Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 2 - Halfwave Rectifier
Week 2 - Halfwave Rectifier
Uploaded by
wyi96670 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views32 pagesOriginal Title
Week 2_halfwave rectifier
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views32 pagesWeek 2 - Halfwave Rectifier
Week 2 - Halfwave Rectifier
Uploaded by
wyi9667Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 32
1
Half Wave Rectifier
Power Electronics and Applications for
Renewable Energy (EEE406)
Week 2
S2, 2023/24
Lecturer: Xuchen Wang
Xuchen.Wang@xjtlu.edu.cn
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
2
Outline
• Resistive Load
• Resistive-Inductive Load
• The Freewheeling Diode
• The controlled Half-Wave rectifier
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
3
Questions
• What is a rectifier?
• Calculate the load current and load power of the half-
wave rectifier with a resistive load.
• Calculate the load current and load power in a half-wave
rectifier with an RL load.
• What is the function of a freewheeling diode and how to
calculate the average and rms load current?
• How to control the output current and voltage of the
controlled (SCR) half-wave rectifier.
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
4
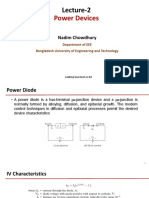
Introduction
• Half-wave rectifier is a rectifier converts ac to dc.
• Power transfer is from the ac to the dc load.
• The purpose of a rectifier may be to produce an output
that is purely dc component, or the purpose may be to
produce a voltage or current waveform that has a
specified dc component.
• The half-wave rectifier is used most often in low-power
applications because the average current in the supply will
not be zero, which will influence the transformer
performance.
• Therefore, we are not going to use the half-wave rectifiers
very often in practice. But it do help you to understand
more complicated circuits in the future.
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
5
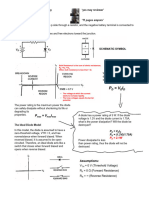
Resistive Load
What is the voltage waveforms across the source,
load and diode?
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
6
Resistive Load
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
7
Resistive Load
The average load voltage and average current are :
The rms load voltage and rms load current are:
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
8
Example 1
For the half-wave rectifier with resistive load, the source is
a sinusoid of 120 V rms at a frequency of 60 Hz. The load
resistor is 5 Ω. Determine (a) the average load current, (b)
the average power absorbed by the load and (c) the power
factor of the circuit.
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
9
Resistive-Inductive Load
Can you figure out the waveforms
on the right hand side?
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
10
Resistive-Inductive Load
• According to Kirchhoff voltage law:
• This is a first-order ODE function, the
solution can be expressed as:
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
11
Resistive-Inductive Load
• The solution of forced response is:
• The solution of natural response is:
• The complete response is:
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
12
Resistive-Inductive Load
• Assuming the initial inductor current is zero,
• The final solution is:
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
13
Resistive-Inductive Load
• Write the function in terms of the angle ωt rather than
time:
• Note this current equation is only valid for 0<ωt<β.
• The first point when the current reaches zero when the
diode turns off is called the extinction angle β (熄弧角).
Can you find the value of β?
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
14
Resistive-Inductive Load
• Substitute β into the current equation (shown last slide):
• Which can be simplified as:
(Then you can find the value β by solving this equation)
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
15
Resistive-Inductive Load
• To summarize, the current equation can be expressed
as:
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
16
Resistive-Inductive Load
• The average power absorbed by the load is , the
average power absorbed by the inductor is zero.
• The rms value of from the current function is:
• The average current is:
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
17
Example 2
For the half-wave rectifier with RL load, R=100 Ω, L=0.1 H,
ω=377 rad/s, and 𝑉𝑉𝑚𝑚 =100 V. Determine (a) an expression
for the current in this circuit. (b) the average current, (c)
the rms current (d) the power absorbed by the RL load,
and (e) the power factor.
For the parameters given,
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
20
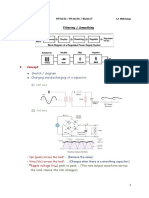
The freewheeling diode
Can you determine when each diode conducts?
It is observed that both diodes cannot be forward-
biased at the same time.
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
21
The freewheeling diode
• Diode D1 will be on when the source is positive, and
diode D2 will be on when the source is negative.
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
22
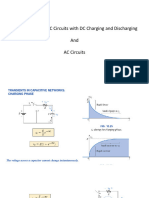
The freewheeling diode
• When the circuit is first energized, the load current is
zero and cannot change instantaneously.
Can you draw load voltage waveform?
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
23
The freewheeling diode
Voltage and currents in steady state:
Load voltage and load current
Diode 1 current
Diode 2 current
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
24
The freewheeling diode
The Fourier series for the half-wave rectified sine wave
for the voltage across the load in steady state is:
∞
𝑉𝑉𝑚𝑚 𝑉𝑉𝑚𝑚 2𝑉𝑉𝑚𝑚
𝑣𝑣𝑜𝑜 (𝑡𝑡) = + sin 𝜔𝜔0 𝑡𝑡 − � cos 𝑛𝑛𝜔𝜔0 𝑡𝑡
𝜋𝜋 2 𝑛𝑛2 − 1 𝜋𝜋
𝑛𝑛=2,4,6...
The current in the load can be expressed as a Fourier
series by using superposition, taking each frequency
separately.
𝑉𝑉𝑛𝑛
𝐼𝐼𝑛𝑛 =
𝑍𝑍𝑛𝑛
where 𝑍𝑍𝑛𝑛 = 𝑅𝑅 + 𝑗𝑗𝑗𝑗𝜔𝜔0 𝐿𝐿
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
25
Example 3
Determine the average load voltage and current, and
determine the power absorbed by the resistor of the half
wave rectifier with freewheeling diode and RL load, where
𝑅𝑅 = 2 Ω and 𝐿𝐿 = 25 𝑚𝑚H, 𝑉𝑉𝑚𝑚 is 100 V, and the frequency is
60 Hz.
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
29
The freewheeling diode
• The inductance affects only the AC terms in the
Fourier series.
• If the inductance is infinitely large, the impedance of
the load to the AC terms in the Fourier series is
infinite, and the load current is purely dc. The load
current is:
• A large inductor with a freewheeling diode provides a
means of establishing a nearly constant load current.
The current ripple in load current can be estimated as
being equal to the amplitude of the first AC term in
the Fourier series, which is:
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
30
Example 4
For the half-wave rectifier with a freewheeling diode and RL
load, the source is 240V rms at 60Hz and 𝑅𝑅 = 8 Ω.
(a) Assume L is infinitely large. Determine the power
absorbed by the load and the power factor as seen by
the source. Sketch 𝑣𝑣𝑜𝑜 , 𝑖𝑖𝐷𝐷1 and 𝑖𝑖𝐷𝐷2
(b) Determine the average current in each diode.
(c) For a finite inductance, determine L such that the peak
to-peak current is no more than 10 percent of the
average current.
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
34
The Controlled Half-Wave Rectifier
• The half-wave rectifiers analyzed in the previous are
uncontrolled rectifiers, which means the dc level of the
output and the power transferred to the load are fixed
values.
How can we control the output of a half-wave rectifier?
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
35
The Controlled Half-Wave Rectifier
What are the two conditions to turn on the SCR?
• The SCR must be forward-biased (𝑉𝑉𝑆𝑆𝑆𝑆𝑆𝑆 > 0).
• A current must be applied to the gate of the
SCR.
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
36
The Controlled Half-Wave Rectifier
• A gate signal is applied to the SCR at , where α
is the delay angle.
What is the load voltage and the SCR voltage?
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
37
The Controlled Half-Wave Rectifier
The power absorbed by the resistor is , where
the rms voltage across the resistor is:
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
38
Example 3
• Design a circuit to produce an average voltage of 40 V
across a 100 Ω load resistor from a 120 V rms 60 Hz ac
source. Determine the power absorbed by the resistance
and the power factor.
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
41
Review Questions
• What is a rectifier?
• Calculate the load current and load power of the half-
wave rectifier with a resistive load.
• Calculate the load current and load power in a half-wave
rectifier with an RL load.
• What is the function of a freewheeling diode and how to
calculate the average and rms load current?
• How to control the output current and voltage of the
controlled (SCR) half-wave rectifier.
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
42
THANK YOU
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education
You might also like
- Powerd 1Document21 pagesPowerd 1KARTHIGEYAN.RNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Design of Flyback ConverterDocument5 pagesDesign of Flyback ConverterNathan SwansonNo ratings yet
- (Power Electronics and Power Systems) Slobodan N. Vukosavic - Grid-Side Converters Control and Design (2018, Springer International Publishing)Document288 pages(Power Electronics and Power Systems) Slobodan N. Vukosavic - Grid-Side Converters Control and Design (2018, Springer International Publishing)Isabella Bianchin100% (2)
- Phy2 11 - 12 Q3 0501 PF FDDocument66 pagesPhy2 11 - 12 Q3 0501 PF FDchristophermaqNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Fullwave RectifierDocument59 pagesWeek 3 - Fullwave Rectifierwyi9667No ratings yet
- Week 4 - DC-DC ConverterDocument43 pagesWeek 4 - DC-DC Converterwyi9667No ratings yet
- Transmission Lines Electricity's Highways: B7kennedy & Associates IncDocument32 pagesTransmission Lines Electricity's Highways: B7kennedy & Associates IncbabuNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document19 pagesLec 2Aye Thein MaungNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Diode, SCR, TriacDocument67 pages1.1 Diode, SCR, Triac727721eumt082No ratings yet
- PH112 Electricity, Magnetism and Thermal PhysicsDocument26 pagesPH112 Electricity, Magnetism and Thermal PhysicsLaiba FarhadNo ratings yet
- (Fisika 2) : Fundamental Physics 2Document6 pages(Fisika 2) : Fundamental Physics 2afra ekaNo ratings yet
- Mirpur University of Science and Technology (Must), Mirpur Mirpur Institute of TechnologyDocument10 pagesMirpur University of Science and Technology (Must), Mirpur Mirpur Institute of TechnologyYounas AhmadNo ratings yet
- I. Diode Equivalent CircuitsDocument5 pagesI. Diode Equivalent CircuitsJohn RivasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document46 pagesChapter 4raven wolfNo ratings yet
- Power Diodes: Engr. Jahangeer Badar SoomroDocument50 pagesPower Diodes: Engr. Jahangeer Badar SoomroJahangeer SoomroNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Fundamentals Luoguomin 6pcsDocument7 pagesPart 1 Fundamentals Luoguomin 6pcsTamim SikderNo ratings yet
- 4 Single Phase Uncontrolled Full-Wave RectifiersDocument12 pages4 Single Phase Uncontrolled Full-Wave RectifiersLuthfan AzizanNo ratings yet
- Power Diodes: Engr. Jahangeer Badar SoomroDocument33 pagesPower Diodes: Engr. Jahangeer Badar SoomroJahangeer SoomroNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8 Reactive Properties of Copper CableDocument29 pagesExercise 8 Reactive Properties of Copper Cableapi-19713349No ratings yet
- 4 Single Phase Uncontrolled Full-Wave RectifiersDocument12 pages4 Single Phase Uncontrolled Full-Wave RectifiersRodrigo PerezNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Ni Bulay Sa ECEDocument11 pagesReviewer Ni Bulay Sa ECEChicken EggNo ratings yet
- Mirpur University of Science and Technology (Must), Mirpur Mirpur Institute of TechnologyDocument15 pagesMirpur University of Science and Technology (Must), Mirpur Mirpur Institute of TechnologyYounas AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document27 pagesChapter 2Ag De Santos Jr.No ratings yet
- PE1 Lect 7 Fully Controlled Wave Rectifiers Diode Neww-RecordedDocument26 pagesPE1 Lect 7 Fully Controlled Wave Rectifiers Diode Neww-RecordedAbdel-aziz SamiNo ratings yet
- EE 152 Chapter 3Document53 pagesEE 152 Chapter 3Gideon AdomNo ratings yet
- 05 - Chapter 13 - Magnetically Couplled CircuitsDocument24 pages05 - Chapter 13 - Magnetically Couplled CircuitsUmar BazafNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Basic ConceptsDocument31 pagesChapter 1-Basic ConceptsedddyNo ratings yet
- Filtering Concept - Lesson 1 PDFDocument3 pagesFiltering Concept - Lesson 1 PDFKeathon ZaneNo ratings yet
- Simple CircuitsDocument36 pagesSimple CircuitsjujuNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 5 Part 2 PEDocument48 pagesLECTURE 5 Part 2 PEAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices For Power Electronics: Prelim PeriodDocument36 pagesSemiconductor Devices For Power Electronics: Prelim PeriodEd RianNo ratings yet
- EEU07302 2223S1 Handouts L2Document11 pagesEEU07302 2223S1 Handouts L2Godlisten NyariNo ratings yet
- Lectures 3&4Document47 pagesLectures 3&4Yong Jian RongNo ratings yet
- Meet Our Presenter: Jerzy (Jurek) KazmierczakDocument57 pagesMeet Our Presenter: Jerzy (Jurek) KazmierczakPaulo Sérgio RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - IntroductionDocument24 pagesWeek 1 - Introductionwyi9667No ratings yet
- Application of Numerical Relays For HV Shunt Reactor ProtectionDocument5 pagesApplication of Numerical Relays For HV Shunt Reactor Protectionalex696No ratings yet
- Basic Components and Electric Circuits: Reproduction or Display. 1Document24 pagesBasic Components and Electric Circuits: Reproduction or Display. 1Rami WahshehNo ratings yet
- Basic Components and Electric Circuits: Reproduction or Display. 1Document24 pagesBasic Components and Electric Circuits: Reproduction or Display. 1zeromeansNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Network Theory - Study NotesDocument16 pagesBasic Concept of Network Theory - Study NotesBORN TO DIENo ratings yet
- Ece 9Document25 pagesEce 9nachiketaanand20No ratings yet
- Continuous-Current Case: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Document20 pagesContinuous-Current Case: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Lab 09 - Power SuppliesDocument47 pagesLab 09 - Power SuppliescrackintheshatNo ratings yet
- An Isolated Bridge Boost Converter With Active Soft SwitchingDocument8 pagesAn Isolated Bridge Boost Converter With Active Soft SwitchingJie99No ratings yet
- Advanced Diode ApplicationsDocument22 pagesAdvanced Diode ApplicationsArif IstiaqNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Full-Wave RectifierDocument21 pagesCH 5 Full-Wave RectifierSYAFIQAH ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Buck Boost ConvertersDocument33 pagesBuck Boost ConvertersMuneerAhmed0% (1)
- DRE2143 Chapter 2 - Rectifier - Part IIDocument30 pagesDRE2143 Chapter 2 - Rectifier - Part IIzulaikha efendiNo ratings yet
- Vector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics: Twelfth EditionDocument118 pagesVector Mechanics For Engineers: Dynamics: Twelfth EditionFabio Orlando Carrillo BlancoNo ratings yet
- Physics WorkbookDocument55 pagesPhysics WorkbookKwan Ye LinNo ratings yet
- Transformer and Inductor Design Handbook Chapter 13Document45 pagesTransformer and Inductor Design Handbook Chapter 13rajeshNo ratings yet
- Analog & Digital Electronics: Course No: PH-218 Lec 3: Rectifier and Clipper CircuitsDocument12 pagesAnalog & Digital Electronics: Course No: PH-218 Lec 3: Rectifier and Clipper CircuitsRahulMondolNo ratings yet
- School of Electrical Engineering and ComputingDocument58 pagesSchool of Electrical Engineering and ComputingYelbe FikruNo ratings yet
- Series-Parallel CircuitsDocument27 pagesSeries-Parallel Circuits구서경No ratings yet
- No. Option A Option B Option C Option DDocument3 pagesNo. Option A Option B Option C Option DNevil ModiNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - 2022Document26 pagesWeek 3 - 2022PayalNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMERDocument5 pagesTRANSFORMERJennymhel 5st6rTuazonNo ratings yet
- AE EEE2039 Lecture4-DiodesDocument30 pagesAE EEE2039 Lecture4-DiodesArvish RamseebaluckNo ratings yet
- AC Power: 01/12/2013 Bahman R. Alyaei 1Document37 pagesAC Power: 01/12/2013 Bahman R. Alyaei 1YAWARNo ratings yet
- W2&W3. Ch2.0 Transmission Line Theory v0.2Document74 pagesW2&W3. Ch2.0 Transmission Line Theory v0.2zetty_rashidNo ratings yet
- Exam RevisionDocument61 pagesExam RevisionRachul heenimNo ratings yet
- Examples SINGLE PHASE CONTROLLED RECTIFIER CIRCUITSDocument2 pagesExamples SINGLE PHASE CONTROLLED RECTIFIER CIRCUITSjaweria fiazNo ratings yet
- Selecting A Current Transformer (CT)Document2 pagesSelecting A Current Transformer (CT)Ali DoostmohammadiNo ratings yet
- Study of Unified Power Quality Conditioner For Power Quality ImprovementDocument76 pagesStudy of Unified Power Quality Conditioner For Power Quality Improvementraghav4life8724No ratings yet
- Nptel: Power Electronic Applications in Power Systems - Web CourseDocument2 pagesNptel: Power Electronic Applications in Power Systems - Web CourseTiya gonekarNo ratings yet
- Lab SheetDocument29 pagesLab SheetKennedy KoluteNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and Drive Lab: Exp1: Single Phase Rectifier Instructor: Eng.: Nazmi Abu AshourDocument11 pagesPower Electronics and Drive Lab: Exp1: Single Phase Rectifier Instructor: Eng.: Nazmi Abu AshourBaha DaoudNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics (KWiki - Ch3 - Choppers) PDFDocument63 pagesPower Electronics (KWiki - Ch3 - Choppers) PDFmadivala nagarajaNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Five Level Diode Clamped Multilevel InverterDocument6 pagesSimulation of Five Level Diode Clamped Multilevel InverterEditor IJRITCCNo ratings yet
- A Transformers - Sep 2020Document22 pagesA Transformers - Sep 2020Abhi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Research of Zero-Crossing Detection For Sensorless BLDC MotorDocument4 pagesResearch of Zero-Crossing Detection For Sensorless BLDC MotornassimNo ratings yet
- Coral App NoteDocument7 pagesCoral App NoteMukhammad Agung RakhmawanNo ratings yet
- PartsForAlternatorsAndStarterMotors 2005 PDFDocument90 pagesPartsForAlternatorsAndStarterMotors 2005 PDFDmitryPribylskyNo ratings yet
- Pod Using HVDCDocument31 pagesPod Using HVDCRajeev JhaNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Modelling and Simulation of Electric Vehicle Using Matlab-Simulink TA. T. Mohd, M. K. Hassan and WMK. A. AzizDocument9 pagesMathematical Modelling and Simulation of Electric Vehicle Using Matlab-Simulink TA. T. Mohd, M. K. Hassan and WMK. A. Azizbhargav gorNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converters For Switch-Mode DC Power Supplies and Dc-Motor DrivesDocument34 pagesDC-DC Converters For Switch-Mode DC Power Supplies and Dc-Motor DrivesDina GaranNo ratings yet
- NXA Catalog 2022 - enDocument63 pagesNXA Catalog 2022 - enMuhammad Jamil ShahidNo ratings yet
- Application of Neural Network For Smart Control of A Buck DC/DC ConverterDocument4 pagesApplication of Neural Network For Smart Control of A Buck DC/DC ConverterHackbart100% (1)
- Power Quality Improvement Using Artificial Intelligence ReportDocument12 pagesPower Quality Improvement Using Artificial Intelligence ReportShubham JindalNo ratings yet
- Sridhar Resume - CompressedDocument2 pagesSridhar Resume - Compressed19EE072 SRIDHAR GNo ratings yet
- Power Converter Topologies: Advanced AC Drive SystemsDocument23 pagesPower Converter Topologies: Advanced AC Drive SystemsBarış Can ÜstündağNo ratings yet
- d10sc4m DiodeDocument11 pagesd10sc4m DiodeHD QuanNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Power Electronics Course Code: 5032 Course Category: A Periods/Week: 4 Periods/Semester: 52 Credits: 4 Time ScheduleDocument4 pagesCourse Title: Power Electronics Course Code: 5032 Course Category: A Periods/Week: 4 Periods/Semester: 52 Credits: 4 Time ScheduleAdvanced Vocational Training System kalamasseryNo ratings yet
- Esign and Construction of A 5kva Automatic Voltage StabilizerDocument10 pagesEsign and Construction of A 5kva Automatic Voltage StabilizerLevinho MillsNo ratings yet
- Design Simulation of UPQC To Improve Power Quality and Transfer Wind Energy To GridDocument16 pagesDesign Simulation of UPQC To Improve Power Quality and Transfer Wind Energy To Gridkanda71No ratings yet
- Modular Multilevel ConverterDocument15 pagesModular Multilevel ConverterAkshaya BondeNo ratings yet
- Onsemiindustrial Drive SolutionsDocument49 pagesOnsemiindustrial Drive Solutionskondurumahi50No ratings yet
- A Wide Compensation Ranged Hybrid Statcom With Low DC - Link Voltage PDFDocument7 pagesA Wide Compensation Ranged Hybrid Statcom With Low DC - Link Voltage PDFInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet