Professional Documents
Culture Documents
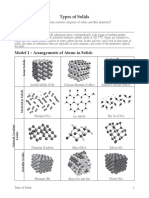
Crystal Types
Uploaded by
nourlina200020Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Crystal Types
Uploaded by
nourlina200020Copyright:
Available Formats
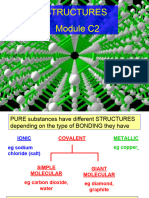
CRYSTAL TYPES
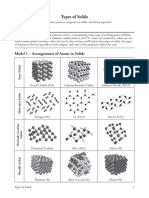
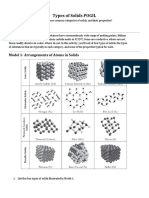
There are five types of structure: monatomic, simple molecular, ionic, giant covalent and metallic.
Monatomic substances are all gases at room temperature, but there are examples of substances with each of the other four
types of structure that are solids. This looks closely at one example of a solid with each of the four remaining types of
structure to reinforce and test your ideas of structure and bonding. Each of the four examples occur as crystalline solids at
room temperature – hence this refers to a discussion of the four types of crystal.
1) IONIC (e.g. sodium chloride)
This shows very well how the ions are Note that this diagram only shows the centre of ions to help us
packed close together see how the ions s are arranged in a cubic shape. Although it may
look like it, there are NO covalent bonds between the ions.
ions
Property Explanation
Melting & boiling points
Electrical conductivity
Strength
Solubility
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 5-Jun-2015 Chemsheets AS 1014
2) METALLIC (e.g. magnesium)
2+ 2+ 2+
2+ 2+
2+ 2+ 2+
Property Explanation
Melting & boiling points
Electrical conductivity
Strength
Solubility
3) GIANT COVALENT (e.g. diamond)
Property Explanation
Melting & boiling points
Electrical conductivity
Strength
Solubility
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 5-Jun-2015 Chemsheets AS 1014
graphite
Property Explanation
Melting & boiling points
Electrical conductivity
Strength
Solubility
graphene
Property Explanation
Melting & boiling points
Electrical conductivity
Strength
Solubility
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 5-Jun-2015 Chemsheets AS 1014
4) SIMPLE MOLECULAR (e.g. iodine)
Property Explanation
Melting & boiling points
Electrical conductivity
Strength
Solubility
e.g. ice
Property Explanation
Melting & boiling points
Electrical conductivity
Density of ice v water
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 5-Jun-2015 Chemsheets AS 1014
You might also like
- Types of Solids POGIL - Student VersionDocument6 pagesTypes of Solids POGIL - Student VersionJesse SchwartzNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Chemical BondingDocument58 pagesUnit 3 - Chemical BondingTrang Vũ Thị BằngNo ratings yet
- MerkabahDocument8 pagesMerkabahbrozacaNo ratings yet
- Bible - To Love, Honor and Vacuum PDFDocument9 pagesBible - To Love, Honor and Vacuum PDFDiana ArunNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding 1 1Document46 pagesIonic and Covalent Bonding 1 1Ivan LazaroNo ratings yet
- Method Statement Risk Assessment For Pump Installation 2 PDFDocument4 pagesMethod Statement Risk Assessment For Pump Installation 2 PDFALTHAF HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- 03 - Leviticus PDFDocument162 pages03 - Leviticus PDFGuZsolNo ratings yet
- The Discipline of CounselingDocument18 pagesThe Discipline of CounselingIekzkad Realvilla0% (1)
- Client Conversations: Insights Into Successful Project OutcomesDocument28 pagesClient Conversations: Insights Into Successful Project OutcomesKNo ratings yet
- Rizal General Chemistry 2 q3 Slm4Document12 pagesRizal General Chemistry 2 q3 Slm4Darlene OpeñaNo ratings yet
- 11 Types of Solids - SDocument6 pages11 Types of Solids - SHP400% (7)
- Healthcare Sector Report Oct 16 EDEL PDFDocument194 pagesHealthcare Sector Report Oct 16 EDEL PDFshivangNo ratings yet
- CHEM Types of Solids POGILDocument7 pagesCHEM Types of Solids POGILKosakenNo ratings yet
- Compounds - Bonding U1 N U2Document19 pagesCompounds - Bonding U1 N U2muhajireenNo ratings yet
- A2AS CHEM REVISED Support 20837Document6 pagesA2AS CHEM REVISED Support 20837Tianming KingsleyNo ratings yet
- The Structures of Crystalline SolidsDocument76 pagesThe Structures of Crystalline SolidsgingerootNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent Structures (Macromolecules)Document33 pagesGiant Covalent Structures (Macromolecules)ananya.aNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument25 pagesChemical Bondingjoannavera2020No ratings yet
- Xture of SolidsDocument12 pagesXture of Solidsmuonekechibukeleonard52No ratings yet
- Structures of SolidsDocument6 pagesStructures of SolidsAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- Copia de Copy of F2 Diamond Graphite Silicon DioxideDocument21 pagesCopia de Copy of F2 Diamond Graphite Silicon DioxideClovis Erick Rengel DominguezNo ratings yet
- Che 513 Introduction To Polymer EngineeringDocument19 pagesChe 513 Introduction To Polymer EngineeringHappyNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent MoleculesDocument34 pagesGiant Covalent MoleculesaqutiaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Bonding and Structure (Answers)Document10 pages4.1 Bonding and Structure (Answers)Deeyana DeenNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 - Q3 - SLM4Document11 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 - Q3 - SLM4Jonnel RoqueNo ratings yet
- Resitters Lesson 4 Shapes and Bonding TypesDocument19 pagesResitters Lesson 4 Shapes and Bonding Typesonion2012No ratings yet
- 4.chemzone - Formulas and Names of CompoundsDocument14 pages4.chemzone - Formulas and Names of CompoundsIANo ratings yet
- LBC Alchemy SE Lesson26Document5 pagesLBC Alchemy SE Lesson26Sean MartinsonNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2Document15 pagesAssignment - 2padhiyararpitaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Learning Activity SheetDocument55 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Learning Activity Sheetmary joy nemenzoNo ratings yet
- Types and Properties of SolidsDocument13 pagesTypes and Properties of SolidsShaila DelatorreNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10.2 The Solid StateDocument14 pagesLesson 10.2 The Solid StatefitriNo ratings yet
- Giant CovalentDocument25 pagesGiant CovalentPaarth BansalNo ratings yet
- 《 》Assignment Chapter 2 你所在的班级/学号/姓名 (class/ID/Chinese name):193519014 / Emil Salim (Document5 pages《 》Assignment Chapter 2 你所在的班级/学号/姓名 (class/ID/Chinese name):193519014 / Emil Salim (Emil SalimNo ratings yet
- Structure of Solids 1Document5 pagesStructure of Solids 1zakNo ratings yet
- 8 Thhourlab 9 BakerbrunatikallalkaneoberlanderDocument5 pages8 Thhourlab 9 Bakerbrunatikallalkaneoberlanderapi-297169088No ratings yet
- Class 12th Chemistry WorksheetDocument244 pagesClass 12th Chemistry WorksheetAswathNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 Properties of SolidDocument6 pagesActivity 4 Properties of Solidjoninna monesNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Chemistry Week 8 Lesson 1 Worksheet 1 and SolutionsDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Chemistry Week 8 Lesson 1 Worksheet 1 and SolutionsNikoli MajorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6-Ceramics GlassesDocument39 pagesLecture 6-Ceramics GlassesRUGERO KeslyneNo ratings yet
- New Note Chapter 9 Structures and Properties of Substances - 2020 - Student VersionDocument46 pagesNew Note Chapter 9 Structures and Properties of Substances - 2020 - Student VersionkarinhyhoNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements and Compounds RevisionDocument40 pagesAtoms, Elements and Compounds RevisionAbha RathoreNo ratings yet
- Number of Valence Electrons Group NumberDocument20 pagesNumber of Valence Electrons Group NumberManonmani PalaniswamyNo ratings yet
- Comparing Covalent and Ionic Lattices S4Document3 pagesComparing Covalent and Ionic Lattices S4Fatima Ahmed-VeriterNo ratings yet
- The Solid State ModifiedDocument70 pagesThe Solid State ModifiedR220603 THAMMINENI MALLIKARJUNANo ratings yet
- The Solid State PDFDocument69 pagesThe Solid State PDFVNS TechNo ratings yet
- Ionic and CovalentDocument21 pagesIonic and CovalentRobeth EspanoNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument27 pagesMetalsrituNo ratings yet
- Assignment Chapter 2 (class/ID/Chinese Name 193519014 / Emil Salim (Document5 pagesAssignment Chapter 2 (class/ID/Chinese Name 193519014 / Emil Salim (Emil SalimNo ratings yet
- Describe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument6 pagesDescribe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent Compoundsmadhuri pawarNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument50 pagesChemical BondingLeila BonNo ratings yet
- 11.1 Group IV ElementsDocument24 pages11.1 Group IV ElementsTrevor TatendaNo ratings yet
- Hi HowDocument245 pagesHi HowZach BilsonNo ratings yet
- 9.2: The Solid State of Matter: Skills To DevelopDocument7 pages9.2: The Solid State of Matter: Skills To DevelopGraviton Manzano OlarteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document9 pagesChapter 3JeromeNo ratings yet
- RW-1 2 3 4 5 6 7Document7 pagesRW-1 2 3 4 5 6 7Smahs ZabirNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Revision Notes The Solid StateDocument21 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Revision Notes The Solid StateAfreen AnzNo ratings yet
- Chem M1 PDFDocument11 pagesChem M1 PDFZarylle De AsasNo ratings yet
- Module-Ii Chemical Bonding: General Chemistry CHEM-1001Document193 pagesModule-Ii Chemical Bonding: General Chemistry CHEM-1001Shivansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 SolidsDocument13 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 SolidsRicardo ErioNo ratings yet
- Math Tutor: Drawing Lewis StructuresDocument7 pagesMath Tutor: Drawing Lewis Structuresjaber bentabetNo ratings yet
- Ions:: No. of Protons No. of Electrons No. of Neutrons Mass NumberDocument18 pagesIons:: No. of Protons No. of Electrons No. of Neutrons Mass NumberTaffiNo ratings yet
- ESlide Unit 9 EDocument196 pagesESlide Unit 9 EhihiNo ratings yet
- Final PDF For Grade 9 PDFDocument5 pagesFinal PDF For Grade 9 PDFmadhuri pawarNo ratings yet
- Classification of Crystaline Solids-Sneha LathaDocument18 pagesClassification of Crystaline Solids-Sneha LathaTarun YadavNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 9Document196 pagesChemistry Unit 9yuki100% (1)
- Gender Balance in The UaeDocument7 pagesGender Balance in The Uaenourlina200020No ratings yet
- DIRT Test 4 AISLDocument10 pagesDIRT Test 4 AISLnourlina200020No ratings yet
- Test 5 Final VersionDocument4 pagesTest 5 Final Versionnourlina200020No ratings yet
- MOLAR VOLUME WorksheetDocument2 pagesMOLAR VOLUME Worksheetnourlina200020No ratings yet
- What Is The Significance of Glycolysis in Anaerobic ConditioDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Significance of Glycolysis in Anaerobic Conditionourlina200020No ratings yet
- Mass Moles Molecules WorksheetDocument2 pagesMass Moles Molecules Worksheetnourlina200020No ratings yet
- Gas Laws Worksheet 2024Document4 pagesGas Laws Worksheet 2024nourlina200020No ratings yet
- Water Quiz MARK SCHEMEDocument4 pagesWater Quiz MARK SCHEMEnourlina200020No ratings yet
- Essay OthelloDocument2 pagesEssay Othellonourlina200020No ratings yet
- ResumeatbapujiDocument2 pagesResumeatbapujiEllur AnandNo ratings yet
- Man Accused of Shooting Waffle House Cook After Face Mask Dispute in Aurora MyforeskinisonsandraDocument51 pagesMan Accused of Shooting Waffle House Cook After Face Mask Dispute in Aurora MyforeskinisonsandraadamfugueNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Digital Illustration TechniqueDocument5 pagesWorksheet Digital Illustration TechniqueJago100% (1)
- RCI Root Cause InvestigationDocument24 pagesRCI Root Cause InvestigationCarlos Jose Sibaja CardozoNo ratings yet
- Compresor Atlas Copco GA30Document16 pagesCompresor Atlas Copco GA30Florin Maria Chirila100% (1)
- Morphology and Culture - MoldsDocument8 pagesMorphology and Culture - Moldslisa.angle204No ratings yet
- DLL - Science 4 - Q4 - W2Document3 pagesDLL - Science 4 - Q4 - W2allan arugayNo ratings yet
- Lab Heat Experment 2Document5 pagesLab Heat Experment 2حسين عمريNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Different Models of Ob (Autocratic, Custodial, Supportive and Collegial, ETC.)Document15 pagesUnit 4 Different Models of Ob (Autocratic, Custodial, Supportive and Collegial, ETC.)Aditya GoyalNo ratings yet
- Geography: (Mains) Question Paper 1988 Paper - IDocument3 pagesGeography: (Mains) Question Paper 1988 Paper - INakka JaswanthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Nur-WPS OfficeDocument11 pagesChapter 16 - Nur-WPS Officemichelle marquezNo ratings yet
- Examination of Nutrition Knowledge, Attitude, and Dietary Behaviors of College Student Vegetarians, Semi-Vegetarians, and Non-VegestariansDocument11 pagesExamination of Nutrition Knowledge, Attitude, and Dietary Behaviors of College Student Vegetarians, Semi-Vegetarians, and Non-VegestariansMeilindaNo ratings yet
- Heating Cable Selection GuideDocument4 pagesHeating Cable Selection Guidehassan3012No ratings yet
- Europump Atex Guide - II-rev2019 1.0Document14 pagesEuropump Atex Guide - II-rev2019 1.0Antonio MakkarovNo ratings yet
- SQLite Pass - Major ChangesDocument12 pagesSQLite Pass - Major ChangesFrancis JSNo ratings yet
- Applied Econ Week 1Document8 pagesApplied Econ Week 1franklinNo ratings yet
- Hammer Mill Troubleshooting GuidelinesDocument2 pagesHammer Mill Troubleshooting GuidelinesbalasridharNo ratings yet
- Shifting SandsDocument7 pagesShifting Sandsapi-306943014No ratings yet
- Free Online Auto Repair Manualhbydr PDFDocument1 pageFree Online Auto Repair Manualhbydr PDFcoachtable3No ratings yet
- Extended Revision Exercises: Algebra: Worksheet 18: Curved GraphsDocument2 pagesExtended Revision Exercises: Algebra: Worksheet 18: Curved Graphsmk hatNo ratings yet
- Criticism of The 2024 Election From The Perspective of The Qur'an, Samarinda-1Document14 pagesCriticism of The 2024 Election From The Perspective of The Qur'an, Samarinda-1KhildaAlfaqirahNo ratings yet
- maxDPUTools A1Document117 pagesmaxDPUTools A1Deepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Second Law Part 2Document10 pagesSecond Law Part 2Sivan RajNo ratings yet