Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formulas 2
Uploaded by
ryancalebshopOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formulas 2
Uploaded by
ryancalebshopCopyright:
Available Formats
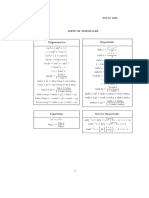
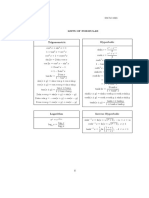
f g0 = f g − f 0 g and
R R R R
Integration by parts: udv = uv − vdu.
1
sin2 x + cos2 x = 1 sin x cos x = 2 sin 2x.
1
sin 2x = 2 sin x cos x sin2 x = 2 − 21 cos 2x
1
cos 2x = 2 cos2 x − 1 cos2 x = 2 + 12 cos 2x
1 1
sin A sin B = 2 cos(A − B) − 2 cos(A + B)
1 1
cos A cos B = 2 cos(A − B) + 2 cos(A + B)
1 1
sin A cos B = 2 sin(A − B) + 2 sin(A + B)
Table 1: Trig formulae for Section 7.2
Expression Substitution dx/dθ Trig identity
√
a2 − x2 x = a sin θ a cos θ 1 − sin2 θ = cos2 θ
√
a2 + x2 x = a tan θ a sec2 θ 1 + tan2 θ = sec2 θ
√
x2 − a2 x = a sec θ a sec θ tan θ sec2 θ − 1 = tan2 θ
Table 2: Trig substitutions for Section 7.3
sec2 x dx = tan x + C
R R
sec x dx = ln | sec x + tan x| + C
R R
tan x dx = ln | sec x| + C sec x tan x dx = sec x + C
tan2 x dx = tan x − x + C
R R
cot x dx = ln | sin x| + C
Table 3: Antiderivatives used in Section 7.3
Approximation methods Tn , Mn , Sn for f (x) on [a, b] with n subintervals.
∆x
Trapezoidal rule Tn = 2 [f (x0 ) + 2f (x1 ) + · · · + 2f (xn−1 ) + f (xn )].
xi−1 +xi
Midpoint rule Mn = ∆x[f (x̄1 ) + f (x̄2 ) + · · · + f (x̄n )] where x̄i = 2 .
K(b − a)3 K(b − a)3
|ET | ≤ and |EM | ≤ where K ≥ max |f 00 (x)|.
12n2 24n2 a≤x≤b
∆x
Simpson’s rule Sn = 3 [f (x0 ) + 4f (x1 ) + 2f (x2 ) + 4f (x3 ) + · · · + 2f (xn−2 ) + 4f (xn−1 ) + f (xn )].
K(b − a)5
|ES | ≤ where K ≥ max |f 0000 (x)|.
180n4 a≤x≤b
You might also like
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- MAST10006 Calculus 2 Exercise Sheets 2023s1Document34 pagesMAST10006 Calculus 2 Exercise Sheets 2023s1Shyam MahendraNo ratings yet
- Review3Document2 pagesReview3xesef93262No ratings yet
- MATH 259 - Review Sheet (Prerequisite Topics) : (This Is NOT A Comprehensive List!)Document4 pagesMATH 259 - Review Sheet (Prerequisite Topics) : (This Is NOT A Comprehensive List!)Celal KermangilNo ratings yet
- AMA1110 Tutorial - 2sDocument3 pagesAMA1110 Tutorial - 2sBrian LiNo ratings yet
- FormulaDocument1 pageFormulabrentbasha17No ratings yet
- List of FormulaDocument4 pagesList of Formulasofiea hazriNo ratings yet
- List of Formula sscm1023 Chap1 To 4Document4 pagesList of Formula sscm1023 Chap1 To 4Aisyah NadhirahNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Integrals-Solutions: ReviewDocument3 pagesTrigonometric Integrals-Solutions: ReviewMarCheLinaNo ratings yet
- Tabela de IntegraisDocument1 pageTabela de IntegraisNak ParrNo ratings yet
- Tabela de IntegraisDocument1 pageTabela de IntegraisNak ParrNo ratings yet
- Ssce 1793 Test 1 201420152Document4 pagesSsce 1793 Test 1 201420152Gantan Etika MurtyNo ratings yet
- Integration of Sec X and Sec XDocument2 pagesIntegration of Sec X and Sec XAkagra VermaNo ratings yet
- Step Formula Booklet PDFDocument24 pagesStep Formula Booklet PDFA FryNo ratings yet
- Re 58344Document2 pagesRe 58344spaNo ratings yet
- 常用數學與微積分公式定理Document6 pages常用數學與微積分公式定理李政彥No ratings yet
- 微積分基本公式Document6 pages微積分基本公式enwei100% (6)
- Integral Calculus QuizDocument2 pagesIntegral Calculus QuizJhan Bryan NeraNo ratings yet
- AppendixDocument1 pageAppendixLee Zhiyi (Angelene)No ratings yet
- Unit3 Review ExercisesDocument1 pageUnit3 Review ExercisesMartín Agirre GarciaNo ratings yet
- List of Formulae Trigo-Sscm1023Document3 pagesList of Formulae Trigo-Sscm1023aieyinHengNo ratings yet
- Basic Trigonometric FormulaDocument1 pageBasic Trigonometric Formulakotekatbasil0000No ratings yet
- Integrals Wo WatermarkDocument12 pagesIntegrals Wo Watermarkmeghashyam.raju1210No ratings yet
- Tan X Sin X Cos X Cot X Cos X Sin X CSC X 1 Sin X Sec X 1 Cos X Cot X 1 Tan X Sin Tan CotDocument3 pagesTan X Sin X Cos X Cot X Cos X Sin X CSC X 1 Sin X Sec X 1 Cos X Cot X 1 Tan X Sin Tan CotAudrey LeeNo ratings yet
- Formula For Final Exam UpdatedDocument5 pagesFormula For Final Exam Updatedalyaa nishaNo ratings yet
- NaturemathfDocument3 pagesNaturemathfzdfbdfb12No ratings yet
- 201900MA112FAssign2 SolutionDocument7 pages201900MA112FAssign2 SolutionAndrew JnrNo ratings yet
- List of FormulaDocument3 pagesList of FormulaAnggun AureolaNo ratings yet
- Table of Formula ODEDocument3 pagesTable of Formula ODEalif ismaNo ratings yet
- Form (Integration3)Document9 pagesForm (Integration3)api-3724082No ratings yet
- Trigonometric: Formulae and TricksDocument25 pagesTrigonometric: Formulae and TricksHariom SaxenaNo ratings yet
- F Ormulas Trigonom EtricasDocument2 pagesF Ormulas Trigonom EtricasDerly Pari100% (1)
- Ma1505 FormulasDocument7 pagesMa1505 FormulasSherman LiamNo ratings yet
- Integration Formulas-1 PDFDocument2 pagesIntegration Formulas-1 PDFYashvardhan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- TABLE OF INTEGRALS FOR ELEMENTARY AND MORE COMPLICATED FORMSDocument2 pagesTABLE OF INTEGRALS FOR ELEMENTARY AND MORE COMPLICATED FORMSakku jainNo ratings yet
- Level NS Calculus I Course Questions Solutions UpdatedDocument158 pagesLevel NS Calculus I Course Questions Solutions UpdatedssNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus: F (X) On I Is Given byDocument32 pagesIntegral Calculus: F (X) On I Is Given byJEYADURGANo ratings yet
- Elektrodinamika DemostratureDocument20 pagesElektrodinamika DemostratureMarijaElricNo ratings yet
- Function of A Real Variable: Zahmoul KhalilDocument6 pagesFunction of A Real Variable: Zahmoul KhalilGhassen Ben HadidNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Formulas and ExamplesDocument46 pagesDifferentiation Formulas and ExamplesBajirao JetithorNo ratings yet
- Integration by PartsDocument1 pageIntegration by PartsKim RobynNo ratings yet
- F17XB2 2013-14 Class Test Mathematics For Engineers and Scientists 2 Attempt All Questions (B)Document2 pagesF17XB2 2013-14 Class Test Mathematics For Engineers and Scientists 2 Attempt All Questions (B)Rza AbdullayevNo ratings yet
- 104 Spring 06 AnswDocument5 pages104 Spring 06 AnswJanry GarciaNo ratings yet
- Tabla Derivadas e IntegralesDocument2 pagesTabla Derivadas e Integralesandrea valdiriNo ratings yet
- Class XII - Math Chapter: Integral CalculusDocument5 pagesClass XII - Math Chapter: Integral CalculusSunita MauryaNo ratings yet
- Test2 - 20182019 SchemeDocument11 pagesTest2 - 20182019 SchemenorsyahirahafiqahNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Solutions 1. (20 PTS.) Evaluate The Following Indefinite IntegralsDocument15 pagesFinal Exam Solutions 1. (20 PTS.) Evaluate The Following Indefinite IntegralsАрхи́пNo ratings yet
- Integration Using Trig IdentitiesDocument19 pagesIntegration Using Trig IdentitiesJose VillegasNo ratings yet
- Math3B TrigIntegrals SolutionsDocument8 pagesMath3B TrigIntegrals SolutionsZander Rein FernandezNo ratings yet
- 04 Repaso - PreDocument7 pages04 Repaso - PreWILBER RAMOS CARTANo ratings yet
- Latihan Praktikum 3 Helda SafiraDocument1 pageLatihan Praktikum 3 Helda Safiradik rushcompNo ratings yet
- AddMath Formula SheetDocument5 pagesAddMath Formula SheetHidayah TeacherNo ratings yet
- Cal1 TD2 (2023 24)Document2 pagesCal1 TD2 (2023 24)Da VyNo ratings yet
- Formulae,,key Points,, Algorithm (For Class 12 TH Maths)Document23 pagesFormulae,,key Points,, Algorithm (For Class 12 TH Maths)angusingh60No ratings yet
- Mat120 Assignment 5Document5 pagesMat120 Assignment 5Tanjim RijuNo ratings yet
- End of Stage 1/AS Mathematics:: Mathematics A (H230, H240) Paper 2: Pure Mathematics and MechanicsDocument21 pagesEnd of Stage 1/AS Mathematics:: Mathematics A (H230, H240) Paper 2: Pure Mathematics and MechanicsrebeccaNo ratings yet
- PrelimExam SolutionDocument3 pagesPrelimExam SolutionNeil MonteroNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Point & Straight LineDocument24 pagesPoint & Straight LineUser name TakenNo ratings yet
- GEOMETRY CH 5 Law of SinesDocument2 pagesGEOMETRY CH 5 Law of SinesJackson LudtkeNo ratings yet
- Practice Sat Questions: Chapter 11 / Triangles 135Document5 pagesPractice Sat Questions: Chapter 11 / Triangles 135Mark GalstianNo ratings yet
- 3D Angles QuestionsDocument4 pages3D Angles QuestionsyddapNo ratings yet
- Inter First YearDocument40 pagesInter First YearpooririthwikNo ratings yet
- IB Trig Exam Style QuestionsDocument30 pagesIB Trig Exam Style QuestionsMei wins PoiNo ratings yet
- Aberte, Hercheys A. Precal CatalogueDocument11 pagesAberte, Hercheys A. Precal Cataloguehercheys aberteNo ratings yet
- Nsejs Geometry Sa2Document6 pagesNsejs Geometry Sa2gobinda prasad barmanNo ratings yet
- PrmoDocument6 pagesPrmoLakshitha SKNo ratings yet
- Higher Math 1 - HSC 2022Document9 pagesHigher Math 1 - HSC 2022Supar aspNo ratings yet
- Mathematics P2 Nov 2016 Memo Afr & EngDocument26 pagesMathematics P2 Nov 2016 Memo Afr & Engaleck mthethwaNo ratings yet
- Vector direction cosines and ratiosDocument17 pagesVector direction cosines and ratiosSristi RajNo ratings yet
- IB Math Studies - Triangle Trigonometry Practice Key: MarkschemeDocument45 pagesIB Math Studies - Triangle Trigonometry Practice Key: MarkschemeRafael Tayo0% (1)
- Subdivision Survey Example and ExerciseDocument17 pagesSubdivision Survey Example and ExerciseJordan RodriguezNo ratings yet
- MATH9-Q3-MODULE-7-Proving The Conditions For Similarity of Triangles-FFHNASDocument32 pagesMATH9-Q3-MODULE-7-Proving The Conditions For Similarity of Triangles-FFHNASEmmanuel Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7C: 1 A I J 2 ADocument5 pagesExercise 7C: 1 A I J 2 AnasehaNo ratings yet
- Method 3 and ConclusionDocument2 pagesMethod 3 and Conclusion倩影No ratings yet
- Trigonometry: John Ryan D. Regalario, ECEDocument51 pagesTrigonometry: John Ryan D. Regalario, ECEErnesto Ayoub Ching100% (1)
- EC ORTID Maths Gr12 April 2021Document10 pagesEC ORTID Maths Gr12 April 2021Levy MpangulaNo ratings yet
- 1.4.3 Practice - Intro To TrigDocument3 pages1.4.3 Practice - Intro To TrigCorrelanderNo ratings yet
- Drill MathsDocument36 pagesDrill MathsBulbulNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry SheetDocument4 pagesTrigonometry SheetKelah AligNo ratings yet
- ABC Tables (Refined)Document59 pagesABC Tables (Refined)Abu Syeed Md. Aurangzeb Al Masum100% (1)
- ArccosDocument2 pagesArccosruben.berenguel4176No ratings yet
- Theory & ExerciseDocument64 pagesTheory & ExerciseRamu Kumar100% (1)
- Circumcentre of triangle PIQ lies on hypotenuse ACDocument6 pagesCircumcentre of triangle PIQ lies on hypotenuse ACKRISHNA RAONo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics (Zimsec)Document7 pagesPure Mathematics (Zimsec)Japhet MubaiwaNo ratings yet
- A Hypotenuse Opposite side Adjacent side: θ Reference AngleDocument4 pagesA Hypotenuse Opposite side Adjacent side: θ Reference AngleJulius BayagaNo ratings yet
- Cbjemacq 08Document17 pagesCbjemacq 08neomatrix70No ratings yet
- CXC MATHS Formula SheetDocument7 pagesCXC MATHS Formula SheetSeleneGoberdhanNo ratings yet