Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PHSI191 Cheat sheet Mk.1
PHSI191 Cheat sheet Mk.1
Uploaded by
beetlefengCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PHSI191 Cheat sheet Mk.1
PHSI191 Cheat sheet Mk.1
Uploaded by
beetlefengCopyright:
Available Formats
A4
Saturday, 20 April 2024 8:37 PM
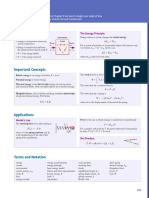
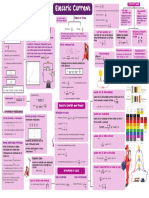
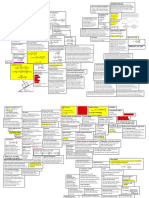
If an object returns to its original shape and size when force is removed, then it behaves elastically.
Latent heat is thermal
energy required to
phase change 1kg of
If L > L0 then tensile strain is positive substance
(lengthen)
U is stored energy
Compressive is opposite.
Q is heat energy
Flow of viscous fluid through pipe required W is work energy
higher pressure at inlet than outlet E is 'food' energy
1000 cal = 1Cal = 1.49kJ
Critical point: temperature where vapour density
and liquid density are the same, above this point
Re < 2000 = laminar, Re > 3000 = turbulent liquid cannot exist and a supercritical fluid
substance forms (no phase change back possible).
Triple point: temperature where solid, liquid and
gas phases are all in thermodynamic equilibrium
(0.01°C for water).
Absolute humidity = Moisture content in air =
mass of water present per kg dry air
Relative humidity = Partial pressure of water /
sat. vapour pressure at that temperature
Dry-bulb temperature = Normal temperature
Absolute temperature measures average measured with a thermometer
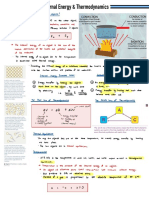
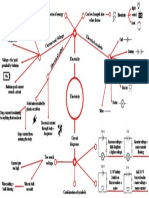
Inelastic = Plastic kinetic energy of a molecule Dew point temperature is the temperature when
Movement of thermal energy due to liquid is formed, RH = 100%
temperature is heat transfer. At RH = 100%, Dew point temp = Dry-bulb temp.
Heat transfer continues until thermal Wet Bulb Temperature = Thermometer reading
equilibrium is reached - at the same while covered in a wet cloth.
temperature. Air passing a wet surface will evaporate the
Thermal equilibrium does NOT mean the water when RH < 100%, cooling the surface to
same thermal energy. wet bulb T, no further. - The temperature of the
Properties of pressure:
cloth will decrease to attain thermal EQ B/C the
- A Fluid exerts pressure in all Directions
evaporating water requires energy
- At a given depth in a stationary liquid, pressure is equal in all directions.
- Fluid pressure always acts perpendicular to surface in contact. Laws of thermodynamics:
- Pascal's principle states pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted 0th - Objects in contact will reach thermal EQ.
undiminished to all parts of the fluid 1st - Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
- Pressure is the same at equal depth in a stationary fluid of uniform density, independent
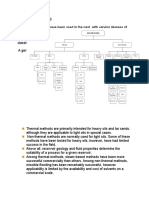
When motion is complicated, of the shape of the container.
use Energy Energy is always conserved
Most gases have the same volumetric
expansion coefficient at atmospheric
pressure: 3411 x 10-6 oC-1 at 20 oC.
Charles' Law: Volume is proportional to
temperature when pressure is constant.
Boyles' Law: Volume is inversely
proportional to pressure when temperature
is constant.
Buoyancy - Archimedes' principle:
Ideal gas law: Charles' + Boyles' Law
A body immersed in a fluid, upwards force exerted
Impulse is external force causes change in momentum by fluid equals weight of fluid displaced by body.
Inelastic collision: E K is NOT, P is conserved. Sticky = Inelastic
Elastic: E K and P are conserved.
Relative velocity before = Relative Velocity after
k is thermal
conductivity.
Total Energy in springs = E k + EP hcond is the
Surface tension - Cohesion is attraction
between like substances, adhesion is the conduction heat
attraction between unlike substances. transfer coefficient.
Capillarity - Phenomenon
where balance between Negative meniscus - Positive meniscus -
cohesive and adhesive forces Cohesive > Adhesive Adhesive > Cohesive
Transverse wave = Vertical Amplitude cause the fluid to climb up.
Longitudinal wave = Horizontal Amplitude
Incompressible - Fluid has constant density. Mass flowing in = Mass flowing out
Distribution of speeds of molecules is called
Viscosity - Internal friction of fluid.
the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution.
Laminar - Steady and Smooth. A is the surface area, T is in K, σ is Stefan -
Turbulent - Occurs at higher velocities Bernoulli's equation - Laminar, incompressible, small Boltzmann constant, ε is emissivity of the
viscosity fluids. e.g. Energy conservation. surface, and hrad is the radiative surface heat
180 degree phase change when wave hits wall transfer coefficient
Nodes have amplitude = 0 Emissivity of black surfaces is between 0.9 and
Higher velocity means less pressure.
Antinodes at peaks and troughs 1, shiny metallic surfaces is less than 0.1.
Fluids and objects go from high pressure to low pressure
Cheat sheet Page 1
You might also like
- Fluid Mechanics Equation SheetDocument11 pagesFluid Mechanics Equation SheetJerone Manley0% (1)
- 1648 ManualDocument29 pages1648 ManualSherif Adel100% (2)
- Physics Revision Booklet (Higher) PDFDocument30 pagesPhysics Revision Booklet (Higher) PDFChandrasekaran SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- F97105 DC HN9 S Ua KMoo UbDocument16 pagesF97105 DC HN9 S Ua KMoo UbPadmanava100% (1)
- Hydraulic Handbook PDFDocument781 pagesHydraulic Handbook PDFMarcosIvanMireles80% (5)
- 2012, WWW - Buydonaldson.com, Hydraulic Filtration - Technical Reference PDFDocument28 pages2012, WWW - Buydonaldson.com, Hydraulic Filtration - Technical Reference PDFVelibor Karanović100% (1)
- Finned Tube Heat ExchangerDocument15 pagesFinned Tube Heat ExchangerAna Quintana0% (1)
- Hydraulic Arm ProjectDocument31 pagesHydraulic Arm ProjectGovind Rajput77% (22)
- Practical Techniques For Centrifugal SeparationsDocument28 pagesPractical Techniques For Centrifugal SeparationsVasile BulibasaNo ratings yet
- Instructor Dr.K. Nagamalleswararao Emp Id: 14768 Associate Professor CDMM Vit, VelloreDocument148 pagesInstructor Dr.K. Nagamalleswararao Emp Id: 14768 Associate Professor CDMM Vit, VellorePriyesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Sand TrapDocument11 pagesSand TrapavgpaulNo ratings yet
- Soluble SilicatesDocument311 pagesSoluble SilicatesSomboon BoonsomNo ratings yet
- Randall Knight - Physics For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach With Modern Physics-Pearson Education Limited (2022)Document25 pagesRandall Knight - Physics For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach With Modern Physics-Pearson Education Limited (2022)laraNo ratings yet
- % Energy EpDocument1 page% Energy Epgabby fosterNo ratings yet
- 3 Forces, Work and Materials: Types of Force Turning Effects of ForcesDocument1 page3 Forces, Work and Materials: Types of Force Turning Effects of ForcesSyed Wajahat AliNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument10 pagesDynamicsjohnsmacks7No ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of MatterDocument9 pagesThermal Properties of MattermalnourishedandstupidNo ratings yet
- Revision-Map Chapter 10Document1 pageRevision-Map Chapter 10Megha BishtNo ratings yet
- A1 Exam NotesDocument161 pagesA1 Exam NoteshadiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (Bernoulli's Energy Equation) PDFDocument2 pagesLecture 3 (Bernoulli's Energy Equation) PDFJoshua TesoroNo ratings yet
- Is The Capacity To Do Work.: EnergyDocument7 pagesIs The Capacity To Do Work.: EnergyElla Mae AtienzaNo ratings yet
- THERMODYNAMICSDocument1 pageTHERMODYNAMICSDeivaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics PracticalsDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics PracticalsBikash ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Knowledge Mat Topic 8 Energy Forces Doing Work V1 2Document4 pagesEdexcel Knowledge Mat Topic 8 Energy Forces Doing Work V1 2NetkoNo ratings yet
- Work Power Energy: Mathematical Expression Forms of EnergyDocument1 pageWork Power Energy: Mathematical Expression Forms of EnergyRavi BNo ratings yet
- 5th ChapterDocument9 pages5th ChapterMOHAMMAD SHOHEL RANANo ratings yet
- 4 Work Energy PowerDocument7 pages4 Work Energy PowerAdam JrNo ratings yet
- HTTPSWWW - Thamesmead.surrey - Sch.ukwp Contentuploads201909AQA Physics Equations PDFDocument1 pageHTTPSWWW - Thamesmead.surrey - Sch.ukwp Contentuploads201909AQA Physics Equations PDFMariam HossamNo ratings yet
- Gen. Phys - 1 - Work and EnergyDocument50 pagesGen. Phys - 1 - Work and EnergyDave Lustin A. CainongNo ratings yet
- Physics 8 - EnergyDocument54 pagesPhysics 8 - EnergyHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- ConductionDocument2 pagesConduction503-10-Pattarachanok JunthipNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy, Power & Efficiency 1Document80 pagesWork, Energy, Power & Efficiency 1Hrishikesh SumeshNo ratings yet
- Resumen Termo (Video Crash Course - Link en Archivo)Document3 pagesResumen Termo (Video Crash Course - Link en Archivo)cdegraziaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics EquationsDocument1 pageIGCSE Physics Equationsgamer eliteNo ratings yet
- Gravitational Potential EnergyDocument8 pagesGravitational Potential EnergyHaar TambalusiNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 26-Dec-2022Document8 pagesAdobe Scan 26-Dec-2022sonikabansal876No ratings yet
- Heat 2Document4 pagesHeat 2daneesh5eNo ratings yet
- 5 Work Energy PowerDocument11 pages5 Work Energy Powermuhammad abdullah javedNo ratings yet
- Energy TypesDocument1 pageEnergy TypesCharlotte FranklinNo ratings yet
- Energy Work PowerDocument35 pagesEnergy Work PowerMuhammad Amin SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 EnergeticsDocument31 pagesTopic 5 EnergeticsChananNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work and Heat: Lesson 4Document5 pagesEnergy, Work and Heat: Lesson 4Jhelyne FloresNo ratings yet
- Curre NT An D Vol Tage: Form of Energy Can Be Changed Into Other FormsDocument1 pageCurre NT An D Vol Tage: Form of Energy Can Be Changed Into Other FormsMadeleine Agius CarbonaroNo ratings yet
- Fluid Dynamics: Continuity Equation. The Continuity Equation States That The Flow PassingDocument3 pagesFluid Dynamics: Continuity Equation. The Continuity Equation States That The Flow PassingCiero John MarkNo ratings yet
- Energy Work PowerDocument35 pagesEnergy Work PowerMuhammad Amin SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Work Energy Power and MomentumDocument3 pages2.3 Work Energy Power and MomentumEjaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Maths MR Uzairi 13.02.2023Document11 pagesForm 5 Maths MR Uzairi 13.02.2023haffizhNo ratings yet
- P2 - Energy Booklet 2022 AnswersDocument20 pagesP2 - Energy Booklet 2022 AnswersTran Anh Quan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Electronic Configuration-1Document15 pagesElectronic Configuration-1Dyutimoy DanNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency in Pump SpecificationDocument8 pagesEnergy Efficiency in Pump SpecificationFuad Al-AwzariNo ratings yet
- 6.1 6.3 Hooke - S Law and Deforming MaterialsDocument16 pages6.1 6.3 Hooke - S Law and Deforming MaterialsMarshell JonesNo ratings yet
- Electric: 3.1 Current and Potential DifferenceDocument6 pagesElectric: 3.1 Current and Potential DifferenceEv LamNo ratings yet
- WorkDocument5 pagesWorkUmer KhalidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Summary and ReviewDocument12 pagesChapter 9 Summary and ReviewHenry ZaleskiNo ratings yet
- Submerged Body Floating BodyDocument2 pagesSubmerged Body Floating BodyNeha ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 2nd LAW THERMO2Document6 pages2nd LAW THERMO2Ervin MogarNo ratings yet
- Φ) and kinetic energy (E: Mechanical energy General non-relativistic mechanicsDocument7 pagesΦ) and kinetic energy (E: Mechanical energy General non-relativistic mechanicsRam kripa shaNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument64 pagesEnergyMustafa Hatim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Vibration Engineering: By: Engr. Ray H. MalonjaoDocument15 pagesVibration Engineering: By: Engr. Ray H. MalonjaoEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- PushFlow NoAnswers 9upDocument1 pagePushFlow NoAnswers 9upkgrhoadsNo ratings yet
- Electric CurrentDocument1 pageElectric Currentsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Syifa Chaerunisa Putri Anelfia - Work and EnergyDocument4 pagesSyifa Chaerunisa Putri Anelfia - Work and EnergySyifa Chaerunisa PNo ratings yet
- KO 1.4 Energy ConceptsDocument1 pageKO 1.4 Energy ConceptsAbs MahiNo ratings yet
- WA5M 2860a3 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesWA5M 2860a3 Cheat SheetBatza BatsakisNo ratings yet
- Nguo-Rinlu - Onghoatha.ch: HidingDocument2 pagesNguo-Rinlu - Onghoatha.ch: HidingHOANG NHU THAONo ratings yet
- Further Maths - Work, Energy and PowerDocument1 pageFurther Maths - Work, Energy and PowerLola SmithNo ratings yet
- Exergy: Exergy System Exergy System Exergy Exergy ChangeDocument6 pagesExergy: Exergy System Exergy System Exergy Exergy ChangeMr I S A MNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument15 pagesUntitledTural EmirliNo ratings yet
- Models Mems Fluid Structure InteractionDocument16 pagesModels Mems Fluid Structure InteractionhahaerNo ratings yet
- Modul 12 - VolcanoesDocument48 pagesModul 12 - VolcanoesMarikinNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. Chemical Engineering PDFDocument70 pagesB.Tech. Chemical Engineering PDFJogi BogiNo ratings yet
- Rr210201 Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachineryDocument8 pagesRr210201 Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachinerySrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Method To Evaluate Foaming in Petroleum: Fraga, A. K. Rezende, D. A. Santos, R. F. Mansur, C. R. EDocument9 pagesMethod To Evaluate Foaming in Petroleum: Fraga, A. K. Rezende, D. A. Santos, R. F. Mansur, C. R. EAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Laboratory Ii: Segi University Experiment 5: Series and Parallel PumpDocument17 pagesChemical Engineering Laboratory Ii: Segi University Experiment 5: Series and Parallel PumpClinton NdhlovuNo ratings yet
- Vortex Rosemount 8800D (00840-0200-4004)Document24 pagesVortex Rosemount 8800D (00840-0200-4004)SergioNo ratings yet
- 044HTGDocument2 pages044HTGSophia RoseNo ratings yet
- Viscosity Index When Selecting A LubricantDocument6 pagesViscosity Index When Selecting A LubricantANGEL MURILLONo ratings yet
- ISA-RP16.6-1961: Methods and Equipment For Calibration of Variable Area Meters (Rotameters)Document18 pagesISA-RP16.6-1961: Methods and Equipment For Calibration of Variable Area Meters (Rotameters)Sergio LungrinNo ratings yet
- Kauzmann ParadoxDocument10 pagesKauzmann Paradoxkans12No ratings yet
- 174974resultatrapport (L) (3336870)Document49 pages174974resultatrapport (L) (3336870)Anonymous 8te2h1No ratings yet
- Chemtotal Labs Pvt. LTD.: D.Col - XCDDocument1 pageChemtotal Labs Pvt. LTD.: D.Col - XCDDeepak CharanNo ratings yet
- Tds 1221103 enDocument2 pagesTds 1221103 enAnimalNo ratings yet
- Polyflow Extrusion WS03 Cooled DieDocument32 pagesPolyflow Extrusion WS03 Cooled Diewoongs73No ratings yet
- Colloidal Materials: Part IVDocument21 pagesColloidal Materials: Part IVUday Prakash SahuNo ratings yet
- Boundary - Enhanced Sedimentation Due To Settling ConvectionDocument24 pagesBoundary - Enhanced Sedimentation Due To Settling Convection2306노강민No ratings yet
- Pdi - en - Ecocure 20 Ep 4351Document2 pagesPdi - en - Ecocure 20 Ep 4351Darko Pilence ŽivkovićNo ratings yet
- Modelling The Water Injection Induced Fault Slip in An Argillaceous RockDocument4 pagesModelling The Water Injection Induced Fault Slip in An Argillaceous RockMarcelo AguilarNo ratings yet
- TP 301R 02 PDFDocument46 pagesTP 301R 02 PDFClaudiu LupuNo ratings yet