas)
FUELS, COMBUSTION AND REFRACTORIES
II 6 Hrs
2.1 Fuels
Fuel and fossil fuel – Definition – Calorific value – Classification of fuels –
Solid fuels – Wood – Coal – Varieties of Coal – Composition – Specific
uses – Liquid fuels – Petroleum – Fractional distillation – Fractions and
uses – Cracking (Concept only) – Liquid Hydrogen as fuel – Gaseous
fuels – Preparation, composition and specific uses of Producer gas and
Water gas – Composition and uses of CNG and LPG – Relative
advantages of solid, liquid and gaseous fuels.
2.2 Combustion
5 Hrs
Definition – Combustion calculation by mass (for solid and liquid fuels) –
Combustion calculation by volume (for gaseous fuels) – Stoichiometric
calculations – Volume of air required – Excess air – Definition of Flue gas
– Flue gas Analysis – Orsat Apparatus – Simple numerical problems.
2.3 Refractories
Definition – Requirements of a good Refractory – Classification – Acidic, 2 Hrs
Basic and Neutral Refractories – Examples and uses – Uses of Fireclay
bricks, Alumina bricks and Silica bricks.
Unit Name of the Topic Hours
III EXTRACTION OF METALS, POWDER METALLURGY, ALLOYS AND
ABRASIVES
2 Hrs
3.1 Extraction of metals
Extraction of Tungsten and Titanium – Uses of Tungsten and Titanium.
3.2 Powder metallurgy 3 Hrs
Definition – Preparation of Metal Powder – Atomization – Reduction of
Metal Oxide – Applications of Powder Metallurgy.
3.3 Alloys 4 Hrs
Definition – Purpose of alloying – Types – Ferrous Alloys – Composition
and uses of Stainless Steel, Chromium Steel and Vanadium Steel – Non-
ferrous alloys – Composition and uses of Nichrome, Dutch metal,
German silver, Gun metal and Duralumin.
3.4 Abrasives 4 Hrs
Definition – Classification – Hardness in Moh’s scale – Natural abrasives
– Diamond, Corundum, Emery and Garnet – Synthetic abrasives –
Carborundum – Boron carbide – Manufacture – Properties and uses.
IV CEMENT, CERAMICS, LUBRICANTS AND ADHESIVES
4.1 Cement 3 Hrs
Definition – Manufacture of Portland Cement – Wet Process – Setting of
Cement (No equation).
4.2 Ceramics 3 Hrs
White pottery – Definition – Manufacture of White pottery – Uses –
Definition of glazing – Purpose – Method – Salt glazing.
4.3 Lubricants 3 Hrs
Definition – Characteristics of Lubricant – Types of Lubricants – Solid –
Semi-solid –Liquid Lubricants .
4.4 Adhesives 4 Hrs
Definition – Requirements of good adhesives – Natural adhesive – Uses
of Shellac, Starch, Asphalt – Synthetic adhesive – Uses of Cellulose
Nitrate, PVC, Phenol-formaldehyde and Urea-formaldehyde.
You might also like
- Type Your Name:: Student Guide: Enzymes - AP STEM Case and HandbookDocument5 pagesType Your Name:: Student Guide: Enzymes - AP STEM Case and Handbookanna roth75% (4)
- Cellular Respiration Lab ReportDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration Lab Reportbetojaimes83% (6)
- Manufacture of Sodium DichromateDocument84 pagesManufacture of Sodium DichromateAhmed Ali80% (10)
- PLP P-10-2003, Amine Sweetening Process-2nd Ed-RosenDocument49 pagesPLP P-10-2003, Amine Sweetening Process-2nd Ed-Rosenivanov5559No ratings yet
- Theory of Non-Ferrous Metals and Alloys ProcessingDocument83 pagesTheory of Non-Ferrous Metals and Alloys ProcessingHimanshuDeepNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry IDocument5 pagesEngineering Chemistry Isenthil kumaran mNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Materials and MetallurgyDocument16 pages4.1 Materials and MetallurgyVijayKumarNo ratings yet
- 4Document1 page4Alagarsamy GNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry IIDocument4 pagesEngineering Chemistry IISatyam SahuNo ratings yet
- BTech Ceramic SyllabusDocument63 pagesBTech Ceramic Syllabustayep sherifNo ratings yet
- Metals & Non-Metals Class VIIIDocument30 pagesMetals & Non-Metals Class VIIIAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Coal and Petroleum - Notes - 220908 - 185218Document14 pagesCoal and Petroleum - Notes - 220908 - 185218VENKATESH PRABHUNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument2 pagesChemapi-236544093No ratings yet
- MT308 Fuels, Furnaces and RefractoriesDocument3 pagesMT308 Fuels, Furnaces and RefractoriesMerrin John VarkeyNo ratings yet
- SS1 Chemistry First Term NoteDocument25 pagesSS1 Chemistry First Term Notematharuche2011No ratings yet
- 10ce201 Civil Engineering Materials and Geology Credits: 4:0:0 ObjectivesDocument2 pages10ce201 Civil Engineering Materials and Geology Credits: 4:0:0 ObjectivesEsrom AbebeNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Study MaterialDocument37 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Study MaterialelenaNo ratings yet
- Mineral AccountingDocument9 pagesMineral AccountingJudith LlemitNo ratings yet
- ABRASIVES - DoneDocument5 pagesABRASIVES - Donethercode sampNo ratings yet
- Engineering MaterialDocument2 pagesEngineering Materialultimatestatus2279No ratings yet
- Kuliah 1 Pengmin Pebruari 2024Document56 pagesKuliah 1 Pengmin Pebruari 2024naufalpriambodo1No ratings yet
- Allotropes of Carbon With IllustrationDocument15 pagesAllotropes of Carbon With IllustrationIssa umulimaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 - Part 1Document52 pagesCH 1 - Part 1KHUSHI JAINNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 Minerals and Energy Resources NoteDocument6 pagesCh-5 Minerals and Energy Resources Notetanusree1603No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: B.E Semester: 3 Aeronautical EngineeringDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University: B.E Semester: 3 Aeronautical EngineeringjayNo ratings yet
- Chromium Compounds: Historical. Chrome Iron Ore (Chromite) WasDocument15 pagesChromium Compounds: Historical. Chrome Iron Ore (Chromite) WasYusufNo ratings yet
- PDF 27feb24 0948 SplittedDocument4 pagesPDF 27feb24 0948 Splittedks7580713No ratings yet
- Guru Nanak Engineering College: COURSE FILE (2006-2007)Document8 pagesGuru Nanak Engineering College: COURSE FILE (2006-2007)chemistrymasterNo ratings yet
- Art 3A10.1007 2Fs40789 016 0127 0 - 2Document7 pagesArt 3A10.1007 2Fs40789 016 0127 0 - 2aprianisusilawati6No ratings yet
- Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions On Rice Husk: Isotherm Modeling and Error AnalysisDocument8 pagesAdsorption of Heavy Metal Ions On Rice Husk: Isotherm Modeling and Error AnalysisDian Ramadhan RambeNo ratings yet
- Corrosion: ISO Standards HandbookDocument3 pagesCorrosion: ISO Standards HandbookAndrews DanquahNo ratings yet
- CHMT 2009 Week 5 Coal PropertiesDocument38 pagesCHMT 2009 Week 5 Coal PropertiesTiisetso MokwaneNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry: (Elective - I)Document2 pagesEngineering Chemistry: (Elective - I)chamanyusuffNo ratings yet
- Nearby Analysis and Density of CoalDocument9 pagesNearby Analysis and Density of CoalWendyNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering MaterialsDocument6 pagesCivil Engineering Materialsvipar snikeNo ratings yet
- Carbon STD 9Document5 pagesCarbon STD 9yuvrajNo ratings yet
- A Review On The Existence of Chrome in Cement and Environmental Remedies To Control Its EffectDocument7 pagesA Review On The Existence of Chrome in Cement and Environmental Remedies To Control Its EffectMUHAMMAD RIZAL MAULANANo ratings yet
- Grade 11Document2 pagesGrade 11Julianna PersaudNo ratings yet
- Coal Petrology PDFDocument14 pagesCoal Petrology PDFS Hashim RizviNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Variety of Minerals MODULEDocument3 pages4.1 Variety of Minerals MODULESY ChowNo ratings yet
- Control Environmental PollutionDocument7 pagesControl Environmental Pollutionhassannjenga589No ratings yet
- Heavy Metal Distribution in Contaminated Oil - Based Mud From A Selected Oilfield in GhanaDocument7 pagesHeavy Metal Distribution in Contaminated Oil - Based Mud From A Selected Oilfield in GhanaemefakoveNo ratings yet
- 7 MetallurgyDocument2 pages7 MetallurgyNarasimha Murthy InampudiNo ratings yet
- Refractories 01Document22 pagesRefractories 01dika wahyu0% (1)
- Mineral Processing Lecture NotesDocument943 pagesMineral Processing Lecture NotesGeorge GomezNo ratings yet
- 02 Raw MaterialDocument14 pages02 Raw MaterialGustavo Alberto De Almeida PezaoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BE MergedDocument95 pagesSyllabus BE MergedSANGITA CHIRANJIBI POKHRELNo ratings yet
- Extraction of MetalsDocument31 pagesExtraction of MetalsTadiwa RylyNo ratings yet
- Pollution - Pengantar Teknik Kimia - 2018Document22 pagesPollution - Pengantar Teknik Kimia - 2018Annisah MardiyyahNo ratings yet
- Engg Metallurgy Study MaterialDocument178 pagesEngg Metallurgy Study Material7 D24 ANSHUMAN PATILNo ratings yet
- Foundry Technology: Reference BooksDocument34 pagesFoundry Technology: Reference BooksGowtham VishvakarmaNo ratings yet
- Engineering MaterialsDocument27 pagesEngineering MaterialsanieshNo ratings yet
- MetalworkDocument10 pagesMetalworkMr Dampha100% (1)
- Material Paper - 2Document17 pagesMaterial Paper - 2Syamsul Bahry HarahapNo ratings yet
- A Project ReportDocument29 pagesA Project ReportchikubadgujarNo ratings yet
- Wlfely Table 1Document10 pagesWlfely Table 1Hashani Anuttara AbeygunasekaraNo ratings yet
- Spontaneous Combustion of Coal in Stockpiling Case StudyDocument18 pagesSpontaneous Combustion of Coal in Stockpiling Case StudyKanumalli JitinNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Physicochemical and Thermal Characterisation of Dolomite and Limestone Samples For Use in Ironmaking and SteelmakingDocument10 pagesA Study On The Physicochemical and Thermal Characterisation of Dolomite and Limestone Samples For Use in Ironmaking and SteelmakingArina SaukiNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1 - Introduction To Particle TechnologyDocument10 pagesLECTURE 1 - Introduction To Particle TechnologyLucienne IrianaNo ratings yet
- Engineering ChemistryDocument3 pagesEngineering ChemistrydivNo ratings yet
- Amp SyllabusDocument1 pageAmp SyllabusKathirvel KNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry II: Course DescriptionDocument4 pagesEngineering Chemistry II: Course DescriptionSubas ShresthaNo ratings yet
- The Determination of Impurities in Nuclear Grade Sodium MetalFrom EverandThe Determination of Impurities in Nuclear Grade Sodium MetalNo ratings yet
- PDF 27feb24 0948 SplittedDocument3 pagesPDF 27feb24 0948 Splittedks7580713No ratings yet
- PDF 27feb24 0941 SplittedDocument2 pagesPDF 27feb24 0941 Splittedks7580713No ratings yet
- PDF 27feb24 0941 SplittedDocument2 pagesPDF 27feb24 0941 Splittedks7580713No ratings yet
- Getting Started With C++Document5 pagesGetting Started With C++ks7580713No ratings yet
- Nstse 12PCMDocument8 pagesNstse 12PCMAim JEE 2023No ratings yet
- Gas Engines Emissions & Exhaust After-Treatment A&i GuideDocument36 pagesGas Engines Emissions & Exhaust After-Treatment A&i GuidelamNo ratings yet
- Weld On Industrial Brochure DEC2015Document40 pagesWeld On Industrial Brochure DEC2015SREENATH SREEDHARANNo ratings yet
- Chem Final Lab ReportDocument2 pagesChem Final Lab ReportAkshat LalNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 - Week 1:: ScienceDocument19 pagesQuarter 4 - Week 1:: ScienceLEANo ratings yet
- D 6894 - 03 - Rdy4otqDocument13 pagesD 6894 - 03 - Rdy4otqNguyễn Bằng NộiNo ratings yet
- 02 Solved ProblemsDocument16 pages02 Solved ProblemsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Gas Absorption: I. AbstractsDocument3 pagesGas Absorption: I. AbstractsFarah AtiqahNo ratings yet
- Paper No 1.3: Submitted By: Group No. 3Document11 pagesPaper No 1.3: Submitted By: Group No. 3Joash SalamancaNo ratings yet
- Brewing With Cannabis Sativa Vs Humulus Lupulus A ReviewDocument9 pagesBrewing With Cannabis Sativa Vs Humulus Lupulus A ReviewJusepe Hbk LópezNo ratings yet
- Cracking Bgcse Chemistry PDFDocument52 pagesCracking Bgcse Chemistry PDFKordell leyd100% (1)
- JEE Main 30-01-2024 (Morning Shift) : QuestionsDocument40 pagesJEE Main 30-01-2024 (Morning Shift) : QuestionsMahir KachwalaNo ratings yet
- Lectura 2. The Yin and Yang in The Development of Catalytic Processes. Catalysis Research and Reaction EngineeringDocument18 pagesLectura 2. The Yin and Yang in The Development of Catalytic Processes. Catalysis Research and Reaction EngineeringTRIANA FORERO GABRIEL RICARDONo ratings yet
- MSDS 000000000030269688 enDocument12 pagesMSDS 000000000030269688 enjuanfelipehincapieNo ratings yet
- ArticuloDocument4 pagesArticuloLAURA1234567No ratings yet
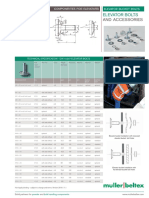
- AND Accessories: Elevator BoltsDocument3 pagesAND Accessories: Elevator BoltsmaiquelernNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13.1 QuestionsDocument6 pagesChapter 13.1 QuestionsLeena BhaiNo ratings yet
- A Short-Sleeved Casual Top, Generally Made of Cotton, Having The Shape of A T When Spread Out FlatDocument14 pagesA Short-Sleeved Casual Top, Generally Made of Cotton, Having The Shape of A T When Spread Out FlatOldemar GarciaNo ratings yet
- 31-The Olefin Metathesis ReactionDocument38 pages31-The Olefin Metathesis ReactionThảo Hoàng PhươngNo ratings yet
- Neet Chemistry Notes-1Document37 pagesNeet Chemistry Notes-1Abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Me8351 MT1 Iq ND19 RejinpaulDocument1 pageMe8351 MT1 Iq ND19 RejinpaulShrinath MPCBNo ratings yet
- MSDS-Sodium MetabisulfiteDocument8 pagesMSDS-Sodium MetabisulfiteAbdullah AbedNo ratings yet
- Hi-Tech Magazine Jan 2022 - How To Start Manufacturing Industry - Project Consultancy ServicesDocument42 pagesHi-Tech Magazine Jan 2022 - How To Start Manufacturing Industry - Project Consultancy ServicesSachin SharmaNo ratings yet
- GenChem2 Q3 Mod3 Colligative Properties and Thermodynamics v4Document33 pagesGenChem2 Q3 Mod3 Colligative Properties and Thermodynamics v4arlene daug40% (5)
- MeltSpinning Genel (Bikomponent)Document32 pagesMeltSpinning Genel (Bikomponent)Uscan UskanerNo ratings yet
- Fibre Reinforced ConcreteDocument41 pagesFibre Reinforced ConcretevamshiNo ratings yet
- Glass - Wikipedia 6 PDFDocument1 pageGlass - Wikipedia 6 PDFA-ReaderNo ratings yet