Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson No 3 (C) Sheet Metal
Uploaded by
exampuja618Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson No 3 (C) Sheet Metal
Uploaded by
exampuja618Copyright:
Available Formats
PAGE SEMESTER:TT-1
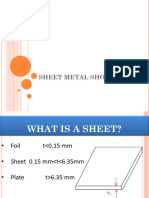
SHEET METAL
Sheet metal work generally regarded as the working of metal from 10 gauges (0.128”) down
to 30 gauges (0.0124”) with hand tools and simple machines, into various form by of cutting forming
into shape and jointing. There are two types of craftsmen they are the tin smith and the sheet metal
worker
The sheets are made from wrought iron, galvanized iron, brass, copper, aluminums, lead,
zinc, etc. They are made by pressing the metal into sheets.
G I Sheet:
The iron sheet coated with zinc is called galvanized iron sheet. Its property is ductile. The
thickness of the sheet metal is measured by wire gauge. The plain sheets are mainly used in roof
works
Tin sheet:
The iron sheet coated with tin is called tin sheet. It is softer and the property is ductile. It is
used for making containers.
Copper and brass sheet:
Copper and brass sheets are available in 100 x 100 mm and 100 x 50 mm or in various size
and thicknesses. Their properties are malleable and ductile. They get hardening when working in
cold condition and so they require annealing often to carry over further operations.
Aluminum sheets:
Aluminum sheets are available in 150 x 100 mm and 100 x 100 mm. and various sizes and
thickness. These sheets are generally used where lightness is required. It is a soft metal and
properties are ductile and little brittleness. It is used by body builders for automobile and aero
engines
Lead sheet:
Lead sheets have the properties of light malleable and softness used for packing materials
SHEET METAL TOOLS
The tools used is sheet metal, may be divided into three groups such as hand tools, bench
tools and machine tools.
The hand tools:
1) Steel rule
2) Steel tape
3) Scriber
4) Divider
5) Trammel
6) Chisel
7) File
8) Snip
9) Shear
10) Hammer
11) Mallet
12) Punch
CITS TRAINING (2016-17) ATI CALICUT -673016
PAGE SEMESTER:TT-1
13) Groover
14) Rivet set
15) Soldering iron
16) Wire gauge
17) Blow lamp, etc.
The machine tool:
1) Treadle machine
2) Bench lever shear
3) Wheeling machine
4) Rolling machine
5) Folding machine
6) Swaging machine
7) jenny machine
8) Grinding machine, etc.
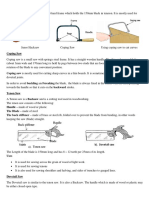
SNIPS:
Snips are cutting tool, and are used for cutting thin sheets of metal.
There are two types of snips.
1. Straight snip
2. Bent snip
Straight snip:
A straight snip has straight blades for straight line cutting. It can also be used for external
curved cuts.
Parts of snips
1. Handle
2. Blade
3. Stop
Bent snip:
Bent snips have a curved blades used for cutting internal curves. For trimming a cylinder
keep the lower blade on the outside of cut.
STRAIGHT SNIP BENT SNIP
FOLDING TOOLS
The common tools used in the folding of sheet metal are
1. Angle sheet and folding bar
2. ‘C’ clamp
3. Stakes
4. Mallet
CITS TRAINING (2016-17) ATI CALICUT -673016
PAGE SEMESTER:TT-1
Angle sheet:
Two pieces of angles are used for folding at 900. For longer sheets lengthy angles will be
used along clamp or hand vice.
Folding bar:
The sheet metal to be bent is clamped in the folding bars. The folding bars are clamped in the
voice
‘C’ Clamp:
The shape of the clamp is in the form of the letter ‘C’. ‘C’ Clamp is the holding device. This
clamp is used when the piece has to be securely fixed to another piece. It is available in different
sizes according to the opening of the jaws.
STAKES:
Stakes are used for bending, seaming and forming of sheet metal that cannot be done on any
regular machine. For the above purpose, different stakes are used. Stakes are made of forged alloy
steel or caste steel.
A stake used for sheet metal consists of a shank and a head or horn. The shank is designed to
fit in to a tapered bench-socket.
Types of stakes
1. Hatchet stake
2. Half-moon stake
3. Funnel stake
4. Beak or Bick iron
5. Creasing iron
6. Planishing anvil
7. Horse
Hatchet stake
The hatchet stake has a sharp edge, beveled along one side. It is very use full for making
sharp bends, folding the edges of sheet metal, forming boxes and pans by hand.
Half-moon stake
This stack has sharp edge in the form of an arc of a circle, beveled along one side. It is used
for throwing up flanges on metal discs.
Funnel stake
This stake is used when shaping and seaming funnels and tapered articles.
CITS TRAINING (2016-17) ATI CALICUT -673016
PAGE SEMESTER:TT-1
Beak or Bick iron
This stakes have two horns, one of which is tapered, the other is a rectangular shaped anvil.
The thick tapered horn or beak is used when marking spouts and sharp tapering articles. The anvil
may be used for squaring corners, seaming and light riveting.
Creasing iron
This has two rectangular shaped horns, one of which is plain. The other horn contains a
series of grooving slots of various sizes. The grooves are used when ‘sinking’ a bead on straight
edge of a flat sheet. This is also used when making small diameter tubes with thin gauge metal.
Planishing anvil
It is used for planishing all types of flat and shaped works. It is highly polished on its working
surface.
Horse
This stakes provides a double- ended support. At the end of each arm- one of which is usually
cranked down words for clear purpose-there is a square hole for the reception of a wide verity of
heads
The condition of stake is important for the workman ship of the finished articles. Therefore, care
must be taken to avoid any damage to the stake when center punching or cutting with cold chisel.
Apart from these stakes, special type of stakes is also made to suit the different types of jobs
CITS TRAINING (2016-17) ATI CALICUT -673016
PAGE SEMESTER:TT-1
WOODEN MALLET
Mallets are soft hammer are made of raw hide, hard rubber, copper, brass, lead, or wood and
are used to strike a soft and light blow on the metal.
Types and uses:
Standard wooden mallets are used for general purpose work like flattering bending etc.
Bossing mallets are used for hollowing panel beating, etc.
An end – flaked mallet is used for stretching, hammering, etc.
NOTCHES
Notches are the spaces provided for joining the edges when sheet metals are cut from the
layout.
Purpose of notches
1. To prevent the excess material from over lapping and causing a bulge at the seam and edges
2. To allow the work to be formed to the required size and shape
3. To allow the work to assemble better.
Types of notches
A straight notch or slit is a straight cut made in the edge of the sheet where it is to be bent of 450
to the corner of the sheet. It is used when a single hem meets at right angles.
A square notch is used when forming a square rectangular box
A slant notch is cut at an angle of 450 to the corner of the sheet. it is used when a single hem
meets at right angle.
In a ‘V’ notch both the sides are cut at 450 angle to the edge of the sheet. the sides of the notches
meet at 900.this notch is used when making a job with a 900 bent and an inside flange.
RIVETS
Rivets are used to join together two or more sheets of metal permanently. In sheet metal
work done where:
Brazing is not suitable
The structure changes owing to welding heat
The distortion due to welding cannot be easily removed, etc.
Specification of rivets
Rivets are specified by their length, material, size and shape of head.
CITS TRAINING (2016-17) ATI CALICUT -673016
PAGE SEMESTER:TT-1
The material used for rivets are mild steel, copper, yellow brass, aluminum, and their alloys.
Types of rivets
The four common type’s rivets are
1) Tinmen’s rivet
2) Flat head rivet
3) Round head rivet
4) Countersunk head rivet
Selection of rivet size: the diameter of the rivet is calculated by using the formula
D = (21/2 to 3) × T where T is total thickness.
The shank length is given by
L = T+T+ (11/2×D)
Where ‘T’ is the sheet thickness and ‘D’ is the diameter of the rivet.
Method of riveting
Riveting may be done by hand or by machine, while riveting by hand, it can be done with a
hammer and a rivet set.
Rivet set
a cross- section of a rivet set is shown in the figure. The shallow, cup-shaped hole is used to
draw the sheet and the rivet together. The outlet of the side allows the slug to drop out.
The cup shape is used for forming the rivet head.
CITS TRAINING (2016-17) ATI CALICUT -673016
PAGE SEMESTER:TT-1
The rivet set selected should have a hole slightly larger than the diameter of the rivet.
Spacing of rivet
The space or distance from the edge of the metal to the center of any rivet should be at least
twice the diameter of the rivet to avoid tearing. The ‘Lap’ distance (4D).
The minimum distance between the rivets (pitch) should be sufficient to allow the rivets to be driven
without interference of the sheet or above.
The maximum distance should never exceed 24 times of the thickness of the sheet otherwise
buckling will take place as shown in figure.
CITS TRAINING (2016-17) ATI CALICUT -673016
PAGE SEMESTER:TT-1
CITS TRAINING (2016-17) ATI CALICUT -673016
You might also like
- Sheet Metal ShopDocument43 pagesSheet Metal ShopBhaskar KandpalNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Metal-Working (Illustrated)From EverandAn Introduction to Metal-Working (Illustrated)Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Spreadsheet Practice Exercises-2017Document43 pagesSpreadsheet Practice Exercises-2017Sur Velan100% (1)
- Introduction To Smaw Classification of ToolsDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Smaw Classification of ToolsJensly Tias100% (1)
- K To 12 Smaw Welding Learning ModuleDocument11 pagesK To 12 Smaw Welding Learning ModuleJha Zel89% (9)
- Carpentry Workshop ManualDocument56 pagesCarpentry Workshop Manualarun50% (2)
- Tools and Machines Used in Carpentry Lab Part 5Document10 pagesTools and Machines Used in Carpentry Lab Part 5Lo M'hNo ratings yet
- HAND TOOL For EASA/CAR - 66 EXAMINATIONDocument201 pagesHAND TOOL For EASA/CAR - 66 EXAMINATIONManish Mishra100% (1)
- Sheet Metal Shop ToolsDocument18 pagesSheet Metal Shop ToolsAnandNo ratings yet
- Milling CutterDocument39 pagesMilling Cuttersamurai7_77No ratings yet
- Sheet MetalDocument16 pagesSheet MetalYusha Patel100% (1)
- Junior hacksaw guideDocument7 pagesJunior hacksaw guideOsei Kwadwo Hyiamang KorantengNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Work Guide with Tools & ProcessesDocument15 pagesSheet Metal Work Guide with Tools & ProcessesIndunil Prasanna Bandara Warnasooriya100% (1)
- Jewelry Making for Beginners: 32 Projects with MetalsFrom EverandJewelry Making for Beginners: 32 Projects with MetalsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Fitting Shop Tools Classification and UsesDocument8 pagesFitting Shop Tools Classification and UsesZatchBellNo ratings yet
- Workshop PracticeDocument87 pagesWorkshop Practiceahmedkhalidhussain100% (2)
- Sheet Metal MaterialDocument54 pagesSheet Metal MaterialRoyalmech100% (1)
- Use Basic Hand Tools and Equipment: Effective Alternative Secondary Education (Ease) ProgramDocument18 pagesUse Basic Hand Tools and Equipment: Effective Alternative Secondary Education (Ease) ProgramJoseph Caloscos100% (5)
- Metalworking Tools Guide for Cutting, Filing & Fastening MetalDocument6 pagesMetalworking Tools Guide for Cutting, Filing & Fastening MetalHoai nam100% (1)
- FITTING SHOP WORKSHOP #4Document21 pagesFITTING SHOP WORKSHOP #4SaadFarooq100% (1)
- LP Fuel Gas SystemDocument6 pagesLP Fuel Gas SystemAnonymous QSfDsVxjZNo ratings yet
- A Concise Note On Workshop Technology: Nepal Students' Union Purwanchal Campus CommitteeDocument14 pagesA Concise Note On Workshop Technology: Nepal Students' Union Purwanchal Campus CommitteeAashiz PoudelNo ratings yet
- Apollo System Engineering Manual. Environmental Control SystemDocument137 pagesApollo System Engineering Manual. Environmental Control Systemjackie_fisher_email8329100% (2)
- Classic Handplanes and Joinery: Essential Tips and Techniques for WoodworkersFrom EverandClassic Handplanes and Joinery: Essential Tips and Techniques for WoodworkersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Cars and Trucks With Mitsubishi TD04 TurbochargerDocument17 pagesCars and Trucks With Mitsubishi TD04 TurbochargersampapaNo ratings yet
- The Future of Luxury Fashion ReportDocument70 pagesThe Future of Luxury Fashion Reportsalma andjaniNo ratings yet
- Mesuring Tape HE - mt.001Document2 pagesMesuring Tape HE - mt.001Chethan Nagaraju KumbarNo ratings yet
- Fitting BookDocument12 pagesFitting BookOryon FooNo ratings yet
- Sheet MetalDocument11 pagesSheet Metalshah_faizan123No ratings yet
- Cutting ToolsDocument5 pagesCutting ToolsBhavdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Study of Sheet MetalDocument10 pagesStudy of Sheet MetalRaskshannaNo ratings yet
- Exp 11Document22 pagesExp 11ManavNo ratings yet
- Use Hand ToolsDocument52 pagesUse Hand ToolsChester Allan F. BautistaNo ratings yet
- Personalized Module in Grade 7 SMAWDocument9 pagesPersonalized Module in Grade 7 SMAWLorenzo InofreNo ratings yet
- Countersink, Counterbore & SpotfaceDocument8 pagesCountersink, Counterbore & SpotfaceŤhe Đûke100% (1)
- B.Naresh Kumar Workshop - WordDocument61 pagesB.Naresh Kumar Workshop - WordJyotshna DaamagatlaNo ratings yet
- Sheet MetalDocument29 pagesSheet Metalbtbte23080architaNo ratings yet
- Workshop Technology Eim 118 Module 2: Hand Tools: Dzanya M.TDocument18 pagesWorkshop Technology Eim 118 Module 2: Hand Tools: Dzanya M.TBriaydon TawandaNo ratings yet
- Fitting ManualDocument6 pagesFitting ManualpriyatoshNo ratings yet
- Epl RecordDocument63 pagesEpl RecordTishbian MeshachNo ratings yet
- Fitting Workshop ReportDocument17 pagesFitting Workshop ReportAkshay kumarNo ratings yet
- Standard methods for checking shafts, ovality, and bendsDocument38 pagesStandard methods for checking shafts, ovality, and bendsraj mohanNo ratings yet
- Work Shop Manual I Year-QisDocument69 pagesWork Shop Manual I Year-QisSeshaiah TurakaNo ratings yet
- Metal Cutting Tools Guide: Snips and HacksawsDocument12 pagesMetal Cutting Tools Guide: Snips and HacksawsRonald Vincent GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Metalworking Hand ToolDocument2 pagesMetalworking Hand ToolashokkumarNo ratings yet
- Mod 7 Book 2 ToolsDocument83 pagesMod 7 Book 2 Toolsranjit prasadNo ratings yet
- Smaw PPT1Document50 pagesSmaw PPT1adiksayoo12333100% (1)
- Woodworking Lab ReportDocument4 pagesWoodworking Lab ReportLaiba KhanNo ratings yet
- CHISELS NewDocument16 pagesCHISELS NeweijuNo ratings yet
- Central Workshop Manual For Mechanical Workshop CourseDocument60 pagesCentral Workshop Manual For Mechanical Workshop Courseankitbugalia56No ratings yet
- Common Tools Used in CarpentryDocument8 pagesCommon Tools Used in CarpentryRoslie AbdullahNo ratings yet
- L - 15 CHT Cutting Tools I (M7.3) - 1Document6 pagesL - 15 CHT Cutting Tools I (M7.3) - 1Rama SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fitting Workshop EssentialsDocument16 pagesFitting Workshop EssentialsHuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Work, Bench Work and FittingDocument63 pagesSheet Metal Work, Bench Work and FittingSolcastic SoulNo ratings yet
- UNIT OF COMPETENCE: - Perform Bench Work MODULE TITLE: Performing Bench Work LO1: Lay-Out and Mark Dimensions/ Features On Work PieceDocument63 pagesUNIT OF COMPETENCE: - Perform Bench Work MODULE TITLE: Performing Bench Work LO1: Lay-Out and Mark Dimensions/ Features On Work Pieceahmed jemal100% (1)
- Smithy: Applications of ForgingDocument8 pagesSmithy: Applications of Forginghuman kindNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing LabDocument26 pagesManufacturing LabramkishorNo ratings yet
- JIG Part 1Document11 pagesJIG Part 1TemuNo ratings yet
- Mapúa University: Shop Exercise No. 1Document15 pagesMapúa University: Shop Exercise No. 1Eriane GarciaNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Work, Bench Work and FittingDocument62 pagesSheet Metal Work, Bench Work and FittingSolcastic SoulNo ratings yet
- Drill Bit - WikipediaDocument55 pagesDrill Bit - Wikipediaaddisugebre2125No ratings yet
- Features of A Milling CutterDocument8 pagesFeatures of A Milling CutterAnuj KrNo ratings yet
- Drill BitDocument22 pagesDrill BitPinto JovitaNo ratings yet
- CarpentryDocument35 pagesCarpentrySadasiva Rao TNo ratings yet
- Presentation MolesworthDocument13 pagesPresentation Molesworthapi-630754890No ratings yet
- SCAQMD Method 3.1Document27 pagesSCAQMD Method 3.1Jonathan Aviso MendozaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HAPDocument6 pagesIntroduction To HAPMaheshSukhadiyaNo ratings yet
- Recent Progress in Medium-Mn Steels Made With New Designing Strategies A ReviewDocument8 pagesRecent Progress in Medium-Mn Steels Made With New Designing Strategies A ReviewMATHEWS LIMA DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Monika Soni PDFDocument16 pagesMonika Soni PDFdeepak guptaNo ratings yet
- Snowden Documents Demand 14 0714 PDFDocument4 pagesSnowden Documents Demand 14 0714 PDFSander BelouNo ratings yet
- Murray NYC Group MeteringDocument5 pagesMurray NYC Group MeteringKannon TamNo ratings yet
- Scope of WorkDocument4 pagesScope of WorkMathivanan AnbazhaganNo ratings yet
- hts336555 Philips Manual PDFDocument35 pageshts336555 Philips Manual PDFSalomão SouzaNo ratings yet
- Lisa Van Krieken CVDocument1 pageLisa Van Krieken CVapi-525455549No ratings yet
- Z22 Double-Suction Axially-Split Single-Stage Centrifugal PumpDocument2 pagesZ22 Double-Suction Axially-Split Single-Stage Centrifugal Pumpmartín_suárez_110% (1)
- Container Generator Qac Qec Leaflet EnglishDocument8 pagesContainer Generator Qac Qec Leaflet EnglishGem RNo ratings yet
- (Manual) Design Standards For Stormwater Detention and Retention - 14-05 VersionDocument113 pages(Manual) Design Standards For Stormwater Detention and Retention - 14-05 VersionMarcos JulianoNo ratings yet
- Monopolistic screening in the labor marketDocument6 pagesMonopolistic screening in the labor marketKand HroppaNo ratings yet
- HXPM8XBBYY19065T2CDocument1 pageHXPM8XBBYY19065T2CЕвгений ГрязевNo ratings yet
- Crown Platform Crown Battery Operated Pallet TruckDocument7 pagesCrown Platform Crown Battery Operated Pallet Truckgaurav champawatNo ratings yet
- 65-1501 Victor Reguladores FlujometrosDocument7 pages65-1501 Victor Reguladores FlujometroscarlosNo ratings yet
- El 5036 V2 PDFDocument86 pagesEl 5036 V2 PDFCriss TNo ratings yet
- 909design of High Efficiency Pelton Turbine For Micro-HydropowerDocument13 pages909design of High Efficiency Pelton Turbine For Micro-HydropowerrachidtuNo ratings yet
- KaduwaDocument34 pagesKaduwaRohini WidyalankaraNo ratings yet
- DLP November 7 11 2022Document11 pagesDLP November 7 11 2022Harvey RabinoNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Dividend Policy On Stock Price: Evidence From The Indian MarketDocument9 pagesThe Effect of Dividend Policy On Stock Price: Evidence From The Indian MarketWilson SimbaNo ratings yet
- Manual of Establishment Sections 05ff58f7947ffb7 76283342Document271 pagesManual of Establishment Sections 05ff58f7947ffb7 76283342Vijaya KumariNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Earthquake-Induced Cracking of Embankment DamsDocument21 pagesEvaluation of Earthquake-Induced Cracking of Embankment DamsMARCOS ABRAHAM ALEJANDRO BALDOCEDA HUAYASNo ratings yet