Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics All Formulae
Physics All Formulae
Uploaded by
hyunjinsblueorbsOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics All Formulae
Physics All Formulae
Uploaded by
hyunjinsblueorbsCopyright:
Available Formats
ML Aggarwal RS Aggarwal Goyal S.
Chand Selina Dalal Nootan
Typing Jobs
Receptix Open
Physics Formula ICSE 10 Class Standard Chapter-Wise
February 16, 2020 by PANDEY TUTORIAL
Physics Formula ICSE 10 Class Standard Chapter-Wise. Applicable in All publications of ICSE Class-10 Physics. Formula of ICSE
Physics Class 10 is very important to solve the problems. Concise Selina Publishers Physics Formula for ICSE Class 10. we advice you to
view ICSE class-10 mathematics formula chapter-wise.
Physics Formula ICSE 10 Class Standard Chapter-Wise
Important unit is given for ICSE Class 10 Physics Formula Topics.
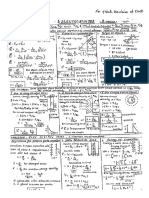
Chapter -1 Force
Newton'ssecondlaw FaAp/At Forceisdirectlyproportionaltotherateofchange
ofmomentumandindirectlyproportionaltorate
ofchangeoftime
Momentum p=mV Momentumistheproductofmassandvelocity
Changeinmomentum Ap=A(mu)ormAv
Rateofchangeof Ap =Amu/At
momentum At
Rateofchangeof Ap Force=MassXAcceleration
momentum Ar
1N=10°Dynes NewtonistheSIunitandDyneisCGSUnit
Gravitationalunitof amg
force
Equationofmotion
2082
Smut+
v2aum2as
1Nm=10°dynescm
1kgfXm=9.8Nm
1gfXcm=980dynecm
Principleofmoments simGekwsemoments
=Sumanticlockwise
moments
Typing Jobs
Receptix Open
Chapter-2 Work Power energy
Work W=Fxs Workdone=ForceX
Displacement
Work W=FSCose Whentheworkdonebytheforce
whenthedisplacementisnot
alongtheforce
PositiveWork W=FS When6=0,examplePositive
workdonebyaforceofgravityin
freefall
Teroworkcone [W=FSCos®,when@=90,W= Workconov.onamoleis
carryingsomeloadonhishead
moveshorizontaliv.
More•Teroworkconeov
centripetalforce.
Negativeworkdone W=-FS Workconos-ypwhen~=180
ExamplewhenaballisthrownGo
inthear
Workdonebyforceof W=FXS=mgh
gravity
Unitofwork W=FS=1joule=1N*1m
Kilojoules=1000Joules
CGSUnitofwork 1erg=1dynex1cm
ConversionofJoulesto1Joule=10erg IN=10°dyneand1m=10cm
ergs ¿1Joule=10'X10°=10°erg
rower Therateofdoingworkiscalled
Dower
Powerisalsotheproductofforce FrS
andaveragespeed
Pa: =FXV
Unitofpower SIUnitofpowerisWatts
1Wattm 1joule=js
ConversionofSiunitto 1Watt=¡S'=10'ergsS
CGSUnits
1HP=746W=0.746kW
Energy Theenergyofabodyistheabilityto
dowork
Unitofenergy 1Watthour=1wattx1hour
=1]SX3600s=3.6kJ
1Kilowatthour=3.6X10°J
Heatenergy Heatenerevisusualymeasuredin
calorie.1Calorieofheatenergy
requiredtoraisethetemperature
of1gofwaterfrom14.5°Cto15.5°
RelationshipofCalorie 1]=0.24Calorie
andJoule 1Calorie=4.18Joule
1kiloCalorie=4180Joule
Electronvolt TheEnergyofatomicparticleisvery
small.Itismeasuredintermsof
electronvolt(eV)
1eV=1.6X108J
Kineticenergy Theenergyprocessedbyabodybyvirtue
ofitsdateormotion
Thekineticenergypossessedbyamoving
bodycanbemeasuredastheamountof
workwhichthemovingbodycanperform
beforeitcomestorest
Measurementof
kineticenergy
kelationshipbetween
momentumandkinetic
DEmowereDischemomenamm
Cherry
"p=v(2mK)
K=R°
2m
Workenergytheorem Workdonebyaforceonamovingbodyis
equaltotheincreaseinkineticenergy.
Proof W=FXS
v2-u?=2as
fromtheequationofmotion
OnSimplificationu?-u?
2a
aW=maX(-
2a
W=
¿(mut)-¿(mut)
W=Kf-Ki
TypesofKineticenergyTranslationalkineticenergy Carmovineinastraight
Freefalingobject
Rotationalkineticenergy Spinningtop
Vibrationalkineticenergy movementtoandirofrom
ameanpostionexamole
pluckingaguitarstring
Potentialenergy Energypossessedbyabodyatrest
Formsofpotential Mechanicalpotentialenergy
energy Gravitationalpotentialenergy
Elasticpotentialenergy
Gravitationalpotential Uamgh
energy
Conservationofenergyandenergydegradation
Energydegradation Thegradualdecreaseofusefulenergydue
toradiationloss,frictionallossetciscalled
degradationofenergy
Lawofconservationof Energycanneitherbecreatedor
energy destroyed
Chapter-3 Machines
Load Theresistiveoropposiveforcetobe
overcomebyamachineiscalledload
Effort Theforceappliedonthemachineto
overcometheloadiscalledEffort
MechanicalAdvantage RatioofLoadtoeffort
MechanicalAdvantageMA MA= Load(2)
Effort(E)
VelocityRatioVR VR=VelocityofeffortVE
Veocitrolloadvi
Theratioofthevelocityof
efforttothevelocityofload
VelocityofLoad d,isthedistancemovedby
theLoadintimet
VelocityofEffort d,isthedistancemovedby
theEffortintimet
VelocityRatioVR V.=dL/dE Notevelocityratiohasnounit
asit'saratio
Workinput Theworkdoneonthemachinebythe
effort
WorkOutput Theworkdonebythemachineonthe
load
Efficiency(n) Theratiooftheusefulworkdonebythe Efficiency(n)
machinetotheworkputintothe =WorkOutput/WorkInput
machinebytheeffort
Idealmachine Amachineinwhichthereisnolossof Theefficiencyofanideal
energyinanymanner machineis100%
ActualMachine Anactualmachinehasanefficiency
alwayslessthan100%becausethe
movingpartsareneitherweightlessor
_trictionles
Stringsarenotperfectlyelasticandthe
differentpartsarenotrigid
RelationshipbetweenefficiencyMA=VRXn
mechanicaladvantageand
velocityratio
GaSSETLOVE Fulcrumisinbetweentheeffortand SeeSaw,Plier,crowbar,
loadEffortandLoadareinthesame
direction
MAcanbe<1m1or>1
Class2Lever Mechanicaladvantageoftheleveris Bottleopener,Nutcracker
always>1
classstever EffortisinbetweenthefulcrumandtheSugartongs,Knifespade
loadMAisalways<1
Typing Jobs
Earn Rupee 10000 daily by Just Typing Task Daily Payout
Apply Now
Receptix Open
Inclined Plane and Gear (Not n syllabus-2021)
MAandVRofaninclinedplaneVR=MA=. Thisistrueintheabsenceoffriction
Gear Awheelwithteetharoundits
rim
GearRatio GearRatio= WhereNaisthenumberofteethinthe
drivingandNbisthenumberofteeth
Relationshipbetweennumber
Na
ofteeth,radiusandthespeed
ofrotation
Pulley
SingleFixedPulley Apulleywhichhasitsaxisof
rotationfixednpostionk
calledfixedpulley
MA..
SingleMovablepulley Apulleywhoseaxisof
rotationbnotfixedin
positioniscalledamovable
pulley.Itisalsocalledasa
Morcemultiones
MA=
CombinationPulleys Onefixedandothermovable
Pulleys
MAVR=2*
106
BlockandTacklepulley MA=
VR=nd
Chapter-4 Refraction of Light at plane surface
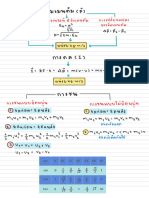
TheSnell'slawsofrefractionare:
1.Theincidentray,therefractedrayandthenormalatthepointof
incidence,alllieinthesameplane.
2.Theratioofthesineoftheangleofincidencetothesineofthe
angleofrefractionisconstantforthepairofthegivenmedia.
sini
sinr
whereallisknownastherefractiveindexofthesecondmediumwith
respecttothefirstmedium.
Refractive Index = (Speed of Light in Vacuum)/(Speed of Light In Medium)
Delta δ=(i¹ + i²) – (r¹ +r²)
r¹ +r² =A
i¹ + i² =A + δ
δ(min) = 2 i-A
Chapter-5 Refraction through a lens
Sign Convention
The axis along which the distances are measured is called as the principal axis. These distances are measured from the optical centre of
the lens.
All the distances which are measured along the direction of the incident ray of the light are taken positive, while the distances opposite to
the direction of the incident ray are taken as negative.
and All the lengths that are measured above the principal axis are taken positive, while the length below the principal axis is considered
negative.
The focal length of the convex lens is taken positive and that of concave lens is negative.
(Derivation of Lens formula not in syllabus-2021)
where The distance of the object from the optical centre is called the object distance (u).
and The distance of the image from the optical centre is called the image distance (v).
The distance of the principal focus from the optical centre is called the focal length (f).
Magnification ‘m’ is the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object.
Magnification ‘m’ = ( Hight of Image)/ ( hight of Object)
Magnification ‘m’ = -v / u
Power of lens = 1 / focal length (in Metre)
Chapter-7 Sound
Chapter-8 Current Electricity
Chapter-9 Household Circuits
Chapter-10 electro-magnetism (Not in syllabus-2021)
Right hand thumb rule determines the direction of magnetic field around a current carrying wire.
It states that if we hold the current carrying conductor in right hand such that the thumb points in the direction of flow of current, then the
fingers encircle the wire in the direction of the magnetic fields lines.
Chapter-11 Calorimetry
(Numericals on specific heat is in syllabus-2021 but Numericals on Latent heat is not in syllabus-2021)
Chapter-12 Radioactivity
Atomic Number (Z) = Number of Proton = Number of Electron (if atom is neutral)
To calculate atomic mass
Atomic Mass (A) = Mass of Nucleus
Atomic Mass (A) = Number of Proton + Number of Neutron
Atomic Mass (A) = Number of Electron + Number of Neutron
Atomic Mass (A) = Atomic Number (Z) + Number of Neutron
To calculate neutron
Number of Neutron = Atomic Mass (A) – Atomic Number (Z)
Number of Neutron = Atomic Mass (A) – Number of Proton
Number of Neutron = Atomic Mass (A) – Number of Electron
Law of Emission
When an An alpha particle emmit :the atomic number decreases by 2 and mass number decreases by 4 in new element.
When A beta particle emmit : The atomic number increases by one, but mass number does not change in new element .
Gamma particle: it does not change anything in the nucleus
Nuclear Energy
(Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion Exercise of Radioactivity is not in syllabus-2021)
1 amu = 931 MeV
E = mc² where m is mass and c is velocity of light
1 Kg Mass = 9×1016 j or 2.5 x 1010 KW H
–: End of Physics Formula for ICSE class-10 Chapter-Wise :–
Thanks
Return to – ICSE Class-10 Textbook Solution, Syllabus, Notes and Paper
Please Share with your ICSE friends if it is helpful
Chemistry Specimen 2024: Sec-B ISC Chemistry Specimen 2024: Sec-A ISC English Literature Specimen 2024: Sec-B
Sample Model Paper Solved Sample Model Paper Solved Que-5 ISC Sample Paper Solutions
ICSE BOARD, ICSE CLASS 10, ICSE PHYSICS CLASS 10
2 thoughts on “Physics Formula ICSE 10 Class Standard Chapter-Wise”
vaishali kurdikar
January 21, 2021 at 4:50 pm
Dear Sir ,
can we get the PDF of the formulae compilation
Reply
PANDEY TUTORIAL
January 22, 2021 at 9:58 am
Dear student / well wisher
It is advice to you write the formula on your note book with your hand writing twice or thrice and also on a chart which help
you memorise the formula . Put chart on study table we do not provide pdf.
thanks
icsehelp
Reply
Leave a Comment
Name *
Email *
Website
Post Comment
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
© 2024 ICSEHELP
You might also like
- Chapter 06 Homework AssignmentDocument15 pagesChapter 06 Homework AssignmentMohammed ElnaggarNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Check Answers: Part 1: Non-FictionDocument45 pagesDiagnostic Check Answers: Part 1: Non-FictionMay Youssef100% (2)
- Note 08-Aug-2023Document4 pagesNote 08-Aug-2023Taimoor EhsanNo ratings yet
- Group A Form 4 Physics MR Ameerul Hazeeq 27.02.2023 - Ameerul HazeeqDocument25 pagesGroup A Form 4 Physics MR Ameerul Hazeeq 27.02.2023 - Ameerul HazeeqSolihin KarimNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power PDFDocument2 pagesWork, Energy and Power PDFTanmay GuptaNo ratings yet
- As Review 2Document7 pagesAs Review 2minglei caiNo ratings yet
- 4 - BhattiAcademy - Com - Physics - 6. Scohlar SeriesDocument19 pages4 - BhattiAcademy - Com - Physics - 6. Scohlar SeriesBabar AliNo ratings yet
- 9B WepDocument5 pages9B WepRohan NautiyalNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of A Particle Live Class-1 Teacher NotesDocument18 pagesDynamics of A Particle Live Class-1 Teacher Notesnotime ReactionNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Physics MR Ameerul Hazeeq 27.02.2023Document14 pagesForm 4 Physics MR Ameerul Hazeeq 27.02.2023Shadow ElementNo ratings yet
- Conservation of EnergyDocument8 pagesConservation of EnergyDEEPAK UPADHYAYNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform: Ñwskéwo%ÑñDocument5 pagesLaplace Transform: Ñwskéwo%ÑñCHAYANIN AKETANANUNNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy: Dynasty D. Chen November 24, 2021Document16 pagesWork and Energy: Dynasty D. Chen November 24, 2021nonononoNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet PhysicsDocument26 pagesFormula Sheet Physicsmsa.0.70920No ratings yet
- Physics Y1 ReviewDocument5 pagesPhysics Y1 ReviewRakeem McFarlaneNo ratings yet
- Statics and Strength of M: Aterials Formula SheetDocument1 pageStatics and Strength of M: Aterials Formula Sheetpaolo martin reyesNo ratings yet
- Dynamics NotesDocument36 pagesDynamics Notestayyab10ahmedNo ratings yet
- Circle of SuccessDocument1 pageCircle of SuccessIwan NovaNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and PowerDocument17 pagesWork, Energy and PowersmollilnubNo ratings yet
- Adsee Practice Test THRUST Q1Document16 pagesAdsee Practice Test THRUST Q1DellonsNo ratings yet
- Equations+Sheet DynamicsDocument1 pageEquations+Sheet DynamicsMamon HoroubNo ratings yet
- Integrating ( M) With Respect To Displacement: Work and EnergyDocument27 pagesIntegrating ( M) With Respect To Displacement: Work and EnergyAsadNo ratings yet
- 2.18 Work and Energy With Varying Forces, Power-1 PDFDocument21 pages2.18 Work and Energy With Varying Forces, Power-1 PDFJoanna Angela LeeNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet (1) (1) - 7Document1 pageCheat Sheet (1) (1) - 7poziraNo ratings yet
- Mass Weight: QuantityDocument18 pagesMass Weight: QuantityraajNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 Work Energy and PowerDocument34 pagesChapter - 6 Work Energy and PowerNafees FarheenNo ratings yet
- Energy and Momentum SummaryDocument46 pagesEnergy and Momentum SummaryKritik CreationsNo ratings yet
- Work PowerDocument46 pagesWork PowerAnand patilNo ratings yet
- Actual Questions in MMUP Exam For CivilDocument1 pageActual Questions in MMUP Exam For CivilAnonymous RRTcbwUNo ratings yet
- Section 14.5-14.6 - RawDocument15 pagesSection 14.5-14.6 - RawAsadNo ratings yet
- Dyn 3Document71 pagesDyn 3Do Thi My LeNo ratings yet
- Physics Xi (Formulae - 1) : Chapter No 2Document1 pagePhysics Xi (Formulae - 1) : Chapter No 2Meer UmarNo ratings yet
- UCS Lectures PDFDocument100 pagesUCS Lectures PDFgoeffNo ratings yet
- Field Work Instruction Workseet For: REVEGETATION SERVICES (Maintenance)Document1 pageField Work Instruction Workseet For: REVEGETATION SERVICES (Maintenance)Asdar A.No ratings yet
- Periodic Motion NotesDocument9 pagesPeriodic Motion Noteschlorine169No ratings yet
- Chapter No 14: (SECTIONS 14.1-14.4, 14.6)Document63 pagesChapter No 14: (SECTIONS 14.1-14.4, 14.6)Farhan ShahriarNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure-RemainingDocument68 pagesAtomic Structure-RemainingDevansh DuhanNo ratings yet
- 5.work Energy PowerDocument2 pages5.work Energy Powerkaunteya.mayank2006No ratings yet
- Lecture 11-Section-14.1-14.3Document30 pagesLecture 11-Section-14.1-14.3ericjrayman31No ratings yet
- EMT Short Questions For MSCDocument38 pagesEMT Short Questions For MSCJunaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Gas Power CyclesDocument12 pagesGas Power CyclesSehar FatimaNo ratings yet
- 0223微積分A二Document9 pages0223微積分A二江品萱No ratings yet
- As 6Document2 pagesAs 6kiad.thariyaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Kaksha Formula Sheets Chemistry Class 11thDocument18 pagesNcert Kaksha Formula Sheets Chemistry Class 11thABCD Play school100% (4)
- 6 Friction and EquilibriumDocument31 pages6 Friction and EquilibriumCyrus Flores,No ratings yet
- Schriftelijke Opdrachten - Week 2 - SolutionsdocxDocument3 pagesSchriftelijke Opdrachten - Week 2 - SolutionsdocxJorn HoekstraNo ratings yet
- Physics Equations v2020.1Document1 pagePhysics Equations v2020.1kateNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion &projectileDocument5 pagesCircular Motion &projectileLazar BeamNo ratings yet
- AC Notes Zaki SaudagarDocument18 pagesAC Notes Zaki Saudagaraltashabts7No ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet of PhysicsDocument6 pagesCheat Sheet of Physicsaliayanraza5No ratings yet
- DocScanner 25-Apr-2024 7-54 AmDocument19 pagesDocScanner 25-Apr-2024 7-54 Ammahalakshmi periyasamyNo ratings yet
- @physics - 11class Vectors and ForcesDocument69 pages@physics - 11class Vectors and ForcesPranav RoyNo ratings yet
- Marked 1Document22 pagesMarked 1hassanbucheeri10No ratings yet
- Strain EnergyDocument13 pagesStrain EnergyMalingha SamuelNo ratings yet
- สรุปฟิสิกDocument12 pagesสรุปฟิสิกFeLiNaNo ratings yet
- B.SC - II - (PHYSICS) (Paper I-TITLE-FRAUNHOFER DIFFRACTION) BY-DR. ANAND KUMAR DWIVEDI-HEAD DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICSDocument12 pagesB.SC - II - (PHYSICS) (Paper I-TITLE-FRAUNHOFER DIFFRACTION) BY-DR. ANAND KUMAR DWIVEDI-HEAD DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICSShubham PendhareNo ratings yet
- STPDF1 - Subtopic PDF 1 Flexural and Shear Stresses in BeamsDocument22 pagesSTPDF1 - Subtopic PDF 1 Flexural and Shear Stresses in Beamsnaughty dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Important Es Assignment QuestionsDocument6 pagesImportant Es Assignment Questionssahej singhNo ratings yet
- Toyota 5e Fhe 1 PDFDocument13 pagesToyota 5e Fhe 1 PDFJuan Carlos Díaz Cardozo100% (2)
- The Audiolingual PresentationDocument21 pagesThe Audiolingual Presentationapi-312916451No ratings yet
- Experiment 5: Factor Affecting Reaction Rate: Ho Chi Minh International UniversityDocument7 pagesExperiment 5: Factor Affecting Reaction Rate: Ho Chi Minh International UniversityBùi Nhật MaiNo ratings yet
- TyroliaDocument89 pagesTyroliadramljak760167% (3)
- Logic 24,30,35Document68 pagesLogic 24,30,35Richard DruryNo ratings yet
- A 4 InchesDocument32 pagesA 4 InchesStephanie ParkNo ratings yet
- M00224 HE CoreCurriculum OrgBehavior July2018 PDFDocument2 pagesM00224 HE CoreCurriculum OrgBehavior July2018 PDFmicNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Office Prodeos OcDocument18 pagesMicrosoft Office Prodeos OcdaniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theorist: Florence Nightingale Theory: Environmental Theory Nursing BackgroundDocument3 pagesNursing Theorist: Florence Nightingale Theory: Environmental Theory Nursing BackgroundAlcala, Mariaden A.No ratings yet
- First Checking Alon Et Al Installation of CCTV in Barangay Sta. Rita Karsada Batangas Revise 3Document66 pagesFirst Checking Alon Et Al Installation of CCTV in Barangay Sta. Rita Karsada Batangas Revise 3Karl LandichoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Engineering EconomyDocument9 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Engineering EconomyFirdaus JamsanNo ratings yet
- FINALCAD-Tower 2 Pakubuwono Spring-Unit F Zone 20170821 134155Document4 pagesFINALCAD-Tower 2 Pakubuwono Spring-Unit F Zone 20170821 134155muhammad hilmiNo ratings yet
- Shanile Williams SBADocument12 pagesShanile Williams SBAshanile williamsNo ratings yet
- Ashrae 15 A Review and Update MN Chapter 2013Document43 pagesAshrae 15 A Review and Update MN Chapter 2013MoriyasuNguyenNo ratings yet
- Lab No2 To Find Unknown Branch Current in A Circuit Containing Dependent SourceDocument3 pagesLab No2 To Find Unknown Branch Current in A Circuit Containing Dependent SourcedaudNo ratings yet
- 65 Free Data Science Resources For Beginners PDFDocument19 pages65 Free Data Science Resources For Beginners PDFgirishkumarNo ratings yet
- r2900g Xtra.Document4 pagesr2900g Xtra.percyNo ratings yet
- Terminal Sub Part 5Document2 pagesTerminal Sub Part 5Uzair AliNo ratings yet
- KIRLOSKAR HVAC BrochureDocument24 pagesKIRLOSKAR HVAC Brochureedward baskaraNo ratings yet
- Strategy Lesson 5 AdditionalDocument16 pagesStrategy Lesson 5 AdditionalMahlet AbrahaNo ratings yet
- Life Skills: Giving PresentationsDocument2 pagesLife Skills: Giving PresentationsВіта МоскаленкоNo ratings yet
- Church of Light-JupiterDocument20 pagesChurch of Light-JupiterNatalia PorroNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Business IntelligenceDocument4 pagesAssignment 3 Business IntelligencerebornphenNo ratings yet
- JGR Catalog 2021 HDocument47 pagesJGR Catalog 2021 HChandra Arief BudimanNo ratings yet
- Historia de Jan DodonnaDocument10 pagesHistoria de Jan DodonnaJuan AndresNo ratings yet
- Message of Congratulations-9Document22 pagesMessage of Congratulations-9Do Something GoodNo ratings yet
- Six Approaches To Stylistic Analysis - WDocument5 pagesSix Approaches To Stylistic Analysis - WAdelNo ratings yet
- Rogue One ScriptDocument56 pagesRogue One Scriptspirit469No ratings yet