Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET 2 (Properties of Gases) - Science 10 (4th Quarter)
Uploaded by
cherrymaeregalario20010 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views2 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET 2 (Properties of Gases) - Science 10 (4th Quarter)
Uploaded by
cherrymaeregalario2001Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
SCIENCE 10
Name: __________________________________________ Grade & Section: _________________________ Date: _______________
Properties of Gases & Kinetic Molecular Theory
Objectives
The learners will be able to: Part II.
a. describe the properties and behavior of gases in Kinetic
What you have to do:
Molecular Theory;
b. develop an appreciation of the importance of gases in 1.Blow air into a plastic bag and tie
daily life through oral recitation; and the open end.
c. demonstrate active participation and listening skills by 2.Squeeze and press it gently
asking clarifying questions 3.Observe what happens.
What’s In These students did the same activity described above.
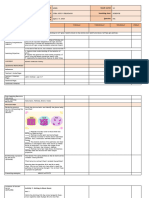
A. In Grade 9, you have a better picture of how the particles Question 2: Which two students describe what they observed?
are arranged in the three phases of matter: solid, liquid and Lito: The plastic bag is filled with air.
gas. Study the models below, then identify the phase being Mario: The plastic bag becomes smaller when squeezed
described. Write your answer answers on a separate sheet of Ana: The plastic bag burst when pressed gently.
paper. Susan: The air particles inside become smaller when the plastic
bag was squeezed.
Answer: ____________________________
https://images.app.goo.gl/jwhWmZgkR9UMPoMa7 Part III.
______1. Particles are very close to each other and move in a What you have to do:
fixed position 1.Spray a very small amount of perfume
______2. Particles are far apart and move freely or cologne into the air.
______3. Particles are able to vibrate about their fixed position. 2.Answer the following:
Thus, attractions between them are very strong.
a. Can you see the particles of perfume
______4. The random motion of the particles and their freedom
or cologne? _______________________
to slide against each other result in weaker forces of attraction. It
b. How did it reach your nose? ____________________________
assumes the shape of the containers. However, the volume is
_____________________________________________________
definite
______5. Particles have very weak forces of attraction between
them and account for their unique properties These students did the same activity described above.
Question 3: Which two students made incorrect interpretations?
Lito: Gas particles move in all directions
What’s New
Mario: Gas particles can spread out in one direction and fill up
Part I. only a limited space
What you have to do: Ana: Gas particles are held together to forces which prevent them
1. Fill your mouth with air. Press your from moving
cheeks with your fingers. Susan: Gases are made up of tiny particles which move around
2. Answer the following questions: all the time.
a. Did air occupy space in your mouth?
________________________________ Answer: ________________________
b. Were you able to press your cheeks
with your fingers? Why?
___________________________________ Note
c. When you pressed one of your cheeks, did you feel the air The following generalizations can be inferred from the three
moving to the other side of your cheek? Explain what activities:
happened. __________________________________________ Gases can be compressed; hence they can occupy a
____________________________________________________ small space.
These students did the same activity described above. Gas particles can spread in any direction.
Question 1: What two students have made INCORRECT Gases are made up of tiny particles that are always
statements? moving.
Lito: Air can be squeezed or compressed When gas particles get hot, they move and spread
Mario: Air particles can be made to fill smaller space faster. Thus, they occupy a larger space
Ana: Air particles become smaller when pressed.
Susan: Air particles decrease in number when pressed.
Answer: __________________________________________
What is It
Activity. Getting to Know Gases
The Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) effectively explains the
behavior of gases. As a product of numerous experiments and Direction: Match the drawing with the correct property of
years of investigations by several scientists, the theory closely gas. Write the letter of the correct answer on the space
conforms to reality. provided.
a. Gases have no definite shape or
The Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) consists of several postulates. volume. A gas's volume refers to the
A. A gas is composed of large number of particles, either space of the container in which its
atoms or molecules. They are so small compared to the distance molecules have
separating them that their own size can be considered negligible. range to move.
Compared to the total gas volume, the particles occupy
negligible volume. A considerable empty space exists between b. Gases are highly compressible
particles. when pressure is applied.
B. Gas particles move randomly in straight line motion and
collide with each other and the container frequently. The force of c. Gases expand when heated and
collisions of the gas particles with the walls of the container contract when cooled.
causes pressure.
C. Collisions of gas molecules are perfectly elastic. This means d. Gases have lower density than other
no energy is lost as friction when molecules collide. states of matter, such as solids and
liquids.
D. Gas particles exhibit almost negligible attractions and
repulsions for each other. The molecules thus, move freely as far
e. Gas particles move randomly and
as space will allow.
spread everywhere, even in spaces
E. The average kinetic energy of gas molecules is directly where other gases are already present.
proportional to the absolute temperature (Kelvin). At the same The spreading out of particles is known
temperature, the molecules of all gases will have the same as diffusion.
average kinetic energy
f. Gas molecules collide with one
The Kinetic Molecular Theory also helps us understand the another and with the walls of the
container.
behavior of gases by describing the motion of gas particles and
their interactions. According to this theory:
Additional Activity
Gas Particles: Gas particles are in constant,
random motion. They move in straight lines Did all the activities give you a better understanding of the
until they collide with each other or the walls properties and behavior of gases based on Kinetic Molecular
of their container. Theory? Congratulations for a job well done!
Volume: Gas particles have negligible volume compared to the
volume of the container they are in. Before you return this module to your teacher, kindly fill out
Collisions: Gas particles undergo elastic collisions, meaning that the Self Rating table adapted from Valdoz (2017). Check the
no energy is lost during collisions. appropriate column where your extent of knowledge falls.
Temperature: The average kinetic energy of gas particles is
directly proportional to the temperature of the gas in Kelvin.
Pressure and Volume: The pressure exerted by a gas is directly
proportional to the number of collisions the gas particles make
with the walls of their container. Similarly, the volume occupied
by a gas is inversely proportional to the pressure exerted on it.
These concepts are fundamental to understanding many aspects
of chemistry and everyday life. The following are some of the
importance of gases in our daily lives such as:
Breathing: Gases like oxygen are crucial for respiration.
We need oxygen to breathe, which is a gas. Without it, we
wouldn't survive.
Cooking: Gases are often used in cooking processes.
When we use a gas stove to cook, we're using natural gas as a
fuel source.
Transportation: Gases power vehicles and transportation systems.
Cars and buses run on gasoline, which is a liquid that turns into
gas when burned.
You might also like
- KMT Module 1 G10Document11 pagesKMT Module 1 G10cedrickjamesarestaNo ratings yet
- SCI10 Q4 MOD1.3 Pages 15 23Document20 pagesSCI10 Q4 MOD1.3 Pages 15 23lotacaracasNo ratings yet
- Q3 - Science 8 - Las2Document10 pagesQ3 - Science 8 - Las2heyyouNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter ModuleDocument36 pages3rd Quarter ModuleDela Cruz AraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Properties of Gases and The Kinetic Molecular Theory of GasesDocument4 pagesLesson 1: Properties of Gases and The Kinetic Molecular Theory of GasesAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Q4-Worksheet-Week 2Document7 pagesQ4-Worksheet-Week 2Gian EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 2 - Week 2 Behavior of Gases Part 2Document20 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 2 - Week 2 Behavior of Gases Part 2Mary Ann100% (1)
- G8 Science Q3 Adm Module For PrintingDocument36 pagesG8 Science Q3 Adm Module For PrintingJenn ElardeNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Act 2Document10 pagesGrade 8 Act 2Charis Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Q4 Science 10 Week2Document3 pagesQ4 Science 10 Week2Edison Caringal50% (2)
- SCIENCE-10 Q4 MOD1 Behavior-of-Gases BookletDocument12 pagesSCIENCE-10 Q4 MOD1 Behavior-of-Gases BookletRetep Aren50% (2)
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET 1 - Science 10Document3 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET 1 - Science 10cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q2 - Wks. 1-2) Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q2 - Wks. 1-2) Kinetic Molecular TheoryJeffrey YumangNo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) Grade 8 Level JHS Quarter: 3 Week 2Document7 pagesSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT) Grade 8 Level JHS Quarter: 3 Week 2Jim Alesther Lapina100% (1)
- 1st Summative Test Matter BEPDocument1 page1st Summative Test Matter BEPZENDLE ANN BARRAMEDANo ratings yet
- SDLP-Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument6 pagesSDLP-Kinetic Molecular TheoryJessica SudioNo ratings yet
- Genchem 2 Module 1 - Kinetic Molecular Model & Intermolecular ForcesDocument20 pagesGenchem 2 Module 1 - Kinetic Molecular Model & Intermolecular ForcesMathew LlabresNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 1: The Particle Nature of MatterDocument20 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module 1: The Particle Nature of MatterLarry SantosNo ratings yet
- ADM GEN - CHEMISTRY 2 Lesson 1Document23 pagesADM GEN - CHEMISTRY 2 Lesson 1EDGAR RIVERANo ratings yet
- Name of Teacher: Mr. Yosong C. Yensya School: Anne's Raquel Hillside NHS Semester: FirstDocument3 pagesName of Teacher: Mr. Yosong C. Yensya School: Anne's Raquel Hillside NHS Semester: FirstJT SaguinNo ratings yet
- ...Document44 pages...Mercy'deth MangaoilNo ratings yet
- The Particle Nature of MatterDocument14 pagesThe Particle Nature of MatterDennis Corton TabingaNo ratings yet
- Chem M8 Behavior of GasesDocument18 pagesChem M8 Behavior of GasesDiana Dealino-Sabandal60% (5)
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT)Document8 pagesSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT)Jim Alesther LapinaNo ratings yet
- Science q3 - m2Document24 pagesScience q3 - m2AlexaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarterly Assessment GP 2Document3 pages3rd Quarterly Assessment GP 2Leonardo PigaNo ratings yet
- Sta. Cruz Learning Center: AtomsDocument7 pagesSta. Cruz Learning Center: AtomsJOLINA ALDIANONo ratings yet
- LP Science g8 q3 Week1 Jan16Document5 pagesLP Science g8 q3 Week1 Jan16Iemmee Jane DinglasanNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem2 Module 1 (Q2)Document16 pagesGen Chem2 Module 1 (Q2)Edgardo RoperezNo ratings yet
- Science 10 q4 Wk2 Las3Document1 pageScience 10 q4 Wk2 Las3RIZALINO DUOMANo ratings yet
- MBHTE-ALMS SCIENCE 8 - Quarter3wk2Document14 pagesMBHTE-ALMS SCIENCE 8 - Quarter3wk2Aisha Manuban100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Science Grade 4Document5 pagesLesson Plan in Science Grade 4Lebemma Dawn GonzalesNo ratings yet
- SCI10 Q4 MOD1.3 WordDocument27 pagesSCI10 Q4 MOD1.3 WordEthan AdrianNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 Q2 Module 1Document16 pagesGen Chem 2 Q2 Module 1VANESSA JABAGATNo ratings yet
- Module 12 Mechanical Properties of MatterDocument31 pagesModule 12 Mechanical Properties of MatterJudy Panguito Aralar50% (2)
- Conformed SCI-8 Quarter3 Module 1Document11 pagesConformed SCI-8 Quarter3 Module 1Thea Marie VilladolidNo ratings yet
- 3RD Quarter AssessmentsDocument6 pages3RD Quarter AssessmentsLorraine DonioNo ratings yet
- Phy Ex. 1.1 SolutionDocument3 pagesPhy Ex. 1.1 SolutionDilip deotaleNo ratings yet
- Science 10 LAS 4.1.1 The Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument3 pagesScience 10 LAS 4.1.1 The Kinetic Molecular TheoryHelma Jabello AriolaNo ratings yet
- Sci10 Q4 Mod1.3Document29 pagesSci10 Q4 Mod1.3Vannie MonderoNo ratings yet
- LP 1 - Behavior of GasesDocument11 pagesLP 1 - Behavior of GasesArjean Ledesma100% (2)
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 1: Behavior of GasesDocument32 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 1: Behavior of GasesJoem Nicodemus Samonte86% (7)
- Gases and The Structure of MatterDocument20 pagesGases and The Structure of MatterJaimeNo ratings yet
- Chem M8 Behavior of GasesDocument19 pagesChem M8 Behavior of GasesGrace MagbooNo ratings yet
- Learning Packet G10Document12 pagesLearning Packet G10• Nate •No ratings yet
- s1 Science Omw1Document38 pagess1 Science Omw1RamChimoriyaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document15 pagesModule 1Tsej IsaacNo ratings yet
- 3RD QUARTER GEN CHem2Document2 pages3RD QUARTER GEN CHem2Ainon SalendabNo ratings yet
- Chem Unit 3 Practice Exam PDFDocument6 pagesChem Unit 3 Practice Exam PDFIsaganiViray100% (1)
- Chem Unit 3 Practice Exam PDFDocument6 pagesChem Unit 3 Practice Exam PDFJo PatrickNo ratings yet
- KMTDocument1 pageKMTAnniecah Jed PacatangNo ratings yet
- 3rd SUMMATIVE TEST Final Na JudDocument4 pages3rd SUMMATIVE TEST Final Na JudCarl Anthony Lague Pahuyo100% (1)
- FINAL SCIENCE 8 (Aswers Key)Document3 pagesFINAL SCIENCE 8 (Aswers Key)Jason EspinasNo ratings yet
- 2324 - F3 - Sci Exam - Final (Roi) - AnsDocument8 pages2324 - F3 - Sci Exam - Final (Roi) - Anslmmlm0505No ratings yet
- MatterDocument2 pagesMatterALEJANDRO CORTEZNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 Q4 SLM4.kenitic MoleculartheoryDocument12 pagesSCIENCE 10 Q4 SLM4.kenitic Moleculartheorysharlenelawig5No ratings yet
- General Physics 2: M V B GDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics 2: M V B GLeonardo PigaNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Science 4 Q3 M5 W5 V2Document13 pagesHybrid Science 4 Q3 M5 W5 V2Jj MendozaNo ratings yet
- The slang of astronomers: A small guide to understand the language of astrophysicistsFrom EverandThe slang of astronomers: A small guide to understand the language of astrophysicistsNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument1 pageScriptcherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Boyle's LawDocument4 pagesBoyle's Lawcherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Module 12 (Prof Ed 16 PT)Document10 pagesModule 12 (Prof Ed 16 PT)cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET 4 (Boyle's Law) - Science 10 (4th Quarter)Document2 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET 4 (Boyle's Law) - Science 10 (4th Quarter)cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Script 2Document2 pagesScript 2cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Regalario, CM.R - M5 - Prof. Ed 16Document6 pagesRegalario, CM.R - M5 - Prof. Ed 16cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Module 14 (Prof Ed 16 PT)Document6 pagesModule 14 (Prof Ed 16 PT)Rosario Trino RagosNo ratings yet
- Module 13 (Prof Ed 16 PT)Document5 pagesModule 13 (Prof Ed 16 PT)cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Module 8 (Prof Ed 16 PT)Document7 pagesModule 8 (Prof Ed 16 PT)cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Regalario, CM.R - M3 - Prof. Ed 13Document4 pagesRegalario, CM.R - M3 - Prof. Ed 13cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Module 10 (Prof Ed 16 PT)Document5 pagesModule 10 (Prof Ed 16 PT)cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- TOS For Science 10 - 3rd Periodic ExamDocument1 pageTOS For Science 10 - 3rd Periodic Examcherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Regalario, CM.R - M4 - Prof. Ed 16Document4 pagesRegalario, CM.R - M4 - Prof. Ed 16cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET 3 (Behavior of Gases) - Science 10 (4th Quarter)Document1 pageLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET 3 (Behavior of Gases) - Science 10 (4th Quarter)cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- The Roles of Hormones - DLP 10Document7 pagesThe Roles of Hormones - DLP 10cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Emissivity Manuscript Revision (Final)Document28 pagesEmissivity Manuscript Revision (Final)Praful PatilNo ratings yet
- Check List: Safety Relays Pnozclassic - PnozsigmaDocument33 pagesCheck List: Safety Relays Pnozclassic - PnozsigmafjcervantesNo ratings yet
- AIR BEARINGS - Review and ApplicationsDocument25 pagesAIR BEARINGS - Review and ApplicationsSubhamMohantyNo ratings yet
- 3.6 Solving Systems of Linear Equations in Three VariablesDocument12 pages3.6 Solving Systems of Linear Equations in Three VariablesBorhan Nordin DaudNo ratings yet
- Maths Project PPT RachitaDocument6 pagesMaths Project PPT RachitaVivek KhatriNo ratings yet
- Venus 001Document21 pagesVenus 001Abinava ChandrikaNo ratings yet
- Maxwell Render 1.6 ManualDocument146 pagesMaxwell Render 1.6 ManualKaren AlvNo ratings yet
- Adsorption by BhanuDocument20 pagesAdsorption by BhanuHiren vaghaniNo ratings yet
- Calculation SheetDocument14 pagesCalculation SheetmohitNo ratings yet
- Economic Framework For Power QualityDocument151 pagesEconomic Framework For Power QualityRalf Alc100% (1)
- Pile Foundations - 1Document33 pagesPile Foundations - 1Teo Peng KeatNo ratings yet
- Russell Et Al - 2007Document9 pagesRussell Et Al - 2007Dori AlexaNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Introduction To Construction Materials and TestingDocument8 pages1.0 Introduction To Construction Materials and TestingPearl Mae AngusNo ratings yet
- ZXM7-SP144 Series: 520W丨525W丨530W丨535W丨540WDocument2 pagesZXM7-SP144 Series: 520W丨525W丨530W丨535W丨540Wandre felipe jaramilloNo ratings yet
- SIM Math 2Document17 pagesSIM Math 2Glen Beltran HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Unit 4Document25 pagesComputer Graphics Unit 4mohiddinmtechNo ratings yet
- HW - Apb - C02Document6 pagesHW - Apb - C02Ngoclinh Vo100% (1)
- P Tran Solution 1Document37 pagesP Tran Solution 1MiguelaTayNo ratings yet
- BimRoad TutorialDocument11 pagesBimRoad Tutorialadera1No ratings yet
- Landau RSTDocument11 pagesLandau RSTpbaculimaNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 - History of NumbersDocument1 pageMod 2 - History of Numbersapi-550214604No ratings yet
- BVAA Valve User Issue 13 PDFDocument88 pagesBVAA Valve User Issue 13 PDFrakacyuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Plant Design DDocument12 pagesChemical Plant Design DFebio DalantaNo ratings yet
- Convection and Its MeaningsDocument2 pagesConvection and Its MeaningsEduard MandingNo ratings yet
- The Origin of Mathematical InductionDocument10 pagesThe Origin of Mathematical Inductionjesusdark44No ratings yet
- Differentiation Revision (2020) : Prepared by T. PondoDocument7 pagesDifferentiation Revision (2020) : Prepared by T. PondoCourteney LungileNo ratings yet
- Bolt ConnectionsDocument36 pagesBolt Connectionsboo hu100% (1)
- Mechanical Properties of Metals - IIDocument33 pagesMechanical Properties of Metals - IIarulmuruguNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanical Model - Student NotesDocument36 pagesQuantum Mechanical Model - Student NotesMuhammad KhanNo ratings yet