Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grade 9 Pointers To Review For 4TH Grading Finals
Uploaded by
Sammy ElliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade 9 Pointers To Review For 4TH Grading Finals
Uploaded by
Sammy ElliCopyright:
Available Formats
GRADE 9 POINTERS TO REVIEW FOR 4TH GRADING FINALS
SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY
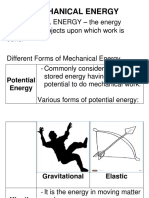
MECHANICAL ENERGY
Is the energy associated with motion.
All objects with the potential to move have mechanical energy.
2 types of Mechanical Energy
1. Kinetic Energy – is the mechanical energy that is being used in the form of motion.
2. Potential Energy – is the mechanical energy that is stored in objects with potential to move.
POTENTIAL ENERGY
2 Types
GRAVITATIONAL ELASTIC POTENTIAL ENERGY
POTENTIAL
ENERGY - is the energy associated with an object’s
- Is the energy associated with an object’s potential potential to move due to deformations
to move due to its position from the ground. in an elastic object.
- It is measured in Joules or J as a unit for energy - It is measured in Joules or J as a unit for energy
FORMULA in Solving Gravitational Potential Energy FORMULA in Solving Elastic Potential Energy
PEgravity = mgh PEelastic = ½ kx2
Where: Where:
PEgravity = gravitational potential energy of an object in PEelastic = elastic potential energy
reference to the ground K= force constant of the spring
m = mass of the object X = length of deformation ( compression or
g= 9.8 m/s2 stretching )
h = height of the object from the ground
KINETIC ENERGY
- Is the mechanical energy associated with motion.
- Fast-moving objects have greater kinetic energy. Objects that have greater mass have greater kinetic energy.
FORMULA in Solving Kinetic Energy
KE = 1/2mv2
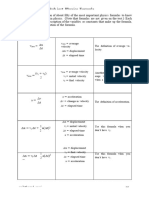
Conservation of Mechanical Energy – energy cannot be created nor destroyed. It can only be converted
from one form to another.
FORMULA in Solving Final Kinetic Energy FORMULA in Solving Final Speed
2
mghinitial – mghfinal = KEfinal ½ m (vinitial) √ 2 KE final = vfinal
m
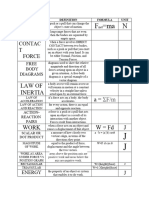
MOMENTUM IMPULSE
- Is the inertia of an object in motion. It - describes how much an
describes how hard it is to stop an object from moving. object has changed
its momentum
FORMULA in Solving Momentum FORMULA in Solving Impulse
p=mv J = mvfinal - mvinitial
where: where:
p= momentum of an object J = impulse of the object
m= mass of an object mv final = final momentum
v= velocity of an object mv initial = initial momentum
IMPULSE-MOMENTUM THEOREM
FORMULA in Solving Force in FORMULA in Solving Final Velocity in
impulse and momentum theorem impulse and momentum theorem
mvfinal - mvinitial Ft + mvinitial
F= = V final
T m
You might also like
- Science Midterm ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience Midterm ReviewerRoseNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy andDocument3 pagesWork, Energy andKyla Mari ValduezaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PhysicsDocument6 pagesReviewer Physicsunknownberries.1No ratings yet
- PHYSICS HandoutDocument2 pagesPHYSICS Handoutjeazelmarzo242No ratings yet
- Advanced Mechanism Design (Ue19Me544) : Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Conservation of EnergyDocument1 pageAdvanced Mechanism Design (Ue19Me544) : Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Conservation of EnergySyed Hafeez Peeran QuadriNo ratings yet
- Kitab Fizik 2016 (Eng)Document20 pagesKitab Fizik 2016 (Eng)Rosmini Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Science Fourth QuarterDocument7 pagesScience Fourth Quarteraarviecaingcoy533No ratings yet
- Pdfa2 13Document1 pagePdfa2 13aizatNo ratings yet
- Physics Nmat ReviewerDocument7 pagesPhysics Nmat ReviewerLeanna DaneNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Work Energy PowerDocument68 pagesWeek 5 Work Energy PowerShare linkNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Science Exams Term 1 Cycle 2 SY 2022 2023Document5 pagesReviewer For Science Exams Term 1 Cycle 2 SY 2022 2023competition.sugiyama1002No ratings yet
- Week 5 Work Energy PowerDocument67 pagesWeek 5 Work Energy PowerRizky Ardias DarmawanNo ratings yet
- 5 Work Energy PowerDocument11 pages5 Work Energy Powermuhammad abdullah javedNo ratings yet
- BSS IX, Handout Final TermDocument31 pagesBSS IX, Handout Final Termrehans.6857No ratings yet
- Mechanical Energy IMsDocument5 pagesMechanical Energy IMsRaymond MimayNo ratings yet
- GenPhysics 1Document4 pagesGenPhysics 1Mary Harry Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- HSC Physics Module 2: DynamicsDocument11 pagesHSC Physics Module 2: DynamicswillNo ratings yet
- Revision-Map Chapter 10Document1 pageRevision-Map Chapter 10Megha BishtNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS SPM DICTIONARY@alinaimanaarif PDFDocument25 pagesPHYSICS SPM DICTIONARY@alinaimanaarif PDFAzrul AkmarNo ratings yet
- Physics Learning JournalDocument17 pagesPhysics Learning JournalMiguel Carlos AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Roller Coaster ProjectDocument35 pagesRoller Coaster ProjectVanitta RangsitananNo ratings yet
- What Is PhysicsDocument5 pagesWhat Is PhysicswatermelonNo ratings yet
- Physics Reviewer 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesPhysics Reviewer 2nd QuarterCardinal RagerNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument6 pagesEnergyChristina LuluquisinNo ratings yet
- Physics Topic 2 Study GuideDocument7 pagesPhysics Topic 2 Study GuideSai 0235No ratings yet
- Work Power Energy: Mathematical Expression Forms of EnergyDocument1 pageWork Power Energy: Mathematical Expression Forms of EnergyRavi BNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics PDFDocument336 pagesFluid Mechanics PDFVinay V GowdaNo ratings yet
- Physics Reference PDFDocument12 pagesPhysics Reference PDFRonald Chester LorenzanaNo ratings yet
- IS - Reviewer 3 - General PhysicsDocument3 pagesIS - Reviewer 3 - General Physicsajuj jerNo ratings yet
- Forces and MotionDocument23 pagesForces and MotionIza Natasha AzaharNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and PowerDocument44 pagesWork Energy and PowerBea OquendoNo ratings yet
- (Encyclopedia of Energy Series) Robert U Ayres, Robert Costanza, Jose Goldemberg, Marija D Ilic, Eberhard Jochem, Robert Kaufmann, Amory B Lovins, Mohan Munasinghe, R K Pachauri, Claudia Sheinbaum Par (1).pdfDocument802 pages(Encyclopedia of Energy Series) Robert U Ayres, Robert Costanza, Jose Goldemberg, Marija D Ilic, Eberhard Jochem, Robert Kaufmann, Amory B Lovins, Mohan Munasinghe, R K Pachauri, Claudia Sheinbaum Par (1).pdfAshchrisNo ratings yet
- Forces, Vectors, Work, Energy, PowerDocument43 pagesForces, Vectors, Work, Energy, Poweranwar9602020100% (1)
- Quiz 3 (Ch.5) : y MG PEDocument3 pagesQuiz 3 (Ch.5) : y MG PEbat.laughNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Mechanical Energy: Potential and Kinetic EnergyDocument51 pagesConservation of Mechanical Energy: Potential and Kinetic EnergyJet TejadaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic and Potential EnergyDocument4 pagesKinetic and Potential Energyapi-150547803No ratings yet
- Physics ReviewerDocument5 pagesPhysics ReviewerJohnny TestNo ratings yet
- Physics A LevelDocument38 pagesPhysics A LevelThoon Nadi NaiNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Work Energy Power and MomentumDocument3 pages2.3 Work Energy Power and MomentumEjaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Physics ReviewerDocument4 pagesPhysics ReviewerROEB AIREE MUEGANo ratings yet
- F4C2 ForcesMotionDocument9 pagesF4C2 ForcesMotionHeng Pei XianNo ratings yet
- Phy 311 Unit 2 - Chap 16-17Document25 pagesPhy 311 Unit 2 - Chap 16-17Alex William JohnNo ratings yet
- General Physics ReviewerDocument15 pagesGeneral Physics ReviewerArviNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Kinetic and Gravitational Potential EnergyDocument20 pagesLesson 1 - Kinetic and Gravitational Potential EnergyMouli MishraNo ratings yet
- Ch7 LectureDocument24 pagesCh7 Lectureecem avcıNo ratings yet
- General Physics PrefinalsDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics PrefinalssarmientojoonsunNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument5 pagesScience ReviewerShanella Andrea TayagNo ratings yet
- Energy - : VocabularyDocument13 pagesEnergy - : Vocabularyrumbi16No ratings yet
- Energy IIDocument6 pagesEnergy IIbat.laughNo ratings yet
- Facts and Formulas 3 RefDocument13 pagesFacts and Formulas 3 Refrania deifNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy - Chapter NotesDocument3 pagesWork and Energy - Chapter NotesAthar ShaikhNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument1 pageScienceChaela ApplebyNo ratings yet
- Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy: E U + K E Mechanical EnergyDocument1 pagePotential Energy and Conservation of Energy: E U + K E Mechanical EnergyBellay KaleesiyNo ratings yet
- Dynamics and MomentumDocument4 pagesDynamics and MomentummustafaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic EnergyDocument3 pagesKinetic Energyleon08jayNo ratings yet
- C3 Momentum & ImpulseDocument1 pageC3 Momentum & ImpulsePriyaa JayasankarNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy - NotesDocument20 pagesWork and Energy - NotesNaman VatsNo ratings yet
- Potential Energy vs. Kinetic Energy - Physics Made Simple - 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPotential Energy vs. Kinetic Energy - Physics Made Simple - 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger (Parallel and Counter Flow)Document5 pagesHeat Exchanger (Parallel and Counter Flow)ommech2020100% (1)
- (YARIV) - Photonics - Optical Electronics in Modern Communications PDFDocument849 pages(YARIV) - Photonics - Optical Electronics in Modern Communications PDFAnonymous GRf0uG90% (21)
- Be Summer 2020Document2 pagesBe Summer 2020dhruvNo ratings yet
- 3M 2820-2821-2822 Data SheetDocument2 pages3M 2820-2821-2822 Data SheetMichael TadrosNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument5 pagesUntitled DocumentIshaan PuriNo ratings yet
- Cape Physics 2008 Unit 1Document10 pagesCape Physics 2008 Unit 1kesnaNo ratings yet
- Kinematic QuestionsDocument2 pagesKinematic QuestionsFirmansyahFandiNo ratings yet
- Free and Forced Convection Lab ReportDocument17 pagesFree and Forced Convection Lab ReportKamal GamalNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 1-General Introduction To SpectrosDocument3 pagesExercise Chapter 1-General Introduction To Spectrosejips2No ratings yet
- Lecture (1 1)Document11 pagesLecture (1 1)mustafa alasadyNo ratings yet
- L3 Impulse and MomentumDocument82 pagesL3 Impulse and MomentumappleNo ratings yet
- I Inteference Diffraction MCQDocument24 pagesI Inteference Diffraction MCQPuneet Kumar Trivedi0% (2)
- Ch7 - 3 Antennas3Document20 pagesCh7 - 3 Antennas3MasterArvinNo ratings yet
- DOM MCQ (1-6) - RevisedDocument112 pagesDOM MCQ (1-6) - RevisedSAURAV KOULNo ratings yet
- Heat Chap05 043Document28 pagesHeat Chap05 043Kerem GönceNo ratings yet
- Constrained Motion Question Bank 01 PDFDocument14 pagesConstrained Motion Question Bank 01 PDFPradeepvenugopalNo ratings yet
- Upcat Reviewer PhysicsDocument7 pagesUpcat Reviewer PhysicsRogelio EscobarNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - Physics (Question Bank) - Dual Natutre of Matter and Radiation (Subj) - 04.02.2022Document4 pagesClass Xii - Physics (Question Bank) - Dual Natutre of Matter and Radiation (Subj) - 04.02.2022Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Radiation Exchange Between Surfaces: 1.1 Motivation and ObjectivesDocument22 pagesRadiation Exchange Between Surfaces: 1.1 Motivation and ObjectivesMiguel OcampoNo ratings yet
- Figure-1: Second Exercise: Horizontal Elastic Oscillator (7 PTS)Document6 pagesFigure-1: Second Exercise: Horizontal Elastic Oscillator (7 PTS)Ali RammalNo ratings yet
- XI-Chemistry Chapter Test-2-Atomic Structure-SolutionsDocument4 pagesXI-Chemistry Chapter Test-2-Atomic Structure-Solutionswaseem chauhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 7Document12 pagesChemistry Chapter 7Heather KieferNo ratings yet
- 6 2nd Quarter Module 1 Activity UV X and Gamma RaysDocument2 pages6 2nd Quarter Module 1 Activity UV X and Gamma RaysAriel RemultaNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review in General Physics 1Document1 pagePointers To Review in General Physics 1Clay 13No ratings yet
- Chem1020 Chapter2a Feb15Document93 pagesChem1020 Chapter2a Feb15Celeste SanchezNo ratings yet
- Past Paper Physics 1st Year BISE Lahore 2009Document5 pagesPast Paper Physics 1st Year BISE Lahore 2009Mian EjazNo ratings yet
- RadiationDocument30 pagesRadiationGadis PodehNo ratings yet
- A Wavefront Is The Locus of Points (Wavelets) Having The Same Phase of Oscillations. WavefrontDocument11 pagesA Wavefront Is The Locus of Points (Wavelets) Having The Same Phase of Oscillations. WavefronthareeshNo ratings yet
- 18PYB101JDocument4 pages18PYB101JPERIYASAMY BALAMOORTHYNo ratings yet
- 02 Dispersive Power of A PrismDocument7 pages02 Dispersive Power of A PrismDHARANYA SNo ratings yet