Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Notes - Chapter 12 Respiration
Uploaded by
balsh374Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Notes - Chapter 12 Respiration
Uploaded by
balsh374Copyright:
Available Formats
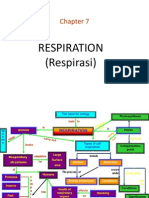
Biology notes : chapter 12 respiration
Respiration: breakdown of food molecules with the release of energy in living cells.
How is respiration controlled? - through a series of reactions that are controlled by
enzymes.
Types of respiration: aerobic and anaerobic
Aerobic respiration: chemical breakdown of food molecules in the presence of oxygen.
(large amount of energy in released)
Anaerobic respiration: chemical breakdown of food molecules in the absence of oxygen.
(lesser oxygen is released)
-Lactic acid is formed during anaerobic respiration in the muscles.
-Lactic acid is the byproduct of anaerobic respiration. It is the fuel for our cell breakdown
during intense exercises. When it is in the body in high amounts, it can cause muscle burns,
fatigue and also tissue damaged after intense workouts.
-Oxygen debt is the oxygen required after intense exercise to oxidise the lactic acid
created from anaerobic respiration
-oxygen debt can be removed from our body by continuation of deeper and faster breathing
or continuation of faster heart rate.
Effects of exercise on breathing:
- frequency and depth of breathing increase. This is because muscles are working harder
and need more oxygen to function. (body breaths through aerobic respiration in default)
-if the energy demand cant be met the body automatically begins to respire anaerobically,
producing lactic acid.
-lactic acid need to be removed after exercise as the low ph can denature the enzymes in
the body and stop bodily process.
-they can be removed by repaying the oxygen debt. The longer it takes the more lactic acid
produced during exercise and greater the oxygen debt that needs to be repaid.
Similarities between aerobic and anaerobic respiration:
- both processes release energy
- both involve the breakdown of food molecules
- both processes require enzyme to catalyse the breakdown of food molecules
Difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration:
Uptake of oxygen by respiring organisms:
- investigating aerobic respiration in living organism by measuring the amount of oxygen
they take from the air. This is done by measuring the change in volume of air in an
enclosed tube. However as they respire they give out carbon dioxide which increases
gas volume. The carbon dioxide needs to be removed from the tube first using
chemicals like soda lime or sodium hydroxide. The apparatus used to measure the air
volume is known as a respirometer. And small organisms can be used in the apparatus like
seeds or arthropods.
Effect on temperature on the rate of respiration:
- To investigate the effect of temperature on the rate of respiration of germinating
seeds, the respirometer can be set up and the tubes submerged in a series of water
baths set at various temperatures.
- The seeds should be kept in the water bath to get acclimated to the temperature.
- As respiration is an enzyme controlled reaction, it is highly unlikely to work faster
beyond around 40 degree celsius as the enzymes will denature.
You might also like
- Respiration: Respiratory SubstrateDocument8 pagesRespiration: Respiratory SubstrateEdwins MaranduNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 12.1 RespirationDocument14 pages12.1 RespirationPranitha RaviNo ratings yet
- Respiratory gymnastics (Translated): Purification - Health - Strength - EnergyFrom EverandRespiratory gymnastics (Translated): Purification - Health - Strength - EnergyNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument5 pagesRespiration Notesjj mayjNo ratings yet
- Bio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .Document21 pagesBio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .naazim mohamedNo ratings yet
- Class 10 RespirationDocument3 pagesClass 10 RespirationHimanshu singh100% (1)
- Respiration 2Document23 pagesRespiration 2api-233649346No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Integrated Science Week 8 Lesson 1Document4 pagesGrade 8 Integrated Science Week 8 Lesson 1Rana HalabyNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 7Document43 pagesChapter - 7AyeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RespirationDocument14 pagesIntroduction To RespirationAzneezal Ar-RashidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document138 pagesChapter 7Bëar MëNo ratings yet
- Kisi2 Biology Fe s4 Sem 2Document15 pagesKisi2 Biology Fe s4 Sem 2Livia XoxoNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument24 pagesRespiration and Gas ExchangeEizelle100% (2)
- Page No - 115Document5 pagesPage No - 115venfone byrappaNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionDocument13 pages7.1 Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionNor Rafidah Che YusofNo ratings yet
- Respiration and BreathingDocument57 pagesRespiration and BreathingHarvagale BlakeNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic and Aerobic Respiration in Living OrganismDocument16 pagesAnaerobic and Aerobic Respiration in Living OrganismrihanniNo ratings yet
- Notebook Work Respiration in OrganismsDocument4 pagesNotebook Work Respiration in OrganismsachlaNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentHannah CastroNo ratings yet
- Oxygen TherapyDocument25 pagesOxygen TherapyIsaiah AmolatoNo ratings yet
- Biodas 8 (Aeman Hakim)Document19 pagesBiodas 8 (Aeman Hakim)aekimNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab #12 Discussion (HOW BREATHING RATE CHANGES WITH EXERCISE)Document3 pagesBiology Lab #12 Discussion (HOW BREATHING RATE CHANGES WITH EXERCISE)Joy-Ann NuptialNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument11 pagesRESPIRATIONCREATIVING TAMILANNo ratings yet
- Document 5Document5 pagesDocument 5kauthar hassanNo ratings yet
- Grade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsDocument22 pagesGrade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsJanardhanNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument9 pagesRespiration in Organismsshreya kashyapNo ratings yet
- S2 - Bio - RevisionNotes 1.1 To 1.4 - PreMidDocument7 pagesS2 - Bio - RevisionNotes 1.1 To 1.4 - PreMidKaung ThihaNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument35 pagesRespirationnabeeha malhiNo ratings yet
- Respiration BiologyDocument32 pagesRespiration BiologyMuhammad KhanNo ratings yet
- Human and Social Biology The Respiratory System 10 1 and 2Document35 pagesHuman and Social Biology The Respiratory System 10 1 and 2Science,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Bio Form 4 Chap 7Document15 pagesBio Form 4 Chap 7Lim Hong ShengNo ratings yet
- What Is Respiration?Document8 pagesWhat Is Respiration?Waleed Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4edain84No ratings yet
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Faida Hamid87% (23)
- Types of Respiration: Aerobic Respiration .Anaerobic RespirationDocument3 pagesTypes of Respiration: Aerobic Respiration .Anaerobic RespirationHahsamNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Organisms: A. Short Answers QuestionsDocument5 pagesRespiration in Organisms: A. Short Answers QuestionsnarayanaNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Organisms Class 7 NotesDocument37 pagesRespiration in Organisms Class 7 Notestrisha.sharma2347No ratings yet
- Ch10 Respiration SummaryDocument26 pagesCh10 Respiration Summaryzuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- Notes RespirationDocument6 pagesNotes Respirationakheel7353No ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismDocument67 pagesRespiration in Organismsangeetha alurNo ratings yet
- Pp19 Cellular RespirationDocument71 pagesPp19 Cellular Respirationu22811495No ratings yet
- L - Life Processes - Respiration Notes and Questions For Note Book WorkDocument7 pagesL - Life Processes - Respiration Notes and Questions For Note Book WorkNotImmortalNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument68 pagesRespirationNorhidayah IsmailNo ratings yet
- Respiration BIOLOGY Year 9 PosterDocument7 pagesRespiration BIOLOGY Year 9 PostererinaNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Document46 pages2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNo ratings yet
- G Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3Document14 pagesG Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3jhaorpratyushNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Respiration in Organisms - Class 7 Biology NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 10 - Respiration in Organisms - Class 7 Biology Notessriniram_2002No ratings yet
- ACFrOgAIQdrJat36J9RtnPUAS9sOmcsu9yLAFerEbaweE0U2K4PAtc8viRq9P9-mZEGIbJ9oaVu5ASblSTXUEe5mPmw8jWZr4 Vn5QSBTLLuo3sGyGO-NAMBcoaKpu NNHBFSN j6xd6tq 7VZFgDocument17 pagesACFrOgAIQdrJat36J9RtnPUAS9sOmcsu9yLAFerEbaweE0U2K4PAtc8viRq9P9-mZEGIbJ9oaVu5ASblSTXUEe5mPmw8jWZr4 Vn5QSBTLLuo3sGyGO-NAMBcoaKpu NNHBFSN j6xd6tq 7VZFgThe Deep Sea IdNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument1 pageRESPIRATIONL NarineNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument2 pagesRespirationmubasherkatbar562No ratings yet
- Energy SystemDocument14 pagesEnergy SystemMaria Alyssa NaranjoNo ratings yet
- FORCEDocument14 pagesFORCEMaria Alyssa NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Bio Respiration Chapter SummaryDocument2 pagesBio Respiration Chapter SummaryYoussef Abdurrahman WeinmanNo ratings yet
- Biology - Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration 2023Document5 pagesBiology - Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration 2023witness vurayayiNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Biology GCE Study BuddyDocument45 pagesRespiration: Biology GCE Study BuddyMaleeha HumayunNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument36 pagesRESPIRATIONnyemarichardssvgNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is of Two TypesDocument3 pagesRespiration Is of Two TypesKyng GamariNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument2 pagesRespirationIndi SafitriNo ratings yet
- Sylvia Wynter & Katherine Mckittrick - On-Being-Human-As-Praxis PDFDocument66 pagesSylvia Wynter & Katherine Mckittrick - On-Being-Human-As-Praxis PDFfirexcracker100% (1)
- Types of Nucleic Acids: Return To TOC 1Document95 pagesTypes of Nucleic Acids: Return To TOC 1Hey itsJamNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 J23Document8 pagesHomework 1 J23Nada Abu ShweimehNo ratings yet
- Spermatogenesis PPTDocument42 pagesSpermatogenesis PPTInsatiable CleeNo ratings yet
- UCSP Graded Recitation QuestionsDocument4 pagesUCSP Graded Recitation QuestionsDarrel Susaya100% (1)
- Phytochemistry (Introduction, Plant Metabolites and PhytochemicalDocument48 pagesPhytochemistry (Introduction, Plant Metabolites and Phytochemicalanisahanifatinr100% (1)
- (Short) Test 02 Verbal - Module 02Document14 pages(Short) Test 02 Verbal - Module 02Hoang MinhNo ratings yet
- Bianda Axanditya 22010110130181 Bab2ktiDocument10 pagesBianda Axanditya 22010110130181 Bab2ktimeiutaNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 - Bradford AssayDocument7 pagesExp 3 - Bradford AssayracelanjelicaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: How Do We Get Proteins From A Bunch of A's, T'S, C's and G's in DNA??Document33 pagesProtein Synthesis: How Do We Get Proteins From A Bunch of A's, T'S, C's and G's in DNA??jodyjodzNo ratings yet
- Glycogenesis and GlycogenolysisDocument55 pagesGlycogenesis and Glycogenolysisclear mindNo ratings yet
- 017 Wuchereria BrugiaDocument21 pages017 Wuchereria BrugiaAyop KhNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and MalocclusionDocument2 pagesNutrition and Malocclusionsrishti jainNo ratings yet
- Chang2013 Morphometric Analysis of The Cranial Base in AsiansDocument8 pagesChang2013 Morphometric Analysis of The Cranial Base in Asianssolodont1No ratings yet
- Inhibitory Control Over Action and MemoryDocument11 pagesInhibitory Control Over Action and MemoryMaryam TaqaviNo ratings yet
- Jung Thomas, Manual Phytophthora MethodsDocument49 pagesJung Thomas, Manual Phytophthora MethodsCriss Guzmán100% (1)
- TEA NotesDocument14 pagesTEA NotesNikhil KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Dake Chu: Cui WeiDocument61 pagesDake Chu: Cui WeiDave UlanNo ratings yet
- Selection of Biomedical Animal ModelsDocument8 pagesSelection of Biomedical Animal Modelsshirley_ling_15No ratings yet
- Chapter 31Document68 pagesChapter 31Anugrah ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Q4 Lesson 4 Plant and Animal ReproductionDocument38 pagesQ4 Lesson 4 Plant and Animal ReproductionPhan MhiveNo ratings yet
- January Examination Timetable !!!Document23 pagesJanuary Examination Timetable !!!Sam MaccuaigNo ratings yet
- Barriers of Protein and Peptide Drug DeliveryDocument12 pagesBarriers of Protein and Peptide Drug DeliveryAashish chaudhari100% (2)
- 1 s2.0 S1319562X19300968 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S1319562X19300968 MainRobert TriarjunetNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive Ecology of Exotic Trachemys Scripta Elegans in An Invaded Area of Southern EuropeDocument10 pagesThe Reproductive Ecology of Exotic Trachemys Scripta Elegans in An Invaded Area of Southern Europewijayanti chantikaNo ratings yet
- Labmax 240Document43 pagesLabmax 240Dharmesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Medical Biotechnology: A Resource Guide For Biotechnology Club SponsorsDocument39 pagesMedical Biotechnology: A Resource Guide For Biotechnology Club Sponsorsim_mogerzNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual of Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics - 1 PDFDocument167 pagesLaboratory Manual of Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics - 1 PDFkdk;lkd33% (3)
- EXP 1 - Wastewater Treatment in Aerobic Batch ReactorDocument10 pagesEXP 1 - Wastewater Treatment in Aerobic Batch ReactorAinin SofiyaNo ratings yet
- CE Biology 2011 Paper2 (E)Document19 pagesCE Biology 2011 Paper2 (E)Tom ChowNo ratings yet