Professional Documents
Culture Documents
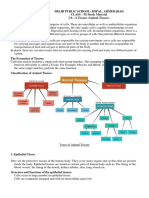
Different Types of Cells in The Human Body: Based On Tissue Formation
Uploaded by
Erika Pacleb0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
77 views39 pagescell types
Original Title
Cell Types
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentcell types
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
77 views39 pagesDifferent Types of Cells in The Human Body: Based On Tissue Formation
Uploaded by
Erika Paclebcell types
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 39
DIFFERENT TYPES OF CELLS
IN THE HUMAN BODY
BASED ON TISSUE FORMATION
OBJECTIVE
• Classify different cell types and specify the
functions of each
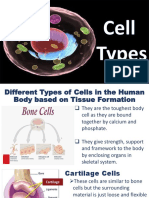
BONE CELLS - OSTEOCYTES
• the toughest body cell as they are
bound together by calcium and
phosphate
• they give strength, support and
framework to the body by enclosing
organs in skeletal system like bones
CHONDROCYTES- CARTILAGE CELLS
• similar to bone cells but the surrounding
material is just loose and flexible compared
to those of bone cells.
• freely bendable
• present in ear bone, in between large bones
to help them bend and move freely like in
between two ribs, spinal bones, joints.
NERVE CELLS - NEURONS
• they are very long and have many
branching at either ends.
• specialty; they never multiply in one's life
time
• they are present all over the body and are
sometimes as long as few meters long
• human brain cells and are found plenty in
brain and the spinal cord and form the
nervous tissue.
EPITHELIAL CELLS
• very simple cells which form covering of other cells
hence they are present in skin, scalp, respiratory
ttract , in the buccal cavity surface among others.
• they serve as barriers for pathogens, fluid loss and
mechanical injuries
• ex: skin cells, mucuos cells
• they differ in shape, some are cuboidal, squamos (
thin & flat) and columnar (tall & narrow).
• epithelium - single layer of cells
• stratified epithelium - made up of several cell layers
MUSCLES CELLS
• long, large and have ability to contract and relax
providing movements.
• THREE TYPES OF MUSCLE CELLS
1. SKELETAL MUSCLE CELL - attached to long bones and
assist in their movement ( by muscle contraction)
2. CARDIAC MUSCLE CELLS - present only in heart
muscle and are responsible for heart beats.
3. SMOOTH MUSCLE CELLS - are flexible yet can
contract and relax and are present in stomach, intestine,
blood vessel walls, helping in movement of food through
the gut.
SECRETORY CELLS
• they form glands and secrete something
important like
– pancreatic cells - secretes insulin,
glucagon
– salivary gland - secrete salivary amylase,
– sebaceous gland - secretes oil in the
skin
ADIPOSE CELLS
• fat cells and are storage by nature to store
fat.
• specially seen in the soles of the palms and
bums
• they reduce friction to the body
BLOOD CELLS
• RBC's, WBC and thrombocytes
• they are always motile and never stay in
one place.
• they have limited span and they never
multiply to form new cells.
TYPES OF CELLS IN THE HUMAN
BODY
BASED ON THEIR FUNCTION
CONDUCTIVE CELLS
• they have internal abillity to conduct an
electric impulse from one regions to other
distant region in the body.
• Example: nerve cells, muscle cells
CONNECTIVE CELLS
• they help connect other cells and tissues
• Example: bone cells, blood cells
GLANDULAR CELLS
• these glands help in production of enzymes,
hormones
• Example: secretory cells like pancreas and
salivary glands
STORAGE CELLS
• they have the ability to store materials
• Example: adipose cells
SPECIAL TYPE OF CELLS
SPERMS
• these cells unlike other cells are haploid
• present only in males after puberty
• have tail which enables them to swim and
move in the female uterus
• hyaluronidase - an enzyme which helps
sperms to penetrate through uterine tissue
and reach oocytes.
OOCYTES
• haploid cells which are present in adult
female genetal system
• they continue to form until the stage of
menopause
• they accept sperm cells to form zygote
STEM CELLS
• basic cells or parent which are
undifferentiated
• They have the potential to become all other
kind of cells in the body
• in the human body are given so much
importance due to their promising role in the
treatment of disorders in the nature.
RODS AND CONES
• these cells are in the eyes and have
capacity to capture image color and light
BLOOD CELLS
• they freely flow in the liquid blood
• some of them are not alive (RBC's)
• others have varied shapes (WBC)
• platelets (spindle shape)
CILIATED CELLS
• these cells are present as lining of
respiratory tract and esophagus and
have a pointed thread-like cilia which
move in one particular direction to
pass material.
SPECIALIZED CELLS IN PLANTS
• ROOT HAIRS – elongated outgrowths from
the outer layer of cells in a root that help
absorb water and minerals
• XYLEM & PHLOEM – the vascular bundles
that come in different shapes and structures.
• They have pits or pores while some are hollow
which help in the process of material transport
CELL MODIFICATION
CELL – CELL JUNCTIONS – the points where
two cells come together. Through the cell
junctions, the cells are joined in long-term
associations, forming tissues and organs.
You might also like
- "Types of Cells": Group 4Document11 pages"Types of Cells": Group 4Althea Dela PazNo ratings yet
- Cell Types: Prepared By: Maricarr Del Mundo - AlegreDocument43 pagesCell Types: Prepared By: Maricarr Del Mundo - AlegreAyesha YusopNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument14 pagesAnimal TissueReshmi SanjayNo ratings yet
- Types: Gwynette de Guzman Chrismaine Bell Rivas Alreah Razel PahayacDocument29 pagesTypes: Gwynette de Guzman Chrismaine Bell Rivas Alreah Razel PahayacchrismaineNo ratings yet
- Cells-and-Tissues 1Document33 pagesCells-and-Tissues 1Susan Batan BandongNo ratings yet
- PPT - TissuesDocument55 pagesPPT - TissuesTarun Bisen100% (1)
- Cell TypesDocument33 pagesCell TypesJanreve Xhylem Martirez OdangoNo ratings yet
- Cell and Tissue of AnimalsDocument27 pagesCell and Tissue of AnimalsUtami100% (1)
- Animal TissueDocument26 pagesAnimal TissueReanne MeregildoNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument42 pagesTissuesJeevitha VanithaNo ratings yet
- Tissues Class 9Document38 pagesTissues Class 9vaidika.soni12009No ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument94 pagesAnimal TissuesRafael SalvatierraNo ratings yet
- B1 - Lesson 4 - Specialised CellsDocument16 pagesB1 - Lesson 4 - Specialised CellsMorgan HarrisNo ratings yet
- Grade Ix Biology Animal Tissues 2021Document55 pagesGrade Ix Biology Animal Tissues 2021Purvi Prakash KNo ratings yet
- DR Kiran: Tissues and Its TypesDocument49 pagesDR Kiran: Tissues and Its TypesAnnie Khan100% (1)
- 7 TissuesDocument111 pages7 TissuesMaria Angelica AlmendrasNo ratings yet
- 3.9 Specialised Cells (Biology Cambridge)Document14 pages3.9 Specialised Cells (Biology Cambridge)Sumaira AkramNo ratings yet
- 2.animal TissuesDocument50 pages2.animal TissuesAhmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- 2.4 HistologyDocument41 pages2.4 Histologyhaiqalfariq07No ratings yet
- Cell OrganisationDocument32 pagesCell OrganisationAtifah ZulaikhaNo ratings yet
- Tissues 1Document42 pagesTissues 1Patricia JalbanNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: Siva PrasadDocument28 pagesCells and Tissues: Siva PrasadAWS DEVELOPERNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationDocument105 pagesStructures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationArvie Jay Castillo100% (1)
- Cell Types & ModificationsDocument9 pagesCell Types & ModificationsIchigoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Form 3 Igcse-1Document31 pagesChapter 2 Form 3 Igcse-1Victor OkosunNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant TissueDocument48 pagesAnimal and Plant TissuePortia EgkenNo ratings yet
- Types of Cells in The Body1Document29 pagesTypes of Cells in The Body1aldrin braganzaNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument19 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsBiju Mylachal100% (1)
- Animal & Plant CellsDocument38 pagesAnimal & Plant CellsVandana KhatorNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue and Muscle TissueDocument13 pagesConnective Tissue and Muscle TissueNyakie MotlalaneNo ratings yet
- Xi New Zoo-Chapt - 3-Tissue Level OrganisationDocument45 pagesXi New Zoo-Chapt - 3-Tissue Level Organisationbalasubash1977No ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument94 pagesAnimal TissuesMercel MacasinagNo ratings yet
- Cell, Tissue, Organ and Organ SystemDocument22 pagesCell, Tissue, Organ and Organ SystemFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Unit-1 PDFDocument27 pagesAnatomy Unit-1 PDFdharmendra kirarNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: Joshua D. Marcial, MDDocument82 pagesAnimal Tissues: Joshua D. Marcial, MDChristine SegundoNo ratings yet
- Zoology 15mo Lecture 1 RecordedDocument85 pagesZoology 15mo Lecture 1 RecordedyannolerouxNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument5 pagesHistologySNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument57 pagesConnective TissueSunil DhatwaliaNo ratings yet
- Cellular ModificationDocument45 pagesCellular ModificationLojo, CejayNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesDocument11 pagesCH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesRishabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Cds Day1Document15 pagesCds Day1Rajkamal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Study of Animal Tissues: Dr. AarifDocument60 pagesStudy of Animal Tissues: Dr. AarifEntirety 4uNo ratings yet
- Tissues: - TissueDocument61 pagesTissues: - Tissueuday xeroxNo ratings yet
- Tissue SystemDocument41 pagesTissue Systemrahul royNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Animal TissuesDocument68 pagesPhysiology of Animal TissuesSudheera SemasingheNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Classification of ElementsDocument24 pagesCH 3 Classification of Elementssachin aggarwal100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology - Lesson 2Document61 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Lesson 2Nilo Delica AloNo ratings yet
- GB1 Mod1 Les4 Cellular Types and Histology of AnimalsDocument64 pagesGB1 Mod1 Les4 Cellular Types and Histology of Animalsjaycervales02No ratings yet
- CellsDocument2 pagesCellsPartyland El Pais de la FiestaNo ratings yet
- 1 Tissues - Part 1Document85 pages1 Tissues - Part 1Madhavarao MaddisettyNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Term 2: Life Science Study NotesDocument26 pagesGrade 10 Term 2: Life Science Study Noteschedza FordNo ratings yet
- Document 3Document5 pagesDocument 3Chelsea MansuetoNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument3 pagesGen BioalulodizeeNo ratings yet
- Cell TypesDocument19 pagesCell TypesRhea GulayNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: Ipshita Kundu (BGKV, Salt Lake)Document9 pagesAnimal Tissues: Ipshita Kundu (BGKV, Salt Lake)Reeddhi KunduNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Plant and Animal Tissue Presentation1Document60 pagesLesson 1 Plant and Animal Tissue Presentation1abdullahfahdelm.adiongNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument29 pagesTissues, Glands, and MembranesGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of TissuesDocument58 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Tissuesflex gyNo ratings yet
- C2-Organisation and Maintenance of The OrganismDocument39 pagesC2-Organisation and Maintenance of The OrganismyourmoNo ratings yet
- English (Respiratory System)Document16 pagesEnglish (Respiratory System)ChitraNo ratings yet
- Paul Ekman Manual FACS Pages 352 357Document6 pagesPaul Ekman Manual FACS Pages 352 357LuisNo ratings yet
- Braddom Lower Extremity DrillsDocument4 pagesBraddom Lower Extremity DrillsKennie RamirezNo ratings yet
- Femoral Acetabular Impingement ImportantDocument43 pagesFemoral Acetabular Impingement ImportantAjeetalbertNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY of PneumoniaDocument7 pagesANATOMY of PneumoniaJanika Rivera HartNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Upper AirwayDocument33 pagesAnatomy of The Upper Airwayukht marutuNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve PDFDocument12 pagesFacial Nerve PDFgunawan121982100% (1)
- Muscle Sinew ChannelsDocument1 pageMuscle Sinew ChannelsRanga NathanNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Injuries in Baseball PlayersDocument7 pagesShoulder Injuries in Baseball PlayersMahayu Firsty RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- CASE REPORT Hip DislocationDocument42 pagesCASE REPORT Hip DislocationvereriNo ratings yet
- Animal Organ SystemsDocument3 pagesAnimal Organ SystemsmaygracedigolNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Potd Part 2Document1 pageGroup 1 Potd Part 2Regina CabelisNo ratings yet
- W11 PPT Presentation Exercises For The Upper ExtremitiesDocument14 pagesW11 PPT Presentation Exercises For The Upper ExtremitieshectorNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Reviewer PDFDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Reviewer PDFArnoldNo ratings yet
- Zimede Medical Catalogue-SpanishDocument16 pagesZimede Medical Catalogue-SpanishDerly PantojaNo ratings yet
- General Orientation To Human Anatomy: Atlas ADocument33 pagesGeneral Orientation To Human Anatomy: Atlas AEmilie ArvidsonNo ratings yet
- Non Locomotor Movement SkillsDocument24 pagesNon Locomotor Movement SkillsDiana Grace CaminadeNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System SeeleysDocument103 pagesIntegumentary System SeeleysAlvinTercianoVitugNo ratings yet
- The Blood Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesThe Blood Circulatory SystemListiyani IsmailNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum Diana BASMADocument23 pagesCerebellum Diana BASMAviorel79No ratings yet
- Polyvagal TheoryDocument24 pagesPolyvagal Theorymkrnhr100% (7)
- Atlas of Common Subluxations of The Human Spine and Pelvis PDFDocument238 pagesAtlas of Common Subluxations of The Human Spine and Pelvis PDFBruno RavazziNo ratings yet
- Science Exam Part I. Write The Parts of The Excretory System. (4 Points)Document5 pagesScience Exam Part I. Write The Parts of The Excretory System. (4 Points)Siria PinedaNo ratings yet
- Gym Workout - Calisthenics + WeightliftingDocument5 pagesGym Workout - Calisthenics + WeightliftingStefanNo ratings yet
- 2 Newborn Assessment 93667Document122 pages2 Newborn Assessment 93667Izziddin YassineNo ratings yet
- Basic Splinting TechniquesDocument5 pagesBasic Splinting TechniquesRicardo BragaNo ratings yet
- Berberis VulgarisDocument21 pagesBerberis VulgarisShah FaisalNo ratings yet
- Visual Images of How To Accomplish The Measurement: Mid-Upper Arm Circumference (Muac) / Waist-Hip RatioDocument5 pagesVisual Images of How To Accomplish The Measurement: Mid-Upper Arm Circumference (Muac) / Waist-Hip RatioggggangNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Headache PDFDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Headache PDFJoshua Christian TopahNo ratings yet
- Significance of Facebow For Dental RestorationsDocument5 pagesSignificance of Facebow For Dental RestorationsMahmoud Ibrahem maanNo ratings yet