Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Theorists and Their Theories Compilation Reviewer
Uploaded by
Joshua Gabriel AntiqueraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Theorists and Their Theories Compilation Reviewer
Uploaded by
Joshua Gabriel AntiqueraCopyright:
Available Formats
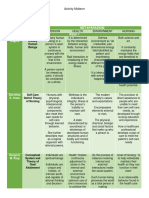
Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory
Faye Abdellah 21 Nursing Problems Theory
Virginia Henderson Nursing Need Theory
Dorothea Orem Self-Care Deficit Theory of Nursing
Callista Roy Roy Adaptation Model (RAM)
Hildegard Peplau Interpersonal Relations Theory
Betty Neuman Neuman Systems Model
Myra Levine Levine’s Conservation Model
Lydia Hall Core, Care, Cure Model
Jean Watson The Theory of Human Caring
Dorothy Johnson Behavioural System Model
Imogene King Goal Attainment Theory
Theory of Culture Care Diversity
Madeleine Leininger
and Universality
Abraham Maslow Hierarchy of Needs
Carmencita Abaquin Prepare Me Theory
Retirement and Role
Sister Letty Kuan
Discontinuities
Sigmund Freud Psychosexual Theory
Erik Erikson Psychosocial Theory
Jean Piaget Cognitive Development Theory
Lawrence Kohlberg Moral Development Theory
Theory Nursing Human/Person Health Environment
The person is referred to as a patient and seen as an
Healthcare profession that focuses on human
individual.
life processes and patterns.
Florence Nightingale Environmental Being well and using every power (resource) to
Nursing is to assist nature in healing the patient.
(FN) Theory People are multidimensional, composed of biological, the fullest extent in living life.
Emphasizes promotion of health for individuals,
psychological, social, and spiritual components.
families, groups, and society as a whole.
Recognizing the nursing problems of the
patient.
Deciding the appropriate actions to take in Emphasis should be placed upon prevention and
Having physical, emotional, and sociological needs.
terms of relevant nursing principles. rehabilitation. Home or community from which the client comes.
21 Nursing
Faye G. Abdellah (FA)
Problems Theory Recipients of nursing, and health, or achieving of it is the
Adjusting total nursing care plan to meet the Holistic approach must be taken by the nurse to Society is included in “planning for optimum health.”
purpose of nursing services.
patient’s individual needs. help the client achieve state of health.
Working with allied health professional in
planning for optimum health.
The ability to perform independently, the 14
basic needs. The effects of 7 components (light, temperature, air movement,
The unique function of the nurse is to assist the
Nursing Need Complete and independent being with biological, atmospheric pressure, proper waste disposal, absence of injurious
Virginia Henderson (VH) individual, sick or well, in the performance of
Theory sociological and spiritual components. Health is basic to human functioning and that chemicals, cleanliness of surroundings) on the life and development of a
activities contributing to health or its recovery.
promotion of health is more important than person.
care of the sick.
Structurally/Functionally whole or sound.
Has physical, chemical, and biological features.
Self-Care Deficit It is helping clients to establish or identify ways Has the capacity to regulate own functioning and
Dorothea E. Orem (DO) One must be able to perform self-care activities.
Theory of Nursing to perform self-care activities. development (self care agency).
It includes the family culture and community.
(Illness is having self-care deficit).
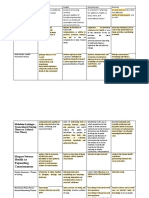
Theory Contents of Theory Assumptions/Theoretical Assertions Theory Model
12 Canons Environmental model focuses on the
Physical manipulation of physical and social
Ventilation & Warmth | Light | Cleanliness | Health of Houses factors that affect health and illness.
| Noise | Bed & Bedding | Personal Cleanliness | Taking Food
Florence Psychological Physical environment is a critical
Environmental
Nightingale Variety | Chattering Hopes & Advices component in both health and
Theory
(FN) Social illness.
Social Considerations | Observation of the SIck
Healthy surroundings are necessary
5 Essential Components of Environmental Health for proper nursing care and
Pure air | pure water | efficient drainage | cleanliness | light. restoration/maintenance of health.
11 Skills in Developing NCP
Observation of Health Status | Skills of Communication |
Application of Knowledge | Teaching of Patients and Families |
Planning & Organization of Work | Use of Resource Materials |
Use of Personnel Materials | Problem-Solving | Direction of Work
of Others | Therapeutic Use of Self | Nursing Procedure
The theory has combined the
concepts of health, nursing
21 Nursing Problems
problems, and problem-solving.
Basic to All Patients
Good Hygiene | Physical Comfort | Exercise, Rest, Sleep |
Problem-solving is an activity that is
Prevention of Accidents, Injury, Trauma, Infection | Good
inherently logical in nature.
Body Mechanics & Correcting Deformity
The framework focuses on nursing
Sustenal Care Needs
practice and individual patients.
Facilitating maintenance of
oxygen supply & nutrition to all body cells, waste
The nursing problem and nursing
elimination, fluid & electrolyte balance, regulatory
Faye G. treatment typologies are the
21 Nursing mechanisms and functions, and sensory function.
Abdellah principles of nursing practice and
Problems Recognize physiological responses of the body to disease
(FA) constitute the unique body of
conditions.
knowledge that is nursing.
Remedial Care Needs
Correct identification of the nursing
Identify and accept positive and negative expressions,
problem influences the nurse's
feelings, reactions, and interrelatedness of emotions to
judgment in selecting steps in solving
organic illness.
the patient's problem.
Facilitate effective verbal/non-verbal communication,
progress toward achievement of personal & spiritual goals,
The core of nursing is patient/client
and awareness of self according to varying needs.
problems that focus on the patient
and his/her problems.
Restorative Care Needs
Accept the optimum possible goals in the light of limitations,
physical and emotional.
Use community resources as an aid in resolving problems
arising from illness.
Understand the role of social problems as influencing
factors in the case of illness.
14 FUNDAMENTAL NEEDS OF HUMANS Henderson’s 14 Components
Breathe normally as applied to Maslow’s
Eat & drink adequately Hierarchy of Needs
Nurses care for patients until patient
Eliminate body wastes
can care for themselves once again.
Move and maintain desirable postures
Sleep & rest
Nurses are willing to serve and that
Virginia Select suitable clothes
Nursing Need nurses will devote themselves to the
Henderson Keep body clean & groomed; protect integument
Theory patient day and night.
(VH) Maintain body temperature
Avoid dangers in environment and avoid injuring others
Nurses should be educated at the
Communicate with others
university level in both arts and
Worship according to one’s faith
sciences.
Work in such a way that there is sense of accomplishment
Recreational activity
Learn, discovery, satisfy curiosity
Key Concepts
Self Care (acts to achieve health)
Agency (innate ability)
Demand (care needed)
Propositions
Requisites (action towards provision of self care)
The individual is capable of providing
Deficit (unable to meet self-requisites)
self-care to meet some health needs.
Activities to
Therapeutic Self-care (care provided by nurse) achieve health
The nurse compensates for the
patient’s inability to engage in self-
Nursing Agency (knowledge & abilities of nurse to meet client’s
care by providing care. Capacity of a
self-care demand)
person
The patient resumes self-care actions
Nursing Systems
as he/she regains ability to do so.
Wholly Compensatory (nurse does everything for patient’s
Dorothea E. Self-Care Deficit
self care)
Orem (DO) Theory of Nursing Assumptions
Partially Compensatory (nurse & patient act for self care)
Human require continuous,
Supportive-Educative (patient independently performs self
deliberate self-care for health
care & nurse regulates self-care agency)
development and well-being.
Self Care Requisites
Maintenance of
Individuals have the power to make Care needed
decisions about their self care. of a person
Sufficient air, water, and food intake
Balance between activity & rest
Nurses maintain the capacity of
Balance between solitude & social interaction
individual for self-care and assist
Knowledge &
Prevention of hazards to human life, functioning, and well-being abilities of nurse
when he/she is unable to do so.
Provision of care associated with elimination processes and
excrements.
Promotion of human functioning and development within social
groups.
Theory Nursing Human/Person Health Environment Adaptation
“Health is a state and a process of Environment is “all the conditions, circumstances, and
Humans are holistic, adaptive systems. As an being and becoming integrated and a influences surrounding and affecting the development and The process and outcome whereby thinking and
Healthcare profession that focuses adaptive system, the human system is whole person. It is a reflection of behavior of persons or groups, with particular consideration feeling persons, as individuals or in groups, use
on human life processes and described as a whole with parts that function adaptation, that is, the interaction of of the mutuality of person and earth resources that includes conscious awareness and choice to create human
patterns. as unity for some purpose. the person and the environment.” focal, contextual, and residual stimuli.” and environmental integration.”
Callista Roy Roy Adaptation
(CR) Model (RAM)
Emphasizes promotion of health for Human systems include people as Adaptation is a process of promoting “It is the changing environment [that] stimulates the person Rather than being a human system that simply
individuals, families, groups, and individuals or in groups, including families, physiological, psychological, and to make adaptive responses.” strives to respond to environmental stimuli to
society as a whole. organizations, communities, and society as a social integrity, and that integrity maintain integrity, every human life is purposeful in
whole. implies an unimpaired condition Any environmental change demands increasing energy to a universe that is creative, and persons are
leading to completeness or unity. adapt to the situation. inseparable from their environment.
Therapeutic interpersonal process. Health is defined as “a word symbol
Man is an organism that “strives in its own that implies forward movement of
Interpersonal
Hildegard Peplau Functions cooperatively with other way to reduce tension generated by needs.” personality and other ongoing human Existing forces outside the organism and in the context of
Relations
(HP) human process that make health processes in the direction of creative, culture.
Theory
possible for individuals in The client is an individual with a felt need. constructive, productive, personal,
communities. and community living.”
The client or client system. A composite of
“Health is a condition in which all
Is concerned with the whole person, five interacting variable areas: The totality of the internal and external forces which
parts and subparts (variables) are in
a unique profession concerned with surround a person and with which they interact at any given
harmony with the whole of the
all the variables affecting clients in Physiological, psychological, sociocultural, time.
Betty Neuman Neuman client.”
their environment actions which developmental, and spiritual.
(BN) Systems Model
assist individuals, families and groups Internal (intrapersonal), external (interpersonal), and
The condition or degree of system
to maintain a maximum level of An open system that interacts with both created (unconsciously developed used by the client to
stability is viewed as a continuum
wellness internal and external environmental forces support coping) environments.
from wellness to illness.
or stressors and is in constant change.
Includes both the internal (complex biochemical;
physiological and pathophysiological process) and external
environment.
The human interaction relying on a. Perceptual aspects - interpreted by the individual
Levine’s
communication, rooted in the with the five senses.
Myra Levine Conservation Is a unique individual in unity and integrity, Health is the patterns of adaptive
organic dependency of the individual
(ML) Model feeling, believing, thinking, and whole. change of the whole being.
human being in his relationships with b. Operational components - physically affects a person
other human beings. but can not be seen.
c. Conceptual aspects - characterized by cultural
patterns, spirituality and mediated through symbols of
language, thought, and history.
It is helping others to move in the
direction of self-awareness. Unique, capable of growth and learning, and
It is the state of being able to achieve
Lydia Hall Core, Care, requiring a total person approach (Goal The concept of society or environment is dealt with in
self-awareness thereby releasing own
(LH) Cure Model Nursing is identified as consisting of setting and action plan). relation to the individual.
power to heal.
participation in the care, core, and
cure aspects of patient care.
Unity and harmony within the mind,
body, and soul.
A human science of persons and Caring and nursing has existed in every society. The nurse is
A valued person to be cared for, respected,
human health–illness experiences Health is associated with the degree part of the environment.
Jean Watson The Theory of nurtured, understood, and assisted.
that are mediated by professional, of congruence between the self as
(JW) Human Caring
personal, scientific, esthetic, and perceived and the self as Nurse should ensure a caring-healing environment capable
Unity of mind/body/spirit/nature.
ethical human care transactions. experienced. (patient is healthy when of transformative measures.
he sees himself healthy; unity is
present)
To maintain and restore the person’s
behavioral system of balance and
stability or to help the person
achieve a more optimum level of
A behavioral system with patterned Elusive, dynamic state influenced by
Dorothy Johnson Behavioural balance and functioning.
repetitive, and purposeful ways of behaving biological, psychological, and social
(DJ) System Model
that link the person with the environment. factors.
Nursing is an external force acting to
preserve the organization and
integration of the patient’s behavior
to an optimal level.
Theory Contents of Theory Assumptions/Theoretical Assertions Theory Model Theory Contents of Theory Assumptions/Theoretical Assertions Theory Model
Stimuli Core (The Person)
Focal Therapeutic use of self.
Contextual Addressing patient’s social and emotional needs for effective 1. The motivation and energy necessary for healing exist within
Residual communication and comfortable environment. the patient, rather than in the healthcare team.
The Roy Adaptation Model (RAM) focuses on the interrelatedness
Four Adaptative Modes
Callista of four adaptive systems. Care (The Body) 2. The three aspects of nursing should not be viewed as
Roy Adaptation Physiologic-physical Lydia Hall Core, Care,
Roy It is a deductive theory based on nursing practice. The RAM Providing bodily care for the patient. Helping patient complete daily functioning independently but as interrelated.
Model (RAM) Self-concept-group identity (LH) Cure Model
(CR) guides the nurse who is interested in physiologic adaptation, as biological functions.
Role Function
well as the nurse who is interested in psychosocial adaptation. The nurse’s goal is the comfort of the patient. 3. The three aspects interact, and the circles representing them
Interdependence
Two Subsystems change size, depending on the patient’s total course of
Regulator Cure (The Disease) progress.
Cognator Interventions or actions geared toward treating patient.
The nurse is an active advocate of the patient.
Johari Window
Open-Public - known to us and to other people. characteristics, 10 Carative Factors
behavior, talents, customs, traditions, and everything pertaining Formation of a Human Altruistic System of Values
to ourselves. Instillation of Faith & Hope
Blind-Unaware - characteristics, behaviors, talents, and Cultivation of Sensitivity to Self & to Others
everything pertaining to ourselves that we do not know or are Development of a Helping-Trust Relationship
unaware of but what other people are aware of. We usually can’t Promotion and Acceptance of the Expression of Positive and Negative
see ourselves, but others can see them in us. Feelings
Hidden-Private - keeping to ourselves; not visible to others, Systematic Use of Scientific Problem-Solving Method for Decision Making Caring can be effectively demonstrated and practiced only
undisplayed to other people. Promotion of Interpersonal Teaching-Learning interpersonally.
Nurse and patient can interact. Provision for Supportive, Protective, and Correctional Mental, Physical,
Unknown - discovering more about ourselves by interacting with
other people, growing by the years, we progress to learn more Sociocultural, and Spiritual Environment (Holistic) Caring consists of carative factors that result in the
Both the patient and nurse mature as the result of the Assistance with Gratification of Human Needs satisfaction of certain human needs.
about ourselves.
therapeutic interaction. Allowance for Essential Existential-Phenomenological Forces
Four Psychobiological Experiences
Hildegard Interpersonal Effective caring promotes health and individual or family
Needs
Peplau Relations Communication and interviewing skills remain fundamental Transpersonal Caring Relationship growth.
Frustrations
(HP) Theory nursing tools. Nurse’s commitment to protecting and enhancing human dignity.
Conflicts
Anxieties Caring responses accept person not only as he or she is now
Nurses must clearly understand themselves to promote their Jean
Six Nursing Roles The Theory of The ‘nurses' caring and connection have the potential to heal since the but as what he or she may become.
client’s growth and to avoid limiting client’s choices to those that Watson
Stranger Human Caring experience, intention, and perception are taking place.
nurses value. (JW)
Resource Person A caring environment is one that offers the development of
Teacher Nursing goals beyond an objective assessment and shows concern for potential while allowing the person to choose the best
Leader the patient's health care. action for himself or herself at a given point in time.
Surrogate Example: Person-Centered Care for an Elderly Resident in a
Counselor Caring Moment/Caring Occasion Long-Term Care Facility.
Phases of Nurse-Patient Relationship and Its Process A caring occasion is the moment when the nurse and another person
Orientation (Problem-defining phase) come together in such a way that an occasion for human caring is Caring is more “healthogenic” than is curing. A science of
Identification created. caring is complementary to the science of curing.
Exploitation
Resolution Both persons come together in a human-human transaction. The practice of caring is central to nursing.
The one caring for and the one being cared for are influenced by the
Nurse is an active participant in a reciprocal relationship with choices and actions decided within the relationship.
the client, keeping the client system stable.
Wellness-Illness Continuum Caring-Healing Modalities
Wellness = Available Energy > Needed Energy Primary Prevention Caring-healing modalities are often noninvasive, nonintrusive, natural-
Illness/Death = Available Energy < Needed Energy focuses on preventing the occurrence of a health condition or human, energetic environmental field modalities.
disease. It involves interventions to reduce the risk factors
Nursing Process Format and promote overall health and well-being in a population
that is not yet affected by the condition. NURSING
Betty 1. Nursing Diagnosis - assumes that the nurse collects an adequate Goal: To Maintain and restore the person’s behavioral
Neuman Behavior system balance and stability or to help the person
Neuman database from which to analyze variances from wellness to make the Secondary Prevention
Systems Model the output of intra-organismic structures and processes as they are achieve a more optimum level of balance and
(BN) diagnoses. aims to detect and treat health conditions in their early stages
2. Nursing Goals - determined by negotiation with the client for desired when they are more easily managed and before they cause coordinated and articulated by and responsive to changes in sensory functioning.
prescriptive changes to correct variances from wellness. severe complications. stimulation.
3. Nursing Outcomes - confirmation of prescriptive change or System Nursing is an external force acting to preserve the
reformulation of nursing goals is evaluated. Tertiary Prevention a whole that functions as a whole by virtue of the interdependence of organization and integration of the patient’s behavior to
Evaluation - used to confirm that the desired outcomes have been managing and reducing the impact of a health condition once its parts. an optimal level.
achieved it has fully developed. It's often applied to individuals who are Dorothy Behavioral System
Behavioural
already diagnosed with a disease to prevent complications Johnson encompasses the patterned, repetitive, and purposeful ways of PERSON
System Model
and improve their quality of life. (DJ) behaving. A behavioral system with patterned repetitive, and
Subsystems purposeful way of behaving that link the person with the
behavioral system has many tasks to perform thus parts of the system environment
Each individual is an active participant in interactions with the evolved into subsystem with specialized tasks.
Four Conservation Principles environment constantly seeking information from it. HEALTH
The principle of the conservation of energy - balance between Seven Subsystems Elusive, dynamic state influenced by biological,
activity and the person’s available energy. The individual is a sentient being and the ability to interact with Three Functional Elements psychological, and social factors.
the environment seems ineluctably tied to his sensory organs. Four Structural Elements
The principle of the conservation of structural integrity - is the ADTE
basis for nursing interventions to limit the amount of tissue Change is the essence of life and it is unceasing as long as life Assessment, Disorders, Treatment, Evaluation
Levine’s
Myra involvement. goes on. Change is characteristic of life.
Conservation
Levine
Model
(ML) The principle of the conservation of personal integrity - is based Ultimately the decisions for nursing intervention must be based
on nursing interventions that permit the individual to make on the unique behavior of the individual patient.
decisions for himself or participate in the decisions.
Patient centered nursing care means individualized nursing care.
The principle of the conservation of social integrity - is based on It is predicated on the reality of common experience: every man
nursing interventions to preserve the client’s interactions with is a unique individual, and as such he requires a unique
family and the social system to which they belong. constellation of skills, techniques and ideas designed specifically
for him.
You might also like
- Nursing Theories SummaryDocument7 pagesNursing Theories SummaryThrecia RotaNo ratings yet
- The Naturopathic Way: How to Detox, Find Quality Nutrition, and Restore Your Acid-Alkaline BalanceFrom EverandThe Naturopathic Way: How to Detox, Find Quality Nutrition, and Restore Your Acid-Alkaline BalanceNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Theorist (METAPARADIGMS)Document4 pagesCompilation of Theorist (METAPARADIGMS)3amabelle arevaloNo ratings yet
- Activity MidtermDocument7 pagesActivity Midtermreese's peanut butter cupsNo ratings yet
- Nursing MetaparadigmDocument5 pagesNursing MetaparadigmNikzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Metaparadigm Concepts of Major Nurse TheoristsDocument9 pagesNursing Metaparadigm Concepts of Major Nurse TheoristsAllyana Marie LanuganNo ratings yet
- TFN UstDocument81 pagesTFN UstTimi BCNo ratings yet
- DIVINO, Elizz Joy F. Activity MidtermDocument11 pagesDIVINO, Elizz Joy F. Activity Midtermreese's peanut butter cupsNo ratings yet
- Theorist Theory Application To Spiritual Care Florence Nightingale Joyce Travelbee Betty NeumanDocument4 pagesTheorist Theory Application To Spiritual Care Florence Nightingale Joyce Travelbee Betty NeumanJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Chart of Nursing Theories and ModelsDocument3 pagesChart of Nursing Theories and ModelsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument4 pagesFundamentals of NursingYmon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Concept of Man Health and IllnessDocument3 pagesConcept of Man Health and IllnessChristian Shane BejeranoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theory FoundationsDocument3 pagesNursing Theory FoundationsYejiNo ratings yet
- Classifying Nursing Theorists' Concepts of Nursing, Person, Health and EnvironmentDocument2 pagesClassifying Nursing Theorists' Concepts of Nursing, Person, Health and EnvironmentBALDOZA LEO FRANCO B.No ratings yet
- Nursing Theories: Nightingale, Johnson, Abdellah & MoreDocument8 pagesNursing Theories: Nightingale, Johnson, Abdellah & More3amabelle arevaloNo ratings yet
- Colinares Activity02Document7 pagesColinares Activity02hiraethNo ratings yet
- Divino, Elizz Joy F.Document7 pagesDivino, Elizz Joy F.reese's peanut butter cupsNo ratings yet
- Module 2 PDFDocument24 pagesModule 2 PDFElla Nika FangonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Concepts of Health and WellnessDocument5 pagesLesson 1 Concepts of Health and WellnessNil GyiNo ratings yet
- MetaparadigmsDocument2 pagesMetaparadigmsRed DinsonNo ratings yet
- Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory: Metaparadigm PersonDocument15 pagesFlorence Nightingale Environmental Theory: Metaparadigm PersonAnthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals in Nursing Lesson #1 INTRODUCTORY CONCEPTSDocument6 pagesFundamentals in Nursing Lesson #1 INTRODUCTORY CONCEPTSSophia Duquinlay100% (1)
- NCM 103 PrelimDocument6 pagesNCM 103 Prelimkwgchyrn1No ratings yet
- 14 - Fitzpatrick, Leininger, Rogers, Newman, Parse PDFDocument5 pages14 - Fitzpatrick, Leininger, Rogers, Newman, Parse PDFJuan Felipe Jaramillo SalazarNo ratings yet
- TFN FinalsDocument20 pagesTFN FinalsCHESKA LYKA ASILONo ratings yet
- Nursing Theory (1)Document12 pagesNursing Theory (1)bldewnaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theories Focus on Holistic HealthDocument6 pagesNursing Theories Focus on Holistic HealthBuklatin Lyra Elghielyn H.No ratings yet
- General Definition of The Nursing MetaparadigmDocument3 pagesGeneral Definition of The Nursing MetaparadigmDennise Kate CabiedesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theories in 40 CharactersDocument5 pagesNursing Theories in 40 CharactersJam BautistaNo ratings yet
- AUTHORS_ THEORIESDocument2 pagesAUTHORS_ THEORIESCHALSEA DYANN JOIE GALZOTENo ratings yet
- Nursing Theories and DefinitionDocument3 pagesNursing Theories and DefinitionSareno PJhēaNo ratings yet
- Systems TheoriesDocument35 pagesSystems TheoriesJames Kurt CruzatNo ratings yet
- TFN Midterms 2Document3 pagesTFN Midterms 2grapikmsNo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument23 pagesCommunity Health NursingMimi Vee100% (1)
- Bachelor of Science in Nursin Worksheet No. 1 - Theories of Nursing 1 Year-1 Semester-Section 8 Theoretical Foundations in NursingDocument3 pagesBachelor of Science in Nursin Worksheet No. 1 - Theories of Nursing 1 Year-1 Semester-Section 8 Theoretical Foundations in NursingMarybel Maglasang100% (1)
- Nur 016 TableDocument17 pagesNur 016 TableGelie LouiseNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing (Part 1)Document11 pagesFundamentals of Nursing (Part 1)Louie ParillaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledLei Anne AguilorNo ratings yet
- Models of PreventionDocument25 pagesModels of PreventionAMY LALRINGHLUANI M.Sc. Child Health (Paediatric ) NursingNo ratings yet
- KONSEP KEPERAWATAN MEDIKAL BEDAH-Dr - TintinDocument19 pagesKONSEP KEPERAWATAN MEDIKAL BEDAH-Dr - TintinRizky KykyNo ratings yet
- NCMA (TFN) Assignment Oct-20-20Document5 pagesNCMA (TFN) Assignment Oct-20-20MC DARLIN DIAZNo ratings yet
- NCMDocument4 pagesNCMCelestina JalemNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Theories and ConceptsDocument18 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Theories and ConceptsJamaica Manuel Iglesias100% (6)
- Week 5 Lec. NCMA110. Nursing Philosophies Watson, Benner, ErikssonDocument4 pagesWeek 5 Lec. NCMA110. Nursing Philosophies Watson, Benner, ErikssonMai DeiNo ratings yet
- Theory Matrix WorksheetDocument8 pagesTheory Matrix WorksheetCang Cang De ArcaNo ratings yet
- Faye Glenn AbdellahDocument1 pageFaye Glenn Abdellahliza bNo ratings yet
- N1R01A - Transes in Introduction To NursingDocument8 pagesN1R01A - Transes in Introduction To NursingMikhaella GwenckyNo ratings yet
- N1R01A - Transes in Introduction To NursingDocument8 pagesN1R01A - Transes in Introduction To NursingMikhaella GwenckyNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Theorists and Their WorksDocument21 pagesGroup 2 Theorists and Their WorkssheenamarielaruyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theorists' Metaparadigm SummaryDocument2 pagesNursing Theorists' Metaparadigm SummaryKrizzia SuñerNo ratings yet
- Funda ReviewerDocument3 pagesFunda Reviewerabegailsalilin1No ratings yet
- CHN - CoparDocument7 pagesCHN - CoparhelloaNo ratings yet
- Theories of Nursing (Encoded)Document5 pagesTheories of Nursing (Encoded)Shereen AlobinayNo ratings yet
- 1-7 Theorists (THEORY MATRIX)Document16 pages1-7 Theorists (THEORY MATRIX)Princess OlarteNo ratings yet
- Health and IllnessDocument71 pagesHealth and IllnessLondho Londho100% (2)
- Joy Marie LDocument5 pagesJoy Marie LCharesse Angel SaberonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theorists and Their Major ConceptsDocument27 pagesNursing Theorists and Their Major ConceptsPatricia Marie PalenciaNo ratings yet
- Nursing-Theories SummaryDocument5 pagesNursing-Theories SummaryAbby Umali-Hernandez100% (1)
- Post Tonsillectomy Bleeding Clinical Practice GuidelineDocument5 pagesPost Tonsillectomy Bleeding Clinical Practice Guidelinemohamed fahmyNo ratings yet
- A. Gudang Farmasi 2023 (Feni Dwi) UpdateDocument882 pagesA. Gudang Farmasi 2023 (Feni Dwi) UpdatehefikurniasariNo ratings yet
- Admission LetterDocument4 pagesAdmission LetterYasir KNNo ratings yet
- Florence Nightingale TheoryDocument44 pagesFlorence Nightingale TheoryAnsu MaliyakalNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter For Epidemiologist PositionDocument7 pagesCover Letter For Epidemiologist Positiongt7gb636100% (1)
- Pandemic Learning: Migrant Care Workers and Their Families Are Essential in A Post-COVID-19 WorldDocument18 pagesPandemic Learning: Migrant Care Workers and Their Families Are Essential in A Post-COVID-19 WorldThe Wilson CenterNo ratings yet
- Depression Associated With Dementia With Lewy Bodies (DLB) and The Effect of SomatotherapyDocument6 pagesDepression Associated With Dementia With Lewy Bodies (DLB) and The Effect of SomatotherapyRaluca ElenaNo ratings yet
- Details Received From Collectorate - Excellent Dedicated Work - During Pandemic COVID - 19Document2 pagesDetails Received From Collectorate - Excellent Dedicated Work - During Pandemic COVID - 19Vimal kumarNo ratings yet
- Ashgate - Landscape Professional Practice PDFDocument281 pagesAshgate - Landscape Professional Practice PDFyondaimethunderNo ratings yet
- Cagri Karaciklar Fragility Fractures Presentation PDFDocument15 pagesCagri Karaciklar Fragility Fractures Presentation PDFÇağrıNo ratings yet
- Hand Power Tools PDFDocument6 pagesHand Power Tools PDFDankNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Differential Count ImportanceDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 - Differential Count ImportanceIra ReyNo ratings yet
- General Topics: Anesthesia, Analgesia, and Sedation of Small MammalsDocument23 pagesGeneral Topics: Anesthesia, Analgesia, and Sedation of Small Mammalsdoja catNo ratings yet
- Resona r9 Platinum Multi Parametric Breast SolutionDocument2 pagesResona r9 Platinum Multi Parametric Breast SolutionXing LuNo ratings yet
- English File B2 2 Fourth Edition Student S Book and WorkbookDocument241 pagesEnglish File B2 2 Fourth Edition Student S Book and WorkbookPaula AlcañizNo ratings yet
- English Passion Project 2Document9 pagesEnglish Passion Project 2api-462335192No ratings yet
- Career ObjectivesDocument4 pagesCareer ObjectivesJennifer Davis CondimanNo ratings yet
- Course Guide in Trends and Issues in Social StudiesDocument7 pagesCourse Guide in Trends and Issues in Social StudiesRomar M. DavidNo ratings yet
- 6 135Document6 pages6 135Ashok LenkaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1. IdentificationDocument9 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Section 1. IdentificationJivendra KumarNo ratings yet
- A Case Report of Acute Severe Necrotizing Pancreatitis FollowingDocument4 pagesA Case Report of Acute Severe Necrotizing Pancreatitis FollowingalexNo ratings yet
- Revised - Ie18 Final UpdatedDocument120 pagesRevised - Ie18 Final UpdatedLUCAS AndrewsNo ratings yet
- Erba Lisawash Service ManualDocument9 pagesErba Lisawash Service ManualEricj Rodríguez100% (1)
- DR Joe S Freedom From AngerDocument128 pagesDR Joe S Freedom From AngerTouhidul IslamNo ratings yet
- A Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy 1910Document46 pagesA Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy 1910Mohammed AdilNo ratings yet
- 4TH Year Stuide Guide Community MedicineDocument30 pages4TH Year Stuide Guide Community MedicineMohammad Jibran KhanNo ratings yet
- Prof Development & ProtocolDocument8 pagesProf Development & ProtocolNomadOrNahNo ratings yet
- 의약품동등성시험기준 해설서 요약Document137 pages의약품동등성시험기준 해설서 요약Travis JeonNo ratings yet
- Price List UpdatePHM 20jun23Document10 pagesPrice List UpdatePHM 20jun23Joyoboyo PrimaNo ratings yet
- New Sop Piant WorkDocument6 pagesNew Sop Piant WorkBALAL AKRAMNo ratings yet