Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ideal Differential Amplifer
Ideal Differential Amplifer
Uploaded by
pp cc0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesIdeal Differential Amplifer
Ideal Differential Amplifer
Uploaded by
pp ccCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
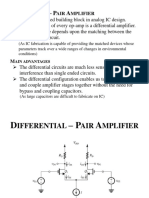
ideal differential amplifer
1. v0 is proportional to (v1-v2)
v0 is output voltage and v1-v2 is difference between two input signals.
2.vd is the differential signal hence vd= v1-v2
3.a comman signal to both the input that is v1=v2=v will produce a zero output voltage
4. differential amplifier as it amplify on difference between input signals
5.gain is Ad or diiferential gain ad = v0/vd
Common mode signal is common signal to both the input terminal were output is zero
Common mode gain
Vc is common mode signal
Vc = v1-v2/2
Vo = Ac * Vc
Common mode rejection ratio
The ability of a differential amplifier to reject a common mode signal is expressed in terms of its CMRR
Cmrr= Ad/Ac
4 differential amplifier config
1 dual input ,balanced output differential amplifier
2 dual input ,unbalanced output differential amplifier
Ideal condition for opamp
Infinite input impedence (Ri=0)
Zero output impedance (Ro=0)
Infinite open loop gain (A=∞)
Vout = 0 when Vin =0
Infinite bandwidth ad slew rate
CMRR = ∞
You might also like
- Differential AmplifiersDocument38 pagesDifferential AmplifiersVianca CamilLe Incognito-Castillo PanganibanNo ratings yet
- 3 Amplifier Common Mode Rejection Ratio Part I FullDocument9 pages3 Amplifier Common Mode Rejection Ratio Part I FullUjjWal MahAjanNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier: Op Amp High Input Impedance Low Output ImpedanceDocument18 pagesOperational Amplifier: Op Amp High Input Impedance Low Output ImpedanceUditha MuthumalaNo ratings yet
- Fnal Op AmpDocument34 pagesFnal Op AmpHeyiNo ratings yet
- Op Amp Differential Amplifier Circuit Age SubtractorDocument9 pagesOp Amp Differential Amplifier Circuit Age SubtractorSai Arja SaiNo ratings yet
- Ecd Lec-1-2Document37 pagesEcd Lec-1-2assad abidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 OP Amp 2-1Document10 pagesChapter 2 OP Amp 2-1SRA893No ratings yet
- Differential Amplifier: Mrs.V.Srirenganachiyar, Ap/Ece Ramco Institute of Technology Academic Year:2017-2018 (Odd)Document13 pagesDifferential Amplifier: Mrs.V.Srirenganachiyar, Ap/Ece Ramco Institute of Technology Academic Year:2017-2018 (Odd)Hitlar MamaNo ratings yet
- Sample WebDocument5 pagesSample WebvijsanNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Op-AmpDocument9 pagesUnit 6 Op-AmpKUMARI SAKSHINo ratings yet
- ppt4 - Operational AmplifiersDocument71 pagesppt4 - Operational AmplifiersMichael Angelo BerjaNo ratings yet
- Opamp PesentationDocument34 pagesOpamp Pesentation2shreedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document32 pagesChapter 4Ram Bahadur KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Op AmpsDocument17 pagesOp AmpsshilpaNo ratings yet
- Chap4a OpAmpDocument37 pagesChap4a OpAmpAl AidenNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier and Its Applications: Unit 5Document20 pagesOperational Amplifier and Its Applications: Unit 5Chiraag ChiruNo ratings yet
- UNIT3 - Introduction To IC Technology - 290617 - EditedDocument82 pagesUNIT3 - Introduction To IC Technology - 290617 - EditedKISHAN SHUKLANo ratings yet
- Op AmpsDocument22 pagesOp AmpsKrishnaveni DhulipalaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Operational AmplifiersDocument32 pagesUnit 2 - Operational AmplifiersVimala ElumalaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 BTE3243Document29 pagesChapter 3 BTE3243Muhammad Shafiq Bin Abdul KarimNo ratings yet
- Differential Amplifier Lab ExperimentDocument4 pagesDifferential Amplifier Lab ExperimentTfNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Operational AmplifiersDocument37 pagesLesson 2 Operational AmplifiersJonjeffrey AgustinNo ratings yet
- Chapter - II Differential AmplifierDocument20 pagesChapter - II Differential AmplifierAbrha FtsumNo ratings yet
- Electronics CircuitDocument0 pagesElectronics Circuitwww.bhawesh.com.npNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of An Op-AMP: PreviousDocument4 pagesBlock Diagram of An Op-AMP: PreviousSarita UmadiNo ratings yet
- Opaamp NewwwDocument20 pagesOpaamp NewwwArpita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifiers: Electronic Devices & Circuit Theory by Boylestad and NashelskyDocument35 pagesOperational Amplifiers: Electronic Devices & Circuit Theory by Boylestad and NashelskyTejinder Singh100% (1)
- OPAMP by COEP ProfDocument171 pagesOPAMP by COEP Profonkarsinare1No ratings yet
- OpampDocument51 pagesOpampMitesh BhagoraNo ratings yet
- Chapter - II Differential AmplifierDocument15 pagesChapter - II Differential AmplifierAbrha FtsumNo ratings yet
- Experiment-1.2 Characterization of Op-Amp: 1.2.1 OBJECTIVEDocument15 pagesExperiment-1.2 Characterization of Op-Amp: 1.2.1 OBJECTIVErajatinthehouseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Intro To Op AmpsDocument14 pagesLecture 1 - Intro To Op AmpsRap JaviniarNo ratings yet
- Differential Amplifier Omp Amplifier GateDocument8 pagesDifferential Amplifier Omp Amplifier GatewatsondalphyNo ratings yet
- Differentialamplifier 181127115932Document13 pagesDifferentialamplifier 181127115932deepa reddyNo ratings yet
- Op Amp ExpDocument23 pagesOp Amp Expram12_leoNo ratings yet
- Diff AmplDocument13 pagesDiff AmplAdeel AnsariNo ratings yet
- Opamp NotesDocument5 pagesOpamp NotesVasim AkramNo ratings yet
- AEC Exp 6 ManualDocument9 pagesAEC Exp 6 ManualChandrahasa reddy ENo ratings yet
- CMRR and PSRR PDFDocument3 pagesCMRR and PSRR PDFManojkumarNo ratings yet
- Intro To OpampDocument20 pagesIntro To OpampmaryambaoNo ratings yet
- Design of Instrumentation AmplifierDocument76 pagesDesign of Instrumentation Amplifierarun93921100% (1)
- Amplification: and The Drain-To-Source Capacitance of The Channel. Because of These Drops FrequencyDocument9 pagesAmplification: and The Drain-To-Source Capacitance of The Channel. Because of These Drops FrequencyAmlan SahariaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Multistage AmplifiersDocument9 pagesLecture 3 Multistage AmplifiersAbdul SheikhNo ratings yet
- 18-Mod 4 (Op Amp) - 22-01-2024Document39 pages18-Mod 4 (Op Amp) - 22-01-2024Sai SharanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 2 Design of An Instrumentation Amplifier: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesLaboratory 2 Design of An Instrumentation Amplifier: ObjectiveChandreshSinghNo ratings yet
- Sensors and ActuatorsDocument43 pagesSensors and Actuatorshitesh reddyNo ratings yet
- Electronics Analog OPAMPDocument51 pagesElectronics Analog OPAMPPrashant SachdevNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifiers 1Document26 pagesOperational Amplifiers 1M. RazaNo ratings yet
- Eee 1217 Op AmpDocument51 pagesEee 1217 Op AmpEbrahim SiddikNo ratings yet
- Elec 2301 BJT DiffDocument14 pagesElec 2301 BJT DiffKeith TsechowNo ratings yet
- Analog & Digital Electronics: Course No: PH-218 Lec-21: Differential AmplifiersDocument13 pagesAnalog & Digital Electronics: Course No: PH-218 Lec-21: Differential AmplifiersKu Ble YanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Op-Amp PDFDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Op-Amp PDFJeswant TSNo ratings yet
- Op Amp 2Document14 pagesOp Amp 2Dhileepan SankarNo ratings yet
- Operational AmplifiersDocument34 pagesOperational AmplifiersLEARNING CENTERNo ratings yet
- Epc M3Document13 pagesEpc M3karanphutane2254No ratings yet
- Differential Pair Using MOS TransistorsDocument5 pagesDifferential Pair Using MOS TransistorsSatish BojjawarNo ratings yet
- Lica NotesDocument20 pagesLica NotesDHANYASRI BOLLANo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Operational Amplifier FundamentalsDocument23 pagesUnit - 1 Operational Amplifier FundamentalsWaleed HåšhįmNo ratings yet