Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phy 3.2
Uploaded by
farahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Phy 3.2
Uploaded by
farahCopyright:
Available Formats
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.
uk
YOUR NOTES
4.2 Linear Momentum & Conservation ⬇
CONTENTS
4.2.1 Conservation of Momentum
4.2.2 Elastic & Inelastic Collisions
4.2.1 CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM
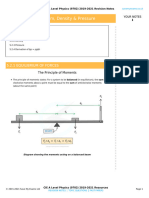
The Principle of Conservation of Momentum
The principle of conservation of momentum is:
The total momentum of a system remains constant provided no external
force acts on it
For example if two objects collide:
the total momentum before the collision = the total momentum after the collision
Remember momentum is a vector quantity. This allows oppositely-directed vectors to cancel
out so the momentum of the system as a whole is zero
Momentum is always conserved over time
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 1
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
4.2 Linear Momentum & Conservation ⬇
External and Internal Forces
External forces are forces that act on a structure from outside e.g. friction and weight
Internal forces are forces exchanged by the particles in the system e.g. tension in a string
Which forces are internal or external will depend on the system itself, as shown in the
diagram below:
Internal and external forces on a mass on a spring
You may also come across a system with no external forces being described as a ‘closed’ or
‘isolated’ system
These all still refer to a system that is not affected by external forces
For example, a swimmer diving from a boat:
The diver will move forward, and, to conserve momentum, the boat will move
backwards
This is because the momentum beforehand was zero and no external forces are present to
affect the motion of the diver or the boat
Collisions in One & Two Dimensions
One-dimensional momentum problems
Momentum (p) is equal to: p = m × v
Using the conversation of linear momentum, it is possible to calculate missing velocities and
masses of components in the system. This is shown in the example below
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 2
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
4.2 Linear Momentum & Conservation ⬇
Worked Example
Trolley A of mass 0.80 kg collides head-on with stationary trolley B at a velocity of 3.0 ms-1.
Trolley B has twice the mass of trolley A.
The trolleys stick together. Using the conservation of momentum, calculate the common
velocity of both trolleys after the collision. Determine whether this is an elastic or inelastic
collision.
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 3
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
4.2 Linear Momentum & Conservation ⬇
To find out whether a collision is elastic or inelastic, compare the kinetic energy before and
after the collision
If the kinetic energy is conserved, it is an elastic collision
If the kinetic energy is not conserved, it is an inelastic collision
Elastic collisions are commonly those where objects colliding do not stick together and
then move in opposite directions
Inelastic collision are where objects collide and stick together after the collision
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 4
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
4.2 Linear Momentum & Conservation ⬇
Two-dimensional momentum problems
Since momentum is a vector, in 2D it can be split up into its x and y components
Review revision notes 1.3 Scalars & Vectors on how to resolve vectors
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 5
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
4.2 Linear Momentum & Conservation ⬇
Worked Example
A ball is thrown at a vertical wall. The path of the ball is shown below
The ball is thrown from S with an initial velocity of 15.0 m s-1 at 60.0° to the horizontal. The mass of
-3 -1
the ball is 60 × 10 kg and rebounds at a velocity of 4.6 m s .
Calculate the change in momentum of the ball if it rebounds off the wall.
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 6
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
4.2 Linear Momentum & Conservation ⬇
Exam Tip
If an object is stationary or at rest, it’s velocity equals 0, therefore, the momentum and kinetic
energy are also equal to 0.
When a collision occurs in which two objects are stuck together, treat the final object as a
single object with a mass equal to the sum of the two individual objects.
In 2D problems, make sure you’re confident resolving vectors. Here is a small trick to
remember which component is cosine or sine of the angle for a vector R:
Resolving vectors with sine and cosine
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 7
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
4.2 Linear Momentum & Conservation ⬇
4.2.2 ELASTIC & INELASTIC COLLISIONS
Elastic Collisions
When two objects collide, they may spring apart retaining all of their kinetic energy. This is a
perfect elastic collision
An elastic collision is one where kinetic energy is conserved
Equation for kinetic energy
Since kinetic energy depends on the speed of an object, in a perfectly elastic collision (head-
on approach) the relative speed of approach = the relative speed of separation
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 8
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
4.2 Linear Momentum & Conservation ⬇
Worked Example
Two similar spheres, each of mass m and velocity v are travelling towards each other. The spheres
have a head-on collision. What is the total kinetic energy after the impact?
Exam Tip
Despite velocity being a vector, kinetic energy is a scalar quantity and therefore will never
include a minus sign. This is because in the kinetic energy formula, mass is scalar and the v2
will always give a positive value whether its a negative or positive velocity
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 9
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
4.2 Linear Momentum & Conservation ⬇
Inelastic Collisions
Whilst the momentum of a system is always conserved in interactions between objects,
kinetic energy may not always be
An inelastic collision is one where kinetic energy is not conserved
Equation for kinetic energy
The kinetic energy is transferred into other forms of energy such as a heat or sound
Inelastic collisions can be when two objects collide and they crumple and deform. Their
kinetic energy may also disappear completely as they come to a halt
A perfectly inelastic collision is when two objects stick together after collision, as shown in
the example below
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 10
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
4.2 Linear Momentum & Conservation ⬇
Worked Example
Two trolleys X and Y are of equal mass. Trolley X moves towards trolley Y which is initially
stationary. After the collision, the trolleys join and move off together. Prove that this collision is
inelastic.
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 11
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
4.2 Linear Momentum & Conservation ⬇
Exam Tip
Although kinetic energy may not always being conserved, remember momentum will
always be conserved.
Exam Question: Easy
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 12
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
4.2 Linear Momentum & Conservation ⬇
Exam Question: Medium
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 13
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Revision Notes savemyexams.co.uk
YOUR NOTES
4.2 Linear Momentum & Conservation ⬇
Exam Question: Hard
> CHECK YOUR ANSWERS AT SAVEMYEXAMS.CO.UK
© 2015-2021 Save My Exams Ltd
CIE A Level Physics (9702) 2019-2021 Resources Page 14
REVISION NOTES TOPIC QUESTIONS PAST PAPERS
You might also like
- Phy 4.2Document24 pagesPhy 4.2farahNo ratings yet
- Phy 1-2Document30 pagesPhy 1-2farahNo ratings yet
- Phy 4.1Document23 pagesPhy 4.1farahNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities & UnitsDocument20 pagesPhysical Quantities & UnitsfarahNo ratings yet
- Measurements & ErrorsDocument25 pagesMeasurements & ErrorsfarahNo ratings yet
- 12-Motion in A CircleDocument17 pages12-Motion in A CircleScarlettNo ratings yet
- 9 ElectricityDocument40 pages9 Electricitypythonfreelancer77No ratings yet
- Atomic PhyDocument31 pagesAtomic PhymwagweNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE Physics Syllabus - Wave Optics, Ray Optics & Magnetism - AskIITiansDocument4 pagesIIT JEE Physics Syllabus - Wave Optics, Ray Optics & Magnetism - AskIITiansTammannaThadaniNo ratings yet
- 12.2 RespirationDocument32 pages12.2 Respirationmptneuro2024No ratings yet
- PDWneicI3Yz xeGIDocument11 pagesPDWneicI3Yz xeGIqasemmohamed777No ratings yet
- A Level Physics CIE: 12. Motion in A CircleDocument15 pagesA Level Physics CIE: 12. Motion in A Circlemaryamafsar00No ratings yet
- Relative Motion - Study Material For IIT JEE - AskIITiansDocument13 pagesRelative Motion - Study Material For IIT JEE - AskIITiansRitwikNo ratings yet
- Compendium ClassXII PhyscisDocument11 pagesCompendium ClassXII PhyscisvarunkohliinNo ratings yet
- 12.motion in AcircleDocument15 pages12.motion in Acirclezzrnwdzpsmhs951003No ratings yet
- Structural Analysis On Composite Laminate With Different OrientationDocument6 pagesStructural Analysis On Composite Laminate With Different OrientationTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8-Shearing Forces and Bending Moments in Beams (DELIVERED)Document30 pagesLecture 8-Shearing Forces and Bending Moments in Beams (DELIVERED)Naledi KetlogetsweNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4: Material Selection and High Level Assembly DesignDocument4 pagesAssignment 4: Material Selection and High Level Assembly DesignAnand BhiseNo ratings yet
- Mech BNL 14.0 L04-PlasticityDocument30 pagesMech BNL 14.0 L04-PlasticitycrisNo ratings yet
- Geometry m1 Mid Module AssessmentDocument16 pagesGeometry m1 Mid Module AssessmentAmmar TawfiqNo ratings yet
- Review Esas 2 (Physics)Document59 pagesReview Esas 2 (Physics)Araiza FloresNo ratings yet
- Fatigue FailureDocument17 pagesFatigue Failureaiman.mohammadNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214785318313646 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S2214785318313646 MainmaximNo ratings yet
- Explicit-STR 16.0 L05 Material ModelsDocument61 pagesExplicit-STR 16.0 L05 Material ModelsRushabh PatelNo ratings yet
- General PhysicsDocument100 pagesGeneral Physicscarrisanicole2No ratings yet
- 1.physical Quantities and UnitsDocument28 pages1.physical Quantities and UnitssifatclashgamingNo ratings yet
- CSE20201 Lecture 9Document9 pagesCSE20201 Lecture 9Ho Fung LeungNo ratings yet
- University of Southeastern PhilippinesDocument2 pagesUniversity of Southeastern Philippinesadonis bibatNo ratings yet
- MEC0125MasterSlides PlasticityDocument269 pagesMEC0125MasterSlides PlasticitymggllNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document17 pagesCH 4Zahim Harki100% (1)
- Screenshot 2023-11-28 at 1.47.22 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-11-28 at 1.47.22 PMAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Measurements and ErrorsDocument11 pagesMeasurements and Errorszhougongyue520No ratings yet
- Formula Booklet Physics XIDocument35 pagesFormula Booklet Physics XILokesh Kumar80% (5)
- CFD PPT Unit 1..Document34 pagesCFD PPT Unit 1..Tejal IkharNo ratings yet
- Test Report of TEST - 14 Steel Structures (SS02) - GATE (CE) : BookmarkDocument9 pagesTest Report of TEST - 14 Steel Structures (SS02) - GATE (CE) : BookmarkhimanshiNo ratings yet
- Dinamica 3Document7 pagesDinamica 3Giuliano Rodriguez RestrepoNo ratings yet
- 2017 Winter Model Answer PaperDocument35 pages2017 Winter Model Answer PaperriteshudakheNo ratings yet
- SEAU Practical Uses of Nonlinear Pushover AnalysisDocument95 pagesSEAU Practical Uses of Nonlinear Pushover Analysisclam2014No ratings yet
- Ramet 1Document6 pagesRamet 1Bojan TanaskovskiNo ratings yet
- Study Material: Free Master Class SeriesDocument21 pagesStudy Material: Free Master Class SeriesRahul RanaNo ratings yet
- Physics Weightage For NEET UG 2022Document1 pagePhysics Weightage For NEET UG 2022Rohit PLRNo ratings yet
- ME216 MOM - CHPT 1Document60 pagesME216 MOM - CHPT 1Sergio Contreras PancorboNo ratings yet
- CIE As Biology (9700) Exams From 2022 CIE As Biology (9700) Exams From 2022 2.2.1 Biological Molecules Key Terms SaveMyExamsDocument40 pagesCIE As Biology (9700) Exams From 2022 CIE As Biology (9700) Exams From 2022 2.2.1 Biological Molecules Key Terms SaveMyExamsRudra Sai Sreeman Reddy MulaNo ratings yet
- KZN ATP Physical Science GRADE 12 2024Document7 pagesKZN ATP Physical Science GRADE 12 2024lebomorena12No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0005109822006173 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0005109822006173 MaincarlosNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven - Deflection of Beams (Dr. Abdulkader)Document22 pagesChapter Seven - Deflection of Beams (Dr. Abdulkader)Sarbast TaqanaNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Review March 2019Document40 pagesPetroleum Review March 2019Murat HojabayevNo ratings yet
- Ntro FluidsDocument35 pagesNtro Fluidsalan roiNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Proteins: 2.3.1 Amino Acids & The Peptide BondDocument24 pages2.3 Proteins: 2.3.1 Amino Acids & The Peptide BondRudra Sai Sreeman Reddy MulaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Binomial Theorem - P and C - Complete ModuleDocument85 pagesMathematics - Binomial Theorem - P and C - Complete ModuleAgain MishraNo ratings yet
- Statics: Engineering MechanicsDocument31 pagesStatics: Engineering MechanicsFrensey JynethNo ratings yet
- Com 4Document28 pagesCom 4Lalit RanjanNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2024 Nkhynogrxghgguide - UpdatedDocument26 pagesJEE Main 2024 Nkhynogrxghgguide - Updatedrajputmayank.7357No ratings yet
- Plastic Collapse Analysis of Beams: Ultimate Load-Bearing CapacityDocument10 pagesPlastic Collapse Analysis of Beams: Ultimate Load-Bearing CapacityDobromir DinevNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Boundary Value Problems in Science and EngineeringFrom EverandNonlinear Boundary Value Problems in Science and EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Barron's Physics Practice Plus: 400+ Online Questions and Quick Study ReviewFrom EverandBarron's Physics Practice Plus: 400+ Online Questions and Quick Study ReviewNo ratings yet
- Laporan Atem 2020Document53 pagesLaporan Atem 2020Boot ChanelNo ratings yet
- Tuttle and Bailey AdministrationDocument8 pagesTuttle and Bailey AdministrationElvis FariasNo ratings yet
- Overview of Ventilation CalculationDocument47 pagesOverview of Ventilation CalculationDixter CabangNo ratings yet
- M30 Knig2461 04 Ism C30Document34 pagesM30 Knig2461 04 Ism C30Hanzala TahirNo ratings yet
- Recording GaugeDocument7 pagesRecording GaugeMarifher Kate Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Distance and Displacement 1 PDFDocument30 pagesDistance and Displacement 1 PDFsfgdfgsdfgdfggNo ratings yet
- DPP+ +WPE+one+shot+++mock+test+Document90 pagesDPP+ +WPE+one+shot+++mock+test+rahul kmNo ratings yet
- CNC Router CalculationsDocument4 pagesCNC Router Calculationsmorteza nourooziNo ratings yet
- JEE Mains 2024 Question Paper Shift 2 27 JanDocument4 pagesJEE Mains 2024 Question Paper Shift 2 27 JanAnjali SahooNo ratings yet
- GR 5 - MATHEMATICS - Student Note 1 - Length and DistanceDocument7 pagesGR 5 - MATHEMATICS - Student Note 1 - Length and Distancejagath2005ukNo ratings yet
- Physics 4.1,4.2Document16 pagesPhysics 4.1,4.2Fatima FiazNo ratings yet
- Cone Plate ViscometerDocument7 pagesCone Plate ViscometerABDULLAHSHARJEEL KHANNo ratings yet
- SC and VD CalculationsDocument25 pagesSC and VD CalculationsAhmed KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Single Stage CompressorDocument16 pagesExperiment 2 Single Stage CompressorTshepo Moloto100% (1)
- Edexcel Ial (A/S Level) 2022 Neranja Weerasinghe: PHYSICS UNIT 01 (Mechanics & Materials)Document2 pagesEdexcel Ial (A/S Level) 2022 Neranja Weerasinghe: PHYSICS UNIT 01 (Mechanics & Materials)Pevin De silvaNo ratings yet
- Phys101 Physics I: Frictional ForceDocument23 pagesPhys101 Physics I: Frictional ForceKhadija B100% (1)
- Astm C 232-2020Document3 pagesAstm C 232-2020Mohammed Ali100% (1)
- MES-A Specifications (En)Document2 pagesMES-A Specifications (En)nizamNo ratings yet
- Rajdhani Scientific Co Bomb Calorimeter Model RSB-5 Instruction ManualDocument5 pagesRajdhani Scientific Co Bomb Calorimeter Model RSB-5 Instruction ManualPartha GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Conductivity ExerciseDocument1 pageConductivity ExerciseMr. Gamingo ChallengiNo ratings yet
- Multímetro Fluke 114,115,116,117Document20 pagesMultímetro Fluke 114,115,116,117Arturo mendozaNo ratings yet
- How To Test Diodes With A Digital Multimeter - FlukeDocument6 pagesHow To Test Diodes With A Digital Multimeter - Flukecooldude.pesiganNo ratings yet
- AS0717.2 (2004) Acoustics - Rating of Sound Insulation in Buildings and of Building Elements - Impact Sound InsulationDocument20 pagesAS0717.2 (2004) Acoustics - Rating of Sound Insulation in Buildings and of Building Elements - Impact Sound Insulationjojo351No ratings yet
- ISO 3 Pillars Metrology, Standarization and Conformity Assesstment PDFDocument4 pagesISO 3 Pillars Metrology, Standarization and Conformity Assesstment PDFRafael GarzónNo ratings yet
- Intro and Theory of XRF-Product Overview (Compatibility Mode)Document30 pagesIntro and Theory of XRF-Product Overview (Compatibility Mode)Yuli Yanti SundeNo ratings yet
- Handout 06-Work and Kinetic EnergyDocument60 pagesHandout 06-Work and Kinetic EnergykimprinceGANo ratings yet
- Sop 1 Calibration Certificate Preparation 20180213Document9 pagesSop 1 Calibration Certificate Preparation 20180213SKPACA100% (1)
- Experiment 1: To Measure Diameter of A Scale Using Vernier CallipersDocument2 pagesExperiment 1: To Measure Diameter of A Scale Using Vernier CallipersManas KhoslaNo ratings yet
- 1MJ6 113-2CA60 Motor of BurnerDocument8 pages1MJ6 113-2CA60 Motor of BurnerMohamed MusaNo ratings yet
- Iso 3302 1 2014Document9 pagesIso 3302 1 2014Sandhya SinghNo ratings yet