Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Task 2 (Cainto)
Uploaded by
Cainto JayveeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Task 2 (Cainto)
Uploaded by
Cainto JayveeCopyright:
Available Formats
JAYVEE CAINTO
BSP 3A
TASK 2: Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology
Instructions: Search for the following terminologies about the Language of Anatomy
a. Directional Terms
Term Definition
1. Right Toward the body’s right side
2. Left Toward the body’s left side
3. Inferior Below
4. Superior Above
5. Anterior Toward the front of the body
6. Posterior Toward the back of the body
7. Dorsal Toward the back
8. Ventral Toward the front
9. Proximal Closer to a point of attachment
10. Distal Farther from a point of attachment
11. Lateral Away from the midline of the body
12. Medial Toward the midline of the body
13. Superficial Toward the surface
14. Deep Away from the surface
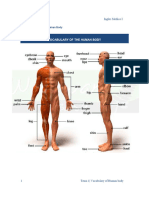
b. Body Parts and Regions
Term Definition
1. Frontal Forehead
2. Orbital Eye
3. Nasal Nose
4. Oral Mouth
5. Cervical Neck
6. Otic Ear
7. Buccal Buccal
8. Mental Chin
9. Clavicular Collarbone
10. Pectoral Chest
11. Sternal Breastbone
12. Mammary Breast
13. Axillary Armpit
14. Brachial Arm
15. Antecubital Front of elbow
16. Antebrachial Forearm
17. Abdominal Abdomen
18. Umbilical Navel
19. Pelvic Pelvis
20. Inguinal Groin
21. Pubic Genital
22. Carpal Wrist
23. Palmar Palmar
24. Digital Fingers and Toes
25. Coxal Hip
26. Femoral Thigh
27. Patellar Kneecap
28. Crural Leg
29. Talus Ankle
30. Dorsum Top of foot
c. Body Planes
A plane is an imaginary two-dimensional surface that passes through the body.
Term Definition
1. Sagittal divides the body into right and left sections.
2. Transversal divides the body into superior and inferior sections.
3. Coronal divides the body into dorsal and ventral sections.
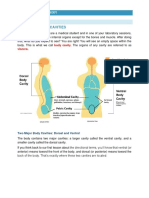
d. Body Cavities
A body cavity is a fluid-filled space inside the body that holds and protects internal organs.
Term Definition
1. Cranial The anterior portion of the dorsal cavity consists of the
space inside the skull. The cranial cavity is the anterior
portion of the dorsal cavity consisting of the space inside
the skull. This cavity contains the brain, the meninges of
the brain, and cerebrospinal fluid.
2. Vertebral The vertebral cavity is the posterior portion of the dorsal
cavity and contains the structures within the vertebral
column. These include the spinal cord, the meninges of
the spinal cord, and the fluid-filled spaces between
them.
3. Thoracic The thoracic cavity is the anterior ventral body cavity
found within the rib cage in the torso. It houses the
primary organs of the cardiovascular and respiratory
systems, such as the heart and lungs, but also includes
organs from other systems, such as the esophagus and
the thymus gland. The thoracic cavity is lined by two
types of mesothelium, a type of membrane tissue that
lines the ventral cavity: the pleura lining of the lungs,
and the pericardium lining of the heart.
4. Abdominal Its upper boundary is the diaphragm, a sheet of muscle
and connective tissue that separates it from the chest
cavity; its lower boundary is the upper plane of the pelvic
cavity. Vertically it is enclosed by the vertebral
column and the abdominal and other muscles. The
abdominal cavity contains the greater part of
the digestive tract, the liver and pancreas, the spleen,
the kidneys, and the adrenal glands located above the
kidneys.
5. Pelvic The pelvic cavity functions as a housing space for the
urinary bladder, the pelvic colon, internal reproductive
organs, and the rectum.
6. Ventral The ventral cavity, the interior space in the front of the
body, contains many different organ systems. The
organs within the ventral cavity are also called viscera.
The ventral cavity has anterior and posterior portions
divided by the diaphragm; a sheet of skeletal muscle
found beneath the lungs.
You might also like
- LAB EXERCISE 1 Organization of The Human BodyDocument8 pagesLAB EXERCISE 1 Organization of The Human Bodyley leynNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomical Terminologies (Final)Document32 pagesBasic Anatomical Terminologies (Final)April Joy PueyoNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyDianne Comon86% (7)
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument23 pagesHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyMuhammad ShahidNo ratings yet
- Summarization About AnatomyDocument12 pagesSummarization About AnatomyJhomer CabasNo ratings yet
- Limchiu, Kyle - ANALab Project 1Document8 pagesLimchiu, Kyle - ANALab Project 1Kyle LimchiuNo ratings yet
- Anatomical PrinciplesDocument4 pagesAnatomical Principleslourd nabNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Human BodyDocument5 pagesParts of The Human BodybruhwahatNo ratings yet
- LAB EXERCISE 1 Organization of The Human Body - BS PSYCH 1 B 1Document10 pagesLAB EXERCISE 1 Organization of The Human Body - BS PSYCH 1 B 1Louise BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Chapter I Structural OrganizationDocument15 pagesChapter I Structural OrganizationTitoMacoyTVNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesBasic Anatomy and PhysiologyDr Shreshta Reddy KNo ratings yet
- Anatomical TermsDocument4 pagesAnatomical TermsLEENo ratings yet
- Cell JunctionsDocument11 pagesCell Junctionslourd nabNo ratings yet
- Language of AnatomyDocument5 pagesLanguage of AnatomyMaria Brooklyn Pacheco100% (2)
- Solution Manual Laboratory Manual For Anatomy Physiology Featuring Martini Art Main Version 5th Edition by Wood SLP1177Document5 pagesSolution Manual Laboratory Manual For Anatomy Physiology Featuring Martini Art Main Version 5th Edition by Wood SLP1177Thar AdeleiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy IntroductionDocument9 pagesAnatomy IntroductionLoyd TuvillaNo ratings yet
- Get Anatomy On Occupational StandardDocument39 pagesGet Anatomy On Occupational StandardmisawNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 OutlineDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 OutlineCJ DaodaoenNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Bojo Suasa, RN Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila College of NursingDocument38 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Bojo Suasa, RN Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila College of NursingVernice OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 INTRODUCTIONDocument7 pagesModule 1 INTRODUCTIONMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Anatomy Gross AnatomyDocument20 pagesMicroscopic Anatomy Gross AnatomyBurak KıvırcıkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Body As A Whole 03032022Document28 pagesIntroduction To The Body As A Whole 03032022Aafia sarwarNo ratings yet
- PATHFIT 1 Module 2 FinalDocument14 pagesPATHFIT 1 Module 2 FinalScarlet VillamorNo ratings yet
- PATHFIT 1 Module 2 FinalDocument14 pagesPATHFIT 1 Module 2 FinalScarlet VillamorNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1629098154770 6832932906945476564Document8 pagesOrca Share Media1629098154770 6832932906945476564Scar ShadowNo ratings yet
- LO 1 Anatomical Positions NOTESDocument14 pagesLO 1 Anatomical Positions NOTESMoza AlaliliNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument9 pagesAnaphy ReviewerJohn Rick OrineNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology: Level of Structural Organization of The BodyDocument6 pagesHuman Physiology: Level of Structural Organization of The Bodyhasan satchetNo ratings yet
- Baquero Act 6 Anaphy DONEDocument11 pagesBaquero Act 6 Anaphy DONEKent TutorNo ratings yet
- ANTY 1401 - Week 1 - : AnswersDocument3 pagesANTY 1401 - Week 1 - : AnswersCarina LattoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To General AnatomyDocument7 pagesIntroduction To General AnatomyPia Abila100% (1)
- Thorax by AurelioDocument39 pagesThorax by AurelioBlü BluNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Language Lab ManualDocument7 pagesAnatomical Language Lab ManualisahNo ratings yet
- In Human AnatomyDocument18 pagesIn Human AnatomyBurak KıvırcıkNo ratings yet
- HSCI 103 Lab 3 The Respiratory SystemDocument7 pagesHSCI 103 Lab 3 The Respiratory SystemMatthewFlecknoeNo ratings yet
- Rat AnatomyDocument4 pagesRat AnatomySophia Ho100% (1)
- Septimo, Ricka Marie D. - Labortaory No. 7. Frog Organ System Part 1Document4 pagesSeptimo, Ricka Marie D. - Labortaory No. 7. Frog Organ System Part 1Black RoseNo ratings yet
- Cavidades Corporales AnatomiaDocument4 pagesCavidades Corporales AnatomiaBOKOR5000No ratings yet
- LECTURE 2 - Terminology and Body PlanesDocument10 pagesLECTURE 2 - Terminology and Body PlanesGGonzales KarlaNo ratings yet
- Body Cavities PrezDocument9 pagesBody Cavities Prezapi-421859429No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Body As A WholeDocument29 pagesIntroduction To The Body As A Wholekhizer hayatNo ratings yet
- Ingles I - TP 1 2021Document5 pagesIngles I - TP 1 2021Mariana Vanesa AndradeNo ratings yet
- Human Body Anatomical TermsDocument2 pagesHuman Body Anatomical TermsMazucatoNo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument5 pagesHuman AnatomyAIRENA RAIN TAMPOSNo ratings yet
- INGLES MEDICO I - Clase 1 - Human Body 2023Document26 pagesINGLES MEDICO I - Clase 1 - Human Body 2023alinelucioalvesNo ratings yet
- Anaphy (Lab) ReviewerDocument3 pagesAnaphy (Lab) ReviewerAgatha Cristie AndradaNo ratings yet
- ملزمة التشريح النظري كاملةDocument157 pagesملزمة التشريح النظري كاملةalidoctor678No ratings yet
- AnaPhy-lab Exercise1Document8 pagesAnaPhy-lab Exercise1CEEJNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument5 pagesAnatomywella wellaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Anatomical TerminologiesDocument11 pagesActivity 1 Anatomical TerminologiesMartina SilerioNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Organization of The Human BodyDocument8 pagesModule 6 - Organization of The Human Body10. Briol AlvinNo ratings yet
- Organization of The Human Body: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesOrganization of The Human Body: Learning ObjectivesDayceNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY EXERCISE 1 Organization of The Human BodyDocument7 pagesLABORATORY EXERCISE 1 Organization of The Human BodyTokyo TokyoNo ratings yet
- M1 L3 Body CavitiesDocument3 pagesM1 L3 Body CavitiesYshi HoranNo ratings yet
- LO 2 Anatomy of Body Compartments (Tanya)Document3 pagesLO 2 Anatomy of Body Compartments (Tanya)nit33vNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - The Human Body - 3 - The Human Body CavitiesDocument4 pagesLesson 1 - The Human Body - 3 - The Human Body CavitiesAlphine DalgoNo ratings yet
- INGLES I TP 2 - Ud 2Document10 pagesINGLES I TP 2 - Ud 2DaniNo ratings yet
- AP1 Lab1 Introduction FA2021Document12 pagesAP1 Lab1 Introduction FA2021Doaa aliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology OutlineDocument13 pagesAnatomy and Physiology OutlineChester RiogelonNo ratings yet
- Intro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1From EverandIntro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1No ratings yet
- Mitosis Meiosis NotesDocument7 pagesMitosis Meiosis NotesSophia Cook100% (1)
- Postreading Self-Assessment and CME Test-Preferred ResponsesDocument10 pagesPostreading Self-Assessment and CME Test-Preferred Responsesdr.cidgutNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. One-Compartment Open Model Intravenous Bolus AdministrationDocument23 pagesChapter 3. One-Compartment Open Model Intravenous Bolus AdministrationbencleeseNo ratings yet
- By: Abduljabbar Hamid Jabbar: University of Baghdad-College of Medicine M. B. Ch. BDocument14 pagesBy: Abduljabbar Hamid Jabbar: University of Baghdad-College of Medicine M. B. Ch. BXena XenaNo ratings yet
- Obat-Obatan ResusitasiDocument21 pagesObat-Obatan ResusitasiCut Thalya Alissya RahmaNo ratings yet
- The Hallmarks of AgingDocument47 pagesThe Hallmarks of AgingNatalia Macarena López López100% (1)
- Basa, Gina Solon 2133027610Document3 pagesBasa, Gina Solon 2133027610ginaNo ratings yet
- Textbook PTTHTM 2022Document534 pagesTextbook PTTHTM 2022bndmghmrczNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument423 pagesHistologydorina0101100% (1)
- Combiscreen PDFDocument3 pagesCombiscreen PDFCristian LaraNo ratings yet
- The Evil Russian SpeaksDocument13 pagesThe Evil Russian SpeaksDmitriKartikeya100% (1)
- BIO-207 (1) Homeostasis Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesBIO-207 (1) Homeostasis Lecture NotesJNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 OPERANT LEARNING FinalDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 5 OPERANT LEARNING FinalWeyvin Maury Onde100% (1)
- The Lymphatics of The Head, Face&NeckDocument41 pagesThe Lymphatics of The Head, Face&NeckJavy BelonioNo ratings yet
- STEP1 Sample Pass Report 2022Document1 pageSTEP1 Sample Pass Report 2022M. Baidar SaeedNo ratings yet
- (Gross A) Lower Extremities, Thorax, and Lungs Practicals Reviewer (Gabasan) (Lab)Document75 pages(Gross A) Lower Extremities, Thorax, and Lungs Practicals Reviewer (Gabasan) (Lab)Kristine Nicole UbanaNo ratings yet
- P.E Training Program NotesDocument4 pagesP.E Training Program Notesjohn smithNo ratings yet
- Guided Meditation Lesson Plan - GimbelDocument3 pagesGuided Meditation Lesson Plan - GimbelKarisma JayNo ratings yet
- GCSE (9-1) Y9 Science Final Exam 15 - 16 With Mark SchemeDocument31 pagesGCSE (9-1) Y9 Science Final Exam 15 - 16 With Mark SchemePaul Burgess33% (3)
- Workout CalendarDocument2 pagesWorkout CalendarKatie Bonick-ColbreseNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Learning Goals - IPHY 4440Document9 pagesEndocrinology Learning Goals - IPHY 4440Geline Joy D. SamillanoNo ratings yet
- Bodybuilding ComDocument38 pagesBodybuilding ComSuruthiPriyan100% (2)
- Ascending and Descending Spinal Tracts 2016Document20 pagesAscending and Descending Spinal Tracts 2016Ayodeji LuckyNo ratings yet
- Start TriageDocument29 pagesStart TriageSyifa FatiyaNo ratings yet
- Major Case 3Document3 pagesMajor Case 3Christine Evan HoNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Septic ShockDocument16 pagesCase Study - Septic ShockIrene Mae Villanueva Ariola100% (2)
- What Is First Aid? A Simple: Definition 1Document3 pagesWhat Is First Aid? A Simple: Definition 1Robert D.PalbanNo ratings yet
- Hypoxia and Its Types SaleemDocument19 pagesHypoxia and Its Types SaleemSanwan NaichNo ratings yet
- Hyper Kale Mia Case ReviewDocument4 pagesHyper Kale Mia Case ReviewSamina AhmadNo ratings yet