Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Spectral Noise Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Yovaraj KarunakaranCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Spectral Noise Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Yovaraj KarunakaranCopyright:
Available Formats
Spectral Noise Logging cheat sheet
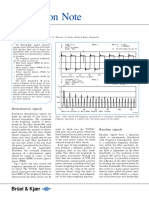
1. Objectives It is common to record a continuous temperature pass 6.2 Noise/cable synchronization
A passive acoustic logging technique that listens to during the RIH for quantitative interpretation, and to If the loaded noise data does not contain depth
the sounds generated by fluid movement. Based on locate zones of interest for station stops. information (only time), Emeraude will prompt the
the sound’s frequency, amplitude and depth, the Once TD is reached, record 30 sec stations with a load of cable depth.
analyst can use noise logs to evaluate: spacing given by the job’s objectives. Reduce the Once both files are loaded, use the Time shift
- Flow through perforations, SSDs, gas lift. spacing between stations for intervals of interest. option to synchronize noise and depth.
- Leaks in the tubulars, not limited to the inner string
- Flow through cement (channelling, microannulus) 6.3 Versus depth spectrogram extraction
- Sand movement This option extracts a single representative
- Plug and packer sealing integrity spectrum from each station. This can be
- Reservoir thickness and sound characteristics based on the Mean or Median along the
station, or an instantaneous ‘At time’ spectrum.
The beginning and end of
the station may include
road noise. Use the From-
Having more than one noise tool in the toolstring helps To columns to exclude
reducing the number of stations. these from the spectrum.
During the job the well must be operated in such a way 7. Results
that the noise to be detected (i.e. channel, leak, etc.) The result of the spectral noise tool processing is one
is active. This requires a ΔP to generate turbulence. The or more versus depth spectrogram, depending on the
2. Noise tools flowing conditions must be designed to maximize the number of tools and extractions. The header of the
The sound is measured using one or more sounds production, for example: spectrogram shows the frequency bins, which can be
piezoelectric hydrophone, which converts acoustic - Well flowing (controlled drawdown) converted to actual frequencies by entering the
energy to an electric signal. Single hydrophone tools - Bleeding one or more annular Sample index (right-click on each track):
are ~0.5 m long, while 2 hydrophone tools are ~ 0.8 - Injecting through tubing
m long. Multiple hydrophones allows to have a
frequency-dependent equalization, with different 5. Data loading
gains for high and low frequency sounds. Load OH logs from for depth correlation and
to complement the analysis. Define
(optional).
It is recommended to start from a single time-driven
file containing all stations and short intervals of cable
movement in between. Use to load raw noise The following statistics are automatically computed:
The sound waves are digitalized by recording points data in .las, .csv or .dlis. Noise and cable data can be - Sound energy: the energy of a spectrum is
at evenly-spaced times and representing each point merged once loaded in Emeraude. If the data is not calculated as:
with a number of bits. The sampling rate determines 𝑁−1
the maximum frequency that the tool can measure identified, add the root mnemonic in .
𝐸𝑛𝑒𝑟𝑔𝑦 = ∑|𝑋[𝑘]|2
(Nyquist theorem). Commercial tools measure up to If the noise data has been processed elsewhere and is
𝑘=0
12.8, 60 and 656 kHz. already versus depth, use the option. Emeraude presents Normalized Energy, with respect
Noise logging interpretation is based of frequency to the maximum energy, to avoid units’ issues.
structure of the sound. A Fourier transform computes Upon loading the stationary periods
the amplitude for n frequencies. are automatically identified based - Spectral centroid: This is the centre of mass of a
on cable speed/depth. Stations can spectral distribution and is a typical way to
be created and edited. characterize the pitch of a sound:
∑𝑁−1
𝑘=0 𝑘 ∗ 𝑋[𝑘]
𝐶𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑟𝑜𝑖𝑑 =
The spectral data consists of hundreds of amplitude ∑𝑁−1
𝑘=0 𝑋[𝑘]
curves for different frequencies (upper track). This is
typically displayed as a spectrogram, showing the From the Well Integrity tab it is possible
various frequency bands with increasing index from to access to the raw versus time data
bottom to top, and the amplitude as colour. and do new extractions with different
setting (i.e. filters). Access the versus
The tool output consists of multiple amplitude curves depth spectrograms to export data and
for n frequencies. Some tools also record the full display frequencies versus depth.
waveform, although its storage and transmission are
often limited by size and bandwidth limitations. 7.1 Merging spectrograms
Sound is typically quantified using Sound Pressure For toolstrings containing more than one noise tool,
Level, calculated as 𝑆𝑃𝐿 (𝑑𝐵) = 20 log(𝑃𝑎𝑣𝑔 ). As the
𝑃 or jobs recorded in separate files, the spectrograms
𝑟𝑒𝑓 can be merged into a
piezoelectric measures a voltage, a calibration factor
𝑚𝑉 6. Processing single one using .
is required ( ).
𝑃𝑎 All Noise processing options are available from the Well Each spectrogram must
contain same number of
3. Toolstring Integrity tab . The steps typically include:
elements.
6.1 Stations identification
- A single spectral noise tool may Stations are identified based on periods of constant
8. Noise interpretation
suffice for short intervals. depth or zero cable speed. Stations are displayed in a
Sounds are pressure waves
- 2 spectral noise tools with 2 or 3 dedicated track. Spurious cable movement can lead to
travelling through media.
meter offset help to reduce the breaks in the station definition (i.e. between S6 and S7
Downhole sounds are generated
number of station stops (see below). Click on the station to delete or interactively
mainly by turbulence, that creates
section 4). edit it.
local pressure fluctuations.
- Temperature is noise’s best
friend, as both can localize fluid
The characteristic sound power of a source is given
movement inside, through, and
by the pressure drops through the restriction and the
behind the inner barrier. rate. Large ΔP*Q generate high noise amplitudes.
- GR, CCL for depth control.
- Memory, battery/telemetry,
The spectrum frequency peak is related to the
weight bars, etc.
kinematic viscosity (𝜈) and the characteristic scale of
- For leak detection and reservoir
turbulence (l) by 𝑓𝑚𝑎𝑥 ~ 𝑙𝜈2 . The smaller the conduit for
characterization jobs, consider
flowmeters and fluid identification fluid flow, the larger the frequency. Wellbore fluid
If a station was not automatically identified, movement produces noises up to 1 kHz. Flow through
tools. use the Create option to interactively define it restrictions like perforations, SSD, GLV, etc. produce
where necessary. 1-3 kHz noises. Cement and formation noises range
4. Operations
In continuous passes the toolstring and cable scratch from 3kHz to +10 kHz.
Use this option to manually edit and label
the inners surface of the pipe generating high- stations. Use
amplitude ‘road noise’. This is uncharacteristic of the Sound that propagates spherically follows:
𝑊
fluid movement and cannot be used for diagnosis Reset stations 𝐼=
4 𝜋 𝑟2
purposes. Therefore, noise logging operations consist to re-launch the stations Sound attenuates 6 dB as the distance doubles. But
of several stationary data recordings along the definition and use also as it goes through walls it will reflect, refract,
interval of interest. constraints on cable diffract, etc. Low frequencies are transmitted more
speed, depth and duration. easily through barriers than high frequencies.
You might also like
- Noise Source Identification Techniques Simple To Advanced ApplicationsDocument6 pagesNoise Source Identification Techniques Simple To Advanced ApplicationscowokNo ratings yet
- Ecg Noise Modelling in Time-Frequency Domain Using The Polynomial ExtrapolationDocument2 pagesEcg Noise Modelling in Time-Frequency Domain Using The Polynomial ExtrapolationVarunSingh_gayaNo ratings yet
- BME4322 Week3-6 UltrasoundHardware 31032022Document49 pagesBME4322 Week3-6 UltrasoundHardware 31032022--No ratings yet
- Application Note: Choose Your Units!Document2 pagesApplication Note: Choose Your Units!jhon vargasNo ratings yet
- Using NS STSF To Investigate Transient Phenomena in Automotive ApplicationsDocument12 pagesUsing NS STSF To Investigate Transient Phenomena in Automotive ApplicationsAndysNo ratings yet
- Icslp2004 AsaDocument5 pagesIcslp2004 AsaSamuel Sam NgNo ratings yet
- Review Analysis of Real World Noise: Dheeraj Joshi, Prashant MoudDocument6 pagesReview Analysis of Real World Noise: Dheeraj Joshi, Prashant MouderpublicationNo ratings yet
- How To Measure LDO NoiseDocument9 pagesHow To Measure LDO Noisesanjeevsoni64No ratings yet
- Spectral Density Estimation - WikipediaDocument9 pagesSpectral Density Estimation - WikipediaEn Iyisi İnşaat MühendisiNo ratings yet
- Identification of Underwater Acoustic NoDocument6 pagesIdentification of Underwater Acoustic Nonhan1999.ntNo ratings yet
- Readme Noise PDFDocument3 pagesReadme Noise PDFjalmeida88No ratings yet
- Vibrato Extraction and Parameterization PDFDocument5 pagesVibrato Extraction and Parameterization PDFGreyce OrnelasNo ratings yet
- Maximum Likelihood Estimates of A Spread-Spectrum Source Position Using A Tetrahedral Ultra-Short Baseline ArrayDocument5 pagesMaximum Likelihood Estimates of A Spread-Spectrum Source Position Using A Tetrahedral Ultra-Short Baseline ArrayXiaofengFanNo ratings yet
- Standard Practice For Measuring Thickness by Manual Ultrasonic Pulse-Echo Contact MethodDocument7 pagesStandard Practice For Measuring Thickness by Manual Ultrasonic Pulse-Echo Contact MethodRenzo BellotaNo ratings yet
- Antenna CH6Document30 pagesAntenna CH6Abraham GadissaNo ratings yet
- Input Impedance Measurements of Conical Acoustic Systems Using The Two - Microphone TechniqueDocument7 pagesInput Impedance Measurements of Conical Acoustic Systems Using The Two - Microphone TechniqueGermán GalarzaNo ratings yet
- Quad 1Document13 pagesQuad 1prakhartripathi826No ratings yet
- Vibration Engineering Reviewer FNDocument12 pagesVibration Engineering Reviewer FNBea Daniella CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Frequency Domain Techniques For Operational Modal AnalysisDocument10 pagesFrequency Domain Techniques For Operational Modal AnalysisAhmed BaheiNo ratings yet
- Elements Can Be Pulsed IndividuallyDocument31 pagesElements Can Be Pulsed IndividuallyjoNo ratings yet
- ME124 Mechanical Engineering Laboratory III Experiment #2: Linear and Nonlinear Flexural Vibrations of A BeamDocument4 pagesME124 Mechanical Engineering Laboratory III Experiment #2: Linear and Nonlinear Flexural Vibrations of A Beamtolomeo10No ratings yet
- Standard Practice For Measuring Thickness by Manual Ultrasonic Pulse-Echo Contact MethodDocument8 pagesStandard Practice For Measuring Thickness by Manual Ultrasonic Pulse-Echo Contact MethodGabriel IbarraNo ratings yet
- Understanding Phase Noise Measurement Techniques - WP - en - 3683 5651 52 - v0100Document12 pagesUnderstanding Phase Noise Measurement Techniques - WP - en - 3683 5651 52 - v0100Robert SavulescuNo ratings yet
- Eurospeech2001 Wavel PDFDocument4 pagesEurospeech2001 Wavel PDFHaripriya RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Transient Detection in Speech and Audio SignalsDocument8 pagesTransient Detection in Speech and Audio SignalsThanuja adepuNo ratings yet
- 0303 BateDocument13 pages0303 BateGilbertoAndresDuarteNo ratings yet
- Spectrum Analyzer PDFDocument18 pagesSpectrum Analyzer PDFAgus SantosaNo ratings yet
- 1KW-73835-0 Keithley 4200A-SCS 1f Current Noise Application Note 083021Document14 pages1KW-73835-0 Keithley 4200A-SCS 1f Current Noise Application Note 083021Dheeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- NT Acou 059 - Rooms - Reverberation Time - Interrupted Noise Precision Method - Nordtest MethodDocument11 pagesNT Acou 059 - Rooms - Reverberation Time - Interrupted Noise Precision Method - Nordtest MethodEMA54No ratings yet
- Lock in AmplifierDocument4 pagesLock in AmplifierMehdi NaderiNo ratings yet
- RevSciInstrum 83 084704Document7 pagesRevSciInstrum 83 084704Data KiswaraNo ratings yet
- Noise Attenuation TechniquesDocument2 pagesNoise Attenuation TechniquesadobiNo ratings yet
- The Application of Spread Spectrum Signaling Techniques To Underwater Acoustic NavigationDocument7 pagesThe Application of Spread Spectrum Signaling Techniques To Underwater Acoustic NavigationXiaofengFanNo ratings yet
- Eco Localization by The Analysis of The Characteristics of The Reflected Waves in Audible FrequenciesDocument6 pagesEco Localization by The Analysis of The Characteristics of The Reflected Waves in Audible FrequenciesJosue Manuel Pareja ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Ac01 AcousticsDocument15 pagesAc01 AcousticsNjabulo JoshuaNo ratings yet
- 03 PDFDocument7 pages03 PDFpkrsuresh2013No ratings yet
- Ultrasound Analog Electronics Primer: by Bill OdomDocument3 pagesUltrasound Analog Electronics Primer: by Bill OdomMaha SoeNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0003682X17300397 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0003682X17300397 MainRohit singhNo ratings yet
- Mesosphere Stratosphere Troposphere (MST) Radar Signal Using DWT With OGSDocument4 pagesMesosphere Stratosphere Troposphere (MST) Radar Signal Using DWT With OGSSureshbabu PNo ratings yet
- Application of Pulse Compression Techniques To Monostatic Doppler SodarDocument4 pagesApplication of Pulse Compression Techniques To Monostatic Doppler SodarAnonymous BrUMhCjbiBNo ratings yet
- Building and Room Acoustics Measurements With Sine-Sweep TechniqueDocument2 pagesBuilding and Room Acoustics Measurements With Sine-Sweep Techniquejabeur rahmaNo ratings yet
- A Simple But Efficient Real-Time Voice Activity Detection AlgorithmDocument5 pagesA Simple But Efficient Real-Time Voice Activity Detection AlgorithmSami FarsiNo ratings yet
- Noise Reduction For Periodic Signals Using High-Resolution Frequency AnalysisDocument19 pagesNoise Reduction For Periodic Signals Using High-Resolution Frequency Analysismahdi cheginiNo ratings yet
- Increasing Handset Performance Using True Polarization DiversityDocument4 pagesIncreasing Handset Performance Using True Polarization Diversitypatrick hanNo ratings yet
- Chen1993 tecnicaPulso-ecoBandaAnchaDocument5 pagesChen1993 tecnicaPulso-ecoBandaAnchaFabian Torres RoblesNo ratings yet
- TIM Square-Sine Inter Modulation MeasuringDocument8 pagesTIM Square-Sine Inter Modulation MeasuringGerardo Angel GentileNo ratings yet
- Meteorological Applications - 2006 - Ito - Design and Performance of An Acoustic Antenna For A Phased Array Doppler SodarDocument8 pagesMeteorological Applications - 2006 - Ito - Design and Performance of An Acoustic Antenna For A Phased Array Doppler SodarMetrach AbdrazakNo ratings yet
- PosterDocument1 pagePoster07vnkls2qNo ratings yet
- Separation of Harmonic Sound Sources Using Sinusoidal ModelingDocument4 pagesSeparation of Harmonic Sound Sources Using Sinusoidal ModelingRodrigo FilhoNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Time-Domain AnalysisDocument4 pagesSampling and Time-Domain Analysisshoaibsaleem001No ratings yet
- Time Series Well LoggingDocument8 pagesTime Series Well LoggingAryan KhanNo ratings yet
- Asme Se 797 (2001)Document8 pagesAsme Se 797 (2001)Brad ReedNo ratings yet
- Power Spectrum Estimation-LabSheetDocument3 pagesPower Spectrum Estimation-LabSheetJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- A Simple But Efficient Real-Time Voice Activity Detection AlgorithmDocument8 pagesA Simple But Efficient Real-Time Voice Activity Detection AlgorithmHarshal PatilNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Seismic Data ProcessingDocument19 pagesChapter-6 Seismic Data Processingtarunag72801No ratings yet
- 2014 - Parker Et Al - Distributed Acoustic SensingDocument9 pages2014 - Parker Et Al - Distributed Acoustic SensingIpalibo GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Noise Figure System1Document8 pagesNoise Figure System1Farhan IuNo ratings yet
- Measuring Ultrasonic Velocity in Materials: Standard Practice ForDocument13 pagesMeasuring Ultrasonic Velocity in Materials: Standard Practice Fortanzil10No ratings yet
- Iwcf ExamsDocument133 pagesIwcf ExamsMoonking 03100% (1)
- MFC in Emeraude Cheat SheetDocument1 pageMFC in Emeraude Cheat SheetYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Free EbookDocument12 pagesFree EbookAnis FarazeeraNo ratings yet
- Slickline BasicsDocument86 pagesSlickline BasicsAmiromaan100% (7)
- GRCCL Processing Data ProcedureDocument11 pagesGRCCL Processing Data ProcedureYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Wireline Logging EngineerDocument46 pagesWireline Logging EngineerYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- JPT November 2023Document108 pagesJPT November 2023Yovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Well InterventionDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Well InterventionYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Journal of Petroleum Technology June 2023Document98 pagesJournal of Petroleum Technology June 2023Yovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Well Integrity - 04 December 2012Document154 pagesIntroduction To Well Integrity - 04 December 2012n73686861No ratings yet
- Norsok Well IntegrityDocument162 pagesNorsok Well IntegrityAshish SethiNo ratings yet
- Slickline Tool ChartDocument3 pagesSlickline Tool ChartMohammed JabbarNo ratings yet
- FULL Course Presentation of Wireline ServicingDocument326 pagesFULL Course Presentation of Wireline ServicingYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Why Is Well Integrity ImportantDocument7 pagesWhy Is Well Integrity ImportantYovaraj Karunakaran100% (1)
- Sondex Continuous Flowmeter Jeweled CFJM SpecDocument1 pageSondex Continuous Flowmeter Jeweled CFJM SpecYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- IWCF Well Intervention SlidebookletDocument582 pagesIWCF Well Intervention SlidebookletYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Capwell and Capline PresentationDocument24 pagesCapwell and Capline PresentationYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- A Review On Sustained Casing PressureDocument62 pagesA Review On Sustained Casing PressureYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Evo-Trieve® EB0 Retrievable Straddle - HalliburtonDocument2 pagesEvo-Trieve® EB0 Retrievable Straddle - HalliburtonYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- B2B Professional Sales - Chapter 6 Sales Activities - QuizDocument13 pagesB2B Professional Sales - Chapter 6 Sales Activities - QuizYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Archer Modular TractorDocument2 pagesArcher Modular TractorYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Authorization Letter To Act On BehalfDocument1 pageAuthorization Letter To Act On BehalfYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Weatherford McMurry GLM - Gas Lift MandrelDocument25 pagesWeatherford McMurry GLM - Gas Lift MandrelYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Mercusys MR70X Router Setting For Maxis FiberDocument5 pagesMercusys MR70X Router Setting For Maxis FiberYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Petronas PTW Level 2 Assessment - Refresher - Answers - 2021Document5 pagesPetronas PTW Level 2 Assessment - Refresher - Answers - 2021Yovaraj Karunakaran61% (23)
- MechanicalCentralizersandDecentralizers PDFDocument1 pageMechanicalCentralizersandDecentralizers PDFYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- 2 Inch HD Releasable Spear, PetrolineDocument14 pages2 Inch HD Releasable Spear, PetrolineYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- 3 Ok-6 PDFDocument16 pages3 Ok-6 PDFYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Mandrels, Round, Machined Pocket Weatherford Gas Lift MandrelDocument2 pagesMandrels, Round, Machined Pocket Weatherford Gas Lift MandrelYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Weatherford Overshot - ReleasableDocument10 pagesWeatherford Overshot - ReleasableYovaraj KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- What Is Science?: Facts Collected For Reference and AnalysisDocument5 pagesWhat Is Science?: Facts Collected For Reference and AnalysisDavid LegkodukhNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Coulombs Law TemplateDocument4 pages7.2 Coulombs Law TemplateAyman HalimeNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced LevelDocument24 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced LevelGaming Core.No ratings yet
- 2.1 SVP Traceability Manual - Addendum - CMC - Report - V7 - 2018 - 10 - 17 - 1Document63 pages2.1 SVP Traceability Manual - Addendum - CMC - Report - V7 - 2018 - 10 - 17 - 1hyarub9No ratings yet
- TD261, A Td262.a Td263ab Td264.a Td265.a Td266.a Td271.a Td272.a Td273.a.b Td274.a TD275, A TD276, ADocument2 pagesTD261, A Td262.a Td263ab Td264.a Td265.a Td266.a Td271.a Td272.a Td273.a.b Td274.a TD275, A TD276, AZé Pontes DetCordNo ratings yet
- Reed's Vol 06 Basic Electrotechnology For Marine EngineersDocument570 pagesReed's Vol 06 Basic Electrotechnology For Marine EngineersXthesinos50% (2)
- Bridges, 3-Ammeter, 3-VoltmeterDocument10 pagesBridges, 3-Ammeter, 3-Voltmeterమారుతీ రామ్. ధరణీప్రగడ.వెం.సుNo ratings yet
- Practice Test: Gas LawsDocument2 pagesPractice Test: Gas LawsAthena AlvarezNo ratings yet
- CIPM MRA Appendix C Calibration and Measurement Capability (CMC) DeclarationsDocument31 pagesCIPM MRA Appendix C Calibration and Measurement Capability (CMC) DeclarationskarthickNo ratings yet
- DPP1Document1 pageDPP115 Kabir Sharma 10 HNo ratings yet
- Science8 q1 Mod3 Potential-And-kinetic-Energy v2Document23 pagesScience8 q1 Mod3 Potential-And-kinetic-Energy v2Keith Genesis Ruiz AglubaNo ratings yet
- 3qs008 Digital Brief AmatekDocument4 pages3qs008 Digital Brief AmatekPhong LeNo ratings yet
- PROJECTS (XII A Physics) FOR CBSE BOARD EXAMINATIONDocument2 pagesPROJECTS (XII A Physics) FOR CBSE BOARD EXAMINATIONsugesh kumarNo ratings yet
- CH 27Document83 pagesCH 27Stephanie Palomares LevitaNo ratings yet
- Pulleys Mark SchemeDocument35 pagesPulleys Mark SchemeAyra MujibNo ratings yet
- Amo MPM - Part 4Document64 pagesAmo MPM - Part 4TatsNo ratings yet
- LK-045-IDN (Temperature, Mass, Volume, Pressure, & Length)Document4 pagesLK-045-IDN (Temperature, Mass, Volume, Pressure, & Length)Aries SupiyantoNo ratings yet
- CH 09 PPT LectureDocument46 pagesCH 09 PPT LectureElizander GalasiNo ratings yet
- Modeling Heat EfficiencyDocument21 pagesModeling Heat EfficiencyAndres MarinNo ratings yet
- 12 KonsolDocument48 pages12 Konsolhilma firdausNo ratings yet
- Mnemonic Scheme For Thermodynamics: J.-C. ZhaoDocument3 pagesMnemonic Scheme For Thermodynamics: J.-C. ZhaoNisharNo ratings yet
- IB Physics SL/HL Study GuideDocument23 pagesIB Physics SL/HL Study GuidemimiNo ratings yet
- Physics XII CH 7 CASE STUDY Alternating CurrentDocument19 pagesPhysics XII CH 7 CASE STUDY Alternating CurrentNjan KL16么PorottaNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Direct and Inverse VariationsDocument26 pagesRD Sharma Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Direct and Inverse Variationsshreepuja558No ratings yet
- Calibration of LPG ProversDocument19 pagesCalibration of LPG ProversanafadoNo ratings yet
- Physics: Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument8 pagesPhysics: Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDevi KusnandarNo ratings yet
- Hotwire Anemometer: Product Datasheet Stock No: 193-8699Document3 pagesHotwire Anemometer: Product Datasheet Stock No: 193-8699Nordalilah Mohd SobriNo ratings yet
- B94-00-4740 Install Guide USDocument14 pagesB94-00-4740 Install Guide US200880956No ratings yet
- Water Pressure Calculator by Depth or Height MetricDocument6 pagesWater Pressure Calculator by Depth or Height MetricTanvir ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument51 pagesBasic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringJayniti Kumari100% (1)