Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Female Reproductive System
Uploaded by
Elthon JohnCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Female Reproductive System
Uploaded by
Elthon JohnCopyright:
Available Formats
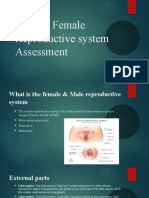
What is the female reproductive system?
The female reproductive system is the body parts that help women or people assigned female at birth
(AFAB):
• Have sexual intercourse.
• Reproduce.
• Menstruate.
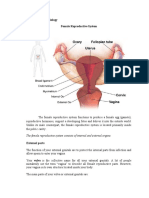
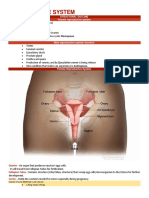
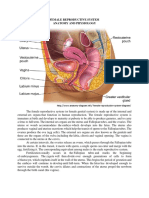
What are the parts of the female reproductive system?
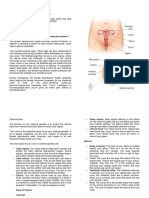
• Vagina: Your vagina is a muscular canal that joins
the cervix (the lower part of uterus) to the outside of
the body. It can widen to accommodate a baby during
delivery and then shrink back to hold something
narrow like a tampon. It’s lined with mucous
membranes that help keep it moist.
• Cervix: Your cervix is the lowest part of your uterus. A
hole in the middle allows sperm to enter and
menstrual blood
menstrual blood to
to exit.
exit. Your
Your cervix
cervix opens
opens (dilates)
(dilates) to
to allow a baby to come out during a vaginal
childbirth.
allow a babyYour cervixout
to come is what prevents
during things
a vaginal like tampons from getting lost inside your body.
childbirth.
•
Your cervix
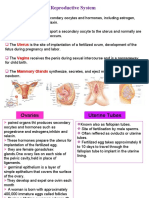
Uterus: Youris uterus
what prevents things
is a hollow, like tampons
pear-shaped from
organ that holds a fetus during pregnancy. Your uterus is
getting lost inside your body.
divided into two parts: the cervix and the corpus. Your corpus is the larger part of your uterus that
• expandsYour
Uterus: during pregnancy.
uterus is a hollow, pear-shaped organ
•
that holdsOvaries
Ovaries: a fetus are
during pregnancy.
small, Your glands
oval-shaped uterus that
is are located on either side of your uterus. Your
divided into two parts:
ovaries produce the hormones.
eggs and cervix and the corpus. Your
corpus is the larger part of your uterus that expands
• Fallopian
during tubes: These are narrow tubes that are attached to the upper part of your uterus and serve as
pregnancy.
pathways for your egg (ovum) to travel from your ovaries to your uterus. Fertilization of an egg by sperm
• Ovaries:
normally Ovaries
occurs inare small,
the oval-shaped
fallopian glands
tubes. The that egg then moves to the uterus, where it implants
fertilized
are
intolocated on either
your uterine side of your uterus. Your ovaries
lining.
produce eggs and hormones.
• Labia majora: Your labia majora (“large lips”) enclose
• Fallopian tubes: These are narrow tubes that are and protect the other external reproductive organs.
attached to the upper part of your uterus and serveDuring as puberty, hair growth occurs on the skin of the
pathways for your egg (ovum) to travel from your labia majora, which also contain sweat and oil-secreting
ovaries to your uterus. Fertilization of an egg by spermglands.
normally occurs in the fallopian tubes. The fertilized
egg then moves to the uterus, where it implants• into Labia minora: Your labia minora (“small lips”) can have
your uterine lining. a variety of sizes and shapes. They lie just inside your
labia majora, and surround the opening to your vagina
(the canal that joins the lower part of your uterus to the
outside of your body) and urethra (the tube that carries
pee from your bladder to the outside of your body). This
skin is very delicate and can become easily irritated and
swollen.
Clitoris: Your two labia minora meet at your clitoris, a small, sensitive protrusion that’s comparable to a penis
in men or people assigned male at birth (AMAB). Your clitoris is covered by a fold of skin called the prepuce and
is very sensitive to stimulation.
Vaginal opening: Your vaginal opening allows menstrual blood and babies to exit your body. Tampons, fingers,
sex toys or penises can go inside your vagina through your vaginal opening.
Hymen: Your hymen is a piece of tissue covering or surrounding part of your vaginal opening. It’s formed during
development and present during birth.
Opening to your urethra: The opening to your urethra is the hole you pee from.
What happens during the menstrual cycle?
Women or people AFAB of reproductive age (beginning anywhere from 11 to 16 years of age) experience cycles
of hormonal activity that repeat at about one-month intervals. With every cycle, your body prepares for a
potential pregnancy, whether or not that’s your intention. The term menstruation refers to the periodic
shedding of your uterine lining when pregnancy doesn’t occur that cycle. Many people call the days that they
notice vaginal bleeding their “period.”
The average menstrual cycle takes about 28 days and occurs in phases. These phases include:
• The follicular phase (the egg develops).
• The ovulatory phase (release of the egg).
• The luteal phase (hormone levels decrease if the egg doesn’t implant).
There are four major hormones (chemicals that stimulate or regulate the activity of cells or organs)
involved in the menstrual cycle. These hormones include:
• Follicle-stimulating hormone.
• Luteinizing hormone.
• Estrogen.
• Progesterone.
How does reproduction work?
In humans, female and male reproductive systems work together to reproduce. There are two kinds of
sex cells — sperm and eggs. When a sperm meets an egg, it can fertilize it and create a zygote. This
zygote eventually becomes a fetus. Both a sperm and an egg are needed for human reproduction.
How many eggs does a woman have?
You’re born with all the eggs you’ll ever produce. During fetal development, you have about 6 million
eggs. At birth, there are approximately 1 million eggs left. By the time you reach puberty, only about
300,000 remain. The number of eggs you have continues to decline as you age and menstruate each
cycle. Fertility also declines with age due to the decreasing number and quality of your remaining eggs.
You might also like
- What Is The Female Reproductive System?: External PartsDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Female Reproductive System?: External PartsKeneth Dave AglibutNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewDocument9 pagesBiology ReviewLia Genelle Rei ConchaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System - ramoNJUANBASILANDocument14 pagesFemale Reproductive System - ramoNJUANBASILANJericho TanalgoNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemJasmaine RivoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology OvaryDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology OvaryFretchell Aripal MontesNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument32 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemSeptember Neckohle AlunanNo ratings yet
- The Parts and The Functions of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument40 pagesThe Parts and The Functions of The Female Reproductive SystemLeo John OctavianoNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Care Module 4. Hormonal Regulation of The Female Reproductive System View As Single PageDocument1 pageAntenatal Care Module 4. Hormonal Regulation of The Female Reproductive System View As Single PageSunshine BocoNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument35 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemandraya.moirNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & FertilizationDocument27 pagesAnatomy & FertilizationBAGAVATHI RNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument22 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemamielle azamingNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System: Dominguez, Nikka EDocument51 pagesFemale Reproductive System: Dominguez, Nikka EGwyneth100% (1)
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument37 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemHu T. BunuanNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System SlidesDocument30 pagesFemale Reproductive System SlidesNyakie MotlalaneNo ratings yet
- Report For Sex Education IntroductionDocument6 pagesReport For Sex Education Introductionpsalmueljtomg19No ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument78 pagesREPRODUCTIONglaizaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System NOTESDocument1 pageFemale Reproductive System NOTESShielo Marie CabañeroNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesMale and Female Reproductive SystemJOSH ELORDENo ratings yet
- Problems With THE Reproductive SystemDocument93 pagesProblems With THE Reproductive SystemJunghoon YangParkNo ratings yet
- Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesReview of Anatomy and PhysiologyRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- LESSON-4 Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument16 pagesLESSON-4 Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionJane EdullantesNo ratings yet
- (Anatomy & Physiology Lecture) REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NOTESDocument21 pages(Anatomy & Physiology Lecture) REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NOTESZen HeartNo ratings yet
- Male & Female Reproductive System AssessmentDocument12 pagesMale & Female Reproductive System Assessmentlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesFemale Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyIkea Balhon100% (3)
- REWIEW OF FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NewDocument49 pagesREWIEW OF FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NewnamitaNo ratings yet
- (Unit 3) Human Reproductive SystemDocument14 pages(Unit 3) Human Reproductive SystemHanif AlfarizkiNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemRodelyn Dahay CalluengNo ratings yet
- MCN NotesDocument71 pagesMCN NotesAbmil Ching TinggalongNo ratings yet
- Nurs 5351 Advanced Reproductive HealthDocument91 pagesNurs 5351 Advanced Reproductive HealthRachel BiokoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemFarlyn Real MoralesNo ratings yet
- GEC SELF Lesson 5-Activity 5Document9 pagesGEC SELF Lesson 5-Activity 5Hannah Lee LumosbogNo ratings yet
- Pandapatan Paler AnaPhyDocument3 pagesPandapatan Paler AnaPhyShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesFemale Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyGeevee Naganag VentulaNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesHuman Reproductive Systemsamanthagracem3No ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesReproductive SystemJason TaburnalNo ratings yet
- Ana Physio ReprodDocument8 pagesAna Physio ReprodTeodoro Lemuel Ramos Gaela100% (1)
- Reproductive System AnatomyDocument7 pagesReproductive System AnatomyEdDa LaIne TotillaNo ratings yet
- Bio Female Sys PresentationDocument4 pagesBio Female Sys PresentationDoc_NeurologistNo ratings yet
- Script AnaphyDocument6 pagesScript AnaphyJesseiah LapitanNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Female Reproductive SystemDocument54 pagesPresentation On: Female Reproductive SystemLetsShop BbsrNo ratings yet
- Definition of The DiseaseDocument17 pagesDefinition of The DiseaseLucille Jane Onlos CalibadanNo ratings yet
- The Human Reproductive System FinalDocument16 pagesThe Human Reproductive System FinalIlac Tristan BernardoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument2 pagesSCIENCERalp Renzel PadillaNo ratings yet
- 8reproductive SystemDocument31 pages8reproductive SystemViola ChepletingNo ratings yet
- Gender & Society Lo4Document6 pagesGender & Society Lo4Mark Eugene DeocampoNo ratings yet
- Quiz Female Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesQuiz Female Reproductive Systemwiwinfitriani2023No ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemsaranya amuNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemAlyanna L. ArquillanoNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproductive System Is A Group of Organs That Work Together To Enable ReproductionDocument5 pagesThe Female Reproductive System Is A Group of Organs That Work Together To Enable ReproductionNica Gobaliza EsquilonaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive PresentationDocument70 pagesFemale Reproductive PresentationCristy Jean ApdianNo ratings yet
- 10FRSDocument27 pages10FRSWakanda ForeverNo ratings yet
- Organ Function Mons Veneris: Labia MinoraDocument5 pagesOrgan Function Mons Veneris: Labia MinoraSabana MedtimbangNo ratings yet
- Organ Function Mons Veneris: Labia MinoraDocument5 pagesOrgan Function Mons Veneris: Labia MinoraNur AleahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyG3-PORTILLA John MartNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemYsthanamhire TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Human Body Flat Design Presentation Pink VariantDocument16 pagesHuman Body Flat Design Presentation Pink VariantAngie MejaritoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyKristine Alejandro100% (1)
- Reporting EPDocument48 pagesReporting EPMaine YukiNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System-1Document43 pagesFemale Reproductive System-1Je Lan NieNo ratings yet
- Ovum, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandOvum, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Conception Rate: Dairy Integrated Reproductive ManagementDocument6 pagesFactors Affecting Conception Rate: Dairy Integrated Reproductive ManagementAh MagdyNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 7Document27 pagesBiology Unit 7joyNo ratings yet
- SEX V GENDER DEBATE PDFDocument18 pagesSEX V GENDER DEBATE PDFMessi VerseNo ratings yet
- Plummer - Male SexualitiesDocument18 pagesPlummer - Male SexualitiesmargitajemrtvaNo ratings yet
- Module I Session 2 Gender Mainstreaming Community Based Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Trainers' TrainingDocument46 pagesModule I Session 2 Gender Mainstreaming Community Based Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Trainers' TrainingProletaNuñezaGomezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction - The Science of Biology: Biol 1020 - Chapter 1 Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 1: Introduction - The Science of Biology: Biol 1020 - Chapter 1 Lecture NotesAria DomingoNo ratings yet
- Human Rep - DPP 1 (2.0)Document42 pagesHuman Rep - DPP 1 (2.0)Upal PramanickNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument10 pagesBiologyNur FarhanimNo ratings yet
- Article On Female Foeticide-Need To Change The MindsetDocument4 pagesArticle On Female Foeticide-Need To Change The MindsetigdrNo ratings yet
- Family Trees 1: © Jonathan Nicholas 2004Document8 pagesFamily Trees 1: © Jonathan Nicholas 2004Jon WendelboeNo ratings yet
- Mating-Intelligence-Sex-Relationships-and-the-Mind-s-Reproductive-System (Study 104) PDFDocument481 pagesMating-Intelligence-Sex-Relationships-and-the-Mind-s-Reproductive-System (Study 104) PDFchopitoNo ratings yet
- Animal Birth ControlDocument15 pagesAnimal Birth Controlvenku07484435No ratings yet
- Sexual Orientation Gender Identity and ExpressionDocument75 pagesSexual Orientation Gender Identity and ExpressionFred Aguilo Gozon100% (1)
- Why Is Sex FunDocument2 pagesWhy Is Sex FunkarinadegomaNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease-SCIENCEDocument7 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease-SCIENCELeanne Marie Paredes TanNo ratings yet
- AFA PPT - Artificial InseminationDocument8 pagesAFA PPT - Artificial InseminationErika Mae Roa BanaayNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Science Yr8 Asexual ReproductionDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Science Yr8 Asexual Reproductionapi-26179694067% (3)
- Pregnant Dog - Pregnancy Signs in Dogs - Dog Article On Pets - Ca What To Expect When Your Dog Is ExpectingDocument3 pagesPregnant Dog - Pregnancy Signs in Dogs - Dog Article On Pets - Ca What To Expect When Your Dog Is Expectingmale nurseNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Contraception WorksheetDocument4 pagesWeek 3 Contraception Worksheetapi-270465022No ratings yet
- Mastering Biology BK2 NotesDocument44 pagesMastering Biology BK2 NotesAlva WongNo ratings yet
- Class - 12-CBSE - Biology - Human Reproduction - Test Paper.Document1 pageClass - 12-CBSE - Biology - Human Reproduction - Test Paper.tanishm7206No ratings yet
- Pure Bio CH 17 Textbook Answers PDFDocument3 pagesPure Bio CH 17 Textbook Answers PDFashaNo ratings yet
- International Obstetric and Gynecology Conference 2019 ScheduleDocument6 pagesInternational Obstetric and Gynecology Conference 2019 ScheduleAndianto IndrawanNo ratings yet
- NCMA 217 Lec Performance Task # 3 Responsible ParenthoodDocument2 pagesNCMA 217 Lec Performance Task # 3 Responsible ParenthoodByren PacpacoNo ratings yet
- COT 1 Lesson Plan Science 7 2021-2022Document3 pagesCOT 1 Lesson Plan Science 7 2021-2022Diana Lynn FaderogaoNo ratings yet
- Fungi-Definition, Examples, Structure, Classification & ReproductionDocument26 pagesFungi-Definition, Examples, Structure, Classification & Reproductionarissa noorNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument210 pagesPlant KingdomAyushNo ratings yet
- Tips For Talking To Transgender, Genderqueer & Gender Non-Conforming PeopleDocument1 pageTips For Talking To Transgender, Genderqueer & Gender Non-Conforming PeopleBasic Rights OregonNo ratings yet
- CH 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce DPP - 01Document1 pageCH 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce DPP - 01HemantBhardwajNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan KSSM Science DLP Form 1 2021Document45 pagesYearly Lesson Plan KSSM Science DLP Form 1 2021Nurasyikin SaidinNo ratings yet