Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewer Fundamental (Lecture)
Uploaded by
SaidinaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reviewer Fundamental (Lecture)
Uploaded by
SaidinaCopyright:
Available Formats
PRELIM REVIEWER Field of Nursing:
World Health Organization (WHO) – defined health as a Hospital or institutional nursing – employed by
state of complete physical chuchu hospital to perform nursing services.
Public health nursing or CHN – refers to the
American Nurses Association – defined health as a practice of nursing in the local, national health
dynamic state of being department.
Private duty or special duty nursing
Wellness – is a dynamic process that is ever changing.
Industrial or occupational health nursing – delivers
Dimension of Wellness: health and safety programs and services to
workers.
Physical – the ability to carry out daily tasks. Nursing education – teaching professional
Social – interact with people and the environment Military nursing – who serves the military
Emotional – ability to manage stress and express School nursing – responsible for the school’s
emotion activities
Intellectual – ability to learn and use information Clinic nursing – nurse acts as receptionist, answer
Spiritual – the belief in some force (nature, phone and chuchu
religion) Independent nursing practice – offer services
Occupational – ability to achieve a balance rather than expect client to seek their help.
between work and leisure time.
Environmental – ability to promote health Two Influential women in the field of nursing:
measures
Elizabeth Fry
Model of Health: -founded the protestant sisters of charity
Florence Nightingale
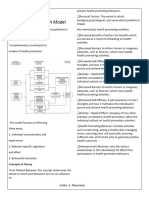
Clinical model – viewed as physiologic systems
Role performance model – ability to fulfil societal The 6 C’s of Caring:
roles.
Care
Adaptive model – creative process
Compassion
Eudemonistic model – comprehensive view of
Competence
health
Communication
Agent-host-environmental model
Courage
Health-illness continuum – measure person’s
perceived level of wellness. Commitment
Well – being – subjective perception of vitality (energy) Self – care – any deliberate activity that nurses do to provide
for their physical, mental well-being.
Disease – reduction of capacities of the normal life span
MODES OF COMMUNICATION:
Etiology – the causation of disease.
Verbal – the use of language to transfer
Levels of Health Care Facilities: information
Nonverbal – use of body language, gestures and
Primary level – are the rural health units, sub- facial expressions
centers Written – act of writing, typing, printing symbols
Secondary level – smaller, non-departmentalized like letters and numbers to convey information
hospital Visual – the act of using photographs, art, drawing
Tertiary level – highly technological and to convey information
sophisticated services offered
Therapeutic Communication – the face-to-face process of
Profession – an occupation that requires extensive interacting.
education
Phases of the Relationship:
Basic Nursing Principles:
Pre-interaction phase – begins before the nurse’s
Safety first contact with the patients.
Therapeutic effectiveness Introductory or Orientation phase – the nurse and
Comfort patient first meet.
Use of resources Working phase – therapeutic work is carried out
Good workmanship during this phase.
Individuality Termination phase – a time to exchange feelings
and memories.
Communication and nursing process
Rehabilitation – the process of restoring ill or injured
people to optimum and functional level of wellness.
You might also like
- Colinares Activity02Document7 pagesColinares Activity02hiraethNo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument4 pagesCommunity Health NursingAbmil Ching TinggalongNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theorists: Nursi NG Theor IstsDocument12 pagesNursing Theorists: Nursi NG Theor IstsBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Dorothea Elizabeth Orem: Self-Care TheoryDocument3 pagesDorothea Elizabeth Orem: Self-Care TheoryE.R.ONo ratings yet
- Dorothea Elizabeth Orem: Self-Care TheoryDocument3 pagesDorothea Elizabeth Orem: Self-Care TheoryE.R.ONo ratings yet
- Dorothea Elizabeth Orem: Self-Care TheoryDocument3 pagesDorothea Elizabeth Orem: Self-Care TheoryE.R.ONo ratings yet
- Concept of NursingDocument3 pagesConcept of NursingCaryl JabagatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theorist TemplateDocument5 pagesNursing Theorist Templatening ningNo ratings yet
- TheoristDocument2 pagesTheoristharutochoky8No ratings yet
- CA 2 - CHN Part 1Document46 pagesCA 2 - CHN Part 1LoraineNo ratings yet
- Funda Lec Midterm End ReviewerDocument39 pagesFunda Lec Midterm End ReviewerphoebeNo ratings yet
- Dorothea Orem: Self-Care TheoryDocument16 pagesDorothea Orem: Self-Care TheoryHazel LezahNo ratings yet
- Theory Matrix WorksheetDocument8 pagesTheory Matrix WorksheetCang Cang De ArcaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Framework of Nursing PracticeDocument3 pagesTheoretical Framework of Nursing Practiceanreilegarde100% (5)
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument18 pagesFundamentals of NursingRommel IsraelNo ratings yet
- Funda LecDocument20 pagesFunda LecJamie Annmari AmboyNo ratings yet
- TFN Midter-ExaminationDocument3 pagesTFN Midter-ExaminationalchriwNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Foundations Of: NursingDocument3 pagesTheoretical Foundations Of: NursingYejiNo ratings yet
- MetaparadigmsDocument2 pagesMetaparadigmsRed DinsonNo ratings yet
- Midterm and Final Exam TFNDocument6 pagesMidterm and Final Exam TFNalchriwNo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument31 pagesCommunity Health NursingVia LatrasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theories 3: Gladys C. Yares, RN RMDocument31 pagesNursing Theories 3: Gladys C. Yares, RN RMJan Oliver YaresNo ratings yet
- Banagen, Philip B. BSN1 - S6: Abraham MaslowDocument5 pagesBanagen, Philip B. BSN1 - S6: Abraham MaslowLegendXNo ratings yet
- Nursing TheoriesDocument67 pagesNursing TheoriesDrPreeti Thakur ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Local Non Nursing ModelsDocument3 pagesLocal Non Nursing ModelsFelica Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Peplaus Theory PresentationDocument17 pagesPeplaus Theory Presentationshannen kate acostaNo ratings yet
- TFN Reviewer Mid Term 1Document16 pagesTFN Reviewer Mid Term 1Eunice AlimenNo ratings yet
- Nursing TheoriesDocument271 pagesNursing TheoriesDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM97% (86)
- Chapter 1Document65 pagesChapter 1Richelle Glynisse Llarenas EstilongNo ratings yet
- Physiologic-Physical ModeDocument4 pagesPhysiologic-Physical ModeCelena LorenaNo ratings yet
- Theories TFNDocument8 pagesTheories TFNMichaella Mae LaurestaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theorists and Their Theories Compilation ReviewerDocument5 pagesNursing Theorists and Their Theories Compilation ReviewerJoshua Gabriel AntiqueraNo ratings yet
- Nursing: Health Care System ModelDocument24 pagesNursing: Health Care System ModelPinky TenshiNo ratings yet
- TFN FinalsDocument20 pagesTFN FinalsCHESKA LYKA ASILONo ratings yet
- Nursing TheoriesDocument203 pagesNursing TheoriesPriscilla Phebe PNo ratings yet
- PRELIMSDocument13 pagesPRELIMSJianne CaloNo ratings yet
- TFN Midterm ReviewerDocument5 pagesTFN Midterm ReviewerRenoa Blanche PerladoNo ratings yet
- Assisting Others in The Provision and Management of Self-Care To Maintain/improve Human Functioning at Home Level of Effectiveness."Document5 pagesAssisting Others in The Provision and Management of Self-Care To Maintain/improve Human Functioning at Home Level of Effectiveness."Phinkpig ShoPpeNo ratings yet
- TFN UstDocument81 pagesTFN UstTimi BCNo ratings yet
- Theories of NursingDocument8 pagesTheories of Nursing3amabelle arevaloNo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument23 pagesCommunity Health NursingMimi Vee100% (1)
- 1 Introduction To Mental Health and Psychiatric NursingDocument6 pages1 Introduction To Mental Health and Psychiatric NursingRose Lyn Camarista VelascoNo ratings yet
- TFN Reviewer MidtermDocument10 pagesTFN Reviewer Midtermashleydimaranan20No ratings yet
- N1R01A - Transes in Introduction To NursingDocument8 pagesN1R01A - Transes in Introduction To NursingMikhaella GwenckyNo ratings yet
- N1R01A - Transes in Introduction To NursingDocument8 pagesN1R01A - Transes in Introduction To NursingMikhaella GwenckyNo ratings yet
- 7.health and IllnessDocument7 pages7.health and IllnessTheresa Bread100% (1)
- Prelims Funda LabDocument42 pagesPrelims Funda LabCATHRYN MAE GAYLANNo ratings yet
- Context-Environment To Which Nursing Act Takes Place Content - Subject of Theory Process - Method by Which Nurse Acts in Nursing Theory NursingDocument22 pagesContext-Environment To Which Nursing Act Takes Place Content - Subject of Theory Process - Method by Which Nurse Acts in Nursing Theory NursingShyenNo ratings yet
- CHN Reviewer PrelimDocument19 pagesCHN Reviewer PrelimCher Ann RuilesNo ratings yet
- Prelim Reviewer HaDocument7 pagesPrelim Reviewer HaSaidinaNo ratings yet
- THE Nursing Theories: Submitted To: Mrs. Paula P. Leanillo Submitted By: Alexis Danielle G. Rosa BSN-1BDocument7 pagesTHE Nursing Theories: Submitted To: Mrs. Paula P. Leanillo Submitted By: Alexis Danielle G. Rosa BSN-1BThrecia RotaNo ratings yet
- Theorist Theory Application To Spiritual Care Florence Nightingale Joyce Travelbee Betty NeumanDocument4 pagesTheorist Theory Application To Spiritual Care Florence Nightingale Joyce Travelbee Betty NeumanJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- "Psychiatric Nurse of The Century" Health:: Interpersonal Conditions)Document6 pages"Psychiatric Nurse of The Century" Health:: Interpersonal Conditions)Kandy Anne Castillo AbuanNo ratings yet
- Nursing: An Art and A Science: "Nutricius" - That Nourishes, Fosters and ProtectsDocument3 pagesNursing: An Art and A Science: "Nutricius" - That Nourishes, Fosters and ProtectsMykristie Jho B. MendezNo ratings yet
- HA PrelimsDocument42 pagesHA Prelimsdizonernest10No ratings yet
- Stress, Emotions and Health - The Manual for Integrative ProfessionalsFrom EverandStress, Emotions and Health - The Manual for Integrative ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- I Know You Know: Integrating Traditional and Contemporary Healing Thinking and ApplicationFrom EverandI Know You Know: Integrating Traditional and Contemporary Healing Thinking and ApplicationNo ratings yet
- The Development of a Model of Human Nature that reflects Patient Presentation in General PracticeFrom EverandThe Development of a Model of Human Nature that reflects Patient Presentation in General PracticeNo ratings yet
- Critical-Care Nurses’ Perceived Leadership Practices, Organizational Commitment, and Job Satisfaction: An Empirical Analysis of a Non-Profit HealthcareFrom EverandCritical-Care Nurses’ Perceived Leadership Practices, Organizational Commitment, and Job Satisfaction: An Empirical Analysis of a Non-Profit HealthcareNo ratings yet
- Antiarthritic Drug StudiesDocument15 pagesAntiarthritic Drug StudiesSaidinaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Fundamental (Lab)Document2 pagesReviewer Fundamental (Lab)SaidinaNo ratings yet
- Prelim Reviewer HaDocument7 pagesPrelim Reviewer HaSaidinaNo ratings yet
- Ethics ReviewerDocument1 pageEthics ReviewerSaidinaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormatDocument2 pagesDrug Study FormatSaidinaNo ratings yet
- Administering EnemaDocument2 pagesAdministering EnemaSaidinaNo ratings yet
- Chess AI: Competing Paradigms For Machine Intelligence: Shiva Maharaj Nick Polson Alex TurkDocument15 pagesChess AI: Competing Paradigms For Machine Intelligence: Shiva Maharaj Nick Polson Alex TurkDomingo IslasNo ratings yet
- Full TextDocument167 pagesFull Textjon minanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document23 pagesLab Report 1hadri arif0% (1)
- Anger Management: Gaurav Sharma 138Document21 pagesAnger Management: Gaurav Sharma 138gaurav_sharma_19900No ratings yet
- Chilere - Unitatile de Racire - Technical - Brochures - NX - 0152P - 0812P - EN PDFDocument72 pagesChilere - Unitatile de Racire - Technical - Brochures - NX - 0152P - 0812P - EN PDFDaniel MilosevskiNo ratings yet
- INS2015 Fundamentals of Finance HungCV 1Document3 pagesINS2015 Fundamentals of Finance HungCV 1Phương Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- History of Computer ReviewerDocument10 pagesHistory of Computer ReviewerNeil Andrew Aliazas78% (9)
- Theory 2 - The Demand of The Society From The Teacher As A Professional (PPST)Document6 pagesTheory 2 - The Demand of The Society From The Teacher As A Professional (PPST)Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Safety Data SheetDocument7 pagesSafety Data SheetJivendra KumarNo ratings yet
- One Wavelength To Loop SkywireDocument2 pagesOne Wavelength To Loop SkywireRobert TurnerNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Medisys Corp The Intense Care Product Development TeamDocument10 pagesCase Study: Medisys Corp The Intense Care Product Development TeamBig BNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Thoughts On EducationDocument30 pagesPhilosophical Thoughts On EducationCharyl Louise MonderondoNo ratings yet
- Jimma UniversityDocument99 pagesJimma UniversityBekan NegesaNo ratings yet
- Pearson Letter To ParentsDocument2 pagesPearson Letter To ParentsPatricia WillensNo ratings yet
- Engine Torque Settings and Spec's 3.0L V6 SCDocument4 pagesEngine Torque Settings and Spec's 3.0L V6 SCMario MaravillaNo ratings yet
- MHSS ItalyDocument9 pagesMHSS Italyromedic36No ratings yet
- UnitPlan (P.E) Grade 6Document13 pagesUnitPlan (P.E) Grade 6Lou At CamellaNo ratings yet
- Shear and Diagonal Tension in BeamDocument16 pagesShear and Diagonal Tension in BeamMouy PhonThornNo ratings yet
- Structure and Operation: 3. Electronic Control Unit Connection DiagramDocument16 pagesStructure and Operation: 3. Electronic Control Unit Connection DiagramAung Hlaing Min MyanmarNo ratings yet
- Secondary GeographyDocument127 pagesSecondary GeographyAbcdNo ratings yet
- KP For RamDocument23 pagesKP For RamMonu NarwarNo ratings yet
- Evolis User ManualDocument28 pagesEvolis User ManualIonmadalin1000No ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/21Document18 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/21Lavanya EaswarNo ratings yet
- Ground Architecture (Mourad Medhat)Document146 pagesGround Architecture (Mourad Medhat)Aída SousaNo ratings yet
- CASBA Directive 2074Document17 pagesCASBA Directive 2074vijaycool85No ratings yet
- Term Test Pointers For Review - 1st TermDocument2 pagesTerm Test Pointers For Review - 1st Termjessica holgadoNo ratings yet
- Studi Tentang Pelayanan Terhadap Kapal Perikanan Di Pelabuhan Perikanan Pantai (PPP) Tumumpa Kota ManadoDocument9 pagesStudi Tentang Pelayanan Terhadap Kapal Perikanan Di Pelabuhan Perikanan Pantai (PPP) Tumumpa Kota ManadoAri WibowoNo ratings yet
- MiningDocument3 pagesMiningDherick RaleighNo ratings yet
- Century 21 South Western Accounting Answer Key Free PDF Ebook Download Century 21 South Western Accounting Answer Key Download or Read Online Ebook Century 21 SouthDocument8 pagesCentury 21 South Western Accounting Answer Key Free PDF Ebook Download Century 21 South Western Accounting Answer Key Download or Read Online Ebook Century 21 SouthJohn0% (4)
- ENGLISH TOEFL Structure (3rd Exercise)Document5 pagesENGLISH TOEFL Structure (3rd Exercise)susannnnnnNo ratings yet