Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Observation Logs Two Students
Observation Logs Two Students
Uploaded by
api-736233077Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Observation Logs Two Students
Observation Logs Two Students
Uploaded by
api-736233077Copyright:
Available Formats
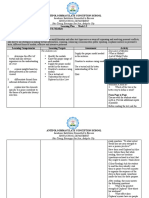
Name: Zachary Rhodanz
I Observation-Getting to Know You
Alternative Ways I Got to Know My 2 Students- Describe what you learned about each child
in the alternative ways other than observations.
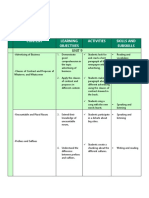
II LOG Format
CHILD Day of the WEEK Content: Strengths and/or Additional Thoughts:
with DATE Weaknesses (i.e.: observed learning style,
(chose 1 or 2 days per Name the content area and state S/E). You may now add
week to ensure only what you observed (hear some personal interpretation
observation of each and see) here.
content
Student 1 1/29 LA - Phonics (Short Vowels) The hesitation with complex
Content: Introduction to words suggests a need for
short vowel sounds. more visual aids and phonics
Strengths: Identifies short games to build confidence. Is
vowels in isolation
the request for
accurately.
Weaknesses: Struggles
demonstrations an indication
with blending sounds to of a visual learning
form words. preference?
1/29 Science - Basic Needs of Engagement with hands-on
Plants aspects was high, yet focus
Content: Exploring the waned during explanations.
roles of sunlight, water, Would visual storyboards or
and soil in plant growth. time-lapse videos of plant
Strengths: Correctly growth cater to visual
identifies the three basic learning needs and sustain
needs of plants. attention?
Weaknesses: Difficulty
understanding diverse
plant requirements.
Student 2 1/29 LA - Phonics (Short Vowels) The student's enthusiasm for
Content: Focused on participation is clear.
identifying and using Interactive games
short vowel sounds in emphasizing vowel sounds
words. could help solidify
Strengths: Shows understanding while keeping
eagerness to participate lessons engaging.
and attempts to blend
sounds.
Weaknesses:
Occasionally
mispronounces vowel
sounds, indicating
confusion.
1/29 Science - Basic Needs of Considering the student's
Plants active engagement,
Content: Introduction integrating a small classroom
to how plants use garden project could provide
sunlight, water, and soil practical experience and
to grow. deepen understanding of
Strengths: plant needs.
Demonstrates
understanding through
correct identification
and enthusiastic
participation in
discussions.
Weaknesses: Shows
some difficulty in
applying this knowledge
to different types of
plants.
Student 1 2/5 LA - Reading Comprehension Struggle with abstract
(Main Idea) concepts suggests a need for
Content: Identifying concrete examples. Graphic
the main idea in short organizers might help.
stories.
Strengths: Can discuss
the main character
and setting
confidently.
Weaknesses: Struggles
to determine the
story's main idea
independently.
2/5 Science - Weather Patterns Interest in personal weather
Content: Describing experiences is high. Personal
and recording weather journals could make
different weather learning more relatable.
conditions.
Strengths:
Enthusiastically shares
observations of
weather changes.
Weaknesses: Difficulty
connecting weather
types to their
characteristics.
Student 2 2/5 LA - Reading Comprehension Vibrant engagement in
(Main Idea) storytelling sessions. Visual
Content: Exploring aids, such as story maps,
the main idea through could reinforce
picture books. understanding of main ideas
Strengths: Actively and details.
predicts story
outcomes and
discusses characters'
actions.
Weaknesses: Needs
prompting to identify
supporting details for
the main idea.
2/5 Science - Weather Patterns Fascination with cloud
Content: Observing shapes and types evident.
cloud formations and Interactive cloud
predicting weather. identification guides could
Strengths: Shows encourage more confident
curiosity in learning weather predictions.
about clouds and their
types.
Weaknesses: Hesitates
to make predictions
about weather based
on clouds.
Student 1 2/12 LA - Writing (Sentence Demonstrates a natural flair
Structure) for storytelling but tends to
Content: Focusing on rush, overlooking
constructing complete punctuation. Incorporating
sentences with a sentence construction games
subject and predicate. that emphasize punctuation
Strengths: Exhibits could be beneficial.
creativity in sentence Highlighting the importance
content. of taking time to review
Weaknesses: work might encourage a
Occasionally omits more meticulous approach to
punctuation, leading writing.
to run-on sentences.
2/12 Science - Animal Habitats Engages well with direct
Content: Exploring matching activities but
various animal appears less confident in
habitats and their reasoning exercises.
importance. Implementing a "habitat
Strengths: Accurately detective" activity, where
identifies animals and students infer habitat needs
their corresponding based on animal
habitats. characteristics, might bolster
Weaknesses: Shows understanding and
hesitation when asked confidence.
to explain why certain
animals live in specific
habitats.
Student 2 2/12 LA - Writing (Sentence Shows promise in initiating
Structure) thoughts but needs guidance
Content: Constructing in developing them fully.
sentences focusing on Could benefit from peer
clarity and coherence. review sessions, where
Strengths: Able to students exchange work and
start sentences suggest sentence completions
strongly with a clear or improvements, fostering a
subject. collaborative learning
Weaknesses: Struggles environment and attention to
with maintaining sentence completion.
focus, leading to
incomplete sentences.
2/12 Science - Animal Habitats Displays a keen interest in
Content: Studying the animal facts, which can be
relationship between harnessed to deepen
animals and their understanding of habitats.
natural habitats. Structuring lessons to
Strengths: Shows include a "fact and fiction"
enthusiasm in group segment might help
discussions about distinguish between
exotic animals and entertaining anecdotes and
their homes. curriculum-relevant
Weaknesses: information, maintaining
Occasionally gets focus on learning objectives.
sidetracked with
unrelated facts or
anecdotes during
explanations.
Student 1 2/19 LA - Vocabulary (Synonyms Enthusiasm for vocabulary
and Antonyms) games is apparent,
Content: Introduction suggesting an interactive and
to and practice with playful approach to learning
synonyms and new words might be
antonyms through effective. Might there be an
various activities. opportunity to use visual
Strengths: Shows good aids, such as matching cards
recall of synonyms for or a word wall, to reinforce
commonly used words. the differences between
Weaknesses: Confuses synonyms and antonyms?
antonyms with Encouraging the use of
synonyms during some newly learned words in daily
exercises. journal entries could also
help solidify understanding.
2/19 Science - Forces and Motion The disparity between hands-
Content: Investigating on engagement and
how different types of verbal/written explanations
forces affect motion suggests a need for strategies
through experiments that bridge experiential
and demonstrations. learning with conceptual
Strengths: Actively understanding. Could
participates in and structured reflection
accurately predicts sessions, where students are
outcomes of guided through the process
experiments of connecting practical
demonstrating force. experiences to scientific
Weaknesses: Struggles concepts, enhance
to articulate the comprehension?
scientific principles
behind observations in
post-activity
discussions.
Student 2 2/19 LA - Vocabulary (Synonyms There's noticeable
and Antonyms) excitement about discovering
Content: Engaging new words but some
with synonyms and reluctance to apply them,
antonyms, identifying especially antonyms, in
them in reading context. Incorporating a
materials, and "word explorer" segment into
creating lists. lessons, where students find
Strengths: and present new synonyms
Demonstrates a strong and antonyms, could make
ability to generate vocabulary expansion more
extensive lists of dynamic and personally
synonyms. relevant. Would pairing
Weaknesses: Hesitates vocabulary study with
when asked to use creative writing tasks help
antonyms in sentences, students feel more
indicating a less firm comfortable using antonyms
grasp. expressively?
2/19 Science - Forces and Motion The preference for practical
Content: Exploring over theoretical learning
basic concepts of points to an experiential
forces and their effects learner. Integrating more
on motion with a focus real-life examples and
on real-life perhaps a class project that
applications. involves designing simple
Strengths: Shows a machines could align well
keen interest in how with this learning style.
everyday objects can Encouraging students to
demonstrate principles explain the science behind
of force and motion. their creations might offer a
Weaknesses: natural bridge to theoretical
Sometimes misses the understanding.
theoretical explanation
in favor of focusing on
the practical
demonstration.
Student 1 2/26 LA - Comprehension Student #1's eagerness to
(Inferencing) participate suggests a strong
Content: Engaging interest in stories, yet there's
with stories to practice a gap in connecting narrative
inferencing skills, clues to inferences. Could
understanding targeted exercises that
characters' motives, scaffold the process of
and predicting finding textual evidence—
outcomes. perhaps through highlighting
Strengths: Shows or note-taking strategies—
enthusiasm in help solidify these skills?
predicting story Incorporating more group
outcomes and engages work where students can
actively in group discuss their inferences
discussions. might also build confidence
Weaknesses: and understanding.
Sometimes finds it
challenging to support
predictions with
evidence from the text.
2/26 Science - Light and Shadows The hands-on approach to
Content: Investigating learning about light and
the properties of light shadows captivates Student
and how it interacts #1. Perhaps introducing a
with objects to create daily shadow tracking
shadows. activity, where students
Strengths: Actively document and discuss
experiments with shadow changes, could
objects and light bridge the gap between
sources to observe observation and
shadow formations. understanding the science
Weaknesses: Has behind it. Visual aids or
difficulty explaining models showing the Earth's
why shadows change rotation relative to the sun
size and position might also help
throughout the day. conceptualize this
phenomenon.
Student 2 2/26 LA - Comprehension Student #2's creativity is a
(Inferencing) strength in making
Content: Focused on inferences but may benefit
developing inferencing from more structured
skills through read- approaches to distinguish
alouds and interactive between imaginative guesses
reading sessions. and inferences firmly rooted
Strengths: Able to in textual evidence. Peer-led
make creative and book clubs, where students
plausible inferences present and debate their
about story events. inferences, could encourage
Weaknesses: deeper textual engagement
Sometimes relies on and analytical thinking.
imaginative leaps
rather than grounding
inferences in the text.
2/26 Science - Light and Shadows The curiosity shown by
Content: Exploring Student #2 indicates a strong
how light travels and foundation for scientific
creates shadows, inquiry. Building on this
including activities interest with more tangible
that allow examples of light reflection
manipulation of light and refraction, such as using
sources and mirrors or lenses, might
observation of results. make these abstract concepts
Strengths: more accessible.
Demonstrates Incorporating stories or
curiosity by asking demonstrations that feature
insightful questions these concepts in everyday
about how and why contexts could also enhance
shadows occur. understanding and retention.
Weaknesses: Struggles
with abstract concepts
related to light, such
as reflection and
refraction.
Student 1 3/11 LA - Reading Fluency and Student #1's enjoyment in
Expression reading aloud is evident,
Content: Practicing especially with texts they
reading fluency with feel confident about. Could
emphasis on integrating a wider variety of
expression and texts in a supportive, small
understanding group setting help build
punctuation's role in confidence and skills with
reading aloud. unfamiliar material?
Strengths: Encouraging voluntary
Demonstrates a good participation in a 'reader's
pace and theater' could also enhance
understanding of fluency and expression in a
expression when fun, engaging way.
reading familiar texts.
Weaknesses: Struggles
to maintain fluency
and expression with
unfamiliar or more
complex texts.
3/11 Science - Plant Life Cycles While Student #1 grasps the
Content: Exploring life cycle conceptually,
the stages of plant life there's a gap in applying this
cycles, with a focus on knowledge linguistically.
flowering plants. Incorporating a vocabulary
Strengths: Accurately journal specific to science
identifies and topics, where students can
sequences the stages of draw, write definitions, and
a plant's life cycle in use words in context, might
interactive activities. bridge this gap. Creating a
Weaknesses: Shows classroom garden where
some confusion in students can observe and
applying vocabulary document plant growth
related to the life cycle
stages could also provide a
stages in written work.practical, hands-on
reinforcement of these
concepts.
Student 2 3/11 LA - Reading Fluency and Student #2's eagerness to
Expression participate positively impacts
Content: Focusing on their fluency development.
improving reading However, the rush to read
fluency and expression quickly may indicate a focus
through group reading on completion over
sessions and individual comprehension. Setting
practice. paced reading challenges,
Strengths: Engages where the goal is to read with
enthusiastically with expressive clarity rather than
group reading speed, could encourage a
activities, showing more balanced approach.
notable improvement Pairing students for peer
in expression. reading sessions might also
Weaknesses: provide opportunities for
Occasionally rushes feedback and reflection on
through reading, pacing and expression.
sacrificing expression
for speed.
3/11 Science - Plant Life Cycles Student #2's strong
Content: Investigating engagement in practical
how seeds grow into activities offers an excellent
plants and the basis for deeper scientific
conditions necessary inquiry. Facilitating small
for each life cycle group discussions post-
stage. observation, possibly led by
Strengths: Shows keen students themselves, could
interest in hands-on provide a comfortable
planting activities, platform for sharing thoughts
observing and and asking questions.
documenting growth. Linking each life cycle stage
Weaknesses: Hesitates to a specific experiment or
to participate in observation task might also
discussions about the help solidify understanding
scientific reasoning and encourage more active
behind observed participation in the scientific
growth stages. discussion.
Student 1 3/18 LA - Informational Texts: Student #1 shows a clear
Features and Comprehension grasp of the textual elements
Content: Engaging designed to aid
with informational comprehension but may
texts to identify key benefit from targeted
features such as activities that highlight the
headings, captions, importance of non-textual
and glossaries, and information in understanding
understanding their content. Could incorporating
purpose. a scavenger hunt through
Strengths: various informational texts,
Successfully identifies focusing specifically on
most features in texts captions and diagrams, help
and explains their emphasize their value?
purpose with minimal Additionally, modeling how
prompting. to integrate this information
Weaknesses: into notes or summaries
Sometimes overlooks could reinforce their utility.
captions and
diagrams, focusing
mainly on the main
text.
3/18 Science - The Water Cycle While conceptual knowledge
Content: Exploring of the water cycle is strong,
the stages of the water applying this understanding
cycle, including to broader environmental
evaporation, concepts poses a challenge.
condensation, Interactive activities that
precipitation, and simulate the water cycle's
collection. effects, such as creating a
Strengths: mini-ecosystem or using
Demonstrates digital simulations, could
understanding of each provide concrete examples of
stage through verbal these impacts. Encouraging
explanation and questions and reflections in a
sequence activities. science journal after these
Weaknesses: Has activities may help deepen
difficulty connecting understanding.
the water cycle's
impact on weather and
climate in discussions.
Student 2 3/18 LA - Informational Texts: Student #2's enthusiasm for
Features and Comprehension new vocabulary is a strength
Content: Learning to that can be leveraged to
navigate and improve comprehension of
comprehend dense informational texts.
informational texts by Pairing glossary work with
identifying text summarization practice,
features. perhaps starting with
Strengths: Shows keen summarizing single
interest in using paragraphs before moving to
glossaries to larger sections, could build
understand new this skill. Peer teaching
vocabulary. sessions, where students
Weaknesses: Struggles explain newly learned words
to summarize main and concepts to each other,
ideas from sections might also reinforce
with dense comprehension and
information. summarization abilities.
3/18 Science - The Water Cycle Student #2’s ability to
Content: Investigating engage with and understand
how water moves the water cycle through
through its cycle, using models suggests a strong
models and diagrams visual learning preference.
to aid understanding. Enhancing verbal
Strengths: Excels in explanations with visual
hands-on model supports, such as cue cards
creation and can or diagrams they can
accurately label each reference during
stage of the cycle. explanations, might boost
Weaknesses: Less confidence and clarity.
confident in explaining Additionally, incorporating
the process verbally storytelling elements, where
without visual aids. students narrate the journey
of a water droplet through
the cycle, could offer a
creative approach to
verbalizing their
understanding.
Student 1 3/27 LA - Narrative Writing: Student #1's creativity and
Crafting Stories ability to initiate stories are
Content: Writing commendable. Introducing
narratives that include structured storyboards or
a clear beginning, graphic organizers might
middle, and end, with help plan out narratives more
emphasis on character completely, ensuring a more
development and plot satisfying conclusion. Peer
structure. review sessions focusing
Strengths: Shows specifically on story endings
creative ideas for could also provide valuable
stories and can start feedback and encourage
with engaging more thought-out
beginnings. conclusions.
Weaknesses: Endings
tend to be abrupt or
lack resolution,
indicating difficulty
with concluding
narratives effectively.
3/27 Science - Habitats and While Student #1 can
Ecosystems identify and categorize
Content: Exploring aspects of habitats and
various habitats and ecosystems, applying the
ecosystems, deeper concept of
understanding the interdependence requires
interdependence of further exploration. Using
organisms within real-life examples or
them. simulations that demonstrate
Strengths: Accurately how changes in one part of
identifies different an ecosystem affect others
habitats and the could clarify this concept.
organisms that live in Group projects focusing on
them. creating and presenting on a
Weaknesses: Struggles specific ecosystem might
with explaining the also encourage deeper
concept of understanding and
interdependence collaborative learning.
within ecosystems.
Student 2 3/27 LA - Narrative Writing: Student #2’s strength lies in
Crafting Stories their creativity and character
Content: Students are development. Introducing
tasked with developing mini-lessons on plot
their own short stories, development and pacing
focusing on narrative could help enhance
structure and creative storytelling skills.
expression. Encouraging the use of
Strengths: Vibrant detailed planning before
imagination evident in writing, perhaps through
story ideas; able to outlining or mapping key
develop complex plot points, might also aid in
characters. achieving a more balanced
Weaknesses: Struggles narrative pace. Writing
with pacing, often workshops where students
rushing through the can share and receive
story, which can lead feedback on their story drafts
to underdeveloped could further refine their
plots. narrative skills.
3/27 Science - Habitats and Student #2's enthusiasm for
Ecosystems ecosystems is a great
Content: Investigating foundation for deeper
the characteristics of learning. Enhancing
various ecosystems accuracy and understanding
and the concept of might involve more targeted
biodiversity. research assignments where
Strengths: students can explore one
Enthusiastically ecosystem in depth. This
participates in could be coupled with
discussions about creative presentation
different ecosystems formats, such as digital
and their importance. slideshows or posters,
Weaknesses: allowing students to
Occasionally, factual consolidate and accurately
inaccuracies creep into share their findings.
oral presentations, Incorporating peer teaching
suggesting some elements, where students
confusion or explain their ecosystem to
misunderstanding. classmates, could also
reinforce learning and ensure
comprehension.
You might also like
- Sample Lesson Plan Illustrating One of The Four Major Skills For Communication: Reading 5 or 6Document3 pagesSample Lesson Plan Illustrating One of The Four Major Skills For Communication: Reading 5 or 6Laikha ColloNo ratings yet
- Map of The Book: 1 PlacesDocument4 pagesMap of The Book: 1 Placesนิธิกุล ศิลาวงศ์No ratings yet
- G10-01 Reflexive and Intensive PronounsDocument4 pagesG10-01 Reflexive and Intensive PronounsOliver Dizon0% (1)
- List The Full Standard With Its NumberDocument5 pagesList The Full Standard With Its Numberapi-345483624No ratings yet
- English Lesson Plan Form 3: at The End of The Lesson, Pupils Should Be Able ToDocument2 pagesEnglish Lesson Plan Form 3: at The End of The Lesson, Pupils Should Be Able ToAzah SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Dll-Demo Teaching Grade 5 EnglishDocument7 pagesDll-Demo Teaching Grade 5 EnglishCarlo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Grade5 Eng Reading - Catch Up FridayDocument4 pagesGrade5 Eng Reading - Catch Up FridayedelbertoNo ratings yet
- Content Learning Objectives Activities Skills and Subskills: Unit 9Document2 pagesContent Learning Objectives Activities Skills and Subskills: Unit 9robert martinezNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Final Lesson Plan 3Document2 pagesUnit Plan Final Lesson Plan 3api-407382996No ratings yet
- 2024 Week2Document6 pages2024 Week2Mi ChellNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Lesson 27Document2 pagesForm 3 Lesson 27GURU DATA SMK TUANKU ABDUL RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Mini Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesMini Lesson Planapi-347962298No ratings yet
- Literacy Unit Summary PlanDocument2 pagesLiteracy Unit Summary PlanEwoirNo ratings yet
- Pre Lesson Pupils List As Many Words Related To Relationship That They Have Learnt in The Previous Lesson in Groups (Using I-Think Map Drawn On Mini Whiteboard) Pupils Share Their AnswersDocument4 pagesPre Lesson Pupils List As Many Words Related To Relationship That They Have Learnt in The Previous Lesson in Groups (Using I-Think Map Drawn On Mini Whiteboard) Pupils Share Their AnswersGURU DATA SMK TUANKU ABDUL RAHMANNo ratings yet
- OSE Lesson Share Dec 2017Document3 pagesOSE Lesson Share Dec 2017Filiberto ColamoreaNo ratings yet
- Oup 7.dise - Ges.evaDocument8 pagesOup 7.dise - Ges.eva- Angy OrdoñezNo ratings yet
- Teaching InternshipDocument11 pagesTeaching InternshipJohn Mark CubarNo ratings yet
- Educ104 ActivityDocument1 pageEduc104 ActivityLimuel PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Interactions: Listening and SpeakingDocument17 pagesInteractions: Listening and Speakingalfadilaltahir119No ratings yet
- Auditory HandicapsDocument8 pagesAuditory Handicapsloumelyn100% (1)
- High School Department Sitio Tanag, Barangay San Jose, Antipolo CityDocument3 pagesHigh School Department Sitio Tanag, Barangay San Jose, Antipolo CityOliver DizonNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Lesson 24Document2 pagesForm 3 Lesson 24Sharizawati SalimNo ratings yet
- Octavo Ingles 2do ParcialDocument6 pagesOctavo Ingles 2do ParcialPamela MabelNo ratings yet
- Unit of WorkDocument15 pagesUnit of Workapi-358178333No ratings yet
- (Weeklong Daily Lesson Log) : Als ReferenceDocument5 pages(Weeklong Daily Lesson Log) : Als ReferenceMary Joy Lucob Tangbawan50% (2)
- Lesson 29 ReadingDocument2 pagesLesson 29 ReadingABDUL ALIFNo ratings yet
- WLL ALS LS1 Q4 Week 1-3listening & SpeakingDocument7 pagesWLL ALS LS1 Q4 Week 1-3listening & SpeakingRJ Baniqued100% (1)
- DLL (Babae Karapatan BLP1)Document4 pagesDLL (Babae Karapatan BLP1)Mary Joyce AriemNo ratings yet
- Three Lesson PortfolioDocument8 pagesThree Lesson Portfolioapi-645797970No ratings yet
- Mapa Mental Efl SupplementaryDocument1 pageMapa Mental Efl SupplementarySantiago JarrinNo ratings yet
- Ngoc - Ga 10 TD U4Document37 pagesNgoc - Ga 10 TD U4Thảo DaisyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Media Resource 2Document4 pagesLesson Plan Media Resource 2Hawa Aziah Binti AzmanNo ratings yet
- Cee C1 RB TB R3Document16 pagesCee C1 RB TB R3Javier AmateNo ratings yet
- 10 Gorgons Head FirstDocument2 pages10 Gorgons Head Firstsci Pantallano100% (1)
- Sow Form 4-2019Document7 pagesSow Form 4-2019mmustasariNo ratings yet
- WLP Life SKills Q1 Module 2session 1 and 2 Interpersonal CommunicationDocument8 pagesWLP Life SKills Q1 Module 2session 1 and 2 Interpersonal CommunicationPridas GidNo ratings yet
- RPT Eng Form 3 2018Document16 pagesRPT Eng Form 3 2018nuraziemahjoibiNo ratings yet
- Health and Environment: Exam Close-UpDocument2 pagesHealth and Environment: Exam Close-UpNORMAIZAN BINTI KHARIS MoeNo ratings yet
- Review of Simple Present and WH QuestionsDocument3 pagesReview of Simple Present and WH QuestionsAnonymous SwA03GdnNo ratings yet
- English LP Wk6 3.2 (Pyp3)Document6 pagesEnglish LP Wk6 3.2 (Pyp3)princess27SNo ratings yet
- SLOs For Learners ADocument5 pagesSLOs For Learners Ashabana yousufNo ratings yet
- Tercero Bachillerato Ingles 2do ParcialDocument6 pagesTercero Bachillerato Ingles 2do ParcialPamela MabelNo ratings yet
- Group 9: Listening & Speaking Skills (English Form 1)Document4 pagesGroup 9: Listening & Speaking Skills (English Form 1)Zolyn FalinyNo ratings yet
- To The Student: Level 1Document5 pagesTo The Student: Level 1Daniela Gómez AriasNo ratings yet
- Exam MethodologicalDocument21 pagesExam MethodologicalNuraiymNo ratings yet
- Minggu 9 ERPHDocument12 pagesMinggu 9 ERPHChian Yik100% (1)
- Educ 302 303 Lesson Plan Macbeth Act 2Document3 pagesEduc 302 303 Lesson Plan Macbeth Act 2api-381233967No ratings yet
- OC11.2 Functions of Communication "How Can I Tell You About It"Document6 pagesOC11.2 Functions of Communication "How Can I Tell You About It"Charley Vill CredoNo ratings yet
- Structure of English SyllabusDocument6 pagesStructure of English SyllabusJacqueline G. BantonNo ratings yet
- DLL - MTB 3 - Q4 - W2Document3 pagesDLL - MTB 3 - Q4 - W2Arriane Sumile JimenezNo ratings yet
- Personal, Relationalships, AppearanceDocument8 pagesPersonal, Relationalships, Appearancenigel noronhaNo ratings yet
- Annual Program Happy Campers 2Document9 pagesAnnual Program Happy Campers 2Josip Palmarez OrdoñezNo ratings yet
- Final Lesson Plan 4Document3 pagesFinal Lesson Plan 4api-348035181No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 22Document33 pagesLesson Plan 22rydelanderson3No ratings yet
- Overview - Unit PlanDocument9 pagesOverview - Unit Planapi-341972606No ratings yet
- Curriculum Map in English 7Document14 pagesCurriculum Map in English 7elaine marieNo ratings yet
- Grade: 11-ABM, HUMSS and GAS No. of Hours: at Least 80 Hours Subject Title: Oral Communication Pre-Requisite: Course DescriptionDocument4 pagesGrade: 11-ABM, HUMSS and GAS No. of Hours: at Least 80 Hours Subject Title: Oral Communication Pre-Requisite: Course DescriptionEmong DodouNo ratings yet
- Outcomes From Alberta Program of Studies: Prior To LessonDocument5 pagesOutcomes From Alberta Program of Studies: Prior To Lessonapi-297100127No ratings yet
- Unit Learning Plan: Notre Dame of Masiag, IncDocument21 pagesUnit Learning Plan: Notre Dame of Masiag, IncThelma LanadoNo ratings yet
- Grammar Practice Simplified: Guided Practice in Basic Skills (Book A, Grades 2-3): Nouns, Verbs, Capital Letters, Periods, Question Marks, and MoreFrom EverandGrammar Practice Simplified: Guided Practice in Basic Skills (Book A, Grades 2-3): Nouns, Verbs, Capital Letters, Periods, Question Marks, and MoreNo ratings yet
- DepEd Form 137 EDocument8 pagesDepEd Form 137 EQueenieRoseB.FloresNo ratings yet
- The Study of Surah Yaseen Lesson 10Document14 pagesThe Study of Surah Yaseen Lesson 10Redbridge Islamic Centre100% (1)
- Master Thesis in LiteratureDocument5 pagesMaster Thesis in Literaturegja8e2sv100% (2)
- UMEI 006-0101 English Pronunciation Spring 2021Document6 pagesUMEI 006-0101 English Pronunciation Spring 2021akibNo ratings yet
- 30 Travel Careers E-BookDocument105 pages30 Travel Careers E-BookRalea SorinNo ratings yet
- Bathinda Edition BTI 24 July 2021 Page 13Document1 pageBathinda Edition BTI 24 July 2021 Page 13mannaviiNo ratings yet
- Resume (Robyne)Document4 pagesResume (Robyne)api-279408086No ratings yet
- RA 7877 - Anti-Sexual Harassment Act of 1995Document5 pagesRA 7877 - Anti-Sexual Harassment Act of 1995Anonymous KgPX1oCfrNo ratings yet
- Classroom Language Vocabulary Exercises Fun Activities Games Oneonone Activities Picture D - 72621Document2 pagesClassroom Language Vocabulary Exercises Fun Activities Games Oneonone Activities Picture D - 72621Gustavo Chuco100% (1)
- ConclusionDocument2 pagesConclusionParimalar Rajindran83% (6)
- Lingüística Aplicada - ApuntesDocument30 pagesLingüística Aplicada - ApuntesJose ALCONCHEL IRANZONo ratings yet
- Terminal Report of EnrollmentDocument4 pagesTerminal Report of EnrollmentJohn Khevin Catimbang GambalNo ratings yet
- Management Trainee Officer (MTO) - The Premier Bank LimitedDocument1 pageManagement Trainee Officer (MTO) - The Premier Bank Limitedsunflower_29960% (1)
- English GlobalizationDocument7 pagesEnglish Globalizationdautgh0% (1)
- (@bohring Bot) 2024 JEE MAIN PHASE I ALL INDIA (@HeyitsyashXD)Document2 pages(@bohring Bot) 2024 JEE MAIN PHASE I ALL INDIA (@HeyitsyashXD)mandaarapucollege123No ratings yet
- Dr. Ramon de Santos National High SchoolDocument19 pagesDr. Ramon de Santos National High SchoolJohn Carlo Valdez100% (1)
- Professional Regulation Commission: Address: SchoolDocument14 pagesProfessional Regulation Commission: Address: SchoolPhilBoardResultsNo ratings yet
- TARGETcorporate - Responsibility - Report 2017Document84 pagesTARGETcorporate - Responsibility - Report 2017Stephanie QuirozNo ratings yet
- GundaniDocument12 pagesGundaniSean GutsaNo ratings yet
- Czarniaswka Social Science ResearchDocument15 pagesCzarniaswka Social Science ResearchhenricbeneschNo ratings yet
- Introducing Sustainable Development Topics Into Computer Science Education: Design and Evaluation of The Eco Jsity GameDocument17 pagesIntroducing Sustainable Development Topics Into Computer Science Education: Design and Evaluation of The Eco Jsity GameHarsh ThakranNo ratings yet
- Vds - 2132en Aproval of Installers of Fire Extinguishing SystemsDocument44 pagesVds - 2132en Aproval of Installers of Fire Extinguishing SystemsCristianLeotescu100% (2)
- Ebook Transformations Women Gender and Psychology PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Transformations Women Gender and Psychology PDF Full Chapter PDFdonald.winkle699100% (26)
- Adult LearningDocument11 pagesAdult Learninghiral mistry100% (2)
- Vapa ActivitiesDocument4 pagesVapa Activitiesapi-402294853No ratings yet
- 4a's Lesson Plan (Resistor Color Coding)Document4 pages4a's Lesson Plan (Resistor Color Coding)Jessa Bahi-an67% (3)
- Case Analysis - Ita 2 - Group 7Document5 pagesCase Analysis - Ita 2 - Group 7Kelly maria RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Business PlanningDocument22 pagesBenefits of Business PlanningSun Shine OalnacarasNo ratings yet
- Hangzhou, China HandbookDocument24 pagesHangzhou, China HandbookterabajtNo ratings yet
- Recto Memorial Natioanl High SchoolDocument5 pagesRecto Memorial Natioanl High SchoolZander Catamio GuerreroNo ratings yet