Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Uscp Reviewer
Uploaded by
GABRIEL LOUIS GUANO0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesOriginal Title
USCP_REVIEWER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesUscp Reviewer
Uploaded by
GABRIEL LOUIS GUANOCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
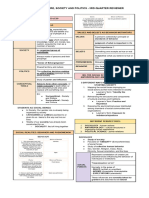
Eugenio, Godfrey D.
12 - Feynman USCP ’23 – ‘24
SOCIETY (DAY 1) IDENTITY AFFAIRS OF THE STATE
- Characteristics that define an
CULTURE, SOCIETY AND individual or shared by a group - Michael Oakeshott
POLITICS - Affairs which do not belong to the state
- Exist in the land of ideas and thoughts
VALUES are not political
- Principle or standards of behavior
- Can’t be seen or touch
- Influence the way we see and BELIEFS DAVID EASTON
experience social beings - Something one accepts as true or real “POLITICS AS THE AUTHORITATIVE
- Held on opinion or conviction
- Have a hold on a phenomenon ALLOCATION OF VALUES IN THE SOCIETY”
- Allows us to form concepts, relate CULTURE To Easton, an allocation of values that is not
them to other concepts, or replace - From the latin word “COLERE” – authoritative is not political and in society. It
means to cultivate
existing ones is in the hands of the state that has the
- Acquired cognitive symbolic aspect or
human existence authority to do such
- SOCIETY – refers to social orgs. of
human life ROBERT DAHL
SOCIAL BEINGS - ASPECTS: “POLITICS ANY ACTIVITY INVOLVING HUMAN
o It is learned – acquired by
BEINGS ASSOCIATED TOGETHER IN
- Categories we possess as individuals being born into a particular
society RELATIONSHIP OF POWER AND AUTHORITY
- Eg: skin color, sex, economic status WHERE CONFLICT OCCURS”
o Symbolic – renders meaning to
- Assigned by the society what people do
- Not natural; socially constructed o Integrated – makes society
work ETHNOCENTRISM
- Shared among domain of relations - apply one's own culture or ethnicity as a
CLAUDE LEVI-STRAUSS frame of reference to judge other
“ANTHROPOLOGY HAS HUMANITY AS ITS ARISTOTLE cultures, practices, behaviors, beliefs,
SUBJECT OF RESEARCH, BUT UNLIKE THE “A HUMAN BEING IS A POLITICAL ANIMAL ; and people, instead of using the
standards of the particular culture
OTHER HUMAN SCIENCE, IT TRIES TO GRASP HE IS NOT HUMAN BUT A BEAST OR A GOD
involved.
ITS OBJECT THROUGH ITS MOST DIVERSE IF HE CAN LIVE OUTSIDE THE STATE”
MANIFESTATIONS”
Eugenio, Godfrey D. 12 - Feynman USCP ’23 – ‘24
SCOPE OF SOCIETY (DAY 2) SOCIOLOGICAL
ANTHROPOLOGY, SOCIOLOGICAL IMAGINATION APPROACHES
SOCIOLOGY AND - an ability to see the context which
shapes your individual decision STRUCTURAL – FUNCTIONAL
POLITICAL SCIENCE making, as well as the decisions made View society as a complex system whose
by others parts work together to promote solidarity
- enables to understand the larger and stability
ANTHROPOLOGY
historical scene in terms of its meaning
- Derived from Anthropos (Human) and
for the inner life and the external
Logos (Though or Reason)
career of a variety of individuals
Accdg. to Robert K. Merton
- enables us to grasp history and 1. MANIFEST FUNCTIONS
biography and the relations between Intended consequences of any social
David Emile Durkheim the two within the society pattern
- Father of all social and - C. Wright Mills
behavioral science
a) TROUBLES (Personal Challenges) 2. LATENT FUNCTIONS
o Occur within the character of the Unrecognized and unintended
SOCIOLOGY individual consequences of any social pattern
- Study of society, social institutions, and o within the range of his immediate
social relationships relations with others
o People have to do with themselves 3. SOCIAL DYSFUNCTION
- Describes and explains human
and with those limited areas of Social pattern that may disrupt the
behavior w/in a social context
social life of which they’re directly operation of society
and personally aware
SOCIAL CONFLICT
POLITICAL SCIENCE b) ISSUES (Larger Social Challenges) Sees society as an arena of inequality that
- associated with how power is gained o Have to do with matters that generates conflict and change
- allied with the GOV’T (ULTIMATE transcend these local
AUTHORITY) environments of the individual
and the range of his inner life SYMBOLIC-INTERACTION
- knowledge derived from experiment
and observation o They have to do with the Sees society as the product of the
organization of many such milieux everyday interactions of individual
overlap and interpenetrate to form
the larger structure of social and MACRO MICRO
historical life broad focus on social close-up focus on
o Poverty, Overpopulation, structures that shape social interaction in a
Unemployment society as a whole specific situation
You might also like
- Ucsp Reviewer 3RD QuarterDocument6 pagesUcsp Reviewer 3RD QuarterKi - ShiNo ratings yet
- DAISS (2nd Grading) Finals ReviewerDocument3 pagesDAISS (2nd Grading) Finals ReviewerYsa ToledoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2, The Self From Sociological PerspectivesDocument3 pagesLesson 2, The Self From Sociological PerspectivesElisa Landingin100% (1)
- USCP NotesDocument4 pagesUSCP NotesHoney SevillaNo ratings yet
- UCSPDocument2 pagesUCSPDiane Nicole EncisoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For UCSPDocument8 pagesReviewer For UCSPAlyssa MirandaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Sociological Perspectives of The Self: EngageDocument7 pagesUnit 2: Sociological Perspectives of The Self: EngageElly John ReliquiasNo ratings yet
- Ucsp NotesDocument7 pagesUcsp NotesMin VictorinoNo ratings yet
- UCSPDocument3 pagesUCSPCaselyn Magat BuzonNo ratings yet
- Sociality-Defined by The Very Categories That We Possess TheDocument2 pagesSociality-Defined by The Very Categories That We Possess TheRouland Ross Anthony B. CeynasNo ratings yet
- M3 Lecture NotesDocument1 pageM3 Lecture NotescoookiecookiecoookieNo ratings yet
- M3 Lecture NotesDocument1 pageM3 Lecture NotescoookiecookiecoookieNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhilosophyDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Philosophyjoyce dionglayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Nature, Goals, and Perspectives in Anthropology, Sociology and Political ScienceDocument14 pagesLesson 1: Nature, Goals, and Perspectives in Anthropology, Sociology and Political ScienceAya GasparNo ratings yet
- Education Sexuality Government & Politics Deviant Behaviors Gender Religion Health/Mental Health Crime Economy Laws Race & CultureDocument3 pagesEducation Sexuality Government & Politics Deviant Behaviors Gender Religion Health/Mental Health Crime Economy Laws Race & Culture21bbxoNo ratings yet
- PHILOSOPHY Reviewer 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesPHILOSOPHY Reviewer 2nd Quarterselwyn duroNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self Notes PDFDocument6 pagesUnderstanding The Self Notes PDFThrisha Joy JuanicoNo ratings yet
- UCSP RealDocument14 pagesUCSP RealhyuhNo ratings yet
- UCSP ReviewerDocument6 pagesUCSP ReviewerJoemerson GuiwanNo ratings yet
- Share Grade 12 (Abm)Document23 pagesShare Grade 12 (Abm)JioNo ratings yet
- Prelims ReviewerDocument24 pagesPrelims ReviewerGERLAINE GAYLE OFEMIANo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: SociologicalDocument38 pagesLesson 2: SociologicalNiziU MaraNo ratings yet
- Ideologies. Culture and Its Social StructureDocument6 pagesIdeologies. Culture and Its Social StructureCalapati, Jhon Rovic R.No ratings yet
- Philosophy ReviewerDocument3 pagesPhilosophy ReviewerJehyne CataluñaNo ratings yet
- Uts Lesson 2Document3 pagesUts Lesson 2kotarobokuto58No ratings yet
- Ucsp Reviewer PrelimsDocument8 pagesUcsp Reviewer Prelimseunicefhaye26No ratings yet
- REVIWEIJIFWIFFEHEFDocument19 pagesREVIWEIJIFWIFFEHEFMargaretteNo ratings yet
- Ucsp ReviewerDocument3 pagesUcsp Reviewerselwyn duroNo ratings yet
- Intensive Review DissDocument3 pagesIntensive Review DissjulzhaideNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Sociology - MidtermsDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Sociology - MidtermsNorielle PonolleraNo ratings yet
- UCSPDocument10 pagesUCSPJasmine Quintana MontemayorNo ratings yet
- (Ucsp - Notes) Sociology, Anthropology, Political ScienceDocument3 pages(Ucsp - Notes) Sociology, Anthropology, Political ScienceMomoNo ratings yet
- SociologyDocument6 pagesSociologyFelice GiulianaNo ratings yet
- Disciplines and Ideas in Social Sciences ReviewerDocument9 pagesDisciplines and Ideas in Social Sciences ReviewerDior EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Uscp ReviewerDocument6 pagesUscp ReviewerArmel BarayugaNo ratings yet
- UCSP 2nd SemDocument12 pagesUCSP 2nd SemkrizhajulaoNo ratings yet
- UCSPDocument10 pagesUCSPkrizhajulaoNo ratings yet
- Cesc 12Document7 pagesCesc 12HANZEL JUDE PIMENTELNo ratings yet
- Sociolgical Imagination & PerpsectiveDocument3 pagesSociolgical Imagination & Perpsectivenicole faye sacayNo ratings yet
- Why Study UCSP?: Various Aspect of Social and Political LifeDocument10 pagesWhy Study UCSP?: Various Aspect of Social and Political LifeHanna0% (1)
- UCSPDocument4 pagesUCSPsydney barcelonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in UcspDocument5 pagesReviewer in UcspEdwin Garcia AbarrientosNo ratings yet
- Ucsp No HighlightDocument11 pagesUcsp No HighlightCAMILLE JELLA ALZOLANo ratings yet
- The Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesDocument24 pagesThe Polytechnic University of The Philippineslolo mopanotNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society and PoliticsSamuel LuNo ratings yet
- PHILOREVIEWERDocument2 pagesPHILOREVIEWERDanielle RochaNo ratings yet
- UCSP ReviewerDocument10 pagesUCSP ReviewerTisha ArtagameNo ratings yet
- UCSP WEEK 1 4.bnikkkiDocument12 pagesUCSP WEEK 1 4.bnikkkiNikki MahinayNo ratings yet
- C1 Intro To CultureDocument20 pagesC1 Intro To CultureYong ZhenNo ratings yet
- LESSON 12 Social StratificationDocument12 pagesLESSON 12 Social StratificationIan Vergel CuevasNo ratings yet
- Sociological Imagination. London: Bloomsbury Academic, 2018. 7-18. Bloomsbury CollectionsDocument13 pagesSociological Imagination. London: Bloomsbury Academic, 2018. 7-18. Bloomsbury Collectionsaulia rahmahNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocument11 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society and PoliticsGrim ReaperNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 FinalDocument3 pagesChapter 1 FinalAllen Simon BaulaNo ratings yet
- UCSP NOTES First SemesterDocument18 pagesUCSP NOTES First SemesterBunnyfuschiaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2-4: What Is PoliticsDocument9 pagesWEEK 2-4: What Is PoliticsQueenie RubioNo ratings yet
- Social Science ReviewerDocument46 pagesSocial Science ReviewerNJ Nicole GuardaNo ratings yet
- UCSP Module 7 HERNANDEZ, MARK ANTHONY A.Document7 pagesUCSP Module 7 HERNANDEZ, MARK ANTHONY A.Krammy HernandezNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society, and PoliticsDocument65 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society, and PoliticsArvin Jhosua RiveraNo ratings yet
- Anthropology Sociology and Political ScienceDocument32 pagesAnthropology Sociology and Political ScienceSamantha Collyn GomezNo ratings yet
- Emile Durkheim: Summarized Classics: SUMMARIZED CLASSICSFrom EverandEmile Durkheim: Summarized Classics: SUMMARIZED CLASSICSNo ratings yet
- PermitDocument1 pagePermitGABRIEL LOUIS GUANONo ratings yet
- Attendance SheetDocument12 pagesAttendance SheetGABRIEL LOUIS GUANONo ratings yet
- Ang Sihay Screening ResultsDocument1 pageAng Sihay Screening ResultsGABRIEL LOUIS GUANONo ratings yet
- Peer Evaluation For Completed Research Projects 2024Document2 pagesPeer Evaluation For Completed Research Projects 2024GABRIEL LOUIS GUANONo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0022460X23006259 MainDocument17 pages1 s2.0 S0022460X23006259 MainGABRIEL LOUIS GUANONo ratings yet
- DSPC Mock Simulation Fact SheetsDocument5 pagesDSPC Mock Simulation Fact SheetsGABRIEL LOUIS GUANONo ratings yet
- Week 7 Social ControlDocument17 pagesWeek 7 Social ControlGABRIEL LOUIS GUANONo ratings yet
- Q2 PracresDocument14 pagesQ2 PracresGABRIEL LOUIS GUANONo ratings yet
- Q2 Genbio 1 1Document9 pagesQ2 Genbio 1 1GABRIEL LOUIS GUANONo ratings yet
- Notes On Data Privacy ActDocument6 pagesNotes On Data Privacy ActRad IsnaniNo ratings yet
- ! Under Two Flags Heinz WeichardtDocument33 pages! Under Two Flags Heinz WeichardtquikjipNo ratings yet
- Napoleon QuestionsDocument4 pagesNapoleon QuestionsValerie Angel MtemaNo ratings yet
- Carbado, Crenshaw, Mays & Tomlinson (2013) IntersectionalityDocument11 pagesCarbado, Crenshaw, Mays & Tomlinson (2013) IntersectionalitySolSomozaNo ratings yet
- Globalization and Prospects of The World Society - SzentesDocument16 pagesGlobalization and Prospects of The World Society - SzentesVincent Hansheng LiNo ratings yet
- Common Law Lien FormatDocument5 pagesCommon Law Lien FormatRevdrAnnie MantzNo ratings yet
- Civil Military RelationsDocument2 pagesCivil Military RelationsSunaina ZakiNo ratings yet
- Tabangao Shell V Pilipinas ShellDocument3 pagesTabangao Shell V Pilipinas ShellmeriiNo ratings yet
- In The High Court of Kerala at ErnakulamDocument7 pagesIn The High Court of Kerala at Ernakulamrkaran22No ratings yet
- SF2 AutomaticDocument26 pagesSF2 AutomaticAnonymous lGEWq3jjNENo ratings yet
- (Applause (Signs The Document) : I Will Now Read The Dispositive Portion of This DecreeDocument1 page(Applause (Signs The Document) : I Will Now Read The Dispositive Portion of This DecreeAvi AlonzoNo ratings yet
- A Flapper's Appeal To Parents Ellen Welles PageDocument13 pagesA Flapper's Appeal To Parents Ellen Welles PageAlejandra Ruiz GuerraNo ratings yet
- Gram Nyayalaya Act 2008Document2 pagesGram Nyayalaya Act 2008pooja.ahluwalia316No ratings yet
- Shelley, Louise. "Blood Money." Foreign Affairs. 21 Feb. 2018. Web. 21 Feb. 2018)Document3 pagesShelley, Louise. "Blood Money." Foreign Affairs. 21 Feb. 2018. Web. 21 Feb. 2018)chrisNo ratings yet
- People of The Philippines vs. Edison Sucro (G.r. No. 93239 March 18, 1991)Document2 pagesPeople of The Philippines vs. Edison Sucro (G.r. No. 93239 March 18, 1991)Ei BinNo ratings yet
- Ra 876Document1 pageRa 876정정No ratings yet
- Case Digest 2-4Document7 pagesCase Digest 2-4Patricia Ann Sarabia ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Cojuangco, Jr. vs. Presidential Commission On Good Gov't.Document37 pagesCojuangco, Jr. vs. Presidential Commission On Good Gov't.Rustom IbañezNo ratings yet
- Federal BureaucracyDocument25 pagesFederal BureaucracyPeped100% (3)
- Community Based Corrections 8th Edition PDFDocument2 pagesCommunity Based Corrections 8th Edition PDFBecky0% (2)
- Accused Who Has Been Acquitted - Discharged Has Right To Live With Dignity - Karnataka HC Directs For Party's Name To Be Masked in Court's Digital RecordsDocument6 pagesAccused Who Has Been Acquitted - Discharged Has Right To Live With Dignity - Karnataka HC Directs For Party's Name To Be Masked in Court's Digital RecordsPrasad VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Cass Sunstein - Constitutions and Democracies An EpilogueDocument30 pagesCass Sunstein - Constitutions and Democracies An EpilogueMilos JankovicNo ratings yet
- Website DuFord CVDocument6 pagesWebsite DuFord CVrduford1No ratings yet
- Rajni Kothari Made HistoryDocument2 pagesRajni Kothari Made HistoryMehar ChandNo ratings yet
- Digest People v. MonerDocument5 pagesDigest People v. Monerclarisse75% (4)
- RB Baker-Miron Charter Revenue PDFDocument56 pagesRB Baker-Miron Charter Revenue PDFNational Education Policy CenterNo ratings yet
- Peole Vs Antonio Z. Oanis and Alberto Galanta G.R. No. L-47722Document2 pagesPeole Vs Antonio Z. Oanis and Alberto Galanta G.R. No. L-47722Jen DioknoNo ratings yet
- Media Intrusion TheoryDocument4 pagesMedia Intrusion TheorySalman Awan100% (3)
- Cooperatives in The Socio Economic Development of The PhilippinesDocument14 pagesCooperatives in The Socio Economic Development of The PhilippinesyenNo ratings yet
- Butina Bond OppositionDocument22 pagesButina Bond Oppositionmary engNo ratings yet