Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sheet (4) (Dynamic Characteristics of Instrument Systems)
Uploaded by
mohamed orifOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sheet (4) (Dynamic Characteristics of Instrument Systems)
Uploaded by
mohamed orifCopyright:
Available Formats
Benha University 3rd Year (Mechanical Power)
Faculty of Engineering at Shoubra 2014/2015
Mechanical Engineering Department Sheet (4)
Measurements & Measuring Instrumentations
1. What is meant by time constant and rise time?
2. Suppose a bulb thermometer originally indicating 𝟐𝟎℃ is suddenly exposed to a fluid
temperature of 𝟑𝟕℃. Develop a model that simulates the thermometer output response. If
the thermometer has a time constant of 20 ms and subjected to a step change in input,
calculate the 𝟗𝟎% rise time.
3. A thermometer has a time constant of 10 seconds and behaves as a first order system. It is
initially at a temperature of 𝟑𝟎℃ and then suddenly subjected to a surroundings
temperature of 𝟏𝟐𝟎℃, calculate the 𝟗𝟎% rise time and the time to attain 𝟗𝟗% of the steady
state temperature.
4. A thermometer acting as a first-order system is initially at a temperature of 𝟑𝟓℃ and is
suddenly subjected to a temperature of 𝟏𝟏𝟎℃. After 8 sec, the thermometer indicates a
temperature of 𝟕𝟓℃. Calculate the time constant and the 90 percent rise time for the
thermometer.
5. A temperature-measuring device approximates a first order. When subjected to a
temperature of 𝟐𝟓 − 𝟏𝟓𝟎℃ shows a temperature of 𝟏𝟎𝟎℃ after 𝟓 seconds. Estimate the
time constant of the device. What temperature would it indicates after a time equals to
five time constant?
6. A thermistor-type temperature sensor is found to behave as a first-order system, and its
experimentally determined time constant 𝛕 is 𝟎. 𝟒 s. The resistance temperature relation
for the thermistor is given as:
𝟏 𝟏
𝐑 = 𝐑 𝐨 𝐞𝐱𝐩 [𝛃 ( − )]
𝐓 𝐓𝐨
Where 𝛃 has been experimentally determined to be 𝟒𝟎𝟎𝟎 K. This temperature sensor is to
be used to measure the temperature of a fluid by suddenly immersing the thermistor into
the fluid medium.
(a) How long one must wait to ensure that the thermometer reading will be in error by no
more than 𝟓 percent of the step change in temperature?
(b) Determine the sensitivity of the thermometer at a temperature of 𝟑𝟎𝟎 K if the
resistance R is 𝟏𝟎𝟎𝟎 Ω at this temperature.
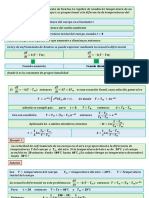
2- Given
𝐅𝐢𝐫𝐬𝐭 − 𝐨𝐫𝐝𝐞𝐫 𝐬𝐲𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐦 𝐓𝟎 = 𝟐𝟎℃
𝐓∞ = 𝟑𝟕℃ 𝐓(𝐭) =? ?
𝛕 = 𝟐𝟎 𝐦𝐬 𝐭 𝐑 =? ?
Solution
𝐀𝐩𝐩𝐥𝐲 𝐞𝐧𝐞𝐫𝐠𝐲 𝐛𝐚𝐥𝐚𝐧𝐜𝐞 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝐚 𝐛𝐨𝐝𝐲: ∴ 𝐐𝐢𝐧 − 𝐐𝐨𝐮𝐭 + 𝐐𝐠 = 𝐐𝐬𝐭
𝐅𝐨𝐫 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐛𝐮𝐥𝐛 𝐨𝐟 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐭𝐡𝐞𝐫𝐦𝐨𝐦𝐞𝐭𝐞𝐫, 𝐰𝐞 𝐜𝐚𝐧 𝐚𝐬𝐮𝐦𝐞 𝐭𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐧𝐨 𝐡𝐞𝐚𝐭 𝐨𝐮𝐭 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐧𝐨 𝐡𝐞𝐚𝐭 𝐠𝐞𝐧𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧
∴ 𝐐𝐨𝐮𝐭 = 𝐐𝐠 = 𝟎
𝐝𝐓
∴ 𝐐𝐢𝐧 = 𝐐𝐬𝐭 ∴ 𝐡𝐀𝐬 [𝐓∞ − 𝐓(𝐭)] = 𝛒𝐕𝐂
𝐝𝐭
𝛒𝐕𝐂 𝐝𝐓 𝐝𝐓 𝛒𝐕𝐂
∴ 𝐓∞ − 𝐓(𝐭) = ∴ 𝐓∞ − 𝐓(𝐭) = 𝛕 𝐰𝐡𝐞𝐫𝐞 𝛕 =
𝐡𝐀𝐬 𝐝𝐭 𝐝𝐭 𝐡𝐀𝐬
𝐝𝛉 −𝐝𝐓
𝐋𝐞𝐭 𝛉 = 𝐓∞ − 𝐓(𝐭) ∴ =
𝐝𝐭 𝐝𝐭
𝐝𝛉 𝐝𝛉 −𝟏
∴ 𝛉 = −𝛕 ∴ = 𝐝𝐭
𝐝𝐭 𝛉 𝛕
𝛉(𝐭)
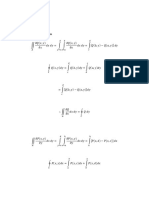
𝐝𝛉 −𝟏 𝐭 𝛉(𝐭) 𝐓∞ − 𝐓(𝐭) −𝐭
∴∫ = ∫ 𝐝𝐭 ∴ 𝐥𝐧 𝛉(𝐭) − 𝐥𝐧 𝛉𝟎 = 𝐥𝐧 = 𝐥𝐧 =
𝛉𝟎 𝛉 𝛕 𝟎 𝛉𝟎 𝐓∞ − 𝐓𝟎 𝛕
𝐓(𝐭) − 𝐓∞
∴ = 𝐞−𝐭⁄𝛕 ∴ 𝐓(𝐭) = 𝐓∞ + (𝐓𝟎 − 𝐓∞ )𝐞−𝐭⁄𝛕
𝐓𝟎 − 𝐓∞
∴ 𝐓(𝐭) = 𝟑𝟕 − 𝟏𝟕𝐞−𝐭⁄𝛕
−𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟏 −𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟏
Ґ = 𝟎. 𝟏 = 𝐞 𝛕 =𝐞 𝟐𝟎 ∴ 𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟏 ≅ 𝟒𝟔. 𝟎𝟓 𝐦𝐬
−𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟗 −𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟗
Ґ = 𝟎. 𝟗 = 𝐞 𝛕 =𝐞 𝟐𝟎 ∴ 𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟗 ≅ 𝟐. 𝟏𝟏 𝐦𝐬
∴ 𝐭 𝐑 = 𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟏 − 𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟗 = 𝟒𝟔. 𝟎𝟓 − 𝟐. 𝟏𝟏 ≅ 𝟒𝟑. 𝟗𝟒 𝐦𝐬
3- Given
𝐅𝐢𝐫𝐬𝐭 − 𝐨𝐫𝐝𝐞𝐫 𝐬𝐲𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐦 𝛕 = 𝟏𝟎 𝐬𝐞𝐜
𝐓𝟎 = 𝟑𝟎℃ 𝐓∞ = 𝟏𝟐𝟎℃
Ґ𝟏 = 𝟏 − 𝟎. 𝟗 = 𝟎. 𝟏 Ґ𝟐 = 𝟏 − 𝟎. 𝟗𝟗 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟏
𝐭 𝐑 =? ? 𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟎𝟏 =? ?
Solution
𝐓(𝐭) − 𝐓∞
Ґ(𝐭) = = 𝐞−𝐭⁄𝛕
𝐓𝟎 − 𝐓∞
−𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟏 −𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟏
Ґ = 𝟎. 𝟏 = 𝐞 𝛕 =𝐞 𝟏𝟎 ∴ 𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟏 ≅ 𝟐𝟑. 𝟎𝟑 𝐬𝐞𝐜
−𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟗 −𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟗
Ґ = 𝟎. 𝟗 = 𝐞 𝛕 =𝐞 𝟏𝟎 ∴ 𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟗 ≅ 𝟏. 𝟎𝟓 𝐬𝐞𝐜
∴ 𝐭 𝐑 = 𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟏 − 𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟗 = 𝟐𝟑. 𝟎𝟑 − 𝟏. 𝟎𝟓 ≅ 𝟐𝟐 𝐬𝐞𝐜
−𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟎𝟏 −𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟎𝟏
∴ 𝐅𝐨𝐫 Ґ = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟏 = 𝐞 𝛕 =𝐞 𝟏𝟎 ∴ 𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟎𝟏 ≅ 𝟒𝟔. 𝟎𝟓 𝐬𝐞𝐜
4- Given
𝐅𝐢𝐫𝐬𝐭 − 𝐨𝐫𝐝𝐞𝐫 𝐬𝐲𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐦 𝐓𝟎 = 𝟑𝟓℃
𝐓∞ = 𝟏𝟏𝟎℃ 𝐭 = 𝟖 𝐬𝐞𝐜
𝐓(𝐭) = 𝟕𝟓℃ 𝛕 =? ? 𝐭 𝐑 =? ?
Solution
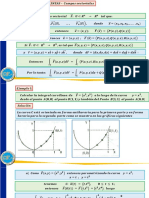
𝐓(𝐭) − 𝐓∞ −𝐭 𝟕𝟓 − 𝟏𝟏𝟎 𝟕 −𝟖
Ґ(𝐭) = =𝐞𝛕 ∴ ≅ =𝐞𝛕 ∴ 𝛕 ≅ 𝟏𝟎. 𝟓 𝐬𝐞𝐜
𝐓𝟎 − 𝐓∞ 𝟑𝟓 − 𝟏𝟏𝟎 𝟏𝟓
−𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟏 −𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟏
Ґ = 𝟎. 𝟏 = 𝐞 𝛕 =𝐞 𝟏𝟎.𝟓 ∴ 𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟏 ≅ 𝟐𝟒. 𝟏𝟖 𝐬𝐞𝐜
−𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟗 −𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟗
Ґ = 𝟎. 𝟗 = 𝐞 𝛕 =𝐞 𝟏𝟎.𝟓 ∴ 𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟗 ≅ 𝟏. 𝟏𝟏 𝐬𝐞𝐜
∴ 𝐭 𝐑 = 𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟏 − 𝐭 Ґ=𝟎.𝟗 = 𝟐𝟒. 𝟏𝟖 − 𝟏. 𝟏𝟏 ≅ 𝟐𝟑. 𝟎𝟕 𝐬𝐞𝐜
5- Given
𝐅𝐢𝐫𝐬𝐭 − 𝐨𝐫𝐝𝐞𝐫 𝐬𝐲𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐦 𝐓𝟎 = 𝟐𝟓℃
𝐓∞ = 𝟏𝟓𝟎℃ 𝐓𝟏 (𝐭) = 𝟏𝟎𝟎℃
𝐭 𝟏 = 𝟓 𝐬𝐞𝐜 𝛕 =? ? 𝐓𝟐 (𝐭) =? ? 𝐭 𝟐 = 𝟓𝛕
Solution
𝐓𝟏 (𝐭) − 𝐓∞ −𝐭 𝟏 𝟏𝟎𝟎 − 𝟏𝟓𝟎 −𝟓
Ґ𝟏 = =𝐞 𝛕 ∴ Ґ𝟏 = ≅ 𝟎. 𝟒 = 𝐞 𝛕 ∴ 𝛕 ≅ 𝟓. 𝟒𝟔 𝐬𝐞𝐜
𝐓𝟎 − 𝐓∞ 𝟐𝟓 − 𝟏𝟓𝟎
𝐓𝟐 (𝐭) − 𝐓∞ −𝐭 𝟐 𝐓𝟐 − 𝟏𝟓𝟎
Ґ𝟐 = =𝐞 𝛕 ∴ Ґ𝟐 = = 𝐞−𝟓 ≅ 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟔𝟕𝟑𝟖 ∴ 𝐓𝟐 ≅ 𝟏𝟒𝟗. 𝟏𝟔℃
𝐓𝟎 − 𝐓∞ 𝟐𝟓 − 𝟏𝟓𝟎
6- Given:
𝐅𝐢𝐫𝐬𝐭 − 𝐨𝐫𝐝𝐞𝐫 𝐬𝐲𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐦 𝛕 = 𝟎. 𝟒 𝐬
𝛃 = 𝟒𝟎𝟎𝟎 𝐊 𝐭 =? ?
Ґ(𝐭) = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟓 𝐊 =? ?
𝐓(𝐭) = 𝟑𝟎𝟎 𝐊 𝐑 𝐓=𝟑𝟎𝟎 𝐊 = 𝟏𝟎𝟎𝟎 Ω
Solution
∵ Ґ(𝐭) = 𝐞−𝐭⁄𝛕 = 𝐞−𝐭⁄𝟎.𝟒 = 𝟎. 𝟎𝟓 ∴ 𝐭 ≅ 𝟏. 𝟏𝟗𝟖 𝐬 ≅ 𝟏. 𝟐 𝐬
𝛛𝐑 𝛛 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏
𝛃( − ) 𝛃( − ) −𝛃 −𝐑 𝛃 −𝟏𝟎𝟎𝟎 ∗ 𝟒𝟎𝟎𝟎
𝐊= | = [𝐑 𝐨 𝐞 𝐓 𝐓𝐨 ] = 𝐑 𝐨 𝐞 𝐓 𝐓𝐨 ( 𝟐 ) = = ≅ −𝟒𝟒. 𝟒𝟒 Ω⁄𝐊
𝛛𝐓 𝐓 𝛛𝐓 𝐓 𝐓𝟐 𝟑𝟎𝟎𝟐
You might also like
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries KRX6 SMDocument244 pagesMitsubishi Heavy Industries KRX6 SMАртур БобкинNo ratings yet
- Sheet (5) (Dynamic Characteristics of Instrument Systems)Document7 pagesSheet (5) (Dynamic Characteristics of Instrument Systems)Md Mainul Hsoen ImonNo ratings yet
- Clase 14 - Mate IV - Cambio de Temperatura 1Document6 pagesClase 14 - Mate IV - Cambio de Temperatura 1alicia morenoNo ratings yet
- Armand File WAG DELETEDocument3 pagesArmand File WAG DELETERay Armand GappiNo ratings yet
- 18 Integration TechniquesDocument18 pages18 Integration Techniquesأيوب عبد الأمير هزبر /تقنية غازNo ratings yet
- Sheet (3) (Uncertainty Analysis)Document10 pagesSheet (3) (Uncertainty Analysis)mohamed orifNo ratings yet
- Tarea #1: Amplificadores Cascodes.: Sonny Dominique Ceja CelisDocument5 pagesTarea #1: Amplificadores Cascodes.: Sonny Dominique Ceja Celisshaaron ceja celisNo ratings yet
- Ex 2 Two Hinge ArchDocument3 pagesEx 2 Two Hinge ArchchandrasekarNo ratings yet
- 1st Grading Lesson 5 - GR 9Document9 pages1st Grading Lesson 5 - GR 9justanotherbroadwayfanNo ratings yet
- Parametric Equations by Chain RuleDocument10 pagesParametric Equations by Chain RuleSyedda Kashf GilaniNo ratings yet
- Ans Equilibrium-1Document9 pagesAns Equilibrium-1dodaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.4 - Solvable Groups of Trigonometric IntegralsDocument19 pagesLesson 3.4 - Solvable Groups of Trigonometric IntegralsChristine TenorioNo ratings yet
- Resumen Ecuaciones Temas 5, 6 y 7 PDFDocument3 pagesResumen Ecuaciones Temas 5, 6 y 7 PDFScottyNo ratings yet
- Differential Equation - p6Document23 pagesDifferential Equation - p6Rondio LopezNo ratings yet
- Ex 1 Two Hinge ArchDocument3 pagesEx 1 Two Hinge ArchchandrasekarNo ratings yet
- For Example Two Variables and One Constraint: C-Lagrange Multiplier Method (Multi-Varaiables)Document5 pagesFor Example Two Variables and One Constraint: C-Lagrange Multiplier Method (Multi-Varaiables)johnNo ratings yet
- U1 AC La Circunferencia VDocument4 pagesU1 AC La Circunferencia VLOKOBRYAN PE7No ratings yet
- Differential Equation - p4Document16 pagesDifferential Equation - p4Rondio LopezNo ratings yet
- Formulario para ImprimirDocument3 pagesFormulario para Imprimirramirezmariadelrosario340No ratings yet
- Formulario para ImprimirDocument3 pagesFormulario para Imprimirramirezmariadelrosario340No ratings yet
- Formulario Fisica Termodinamica e OndasDocument2 pagesFormulario Fisica Termodinamica e OndasAzt RibNo ratings yet
- Solution of Midterm Exam 2Document8 pagesSolution of Midterm Exam 2omarelbdryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document122 pagesChapter 11Rozin FaruqNo ratings yet
- Resolving ForcesDocument6 pagesResolving ForcesdodaNo ratings yet
- Clase 11 - A - Mate III - Integrales Curvilíneas 3Document10 pagesClase 11 - A - Mate III - Integrales Curvilíneas 3Jhoann Andres Torres CocaNo ratings yet
- BASCALQ4Document5 pagesBASCALQ4Marjuline De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Exercise 1Document8 pagesCH 3 Exercise 1Mutee Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Coord - Cilind.y Esfericas.Document27 pagesCoord - Cilind.y Esfericas.MaríaNo ratings yet
- Sesiones 27-28:: Análisis Vectorial y Tensorial Aplicado A La FísicaDocument22 pagesSesiones 27-28:: Análisis Vectorial y Tensorial Aplicado A La FísicaLev LandauNo ratings yet
- Steady State ErrorDocument4 pagesSteady State ErrorAhmed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Clase 11 - Mat IV - Transformada de LaplaceDocument9 pagesClase 11 - Mat IV - Transformada de LaplaceYAN ELIO MANRIQUE MOGOLLONNo ratings yet
- MMC 2019 Grade 7 Division Finals - Team Oral Competition Questions With SolutionsDocument33 pagesMMC 2019 Grade 7 Division Finals - Team Oral Competition Questions With SolutionsNoreenNo ratings yet
- Resistencia de Materiales 2Document23 pagesResistencia de Materiales 2Anyela Sedano QuispeNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Diesel CycleDocument15 pages2.3 Diesel CycleSan Jose, Kyla Mae M.No ratings yet
- Nama: Aisyah Septialara Nim: R1A118022 Penurunan Teorema GreenDocument5 pagesNama: Aisyah Septialara Nim: R1A118022 Penurunan Teorema GreenBondan FebriartaNo ratings yet
- Hormigón Simple Hormigón Reforzado Y Recu Brimien To Hormigón Simple Con Refu Erzos Helicoidal Sin Recu Brimien ToDocument10 pagesHormigón Simple Hormigón Reforzado Y Recu Brimien To Hormigón Simple Con Refu Erzos Helicoidal Sin Recu Brimien ToLuis Fabian Mendoza SuárezNo ratings yet
- Helical Gear Design PSG PDFDocument9 pagesHelical Gear Design PSG PDFMannam YashuNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Quantitative Research: Inferential Statistics Reference of Formulas Hypothesis-Testing ProcessDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2 Quantitative Research: Inferential Statistics Reference of Formulas Hypothesis-Testing Processjessa barbosaNo ratings yet
- EE435 - Chapter5 - Lec1 - Transient Response Analysis - Part A - A.HaddadDocument20 pagesEE435 - Chapter5 - Lec1 - Transient Response Analysis - Part A - A.HaddadIbrahim abdoNo ratings yet
- Inbound 8014800351265628203Document1 pageInbound 8014800351265628203Sidiabdalla MouemelNo ratings yet
- Formulario MaquinasDocument2 pagesFormulario MaquinasArturoNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics - New Formulae & Data BookletDocument11 pagesAQA Physics - New Formulae & Data BookletsciencedocsmanNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods SYMBOL of SUM, Double SUM and MultiplicationDocument24 pagesQuantitative Methods SYMBOL of SUM, Double SUM and MultiplicationCasper DarkusNo ratings yet
- Clase 10 - Mate III - Integrales Curvilíneas 2Document14 pagesClase 10 - Mate III - Integrales Curvilíneas 2Jhoann Andres Torres CocaNo ratings yet
- Clase 4 - Mate IV - Ecuaciones LinealesDocument17 pagesClase 4 - Mate IV - Ecuaciones LinealesPæül AlarconNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.3 - Integration by Trigonometric SubstitutionDocument28 pagesLesson 3.3 - Integration by Trigonometric SubstitutionChristine TenorioNo ratings yet
- Teoría Del Consumidor (Parte II)Document16 pagesTeoría Del Consumidor (Parte II)monique jahuiraNo ratings yet
- Formulario de Funciones MatematicasDocument2 pagesFormulario de Funciones MatematicasJUAN SALVADOR LARA CAMACHONo ratings yet
- A. B. C. D.Document7 pagesA. B. C. D.Islami Farhan SyahputraNo ratings yet
- (201552020012) Ilham Aulia Amanullah Statistika Tugas 8Document7 pages(201552020012) Ilham Aulia Amanullah Statistika Tugas 8Islami Farhan SyahputraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (Problem Solving)Document7 pagesAssignment 1 (Problem Solving)Mostafa Ahmed ZeinNo ratings yet
- 4.3 - Elements of Numerical IntegrationDocument23 pages4.3 - Elements of Numerical IntegrationKamran BabarNo ratings yet
- Formulario DerivadasDocument2 pagesFormulario DerivadasFatima GarcíaNo ratings yet
- 10 Higuera Corrosion y TransporteDocument49 pages10 Higuera Corrosion y TransporteEduardo SorcererNo ratings yet
- Clase 9 - Mate III - Integrales Curvilíneas 1Document18 pagesClase 9 - Mate III - Integrales Curvilíneas 1Jhoann Andres Torres CocaNo ratings yet
- CH#2 Interpolation & Curve Fittings-2nd VersionI-06!11!2023Document79 pagesCH#2 Interpolation & Curve Fittings-2nd VersionI-06!11!2023Muhammad UzairNo ratings yet
- Avances - Tarea - 2 - SEÑALES Y SISTEMASDocument8 pagesAvances - Tarea - 2 - SEÑALES Y SISTEMASRGelectronic RGelectronicNo ratings yet
- Most Probable VelocityDocument2 pagesMost Probable VelocitybatazaiNo ratings yet
- Basilius 3.0Document4 pagesBasilius 3.0Piero yosip Basilio AylasNo ratings yet
- 27 RMM Winter Edition 2022 SolutionsDocument92 pages27 RMM Winter Edition 2022 SolutionsCesar Villalta CuetoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8Document2 pagesAssignment 8mohamed orifNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document1 pageAssignment 4mohamed orifNo ratings yet
- استنتاج2Document30 pagesاستنتاج2mohamed orifNo ratings yet
- PHY 111 Model Answer-Midterm.Document2 pagesPHY 111 Model Answer-Midterm.mohamed orifNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1. PHY111Document7 pagesSheet 1. PHY111mohamed orifNo ratings yet
- DC Machine ConnectionDocument12 pagesDC Machine Connectionmohamed orifNo ratings yet
- TAC MicroNet Sensors - MN-S SeriesDocument4 pagesTAC MicroNet Sensors - MN-S SeriesJ BukhariNo ratings yet
- Car Cooling SystemDocument5 pagesCar Cooling SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Physical ChemistryDocument28 pagesPrinciples of Physical Chemistryqwerty1298No ratings yet
- Heat ExamDocument2 pagesHeat ExamZahraa A. NadeemNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan of Science 6Document7 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan of Science 6lxcnpsycheNo ratings yet
- Manual Cold PointDocument9 pagesManual Cold PointJuan Antonio Alvaro HuaynateNo ratings yet
- Rac 1Document3 pagesRac 1PARWAZ Technical InstituteNo ratings yet
- Modelling Plasma Arcs For Electrical SimulationsDocument4 pagesModelling Plasma Arcs For Electrical Simulationsadmatama221100% (1)
- Non-Destructive Ageing State Determination of Solid Rocket Motors Charges423 - TussiwandDocument19 pagesNon-Destructive Ageing State Determination of Solid Rocket Motors Charges423 - Tussiwandg c agnihotriNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Solids and Structures: M. Naderi, M.M. KhonsariDocument6 pagesInternational Journal of Solids and Structures: M. Naderi, M.M. KhonsariHudson MoraisNo ratings yet
- Ch19 ISMDocument84 pagesCh19 ISMJessamine KurniaNo ratings yet
- 45 G 4 eDocument11 pages45 G 4 eMuskan BatraNo ratings yet
- BODR For HVACDocument3 pagesBODR For HVACMo EmadNo ratings yet
- To Determine Mechanical Equivalent of Heat, J by Callender and Barnes MethodDocument11 pagesTo Determine Mechanical Equivalent of Heat, J by Callender and Barnes Methodaman beniwal 82No ratings yet
- CompiledDocument477 pagesCompiledJim André Taganna50% (2)
- Handbook of Burner Technology For Industrial Furnaces: January 2009Document22 pagesHandbook of Burner Technology For Industrial Furnaces: January 2009Leyston CaicedoNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q4 Module 1Document4 pagesScience10 Q4 Module 1bongatomarieveroniqueNo ratings yet
- Ahu IqDocument5 pagesAhu IqAtul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Thermal RadiationDocument5 pagesThermal RadiationBor OtNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Science - Chapter 5 - Conservation of EnergyDocument32 pagesCambridge Science - Chapter 5 - Conservation of EnergyDK01No ratings yet
- Syllabus - Inspector of Legal MetrologyDocument2 pagesSyllabus - Inspector of Legal MetrologyROEIGHTNo ratings yet
- STULZ Wall-Air Displacement Evolution 0712 enDocument8 pagesSTULZ Wall-Air Displacement Evolution 0712 enAnonymous MVbaaUBSZTNo ratings yet
- Process Control Homework SolutionsDocument6 pagesProcess Control Homework Solutionsafmsqcodt100% (1)
- THERMO1 - 1 Introductory Concepts and Definition - Sample Problems PDFDocument25 pagesTHERMO1 - 1 Introductory Concepts and Definition - Sample Problems PDFEdmark AldeaNo ratings yet
- Code Description Quantity Unit Rate (IDR) Amount (IDR) Total Amount Material Labor Material LaborDocument2 pagesCode Description Quantity Unit Rate (IDR) Amount (IDR) Total Amount Material Labor Material LaborNima GokillNo ratings yet
- Electronic Expansion Valves - ExVDocument2 pagesElectronic Expansion Valves - ExVOndrey Dobro-CkýNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Refrigerant Charge and Outdoor TempeDocument7 pagesThe Effect of Refrigerant Charge and Outdoor Tempeحسن عرقسوسيNo ratings yet
- Dimensional FormulasDocument5 pagesDimensional FormulasPranavNo ratings yet
- Temperature (Physics Presentation)Document9 pagesTemperature (Physics Presentation)Hameed Ahmed Khas Kheli100% (1)