Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Iode Heory: Lecturer: Noman Al Hassan
Uploaded by
KasHif MaHmood0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views16 pagesOriginal Title
DOC-20191022-WA0002.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views16 pagesIode Heory: Lecturer: Noman Al Hassan
Uploaded by
KasHif MaHmoodCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
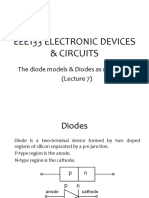
DIODE THEORY
Lecturer: Noman Al Hassan
Email: noman44m@hotmail.com
Objective of Lecture
After studing this chapter, you should be able to know
• Basic Diode.
• Symbol and labeling.
• Diode Curve and its labeling.
• Ideal Diode
Second Approximation.
Third Approximation.
• Bulk Resistance.
• DC Resistance of a Diode.
10/21/2019 Diode Theory 2
Basic Ideas
• Semiconductor device with two terminals, allowing the
flow of current in one direction only.
• Nonlinear Device.
• Schematic Symbol.
• Anode / Cathode.
Basic Diode Circuit
10/21/2019 Diode Theory 3
Diode Curve
• Forward Region.
• Reverse Region.
• Knee Voltage.
• Bulk Resistance.
• Maximum Forward Current.
• Power Dissipation.
10/21/2019 Diode Theory 4
Example: Forward Bias or Reverse Bias?
Fig- 1 Fig- 2
Example: A diode has a power rating of 2 W. If diode
voltage is 1.2 V and current is 1.75 A, what is the power
dissipation? Will the diode be destroyed?
10/21/2019 Diode Theory 5
Ideal Diode
• Most of the time we need exact solution. That’s why we use approximations.
– Perfect Conductor (Zero Resistance).
– Perfect Insulator (Infinite Resistance).
1st Approximation.
• The first approximation ignores leakage current, barrier potential and bulk
resistance.
• When an ideal diode is forward biased, the model is a closed switch.
• When an ideal diode is reverse biased, the model is an open switch.
10/21/2019 Diode Theory 6
Example:
• Calculate the load voltage and load current by using ideal
diode.
10/21/2019 Diode Theory 7
Example:
• Calculate the load voltage and load current by using ideal
diode.
10/21/2019 Diode Theory 8
Diode 2nd Approximation
• This model assumes that no diode current flows until the
forward bias across the diode reaches 0.7 volts.
• Vd is 0.7 for any current.
• Vd < 0.7 no current.
• This model ignores the exact shape of the knee.
• This model ignores the diode’s bulk resistance.
10/21/2019 Diode Theory 9
Example:
• Calculate the load voltage and load current by using
diode 2nd approximation.
10/21/2019 Diode Theory 10
Diode 3rd Approximation
• This model assumes that no diode current flows until the forward
bias across the diode reaches 0.7 volts.
• This model ignores the exact shape of the knee.
• This model does account for the diode’s bulk resistance.
• However, bulk resistance that is less than 1 Ω can be ignored.
10/21/2019 Diode Theory 11
Example:
• Use the third approximation of given circuit having bulk
resistance of 0.23 ohm to calculate the load voltage, load
current and diode power.
10/21/2019 Diode Theory 12
Diode Approximations
10/21/2019 Diode Theory 13
Bulk Resistance
• To analyze diode accurately
• V1 and I1 are voltage and current at some point near knee voltage.
• V2 and I2 are voltage and current at some higher point.
10/21/2019 Diode Theory 14
DC Resistance of a Diode
• It is the ratio of total diode voltage to total diode current.
-Forward Resistance RF. -Reverse Resistance RR.
10/21/2019 Diode Theory 15
THANKS
10/21/2019 Diode Theory 16
You might also like
- Cable Capacity TablesDocument2 pagesCable Capacity TablesEJBSE100% (5)
- Diode Fundamentals and BiasingDocument36 pagesDiode Fundamentals and BiasingSherwin VasquezNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Diodes and Their ApplicationsDocument24 pagesDifferent Types of Diodes and Their Applicationsphoool100% (8)
- EC Chapter 01Document39 pagesEC Chapter 01Muhammad qamar100% (1)
- Aether Gravity TechnologyDocument328 pagesAether Gravity Technologyrossix1100% (2)
- Nonlinear Electronics 1: Nonlinear Dipoles, Harmonic Oscillators and Switching CircuitsFrom EverandNonlinear Electronics 1: Nonlinear Dipoles, Harmonic Oscillators and Switching CircuitsNo ratings yet
- Types of DiodeDocument34 pagesTypes of DiodeAfolabiNo ratings yet
- JKR GuidelinesDocument22 pagesJKR Guidelinessulphurdioxide100% (2)
- Kulite Pressure Transducer HandbookDocument76 pagesKulite Pressure Transducer Handbookpmud123No ratings yet
- Diode Approximations Notes 2Document5 pagesDiode Approximations Notes 2Tobi Uchiha0% (1)
- Lec 9 (Basic Electronics)Document15 pagesLec 9 (Basic Electronics)Farwa JaffriNo ratings yet
- 2 Lecture 2 Diode B Stad - CH - 01Document66 pages2 Lecture 2 Diode B Stad - CH - 01peter brownNo ratings yet
- EEE133 Week 4Document70 pagesEEE133 Week 4CHUAH CHANG HONGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9:: Diodes and Diode CircuitsDocument32 pagesChapter 9:: Diodes and Diode CircuitsAryan KumarNo ratings yet
- Week02 Elka1 Diode TheoryDocument25 pagesWeek02 Elka1 Diode TheoryEstika Vriscilla GintingNo ratings yet
- I. Diode Equivalent CircuitsDocument5 pagesI. Diode Equivalent CircuitsJohn RivasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Part 2 - DiodeDocument27 pagesChapter 1 Part 2 - Diodebatrisyia1979No ratings yet
- Review: Diodes and ApplicationsDocument12 pagesReview: Diodes and Applicationsdjun033No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Part-IIDocument41 pagesChapter 1 Part-IIAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- DiodeDocument35 pagesDiodeEdelrose LapitanNo ratings yet
- Diode As A Switch WorkingDocument4 pagesDiode As A Switch Workingbantu1210% (1)
- 3.2 PN Junction Diode - CKT AnalysisDocument20 pages3.2 PN Junction Diode - CKT AnalysisLaurent VitugNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics (ES-112)Document23 pagesBasic Electronics (ES-112)Bharat LalNo ratings yet
- Diode PDF ReportDocument20 pagesDiode PDF ReportVipul Sonawane100% (2)
- Ways To Test A Diode in CircuitDocument13 pagesWays To Test A Diode in Circuitlangton mwalekaNo ratings yet
- Diode CharacteristicsDocument23 pagesDiode CharacteristicsCarryl BaerNo ratings yet
- Lecture4 1Document11 pagesLecture4 1ehddn0999No ratings yet
- CO2037 - L02 - Diode and Its ApplicationsDocument45 pagesCO2037 - L02 - Diode and Its ApplicationsHào NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Diode TestingDocument29 pagesDiode TestingDipesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Lesson PLan Demo FinalDocument3 pagesLesson PLan Demo FinalPatricia Ann Contreras MercadoNo ratings yet
- Edc Special DevicesDocument50 pagesEdc Special DevicesSurekha PittaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document12 pagesChapter 5Marione FallarcunaNo ratings yet
- Diodes: Voltage Regulation DiodeDocument6 pagesDiodes: Voltage Regulation DiodeMohammad AwalNo ratings yet
- 1 DiodesDocument30 pages1 DiodesSUCHIN AnandNo ratings yet
- 02 - Diode PDFDocument43 pages02 - Diode PDFBlack SkyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: Semiconductor DiodesDocument28 pagesLecture 2: Semiconductor DiodesgokulphdNo ratings yet
- EN1802 - Basic Electronics: S3 - Diodes, Diode Circuits and ApplicationsDocument27 pagesEN1802 - Basic Electronics: S3 - Diodes, Diode Circuits and ApplicationsShazni AhamedNo ratings yet
- DiodesDocument12 pagesDiodesSyed Mohammad FarooqueNo ratings yet
- Diodes and Half-Wave Rectification: 1 AbstractDocument3 pagesDiodes and Half-Wave Rectification: 1 AbstractJannineNo ratings yet
- EECE263 Basic Circuit Analysis Set 7: DiodesDocument30 pagesEECE263 Basic Circuit Analysis Set 7: DiodeswerewaroNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Basic Electronics - DiodesDocument80 pagesTopic 5 Basic Electronics - DiodesJENNIFER SERVONo ratings yet
- Lecture 16-17 - Clippers and Zener DiodesDocument13 pagesLecture 16-17 - Clippers and Zener DiodesCHAITANYA KRISHNA CHAUHANNo ratings yet
- Cathode vs. Anode Diode How To Indicate Placement Orientation of Diodes On Your PCBDocument12 pagesCathode vs. Anode Diode How To Indicate Placement Orientation of Diodes On Your PCBjackNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor DiodeDocument19 pagesSemiconductor DiodeAkashi SeijuroNo ratings yet
- Name: Vandhana.M USN: 1BM18EI060 Report: Aat Topic: DiodeDocument12 pagesName: Vandhana.M USN: 1BM18EI060 Report: Aat Topic: DiodePayal karakotiNo ratings yet
- Diodes - 12jan21Document7 pagesDiodes - 12jan21Sri RamanNo ratings yet
- Exam RevisionDocument61 pagesExam RevisionRachul heenimNo ratings yet
- DiodesDocument3 pagesDiodeslitrakhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document32 pagesLecture 3s231060031-5No ratings yet
- Electrical-Engineering Engineering Analog-Electronics Diode-Circuits NotesDocument41 pagesElectrical-Engineering Engineering Analog-Electronics Diode-Circuits NotesDEEPAK glaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 & 4 Special - Purpose - Diodes and BJTsDocument50 pagesChapter 3 & 4 Special - Purpose - Diodes and BJTsAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- DiodesDocument10 pagesDiodesthinh_hauiNo ratings yet
- Clipper and Clamper Circuits: January 2012Document23 pagesClipper and Clamper Circuits: January 2012Bus BusNo ratings yet
- Diode Test and Familiarization: Table1 1Document3 pagesDiode Test and Familiarization: Table1 1cent carinoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Diode? and What Is Its Function?Document4 pagesWhat Is A Diode? and What Is Its Function?Angel FerreyraNo ratings yet
- Discussion For The Most Part, in Performing This Experiment, We Only Used Diodes of Different Kinds, Multimeters, and A Power SupplyDocument2 pagesDiscussion For The Most Part, in Performing This Experiment, We Only Used Diodes of Different Kinds, Multimeters, and A Power SupplyEj HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Electronics I Lab. ECE 201Document40 pagesElectronics I Lab. ECE 201ajf3215No ratings yet
- Slide Chapter 1v2Document77 pagesSlide Chapter 1v2NGUYỄN DUY ĐẠI THẠCHNo ratings yet
- Diode Theory: ELS 2202 Elektro IDocument27 pagesDiode Theory: ELS 2202 Elektro IYohana Crisma LimbongNo ratings yet
- Dae21303lab1 DiodecharacteristicsDocument20 pagesDae21303lab1 DiodecharacteristicsEsma FarizalNo ratings yet
- Diode DataDocument16 pagesDiode Datainter2176No ratings yet
- What Is A Circuit?: Basic Electronic ComponentsDocument20 pagesWhat Is A Circuit?: Basic Electronic ComponentsazrinaishakNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument36 pagesBasic ElectronicsCarl OlayaNo ratings yet
- INST+ +Measurement+of+FrequencyDocument2 pagesINST+ +Measurement+of+Frequencyhammad100No ratings yet
- June 2021 Question Paper 31Document16 pagesJune 2021 Question Paper 31Phan Minh ViệtNo ratings yet
- C945 PDFDocument4 pagesC945 PDFHenrique Ferreira GonferNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BJT AmplifierDocument69 pagesChapter 1 BJT Amplifiernur_azhra90No ratings yet
- Using GigaProbes Agilent TDR D5Document12 pagesUsing GigaProbes Agilent TDR D5yadamyugandharNo ratings yet
- PT SUPREME CABLE Company Profile 2022Document16 pagesPT SUPREME CABLE Company Profile 2022Mhuez Anhek GheloNo ratings yet
- Field Oriented Controls of Induction Motors: AC Motor Control and EV ApplicationsDocument15 pagesField Oriented Controls of Induction Motors: AC Motor Control and EV ApplicationsKhaled Abushafa AwailiNo ratings yet
- Elspec BONUS 1350KVAr - User ManualDocument126 pagesElspec BONUS 1350KVAr - User Manualkenji1134No ratings yet
- Edc Unit 5 Small Signal Low Freq BJT ModelsDocument61 pagesEdc Unit 5 Small Signal Low Freq BJT ModelsSandeep PatilNo ratings yet
- Priya 456Document54 pagesPriya 456Priya GadirajuNo ratings yet
- Creative Electronics Group BDocument44 pagesCreative Electronics Group BumairNo ratings yet
- XR C7200Document37 pagesXR C7200Selvin ReyesNo ratings yet
- Past Jun - 18MDocument4 pagesPast Jun - 18MTucciy Alentine MaeNo ratings yet
- DS276 Low Power Transceiver Chip: Features Pin AssignmentDocument11 pagesDS276 Low Power Transceiver Chip: Features Pin AssignmentJairo PadronNo ratings yet
- Overview of Voltage Sag MitigationDocument7 pagesOverview of Voltage Sag MitigationJjjjpfNo ratings yet
- Expt 3Document5 pagesExpt 3Aarush GoelNo ratings yet
- VLF-60 DS EN EN Rev4 24Document3 pagesVLF-60 DS EN EN Rev4 24juaan figueroaNo ratings yet
- Agilent Tech., N5770A PW Supplies PDFDocument12 pagesAgilent Tech., N5770A PW Supplies PDFLulu Sweet ThingNo ratings yet
- AcuRev 2100 Multi Circuit Power Energy Meter InstallationDocument11 pagesAcuRev 2100 Multi Circuit Power Energy Meter InstallationDiogo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Devireg 535 PDFDocument28 pagesDevireg 535 PDFFabián GarófaloNo ratings yet
- BEEE (Magnetic Circuits)Document7 pagesBEEE (Magnetic Circuits)Vedu KadamNo ratings yet
- Dlcap DatasheetDocument20 pagesDlcap DatasheetMusa Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Service: MINI-Compact SystemDocument55 pagesService: MINI-Compact SystemEletrônica UniversalNo ratings yet
- Icom OPC-478PIXDocument27 pagesIcom OPC-478PIXBram HtbaratNo ratings yet
- 01v 96 PDFDocument227 pages01v 96 PDFsmftecNo ratings yet