Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2E Mathematical Formulas
Uploaded by
Chaw Wei Heng0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views5 pages2E Mathematical Formulas
Uploaded by
Chaw Wei HengCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
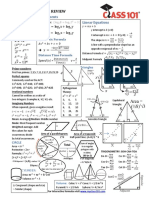
Secondary 2 Mathematical Formulas
Chapter 2: Linear Inequalities
● +¿−¿ ×∨÷ , symbol does not change
● ×∨÷ by a negative number , symbol change
Chapter 3: Expansion and Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions
2 terms :
● Factor out common terms : xy + xy z =xy ( 1+ z )
2 2
2 2
● Special product : x − y =(x− y)(x + y )
3 terms :
● Multiplication Frame
● Special Algebraic Identities ( CHPT 4 )
4 terms :
● Put ∈ groups of 2∧factorise each−group
● ab+ cb=b(a+c )
Chapter 4: Expansion and Factorisation using Special Algebraic Identities
2 2 2
● (a+ b) =a +2 ab+ b
2 2 2
● (a−b) =a −2 ab+ b
2 2
● ( a+ b ) ( a−b )=a −b
Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Graphs
zero product rule :if ab=0 , thena=0∨b=0
Chapter 6: Algebraic Fractions and Formulae
● a−b=−(b−a)
a x
● b = y ∴ ay=bx (cross multiplication)
x
● if y =0 , x=0
2E Mathematical Formula Summary 1
Chapter 7: Direct and Inverse Proportions
● Proportion: y ∝ x , y=kx (k is the constant of proportionality)
k
● Indirect : xy=k , y= x (k isthe constant of proportionality )
Chapter 8: Congruency and Similarity
image
● scale factor : original
2E Mathematical Formula Summary 2
Chapter 9: Pythagoras’ Theorem
2 2 2
● c =a + b ( c is the hypotenuse of triangle )
Chapter 10: Trigonometric Ratios
To find measurement (3sf):
opposite
● tangent = adjacent (TOA)
adjacent
● cosine= hypotenuse (CAH)
opposite
● sine= hypotenuse (SOH)
To find angles – converse of trigonometric ratios (1dp):
● sin A=x , A=( x )
● cos A= y , A=( y )
● tan A=z , A=( z)
Chapter 11: Volume and Surface Area of Pyramids, Cones and Spheres
Pyramids:
1
● Volume= 3 ×base area ×height
● Surface Area=area of base +area of all lateral faces
1 2
● Volume= 3 π r h (cone)
2
● Surface Area=π r + πrl (l is slant height – Pythagoras’ Theorem)
Frustum:
● Volume=vol . of big cone−vol . of small cone
● Surface Area=s . a . of big cone−s . a .of small cone
Sphere:
4 3
● Volume= 3 π r
2
● Surface Area=4 π r
Hemisphere:
2 3
● Volume= 3 π r
2 2
● Surface Area of solid hemisphere=2 π r + π r
2E Mathematical Formula Summary 3
2
● Surface Area of hollow hemisphere=2 π r
Cylinder:
2
● Volume=π r h
2
● Surface Area=2 π r + 2 πrh
2E Mathematical Formula Summary 4
Chapter 12: Probability of Single Events
number of favourable outcomes for event E
● P ( E )= total number of possible outcomes
● P ( not E )=1−P(E)
measure of favourable outcomes for event E
● P ( E )= measure of all posible outcomes
Chapter 14: Averages of Statistical Data
Mean (Average):
● Average=
∑ of data values
number of data values
∑ fx
● x̄= ∑ f ( x is the data value and f is the frequency of data value)
Mode:
● data with highest frequency
Median:
n+1
● Position of median= 2
x +(x+1)
● (if position is x +0.5) median= 2
2E Mathematical Formula Summary 5
You might also like
- Grade 10 Math (Farmulae)Document9 pagesGrade 10 Math (Farmulae)steprhyme93No ratings yet
- Math Formula SheetDocument8 pagesMath Formula SheetHidayah TeacherNo ratings yet
- Math SL Formulae IB PDFDocument9 pagesMath SL Formulae IB PDFluisangeluniNo ratings yet
- Mathematics SL Formula Booklet: Diploma ProgrammeDocument9 pagesMathematics SL Formula Booklet: Diploma ProgrammeidaNo ratings yet
- Formulasheetalgebra 2 TrigDocument4 pagesFormulasheetalgebra 2 Trigapi-265200443No ratings yet
- Northview High School AB Calculus AP Prerequisites PacketDocument11 pagesNorthview High School AB Calculus AP Prerequisites PacketPradyun GREEN CELL VOLUNTEERNo ratings yet
- Math Formulae Class 11Document6 pagesMath Formulae Class 11adhith vaibavNo ratings yet
- MTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 3 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 1.5, 1.6, 2.1, 2.2 and 2.4Document14 pagesMTH4100 Calculus I: Lecture Notes For Week 3 Thomas' Calculus, Sections 1.5, 1.6, 2.1, 2.2 and 2.4Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- MATHS Focus Area Grade 9th and 10th Subject For Entrance ForDocument8 pagesMATHS Focus Area Grade 9th and 10th Subject For Entrance ForLENCHO MAHAMMEDNo ratings yet
- Maths Formulas For Class 10 PDFDocument18 pagesMaths Formulas For Class 10 PDFJivendra Kumar100% (2)
- Pure Maths Revision NoteDocument42 pagesPure Maths Revision NoteJaima Nahin NisheNo ratings yet
- Math H Formula Booklet 2016 WebsiteDocument15 pagesMath H Formula Booklet 2016 WebsiteAmeena LundquistNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document32 pagesLecture 1Chandraveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Algebra 2 TrigDocument4 pagesFormula Sheet Algebra 2 TrigfrancescoabcNo ratings yet
- Formulas PDFDocument8 pagesFormulas PDFSubham Paul100% (1)
- All Maths Formulas Class 10Document54 pagesAll Maths Formulas Class 10Himanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Math 102: Calculus II: in Questions 1-6, Select The Correct Answer. No Justification Is Required (4 Points Each)Document4 pagesMath 102: Calculus II: in Questions 1-6, Select The Correct Answer. No Justification Is Required (4 Points Each)Yousef AlanaziNo ratings yet
- 02 Mathematics PDFDocument30 pages02 Mathematics PDFAvinash SinghNo ratings yet
- Applied Discrete Mathmatics HandoutsDocument420 pagesApplied Discrete Mathmatics HandoutsIkechukwu Octavian AsomughaNo ratings yet
- Dunman High School 2009 Maths D Paper 1Document20 pagesDunman High School 2009 Maths D Paper 1ZeneonNo ratings yet
- Maths FormulaeDocument18 pagesMaths Formulaerishabh_41No ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test: Time: 60 MinutesDocument12 pagesDiagnostic Test: Time: 60 MinutesPreethi VictorNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDFDocument9 pagesVector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDFkavinkumareceNo ratings yet
- Ib Math Applications and Interpretations Summer PacketDocument21 pagesIb Math Applications and Interpretations Summer Packetapi-327140356No ratings yet
- 10th Formulas ListDocument6 pages10th Formulas ListSakshiNo ratings yet
- MGRE Test Unofficial SolutionDocument69 pagesMGRE Test Unofficial SolutionHan JuliaNo ratings yet
- Exam P Formula SheetDocument14 pagesExam P Formula SheetToni Thompson100% (4)
- Purdue MA 166 2018 Final ExamDocument15 pagesPurdue MA 166 2018 Final ExamAndrew SidhuNo ratings yet
- M.phil n2wDocument89 pagesM.phil n2wAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Scientific Computing and Programming Problems PDFDocument103 pagesScientific Computing and Programming Problems PDFandrushkkutzaNo ratings yet
- Final PaperDocument81 pagesFinal PaperRaj RoyNo ratings yet
- Final Revision For GR-10 Ay 21-22Document24 pagesFinal Revision For GR-10 Ay 21-22Sarthak АlurkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter ECCDocument11 pagesChapter ECCIsmail IfakirNo ratings yet
- Math AA SL Booklet 2024Document10 pagesMath AA SL Booklet 2024Diana ReshetnykNo ratings yet
- List of FormulaeDocument4 pagesList of FormulaeMohamed TahmeedNo ratings yet
- 95221Document6 pages95221Anurag YadavNo ratings yet
- Maths Formulas For Class 10 PDFDocument6 pagesMaths Formulas For Class 10 PDFAnmol Jande100% (1)
- Important Quant TipsDocument10 pagesImportant Quant Tipsramesh6989No ratings yet
- MTHS111 Lesson2 2024Document34 pagesMTHS111 Lesson2 2024pearphelokazi45No ratings yet
- Math 11 PreCal STEM Q2-Week 8Document10 pagesMath 11 PreCal STEM Q2-Week 8Jessa Cuanan CaloNo ratings yet
- Q3 Mathematics Peer Tutoring: Students' Advisory BoardDocument93 pagesQ3 Mathematics Peer Tutoring: Students' Advisory BoardKiminiNo ratings yet
- (Practice 4-5) - McGraw-Hill's SAT Subject Test Math-2Document34 pages(Practice 4-5) - McGraw-Hill's SAT Subject Test Math-2Yb Andik Adi CahyonoNo ratings yet
- General Useful Formulae: Complete Study Guide & Notes OnDocument5 pagesGeneral Useful Formulae: Complete Study Guide & Notes OnGauravAroraNo ratings yet
- Important Formulae For CAT: Ratio, Proportion, VariationDocument10 pagesImportant Formulae For CAT: Ratio, Proportion, Variationvenkatakrishnan srinivasanNo ratings yet
- Maths Sat Paper 02 (431102)Document11 pagesMaths Sat Paper 02 (431102)hiNo ratings yet
- 10th STD - Mathematical Formulae - 2Document4 pages10th STD - Mathematical Formulae - 2ambresh.09No ratings yet
- Vector Calculus - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument10 pagesVector Calculus - GATE Study Material in PDFSupriya Santre100% (1)
- Act Math Formulas Interactive 1Document2 pagesAct Math Formulas Interactive 1Isley Quintine YutucNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDF 1Document10 pagesVector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDF 1nazeeraNo ratings yet
- Math Formulas For Class XDocument6 pagesMath Formulas For Class Xravilakra lakraNo ratings yet
- Midterm I - Version B: 1 2 1.5 3 Log NDocument5 pagesMidterm I - Version B: 1 2 1.5 3 Log NNikhil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ah FormulaeDocument5 pagesAh FormulaeVijay RajuNo ratings yet
- GATE Civil 2021 February 10 230PM Converted 1 1Document42 pagesGATE Civil 2021 February 10 230PM Converted 1 1anurag mauryaNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Gre Quant Formulas PDF PRDocument5 pagesToaz - Info Gre Quant Formulas PDF PRPark Min YoungNo ratings yet
- Algebra: X y NC X y N (n+1) A+ BDocument11 pagesAlgebra: X y NC X y N (n+1) A+ BLaissa SerranoNo ratings yet
- Math Formulas From Class 6 To Class 12Document3 pagesMath Formulas From Class 6 To Class 12Rei Misaki100% (1)
- Numerical Methods For CSE Problem Sheet 4: Problem 1. Order of Convergence From Error Recursion (Core Prob-Lem)Document14 pagesNumerical Methods For CSE Problem Sheet 4: Problem 1. Order of Convergence From Error Recursion (Core Prob-Lem)DANIEL ALEJANDRO VARGAS UZURIAGANo ratings yet
- Add Maths NotesDocument98 pagesAdd Maths NotesSriabinaya ChandruNo ratings yet
- Lecture01 HandoutDocument23 pagesLecture01 HandoutYasaman RoudakiNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 Basics A1 LevelDocument303 pagesChapter1 Basics A1 Levelvarshasdm1987100% (1)
- Two Dimensional Co-Ordinate GeometryDocument29 pagesTwo Dimensional Co-Ordinate Geometryshantam777No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 CirclesDocument19 pagesChapter 10 CirclesDileep Kumar RajuNo ratings yet
- Rain of GoldDocument3 pagesRain of GoldCynthia Cortez0% (2)
- Ielts Writing TableDocument2 pagesIelts Writing TableSajid ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Keri Hart Resume - 2016Document2 pagesKeri Hart Resume - 2016api-252395257No ratings yet
- 5 3 Yr9 Linear Equations TestDocument7 pages5 3 Yr9 Linear Equations Testapi-374589174100% (1)
- Barnett Who Goes and Why It MattersDocument16 pagesBarnett Who Goes and Why It MattersEducation JusticeNo ratings yet
- Practice Revision Questions Number SystemsDocument1 pagePractice Revision Questions Number SystemsRavi Prasaath IXNo ratings yet
- Amc2015 Junior PDFDocument7 pagesAmc2015 Junior PDFLe Huu HaiNo ratings yet
- TCS Latest Pattern Questions - 29Document5 pagesTCS Latest Pattern Questions - 29Arnab DasNo ratings yet
- Jennifer Moore ResumeDocument2 pagesJennifer Moore Resumeapi-269293953No ratings yet
- Chapter 33Document9 pagesChapter 33narasimhaNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Methods For AlgebraDocument40 pagesIntermediate Methods For AlgebraAnup SaravanNo ratings yet
- Mesh QualityDocument26 pagesMesh QualityRamesh BammankattiNo ratings yet
- GCB Pbis HandbookDocument21 pagesGCB Pbis Handbookapi-256174152100% (1)
- Operation Word Problems Feb 13thDocument12 pagesOperation Word Problems Feb 13thapi-267315716No ratings yet
- MODULE 7-The Straight LinesDocument18 pagesMODULE 7-The Straight Linesidaman2905No ratings yet
- Test 1-9Document19 pagesTest 1-9Mounira DebibiNo ratings yet
- Dcces Basic SRCDocument21 pagesDcces Basic SRCTimoy CajesNo ratings yet
- Complex Number 1Document25 pagesComplex Number 1pabitra mondalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 - MTH101 IIT KanpurDocument3 pagesLecture 21 - MTH101 IIT KanpurAsish MahapatraNo ratings yet
- Differentiation For TelegramDocument3 pagesDifferentiation For TelegramAkash SNo ratings yet
- Table - Schools by Level, Type, Facilities and Condition, SY 2020 - 2021Document19 pagesTable - Schools by Level, Type, Facilities and Condition, SY 2020 - 2021lenny greciaNo ratings yet
- 4 Circles Take Home QuizDocument5 pages4 Circles Take Home QuizMichael Angelo BunyiNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For MathsDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet For Mathsbobd123No ratings yet
- Hierarchy of Decimal NumbersDocument26 pagesHierarchy of Decimal NumberskunkumabalaNo ratings yet
- Budgeted Lesson in Math CutDocument2 pagesBudgeted Lesson in Math CutWilma Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Math Data BookletDocument14 pagesMath Data Bookletmohammad qassimNo ratings yet
- OlympiadDocument6 pagesOlympiadSukanta MondalNo ratings yet