Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant and Animal Tissues
Uploaded by
Divine Merry Alinghawa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesanimals and plants tissues
Original Title
PLANT AND ANIMAL TISSUES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentanimals and plants tissues
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesPlant and Animal Tissues
Uploaded by
Divine Merry Alinghawaanimals and plants tissues
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
PLANT AND ANIMAL TISSUES
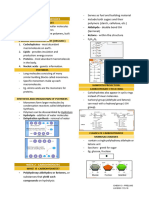
CARBOHYDRATES - are the most abundant organic
compounds
- they function as energy sources and structure
components of the cell.
- Ch2O (formula)
FOUR CHEMICAL GROUP OF CARBOHYDRATES
1.MONOSACCHARIDES - monomers or simple sugar.
- they serve as building blocks of carbohydrate
polymers and other biological molecule.
- examples are glucose, fructose, and galactose with
a chemical formula C6H12O6
2. DISACCHARIDES - composed of two molecules or
simple sugar bonded together glycosidic bond.
- common example is the table sugar or sucrose.
3. OLIGOSACCHARIDES - made up of anywhere from
two or ten monosaccharides units linked by glycosidic
bond.
4. POLYSACCHARIDES - may consists of hundreds of
linked monomer of glucose or other simple sugar.
- examples are starch, cellulose, chitin and glycogen.
STARCH - carbohydrates storage in plants
CELLULOSE - the most abundant biological molecule in
nature.
CHITIN - the major substance in exoskeleton of
arthropods and mollusks
GLYCOGEN - the main storage form of carbohydrates
in animals
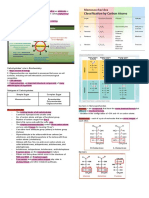
LIPIDS - makes certain food oily.
- includes fats, oils, waxes, steroids, and
phospholipids.
FATS AND OILS - serves as nutrients reserves in animals
and plants.
- corn oil, canola oil, olive oil are typically lipids
extracted from plants.
✔️GLYCEROL
✔️FATTY ACIDS
PHOSPHOLIPIDS - consists of glycerol molecule, a
phosphale group and two fatty acids.
STEROIDS - are organic compounds with four rings
arranged in a specific configuration.
- sterols and terpenes are some example of
steroids
CARBOHYDRATES AND LIPIDS
Sterols such as cholesterol, antrogens, and estrogen,
CARBON COMPOUNDS - carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic
adrenal corticosteroid
acids, proteins
You might also like
- Cellular Healing Diet EbookDocument48 pagesCellular Healing Diet Ebookselva93% (14)
- F3 Final Exam 11-12Document23 pagesF3 Final Exam 11-12jonas hoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry ReviewerDocument20 pagesBiochemistry ReviewerabcdeniselimNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviewerDocument6 pagesBio ReviewerMr. DADANo ratings yet
- Biomolecules HardDocument2 pagesBiomolecules HardChrismaine Bell RivasNo ratings yet
- Annotated GenbioDocument5 pagesAnnotated GenbioJarred HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes 1Document2 pagesBiology Notes 1Paulo AloroNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesBiomoleculesgeecyjane YguintoNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument6 pagesPhysical ScienceCAYABAN, RISHA MARIE DV.No ratings yet
- Biochem MidtermsDocument25 pagesBiochem MidtermsYuki MendezNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Reviewer Final 1Document5 pagesGen Bio Reviewer Final 1Emmanuelle CalleNo ratings yet
- Organic MoleculesDocument7 pagesOrganic MoleculesJames CadizNo ratings yet
- HARPERS - IV Carbohydrates of Physiological SignificanceDocument4 pagesHARPERS - IV Carbohydrates of Physiological SignificancedandiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: A Short CourseDocument31 pagesBiochemistry: A Short CourseEli JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Biology Long TestDocument7 pagesBiology Long TestMarjorie AballaNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules. Monomers: Bio 11O Topic 5 - BiomoleculesDocument8 pagesMacromolecules. Monomers: Bio 11O Topic 5 - BiomoleculesYda TolentinoNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY FinalDocument21 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY FinalJoliem Phya E. IdongNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lesson-1Document18 pagesBiochemistry Lesson-1Priyadarshini LenkaNo ratings yet
- (Poly, Many Mer, Unit) Monomers (Mono, One) : Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O) and Nitrogen (N) PolymersDocument5 pages(Poly, Many Mer, Unit) Monomers (Mono, One) : Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O) and Nitrogen (N) PolymersDaneth Julia TuberaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Week 4 - CarbohydrateDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Week 4 - CarbohydrateMicah JadeNo ratings yet
- 2general Biology 1 Learning Package Final TermDocument19 pages2general Biology 1 Learning Package Final Termashleykategallo361No ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEWER MidtermDocument27 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY REVIEWER MidtermLovelle Pirante OyzonNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - 1 2.5 - The Organic Molecules of Living OrganismsDocument7 pagesGen Bio - 1 2.5 - The Organic Molecules of Living OrganismsBlaire ReyesNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit Review: I. CarbohydratesDocument11 pagesBiology Unit Review: I. CarbohydratesJOSHUA DICHOSONo ratings yet
- Reviewer Science-BiomoleculeDocument2 pagesReviewer Science-BiomoleculeClouie MesiasNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM ReviewerDocument12 pagesBIOCHEM ReviewerKyla JuantaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Prelim CompilationDocument22 pagesBiochem Prelim CompilationKezia MadeloNo ratings yet
- General Biology Reviewer:: - Synthesis of Biological MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology Reviewer:: - Synthesis of Biological MacromoleculesSarah Jane P. CayabyabNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument2 pagesBIOLOGYMyraSimoraNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument8 pagesBIOMOLECULESjorel marcoNo ratings yet
- CarbohydrateDocument4 pagesCarbohydrateAbdullah Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Reviewer FinalsDocument8 pagesPhysical Science Reviewer FinalsKathNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument41 pagesBiological MacromoleculesRyan Dave MacariayNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersJojo LouNo ratings yet
- Gen - Bio DEMO 1Document7 pagesGen - Bio DEMO 1Lielanie NavarroNo ratings yet
- UNITI Biomolecules PDFDocument18 pagesUNITI Biomolecules PDFdrugdrug100% (1)
- Monosaccharides Formula Where Found: 4 QTR - Science The Chemistry of LifeDocument7 pagesMonosaccharides Formula Where Found: 4 QTR - Science The Chemistry of LifeJune Emerson ManalangNo ratings yet
- Biochem Mod 8 PDFDocument3 pagesBiochem Mod 8 PDFtheaNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesBiomoleculesGerald Angelo DeguinioNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument12 pagesCARBOHYDRATESxenia rayaNo ratings yet
- Biology Exam Notes by ConstantinDocument120 pagesBiology Exam Notes by ConstantinbnvjNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-6-micropara (Outline)Document9 pagesCHAPTER-6-micropara (Outline)Jezrylle BalaongNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Study CentreDocument26 pagesBiomolecules: Study CentreNeeraj VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate S: Prepared By: ROBIÑOS, Emily Ann ADocument13 pagesCarbohydrate S: Prepared By: ROBIÑOS, Emily Ann AMarilyn BagayNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument20 pagesBiological MoleculesUbaid Ur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules PDFDocument5 pagesBiomolecules PDFgabo uyNo ratings yet
- Ajssnansnwnnsn Modyol 1Document5 pagesAjssnansnwnnsn Modyol 1Snow Cordelia ThundilliorNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument82 pagesCarbohydratesfa2008294No ratings yet
- Bio 12 AModule 5Document7 pagesBio 12 AModule 5Ivan RamirezNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Carbohydrates 1Document66 pagesChapter2 Carbohydrates 1Alice C. RiveraNo ratings yet
- Secondary OneDocument103 pagesSecondary Oneroqayaehab.elsNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules - 054325Document18 pagesBiomolecules - 054325Baninla NerusNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in General Biology 1Document2 pagesReviewer in General Biology 1Moy ReyesNo ratings yet
- (CN 112) 1st Exam ReviewerDocument6 pages(CN 112) 1st Exam Reviewermariyvonne01No ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2NDDocument5 pagesGen Bio 2NDZyren Joy SamillanoNo ratings yet
- Biology UNIT 2Document72 pagesBiology UNIT 2suba052k09No ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument48 pagesBiomoleculesOliric FabiolasNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules 1Document29 pagesBiomolecules 1jefrillevaldezNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - Biological MacromoleculesDocument18 pagesPhysical Science - Biological MacromoleculesToni GraceNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 BiomoleculesDocument58 pagesUnit 7 Biomoleculesjanellekawaii16No ratings yet
- Outline: Biochemistry LEC CarbohydratesDocument8 pagesOutline: Biochemistry LEC CarbohydratesShardy Lyn RuizNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsFrom EverandAnatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Agricultural ProductionDocument478 pagesModelling of Agricultural ProductionLachezar StoimenovNo ratings yet
- DLL.3rd DemoDocument6 pagesDLL.3rd DemoRhissan Bongalosa Acebuche100% (1)
- Group 2 - Nutritional Care Plan - PPTDocument28 pagesGroup 2 - Nutritional Care Plan - PPTBea ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Finished Version Skinnybible r6Document34 pagesFinished Version Skinnybible r6amirreza jmNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Wardlaws Perspectives in Nutrition 9th Edition Carol Byrd BredbennerDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Wardlaws Perspectives in Nutrition 9th Edition Carol Byrd Bredbennerpelmabanging.568evl100% (37)
- Management of Diet in Coronary Artery Disease With Diabetes MellitusDocument21 pagesManagement of Diet in Coronary Artery Disease With Diabetes MellitusRavi KalraNo ratings yet
- Apex4494 Haeryang Park SITHCCC018Document27 pagesApex4494 Haeryang Park SITHCCC018Tikaram GhimireNo ratings yet
- Most Important Questions of Physical Education Chapter 2 Class 12thDocument15 pagesMost Important Questions of Physical Education Chapter 2 Class 12thPushpesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Benefits of ApplesDocument12 pagesBenefits of ApplesAbdel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Pathfit 3 Module Chapter 2Document18 pagesPathfit 3 Module Chapter 2Marc BorcilloNo ratings yet
- State Council of Educational Research and Training TNCF 2017 - Draft SyllabusDocument9 pagesState Council of Educational Research and Training TNCF 2017 - Draft SyllabusVenkat HariNo ratings yet
- Interchange: Practice For The TOEIC Test For 2ADocument29 pagesInterchange: Practice For The TOEIC Test For 2ARolando100% (1)
- Our FoodDocument10 pagesOur FoodBrahmananda ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Lec - 9 Public Health Nutrition and Importance For Health PromptionDocument44 pagesLec - 9 Public Health Nutrition and Importance For Health Promptiontanvir ahmed0% (1)
- Cohen Diet AnalysisDocument9 pagesCohen Diet Analysisfatmata koromaNo ratings yet
- Sugar Consumption in MalaysiaDocument14 pagesSugar Consumption in MalaysiaShi Yen50% (2)
- Overview On The Mechanisms of Coffee Germination and Fermentation and Their Significance For Coffee and Coffee Beverage QualityDocument17 pagesOverview On The Mechanisms of Coffee Germination and Fermentation and Their Significance For Coffee and Coffee Beverage QualityJohana Marcela AcostaNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION With CONCEPT MAPDocument4 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION With CONCEPT MAPKASHMIR R3No ratings yet
- The Kidney Diet NSNDocument24 pagesThe Kidney Diet NSNCristina Herman Hanuschi100% (1)
- BionutrisiDocument21 pagesBionutrisiEnina Eninta SinuhajiNo ratings yet
- Insulin CorretionDocument5 pagesInsulin CorretionArshad SyahaliNo ratings yet
- Raise Your Testosterone GuideDocument9 pagesRaise Your Testosterone GuidePalamar Jasmin100% (2)
- Presentasi DR.W.SP.B KBDDocument13 pagesPresentasi DR.W.SP.B KBDThesar WaldiNo ratings yet
- RemedialPAS 12 Sem1 2021-2022Document13 pagesRemedialPAS 12 Sem1 2021-2022Fitria AzzahraNo ratings yet
- FCI Paper at Recruitmentindia - inDocument41 pagesFCI Paper at Recruitmentindia - insoumyaNo ratings yet
- B1.1 - Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument4 pagesB1.1 - Carbohydrates and LipidslittleianlauNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Pathfit 1Document5 pagesLecture 4 Pathfit 1Tessa Kaye - Rumol AlfaroNo ratings yet
- MSC Microbiology SyllabusDocument9 pagesMSC Microbiology SyllabusArjun ShethNo ratings yet