Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L8 Photosynthesis What Is in A Leaf
Uploaded by
Victoria WarrenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
L8 Photosynthesis What Is in A Leaf
Uploaded by
Victoria WarrenCopyright:
Available Formats
Photosynthesis: What’s in a Leaf?
What is the relationship between structure and function in a leaf?
Why?
What would the world be like without leaves—no grass for ball fields, no beautiful landscaping? It would
also mean no oxygen for animals and no food for heterotrophs. Leaves are like living machines that recycle
the carbon and oxygen in our environment. This process, driven by the sun’s energy, allows for a constant
supply of oxygen and food for the inhabitants of Earth.
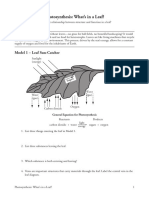
Model 1 – Leaf Sun-Catcher
Sunlight
(energy)
Water
(liquid)
rs
Suga
Water
Water (gas)
(gas)
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
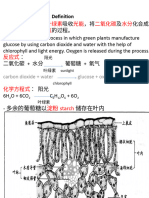
General Equation for Photosynthesis
Reactants Products
light
carbon dioxide + water energy
⎯⎯→ sugars + oxygen
1. List three things entering the leaf in Model 1.
2. List three substances leaving the leaf.
3. Which substance is both entering and leaving?
4. Veins are important structures that carry materials through the leaf. Label the central vein in the
leaf diagram.
Photosynthesis: What’s in a Leaf? 1
5. How is the substance you identified in Question 3 changed between its entry and its exit?
6. Use the general equation for photosynthesis and Model 1 to answer the following questions.
a. What are the reactants for photosynthesis?
b. Where do these reactants enter the leaf?
c. What are the products of photosynthesis?
d. From where do the products leave the leaf?
7. Categorize all the components involved in photosynthesis as either matter or energy.
Model 2 – Cross Section of the Internal Structure of a Leaf
Cuticle
Upper epidermis
Chloroplast
Palisade mesophyll
Vein
Air Space
Spongy mesophyll
Lower epidermis
Cuticle
Guard cell Stoma
8. List the layers of the leaf starting at the upper cuticle all the way to the lower cuticle.
2 POGIL™ Activities for High School Biology
You might also like
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS-Student Worksheet (With Answers)Document8 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS-Student Worksheet (With Answers)Daniella Gabrielle Gerodias50% (10)
- Photosynthesis-What's in A LeafDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesis-What's in A LeafMarvellousNo ratings yet
- Combined Science NotesDocument61 pagesCombined Science NotesShawn ChimbwandaNo ratings yet
- Energy For All!: Engage: Food For CornDocument4 pagesEnergy For All!: Engage: Food For CornBri LavaeNo ratings yet
- Stellite 6 Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesStellite 6 Datasheet PDFEswaran100% (1)
- 2 Photosynthesis-Whats in A Leaf-SDocument6 pages2 Photosynthesis-Whats in A Leaf-Sapi-356824125100% (2)
- Biology Folio Photosynthesis)Document22 pagesBiology Folio Photosynthesis)Nursakinah Najwah100% (1)
- Photosynthesis Mastery BookletDocument18 pagesPhotosynthesis Mastery Bookletapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Topic 7: Photosynthesis and FoodDocument73 pagesTopic 7: Photosynthesis and FoodMadhavi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants: Negros Oriental State UniversityDocument18 pagesRespiration in Plants: Negros Oriental State UniversityGenelie Abuzo CadayonaNo ratings yet
- Science: Mahay Integrated Secondary SchoolDocument8 pagesScience: Mahay Integrated Secondary Schoollavenia acdalNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Module 7 S9LT-Ig-j-31: PhotosynthesisDocument9 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 7 S9LT-Ig-j-31: PhotosynthesisJulia Clarisse Alanza BallonNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis OFFICIALDocument36 pagesPhotosynthesis OFFICIALAsawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- Science9 Q1 WK8Document4 pagesScience9 Q1 WK8jerzelpauloNo ratings yet
- Final Review Package NotesDocument26 pagesFinal Review Package Notesalaa husseinNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Study GuideDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis Study GuideLynda BarrowNo ratings yet
- 1Document4 pages1SashankNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Revision Notes Prd58wDocument5 pagesTopic 6 Revision Notes Prd58wSeve ReyesNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Thesis StatementDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis Thesis Statementdwham6h1100% (3)
- Plant NutritionDocument43 pagesPlant NutritionSubaashNairNo ratings yet
- Advanced Biology: PhotosynthesisDocument31 pagesAdvanced Biology: Photosynthesiszorbax100% (2)
- Photosynthesis: Leaf StructureDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis: Leaf StructureMonica Sario PolicinaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationNikki RØA0% (1)
- Lesson 12Document21 pagesLesson 12Swastik Singh 8A 30No ratings yet
- Phototrophic PDFDocument17 pagesPhototrophic PDFxubrylleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhotosynthesisDocument33 pagesIntroduction To PhotosynthesisKlara EmperadoNo ratings yet
- Structure of A LeafDocument82 pagesStructure of A Leaflevie agacerNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis-and-Cellular-Respiration PrintDocument10 pagesPhotosynthesis-and-Cellular-Respiration PrintJustine FloresNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument36 pagesLife Processes2erwr100% (1)
- CHAPTER 10 Plants&Food REVIEW QUESTION AnswersDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 10 Plants&Food REVIEW QUESTION AnswersMostafa A MansiNo ratings yet
- FB2 Energy in Biology 2021 - 22Document32 pagesFB2 Energy in Biology 2021 - 22Vu Nguyen LENo ratings yet
- 植物的营养Document51 pages植物的营养2375606245No ratings yet
- Notes ON PLANT NUTITION FOR GR 9Document5 pagesNotes ON PLANT NUTITION FOR GR 9PranatiNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 NotesDocument52 pagesBio 1 NotesTadala NsaliwaNo ratings yet
- 5.1.2 Final Exam - Semester 2 Exam (Test)Document20 pages5.1.2 Final Exam - Semester 2 Exam (Test)joonseo81No ratings yet
- Structureoftheleaf Complete LessonDocument28 pagesStructureoftheleaf Complete Lessonjerylle25No ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEM: Life Energy: What I Need To KnowDocument16 pagesECOSYSTEM: Life Energy: What I Need To KnowJunriel Arig BonachitaNo ratings yet
- Core CH 9 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in PlantsDocument6 pagesCore CH 9 Nutrition and Gas Exchange in PlantsommpNo ratings yet
- Plant Transport Systems & Photosynthesis: BiologyDocument19 pagesPlant Transport Systems & Photosynthesis: BiologyJessica MagtagñobNo ratings yet
- This Chapter Looks at PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesThis Chapter Looks at PhotosynthesisGiuseppe CondelloNo ratings yet
- Na Mlbio Ch09Document28 pagesNa Mlbio Ch09Life with CourteneyNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Major Biological Activities of Organisms Tutorial 3.1 PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesUnit 3 - Major Biological Activities of Organisms Tutorial 3.1 PhotosynthesisgayathmipereraNo ratings yet
- Group Challenge 3Document7 pagesGroup Challenge 3Acel PeñalozaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Biochemistry: Biology Semester 1 Review 2018Document20 pagesUnit 1: Biochemistry: Biology Semester 1 Review 2018E NNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 L-1.1 1.2 1.3 Science Grade 8Document24 pagesUnit 1 L-1.1 1.2 1.3 Science Grade 8andeepthiNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (KEY)Document6 pagesPhotosynthesis (KEY)kylevNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument43 pagesPlant NutritionRand Hussein100% (1)
- Photosynthesis & LeavesDocument38 pagesPhotosynthesis & LeavesSanthoshNo ratings yet
- Bio Leaf Structure Lab F21Document4 pagesBio Leaf Structure Lab F21Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument15 pagesPhotosynthesisSultana KhanNo ratings yet
- A Study of The Effect of Light Intensity On The Photosynthesis of Hydrilla Verticellata Sprigs and The Separation of Photosynthesis Pigments by Paper ChromatographyDocument16 pagesA Study of The Effect of Light Intensity On The Photosynthesis of Hydrilla Verticellata Sprigs and The Separation of Photosynthesis Pigments by Paper ChromatographyLouiegi AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Energy Transformation and PhotosynthesisDocument9 pagesEnergy Transformation and PhotosynthesisYumeko JabamiNo ratings yet
- 13 Quarter 1 Module 13-INTRODUCTION-TO-PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument16 pages13 Quarter 1 Module 13-INTRODUCTION-TO-PHOTOSYNTHESISMah Jane Divina100% (1)
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledEinzen EspañolNo ratings yet
- GenBio Q2 M1Document16 pagesGenBio Q2 M1Allaine BenitezNo ratings yet
- STEM General Biology2 3-4Document13 pagesSTEM General Biology2 3-4Jp menorNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Plants - Absorption of Water and MineralDocument1 pageWorksheet - Plants - Absorption of Water and MineralFuadi Anwar WirawanNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument59 pagesPhotosynthesisAima AzharNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document25 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Saraswati PNo ratings yet
- 22 PhotosynthesisDocument12 pages22 Photosynthesisvickytang22072002No ratings yet
- Interpretation of the Ultraviolet Spectra of Natural Products: International Series of Monographs on Organic ChemistryFrom EverandInterpretation of the Ultraviolet Spectra of Natural Products: International Series of Monographs on Organic ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Sugar Fermentation in YeastDocument4 pagesSugar Fermentation in YeastVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Active Transport Color ActivityDocument2 pagesActive Transport Color ActivityVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Moon Phases - Oreo LabDocument2 pagesMoon Phases - Oreo LabVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Sugar Fermentation in Yeast 23Document7 pagesSugar Fermentation in Yeast 23Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Unit 2B - Metabolism - PhotosynthesisDocument11 pagesUnit 2B - Metabolism - PhotosynthesisVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Unit 2B Guided NotesDocument4 pagesUnit 2B Guided NotesVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Bio - Photosynthesis Lab Part 1 F21Document6 pagesBio - Photosynthesis Lab Part 1 F21Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Bio Photosynthesis Lab Color of Light vs. Photosynthesis StationDocument1 pageBio Photosynthesis Lab Color of Light vs. Photosynthesis StationVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Biochem Function Group PracticeDocument1 pageBiochem Function Group PracticeVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Bio Prefix Suffix NEW 2020Document3 pagesBio Prefix Suffix NEW 2020Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Bio Photosynthesis Lab Light Intensity vs. Photosynthesis StationDocument1 pageBio Photosynthesis Lab Light Intensity vs. Photosynthesis StationVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Bio Leaf Structure Lab F21Document4 pagesBio Leaf Structure Lab F21Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- 2021 Population Dynamics NotesDocument18 pages2021 Population Dynamics NotesVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- L3 Darwin NotesDocument2 pagesL3 Darwin NotesVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Atp PogilDocument5 pagesAtp PogilVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- L3 DarwinDocument11 pagesL3 DarwinVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Atp PogilDocument4 pagesAtp PogilVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Symbiotic Relationship Worksheet 2Document3 pagesSymbiotic Relationship Worksheet 2Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- L4 Natural SelectionDocument19 pagesL4 Natural SelectionVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- VIA Institute On Character TestDocument2 pagesVIA Institute On Character TestVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Vocab Words For Symbiotic Lesson 2Document1 pageVocab Words For Symbiotic Lesson 2Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- L2 Geolographic TimeDocument6 pagesL2 Geolographic TimeVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Station 1 - Coloring SheetDocument1 pageStation 1 - Coloring SheetVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Weather Symbols For BinderDocument2 pagesWeather Symbols For BinderVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document20 pagesUnit 5Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Childs Game Psychological Foundations of EducationDocument1 pageChilds Game Psychological Foundations of EducationVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Review For Last QuizDocument11 pagesReview For Last QuizVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Genetics and Evolution CalendarDocument15 pagesUnit 6 - Genetics and Evolution CalendarVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Tech Agreement 23Document1 pageTech Agreement 23Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Digital Participation GapDocument3 pagesDigital Participation GapVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Mlion-Catalogue (2020)Document28 pagesMlion-Catalogue (2020)M.ariefiryuqoriNo ratings yet
- Climatic Subdivisions in Saudi Arabia: An Application of Principal Component AnalysisDocument17 pagesClimatic Subdivisions in Saudi Arabia: An Application of Principal Component AnalysisirfanNo ratings yet
- Vocational Teacher (Maintenance and Repairs of Automobiles)Document7 pagesVocational Teacher (Maintenance and Repairs of Automobiles)Brandon AllenNo ratings yet
- Serie T4 PDFDocument17 pagesSerie T4 PDFRené Isaac Martínez OlivaNo ratings yet
- Data Structure 4Document7 pagesData Structure 4Jiten ThakurNo ratings yet
- Aptitude TestDocument6 pagesAptitude TestMeera SeshannaNo ratings yet
- Datalogic P51 Operator's ManualDocument2 pagesDatalogic P51 Operator's ManualGodzilNo ratings yet
- Carsten Tschierske - Micro-Segregation, Molecular Shape and Molecular Topology - Partners For The Design of Liquid Crystalline Materials With Complex Mesophase MorphologiesDocument25 pagesCarsten Tschierske - Micro-Segregation, Molecular Shape and Molecular Topology - Partners For The Design of Liquid Crystalline Materials With Complex Mesophase MorphologiesDremHpNo ratings yet
- Design of Bolted ConnectionsDocument7 pagesDesign of Bolted ConnectionsEngineerNo ratings yet
- Arduino SARA-R4 DataSheet (UBX-16024152)Document43 pagesArduino SARA-R4 DataSheet (UBX-16024152)abdullahNo ratings yet
- Abstracts About WeldingDocument9 pagesAbstracts About WeldingVinayak BhustalimathNo ratings yet
- 9 - ATPL Questions MeteorologyDocument99 pages9 - ATPL Questions MeteorologyRitwik Chowdhury100% (1)
- DPP - Electricity (Prashant Kirad)Document12 pagesDPP - Electricity (Prashant Kirad)Abhinav SinghNo ratings yet
- Shreya Sharma ReportDocument62 pagesShreya Sharma ReportshreyakesharwaniaryabhataNo ratings yet
- Fractions Improper1 PDFDocument2 pagesFractions Improper1 PDFthenmoly100% (1)
- Lesson 5 - Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocument13 pagesLesson 5 - Colligative Properties of SolutionsKeziah Keren TalampasNo ratings yet
- Samrat Updated 4Document40 pagesSamrat Updated 4Umesh DhakalNo ratings yet
- 05 iPASO LCT Training Manual (Ethernnet) Dec2012-2Document105 pages05 iPASO LCT Training Manual (Ethernnet) Dec2012-2Wubie NegaNo ratings yet
- TBA 1013 Assignment 1 SEM 2 2010/2011Document3 pagesTBA 1013 Assignment 1 SEM 2 2010/2011Zafiera ZukriNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Battery Seminar ReportDocument22 pagesNuclear Battery Seminar ReportPratik Patil100% (1)
- Phy 308 Electronics IDocument310 pagesPhy 308 Electronics ISuresh LNo ratings yet
- Reappraisal of The Autoclave Expansion TestDocument26 pagesReappraisal of The Autoclave Expansion TestCristián JiménezNo ratings yet
- 6.metabolism in FungiDocument67 pages6.metabolism in FungiWahyuni Irmal100% (2)
- Chapter 11: Index NumberDocument7 pagesChapter 11: Index NumberHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual: (Shaker)Document43 pagesOperating Manual: (Shaker)Cardenas Cuito MarcoNo ratings yet
- Cinema - Problem DescriptionDocument10 pagesCinema - Problem DescriptionVladaNo ratings yet
- Electric Power Systems. Vol. I. Electric NetworksDocument843 pagesElectric Power Systems. Vol. I. Electric Networksluciantoma75% (4)
- Bahan PPT PPICDocument19 pagesBahan PPT PPICAoc SidomulyoNo ratings yet
- Automobile Inventory VB - Net ProjectDocument21 pagesAutomobile Inventory VB - Net ProjectAsim MahatoNo ratings yet