Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exxon Risk Tolerance
Uploaded by
Mohamad Khair Shaiful AlamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exxon Risk Tolerance
Uploaded by
Mohamad Khair Shaiful AlamCopyright:
Available Formats
Strategies for Understanding and Addressing
Risk Tolerance
January 2011
Presented by:
D.J. (Dave) Fennell
Senior Safety Advisor, Imperial Oil Resources
Senior Technical Professional –Safety, ExxonMobil Production Company
On behalf of:
ExxonMobil Human Factors Center of Excellence
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
10 Factors Influencing Risk Tolerance
Strategies for Reducing Risk Tolerance
Actions to Address Risk Tolerance at Your Worksite
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Risk Perception and Tolerance Model
Maturity of Supporting Tools at ExxonMobil
Tools in place and
being used,
Hazard Identification “See it”
effectiveness may
lack in some areas
Mature safety culture will be
functional on this topic,
Risk Perception “Understand it” some areas will require more
effort to understand the
consequences of hazards.
Approaches for addressing
tolerance are general weak
Risk Tolerance “Accept or Reject it”
across the company, this is
the focus of this
presentation.
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Root Cause Analysis Flow Chart
Incident,
Incident, Near
Near Miss
Miss or
or Questionable
Questionable Item
Item Occurs
Occurs –– Why?
Why?
Personal
Personal Factors
Factors Job
Job Factors
Factors 8.
8. External
External Factors
Factors
1. Lack of skill or knowledge 5. Lack of or inadequate procedures
6. Inadequate communication of expectations
regarding procedures or standards
2. Doing the job according to procedure
or standards takes more time and effort
7. Inadequate tools or equipment (availability,
condition & use; workplace design)
3. Short-cutting the procedure or
standards has been tolerated
Develop follow up actions
4. In past, not following procedure or
standards did not result in an incident
Implement follow up actions
Verify and validate follow up actions
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Conventional Operations (Sept 3 2009)
RCAF Category Category Count
7. Inadequate Tools or Equipment 301
4. In the Past, No incident occurred 282
1. Lack of Skill or Knowledge 253
42%
6. Inadequate Communication 191
3. Short-Cutting the standard has been Tolerated 148
2. Correct Way Takes More Time/Effort 137
5. Lack of or Inadequate Procedures 30
8. External Factors 24
Grand Total 1366
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Cold Lake Operations (Sept 3 2009)
RCAF Category Category Count
7. Inadequate Tools or Equipment 349
1. Lack of Skill or Knowledge 330
4. In the past, no incident occurred 288
40%
6. Inadequate Communication 244
2. Correct Way Takes More Time/Effort 177
3. Short-Cutting the standard has been Tolerated 152
5. Lack of or Inadequate Procedures 44
8. External Factors 13
Grand Total 1597
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
10 Factors That Influence Risk Tolerance
1. Overestimating Capability/Experience ↑
2. Familiarity with the Task ↑
3. Seriousness of Outcome ↓
4. Voluntary Actions and Being in Control ↑
5. Personal Experience with an Outcome ↓
6. Cost of Non-Compliance ↓
7. Confidence in the Equipment ↑
8. Confidence in Protection and Rescue ↑
9. Potential Profit & Gain from Actions ↑
10. Role Models Accepting Risk ↑
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Hazardrecognitionandrisktolerance
Hazard Recognition and Risk Tolerance
Hazard Recognition = Risk Tolerance
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
January 2009
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
IOR Employees are generally quite good at Hazard
Recognition
2008 Safety Perception Survey
• “Do employees understand the hazards of the
operations they perform?” - 92%
• “Do you initiate action to correct hazards?” - 99%
• “Did you receive adequate safety training?” - 92%
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
• JSA often identifies the hazard
• Hazard is discounted or no follow
through on the mitigation
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
10 Factors That Influence Risk Tolerance
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
10 Factors That Influence Risk Tolerance
1. Overestimating Capability/Experience ↑
2. Familiarity with the Task ↑
3. Seriousness of Outcome ↓
4. Voluntary Actions and Being in Control ↑
5. Personal Experience with an Outcome ↓
6. Cost of Non-Compliance ↓
7. Confidence in the Equipment ↑
8. Confidence in Protection and Rescue ↑
9. Potential Profit & Gain from Actions ↑
10. Role Models Accepting Risk ↑
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Factors Influencing Risk Tolerance
1) Overestimating Capability/Experience
“I can lift 75 kg in the gym ... I can lift this nitrogen bottle”
“I have driven in worse conditions than this and did just fine”
Strategies for Reducing Tolerance
• Reflect on your role as a mentor – the person who is watching may not
have the same skill, experience or capability.
• Acknowledge that despite your ability, the exposure is still there.
• Acknowledge that the capability or skill may be sufficient and then
reinforce the way that it should be done.
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
10 Factors That Influence Risk Tolerance
1. Overestimating Capability/Experience ↑
2. Familiarity with the Task ↑
3. Seriousness of Outcome ↓
4. Voluntary Actions and Being in Control ↑
5. Personal Experience with an Outcome ↓
6. Cost of Non-Compliance ↓
7. Confidence in the Equipment ↑
8. Confidence in Protection and Rescue ↑
9. Potential Profit & Gain from Actions ↑
10. Role Models Accepting Risk ↑
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Factors Influencing Risk Tolerance
2) Familiarity with the Task - Complacency
“He had done this task 500 times “We had stack about 200 of them “I do it about 10 times every day”
without hurting himself” when ...”
Strategies for Reducing Tolerance
• ‘Situational Awareness’ – Treat every time like the first time .... ‘Stop and
Think’
• ‘What could go wrong this time?’
• ‘How would I teach a new person to do this?’
• ‘Do I still do it by the book? Have I just been luck?’
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
10 Factors That Influence Risk Tolerance
1. Overestimating Capability/Experience ↑
2. Familiarity with the Task ↑
3. Seriousness of Outcome ↓
4. Voluntary Actions and Being in Control ↑
5. Personal Experience with an Outcome ↓
6. Cost of Non-Compliance ↓
7. Confidence in the Equipment ↑
8. Confidence in Protection and Rescue ↑
9. Potential Profit & Gain from Actions ↑
10. Role Models Accepting Risk ↑
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Factors Influencing Risk Tolerance
3) Seriousness of the Outcome
‘Pinch Point’ ... what about ‘Crush’ or ‘Amputation’ point
Cable suddenly tightened and
IP’s hand became trapped between cable and wench
“Sweet gas” ?? drum.
“Hot Water” ??
Strategies for Reducing Tolerance
• Stop and Think “How bad could it be? No, really ...How bad could it
be?”
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
The Event:
While backing a truck/trailer onto a barge, the
Signaler Pinned by Truck driver lost sight of the deckhand who was
providing direction.
The driver continued to move the trailer back
after losing sight of the signaler - pinning the
signaler's legs between the back of the trailer
and a toolbox on the deck.
The deckhand suffered soft tissue injuries to
their legs (luckily, no broken bones)
The Learning:
The driver of the truck did not stop when losing
sight of their signaler.
The signaler put themselves in the line of fire
after losing eye contact with the driver.
Several fatalities occur in Alberta each year
where drivers have backed over their signalers.
Deckhand pinned here The standards in the Safety Management
System (Section 6 Subject 11 Page 6-91) state:
Drivers must:
• stop if they lose sight of a signaler
Actions:
Ensure all drivers:
- understand the standards for
signalling,
- understand their responsibility to
maintain eye contact with their signaler
- understand the consequences of
not strictly adhering to this standard.
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
10 Factors That Influence Risk Tolerance
1. Overestimating Capability/Experience ↑
2. Familiarity with the Task ↑
3. Seriousness of Outcome ↓
4. Voluntary Actions and Being in Control ↑
5. Personal Experience with an Outcome ↓
6. Cost of Non-Compliance ↓
7. Confidence in the Equipment ↑
8. Confidence in Protection and Rescue ↑
9. Potential Profit & Gain from Actions ↑
10. Role Models Accepting Risk ↑
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Factors Influencing Risk Tolerance
4) Voluntary Actions and Being in Control
Key factor in off the job risk – 28 times more likely to be hurt off the job
Strategies for Reducing Tolerance
• Integrate ‘Stop and Think’ into your personal activities
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
10 Factors That Influence Risk Tolerance
1. Overestimating Capability/Experience ↑
2. Familiarity with the Task ↑
3. Seriousness of Outcome ↓
4. Voluntary Actions and Being in Control ↑
5. Personal Experience with an Outcome ↓
6. Cost of Non-Compliance ↓
7. Confidence in the Equipment ↑
8. Confidence in Protection and Rescue ↑
9. Potential Profit & Gain from Actions ↑
10. Role Models Accepting Risk ↑
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Factors Influencing Risk Tolerance
5) Personal Experience with an Outcome
If you have seen a serious outcome, you will be less tolerant of the risk
Problem: As Incident Rates improve, fewer people will have had
personal experience and leads to Scepticism
Strategies for Reducing Tolerance
• ‘Expert observers’, supervisors, ‘keepers of the corporate memory’ have
the obligation to ensure workers know :
a) Incidents have occurred because of not following that standard (i.e.
What could go wrong?)
b) Demonstrate that there have been serious consequences (i.e. How bad
could it be?) Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources
Well Servicing Fatality - May 2002
A well servicing worker was fatally injured when he was pulled into the
rotating draw works by the strap on his fall arrest harness.
1) Loose clothing and personal protective equipment around rotating
equipment
2) Equipment guarding
Straps caught here
Draw works guard rail
Re-enactment of how
straps were caught
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
10 Factors That Influence Risk Tolerance
1. Overestimating Capability/Experience ↑
2. Familiarity with the Task ↑
3. Seriousness of Outcome ↓
4. Voluntary Actions and Being in Control ↑
5. Personal Experience with an Outcome ↓
6. Cost of Non-Compliance ↓
7. Confidence in the Equipment ↑
8. Confidence in Protection and Rescue ↑
9. Potential Profit & Gain from Actions ↑
10. Role Models Accepting Risk ↑
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Factors Influencing Risk Tolerance
6) Cost of Non Compliance
Greater cost of non compliance lowers risk tolerance
Aviation industry – Low risk tolerance, strictly regulated, high
cost of non-compliance.
Strategies for Reducing Tolerance
• Identify the cost of non compliance and increase it where necessary
• Remove barriers and increase reward for compliance
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
10 Factors That Influence Risk Tolerance
1. Overestimating Capability/Experience ↑
2. Familiarity with the Task ↑
3. Seriousness of Outcome ↓
4. Voluntary Actions and Being in Control ↑
5. Personal Experience with an Outcome ↓
6. Cost of Non-Compliance ↓
7. Confidence in the Equipment ↑
8. Confidence in Protection and Rescue ↑
9. Potential Profit & Gain from Actions ↑
10. Role Models Accepting Risk ↑
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Factors Influencing Risk Tolerance
7) Confidence in the Equipment
“Ladder is twice as stable, therefore ... ”
• 1995 US Study – Cars with ABS have more accidents, no safety gain
with airbags because drivers became more aggressive.
• Parachuting – Failure to deploy replaced with late deployment
Strategies for Reducing Tolerance
• Training on limitations of the equipment and engineering
• Stop and Think ... What will happen if it does fail?
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
10 Factors That Influence Risk Tolerance
1. Overestimating Capability/Experience ↑
2. Familiarity with the Task ↑
3. Seriousness of Outcome ↓
4. Voluntary Actions and Being in Control ↑
5. Personal Experience with an Outcome ↓
6. Cost of Non-Compliance ↓
7. Confidence in the Equipment ↑
8. Confidence in Protection and Rescue ↑
9. Potential Profit & Gain from Actions ↑
10. Role Models Accepting Risk ↑
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Factors Influencing Risk Tolerance
8) Confidence in Protection and Rescue
•British study – workers with back belts tend to lift greater weights
Strategies for Reducing Tolerance
• Understand the limitations of protection & rescue measures
• See them as ‘last lines of defence’, or ‘not to be relied upon’ ?
• “Every job should be able to be done safely by a 65 year old with a bad
back and ...” Howie Dingle
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
10 Factors That Influence Risk Tolerance
1. Overestimating Capability/Experience ↑
2. Familiarity with the Task ↑
3. Seriousness of Outcome ↓
4. Voluntary Actions and Being in Control ↑
5. Personal Experience with an Outcome ↓
6. Cost of Non-Compliance ↓
7. Confidence in the Equipment ↑
8. Confidence in Protection and Rescue ↑
9. Potential Profit & Gain from Actions ↑
10. Role Models Accepting Risk ↑
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Factors Influencing Risk Tolerance
9) Potential Profit and Gain from Action
• US Highways Study – deaths on highways tracks directly with the
economy
• Alberta WHS – fatalities and lost time incidents in the oil patch increase
and decrease with the price of oil.
Strategies for Reducing Tolerance
• Remove rewards for risk taking
• Eliminate barriers to doing it the ‘right way’
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
10 Factors That Influence Risk Tolerance
1. Overestimating Capability/Experience ↑
2. Familiarity with the Task ↑
3. Seriousness of Outcome ↓
4. Voluntary Actions and Being in Control ↑
5. Personal Experience with an Outcome ↓
6. Cost of Non-Compliance ↓
7. Confidence in the Equipment ↑
8. Confidence in Protection and Rescue ↑
9. Potential Profit & Gain from Actions ↑
10. Role Models Accepting Risk ↑
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Factors Influencing Risk Tolerance
10) Role Models Accepting Risk
• When Role Models in a work group accept a certain level of risk, they
influence the decisions to accept risk by other members of the group.
Strategies for Reducing Tolerance
• Identify and address the risk takers immediately (including yourself – where
are you on the ‘risk-taking’ scale?)
• Recognize ‘Erosion of Standards’ and address immediately
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
What Could Go Wrong?
1) Review the serious incidents that have happened in the past
and learn from these incidents
• Coach workers on how to recognize new hazards
• Recognize potential consequences of those hazards
• Reduce the tolerable level of risk
• Calibrate others so their judgement is at the same lowest
acceptable level of risk
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
How Bad Could It Be?
2) Use ‘safety conversations’ (LPO, Stop and Think, Safety
Meetings) to increase awareness on potential outcomes.
• Keep the ‘corporate memory’ alive
• Risk is impacted by the number of ‘Barriers’ between
actions and outcomes
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
What can I do about this?
2) Follow up on the ‘Personal Risk Behaviours’ identified at
Fresh Start:
a) Hold safety meeting discussions (or one on one during
LPO’s) on what they identified and their progress
b) Ask workers to share their identified personal risks and
commitments to change at safety meetings. (Start by sharing
yours).
c) Continue to use the ‘Personal Risk’ Stop and Think
cards with the expectation of identifying another personal at
risk behaviour
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
“Together with our contractors we can create
the safety culture that lowers Risk Tolerance”
Dave Fennell, Imperial Oil Resources Downloaded from www.avhf.com
You might also like
- Exxon Risk ToleranceDocument44 pagesExxon Risk ToleranceWilliam XavierNo ratings yet
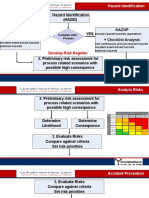
- Hazard Identification (Hazid) NO YES: Checklist Analysis Hazop + Checklist AnalysisDocument7 pagesHazard Identification (Hazid) NO YES: Checklist Analysis Hazop + Checklist AnalysisZeroRecoNo ratings yet
- Accident InvestigationDocument7 pagesAccident InvestigationGarri GarriNo ratings yet
- HFACSDocument37 pagesHFACSPrince KumarNo ratings yet
- Foundation For Safety Culture Improvement - in Pursuit of Safety ExcellenceDocument32 pagesFoundation For Safety Culture Improvement - in Pursuit of Safety Excellencearsaya100% (1)
- Bow Tie Risk Analysis 1641268047Document20 pagesBow Tie Risk Analysis 1641268047VARUN RAOLJINo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log: Domains 1. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson Log: Domains 1. ObjectivesNathaniel Jose FullidoNo ratings yet
- HivePro Uni5 BrochureDocument2 pagesHivePro Uni5 BrochureFamnazfamiNo ratings yet
- 022 - Bored Cast in Place Concrete Piles - Night WorksDocument15 pages022 - Bored Cast in Place Concrete Piles - Night WorksMohammed Adnan100% (1)
- SitescrnDocument2 pagesSitescrnMark CheneyNo ratings yet
- SHELL Resilience Ktenas v.5.1Document88 pagesSHELL Resilience Ktenas v.5.1Panagiotis Ktenas100% (2)
- Project Risk Management HC-MMDocument58 pagesProject Risk Management HC-MMprajjwal patidarNo ratings yet
- Learning Manual SectionDocument5 pagesLearning Manual SectionratkoNo ratings yet
- Risk Management As Applied To Safety, Security and SanitationDocument3 pagesRisk Management As Applied To Safety, Security and SanitationCynthia AyadoNo ratings yet
- 011 - Remedial Works at Yabani BridgeDocument11 pages011 - Remedial Works at Yabani BridgeMohammed Adnan100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Log: Domains 1. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson Log: Domains 1. ObjectivesNathaniel Jose FullidoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Unease - A Method For Achieving Situation AwarenessDocument13 pagesChronic Unease - A Method For Achieving Situation Awarenessmustaffa bakriNo ratings yet
- CORESafety Risk Change ManagementDocument71 pagesCORESafety Risk Change ManagementJaime HernandezNo ratings yet
- To Use This File, Please Download The Cover Sheet To Your Computer (File Download As) or Google Drive (File Make A Copy)Document9 pagesTo Use This File, Please Download The Cover Sheet To Your Computer (File Download As) or Google Drive (File Make A Copy)Victor VilarubiaNo ratings yet
- Root Cause Analysis - 2024Document46 pagesRoot Cause Analysis - 2024Waqas AhmadNo ratings yet
- Human Factors in AccidentsDocument7 pagesHuman Factors in Accidentsdafield.192No ratings yet
- Root Cause Analysis To Reduce Error and Improve Quality in Forensic Science Labs - Hollway.labmgmtDocument16 pagesRoot Cause Analysis To Reduce Error and Improve Quality in Forensic Science Labs - Hollway.labmgmtSaravnan RajendranNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 07 FMEADocument32 pagesLecture # 07 FMEAZeeshan ElahiNo ratings yet
- IC Risk and Opportunity Register Example 11805 WORDDocument3 pagesIC Risk and Opportunity Register Example 11805 WORDNazia KabirNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document15 pagesModule 4Anukriti AroraNo ratings yet
- Managing Failure AnalysisDocument25 pagesManaging Failure AnalysisAndiNo ratings yet
- Personnel RisksDocument2 pagesPersonnel RisksAnushka SeebaluckNo ratings yet
- Disasters Related To BBSDocument38 pagesDisasters Related To BBSVikram TNo ratings yet
- Fiddil Risk AssessmentDocument7 pagesFiddil Risk Assessmentsunday austineNo ratings yet
- Pfmea Process Failure Mode and Effects AnalysisDocument34 pagesPfmea Process Failure Mode and Effects AnalysisRizky SihabNo ratings yet
- 03 - Risk Register PDFDocument18 pages03 - Risk Register PDFabel100% (1)
- Pengenalan Anatomy Process Safety Incident - SHED Indonesia 5 Feb 2022Document28 pagesPengenalan Anatomy Process Safety Incident - SHED Indonesia 5 Feb 2022muhammad arhamNo ratings yet
- Pfmea Process Failure Mode and Effects AnalysisDocument34 pagesPfmea Process Failure Mode and Effects AnalysislittlekheongNo ratings yet
- Risk Based Internal AuditDocument19 pagesRisk Based Internal AuditL N Murthy KapavarapuNo ratings yet
- Health & Safety: Implementation ofDocument14 pagesHealth & Safety: Implementation ofharikeshmn09No ratings yet
- Standard Risk Register ISO 27001Document18 pagesStandard Risk Register ISO 27001Arfi MaulanaNo ratings yet
- 2 Projectriskmanagement 110110060847 Phpapp01Document12 pages2 Projectriskmanagement 110110060847 Phpapp01Vic RabayaNo ratings yet
- Risk Identification & AssessmentDocument51 pagesRisk Identification & AssessmentZak Ryder100% (1)
- 4 - Property Damage & Waste ControlDocument37 pages4 - Property Damage & Waste ControlArnel Jr GamaoNo ratings yet
- Behaviour Based SafetyDocument32 pagesBehaviour Based Safetysanjay s1386% (7)
- MODULE 2 Basic ConceptDocument42 pagesMODULE 2 Basic ConceptYauma IhsanNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Use of FMEA Presented By: Quality Associates InternationalDocument66 pagesIntelligent Use of FMEA Presented By: Quality Associates Internationalpradeep100% (1)
- Rcca Erm 202Document26 pagesRcca Erm 202JorgeMerinoNo ratings yet
- Root Cause Analysis Presentation (RCA)Document21 pagesRoot Cause Analysis Presentation (RCA)beriNo ratings yet
- ISO Standard Clause 6 - FinalDocument74 pagesISO Standard Clause 6 - FinalHarish C NNo ratings yet
- Loss Control Leadership Enemba 7 For StudentDocument40 pagesLoss Control Leadership Enemba 7 For StudentMinaco RinoNo ratings yet
- RCA Intro and ToolsDocument102 pagesRCA Intro and Toolswaran87100% (1)
- Tot SrampDocument23 pagesTot SrampBrhane WeldegebrialNo ratings yet
- Conducting Risk Assessment & Auditing The Internal Control SystemDocument24 pagesConducting Risk Assessment & Auditing The Internal Control SystemIana LopezNo ratings yet
- Organization Level - Internal & External Issues& Requirements of Interested Parties-New 11-11-17Document3 pagesOrganization Level - Internal & External Issues& Requirements of Interested Parties-New 11-11-17Ramdas PaithankarNo ratings yet
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)Document23 pagesFailure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)Anthony Mc CormackNo ratings yet
- Internal Weakness: SWOT Analysis: November 1, 2017 TeamDocument9 pagesInternal Weakness: SWOT Analysis: November 1, 2017 TeamRosinanteNo ratings yet
- ISU Oral Presentation RubricDocument2 pagesISU Oral Presentation RubricSteph PearsonNo ratings yet
- Cocu 5 - First Aid AdministrationDocument15 pagesCocu 5 - First Aid AdministrationIzzati SalbiyanaNo ratings yet
- WSH Guidelines For Investigating Workplace Incidents For SMEsDocument15 pagesWSH Guidelines For Investigating Workplace Incidents For SMEsandrewhw100% (1)
- Materi Safety Awareness Untuk Konsumen Industri - FinalDocument29 pagesMateri Safety Awareness Untuk Konsumen Industri - Finalkesling k3No ratings yet
- Mindmap CG Week 11 - Group 3Document1 pageMindmap CG Week 11 - Group 3Hanbin KimNo ratings yet
- 4 Workers Don't Cause Failure, Workers Trigger Failure: Questions About Your OrganizationDocument1 page4 Workers Don't Cause Failure, Workers Trigger Failure: Questions About Your OrganizationRauf HuseynovNo ratings yet
- Security Leader Insights for Business Continuity: Lessons and Strategies from Leading Security ProfessionalsFrom EverandSecurity Leader Insights for Business Continuity: Lessons and Strategies from Leading Security ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- AN78APP3Document1 pageAN78APP3Mohamad Khair Shaiful AlamNo ratings yet
- AN78APP1Document1 pageAN78APP1Mohamad Khair Shaiful AlamNo ratings yet
- AN38Document1 pageAN38Mohamad Khair Shaiful AlamNo ratings yet
- AN78Document4 pagesAN78Mohamad Khair Shaiful AlamNo ratings yet
- Garmin GTN 650 Installation ManualDocument2 pagesGarmin GTN 650 Installation ManualMohamad Khair Shaiful AlamNo ratings yet
- UG - CAO.00128 Foreign Part 145 Demonstration of 6-24 Months Maintenance ExpeDocument9 pagesUG - CAO.00128 Foreign Part 145 Demonstration of 6-24 Months Maintenance ExpeMohamad Khair Shaiful AlamNo ratings yet
- Cessna Operational & Maintenance Procedures Cessna 208/208B EasaDocument37 pagesCessna Operational & Maintenance Procedures Cessna 208/208B EasaaakashbarotNo ratings yet
- Maintenance RecordsDocument51 pagesMaintenance RecordsMohamad Khair Shaiful AlamNo ratings yet
- Ce 172 MMEL EU RevOriginalDocument41 pagesCe 172 MMEL EU RevOriginalI C2100% (3)
- Human Error in MaintenanceDocument38 pagesHuman Error in MaintenanceKant RaviNo ratings yet
- TalkDocument9 pagesTalkMohamad Khair Shaiful AlamNo ratings yet
- Critical Decision Making: Bill Peterson Fire Chief Plano, Texas Fire - RescueDocument50 pagesCritical Decision Making: Bill Peterson Fire Chief Plano, Texas Fire - RescueMohamad Khair Shaiful AlamNo ratings yet
- TalkDocument9 pagesTalkMohamad Khair Shaiful AlamNo ratings yet
- TalkDocument9 pagesTalkMohamad Khair Shaiful AlamNo ratings yet
- TalkDocument9 pagesTalkMohamad Khair Shaiful AlamNo ratings yet
- Payment RequestDocument1 pagePayment RequestMohamad Khair Shaiful AlamNo ratings yet
- TalkDocument9 pagesTalkMohamad Khair Shaiful AlamNo ratings yet
- Foreign Policy During Mahathir EraDocument7 pagesForeign Policy During Mahathir EraMuhamad Efendy Jamhar0% (1)
- Catalyst 3750 Series Switches TroubleshootDocument19 pagesCatalyst 3750 Series Switches TroubleshootSugumar DuraisamyNo ratings yet
- Utsourcing) Is A Business: Atty. Paciano F. Fallar Jr. SSCR-College of Law Some Notes OnDocument9 pagesUtsourcing) Is A Business: Atty. Paciano F. Fallar Jr. SSCR-College of Law Some Notes OnOmar sarmiento100% (1)
- Process Plant Layout - Becoming A Lost ArtDocument7 pagesProcess Plant Layout - Becoming A Lost ArtRajendraNo ratings yet
- Developing Mental Health-Care Quality Indicators: Toward A Common FrameworkDocument6 pagesDeveloping Mental Health-Care Quality Indicators: Toward A Common FrameworkCarl FisherNo ratings yet
- Course Content: SAP Fiori Implementation (SAPX03)Document3 pagesCourse Content: SAP Fiori Implementation (SAPX03)Jathin Varma KanumuriNo ratings yet
- FS 1 Activity 3.3Document6 pagesFS 1 Activity 3.3HYACINTH GALLENERONo ratings yet
- Lee. Building Balanced Scorecard With SWOT Analysis, and Implementing "Sun Tzu's The Art of Business Management Strategies" On QFD Methodology PDFDocument13 pagesLee. Building Balanced Scorecard With SWOT Analysis, and Implementing "Sun Tzu's The Art of Business Management Strategies" On QFD Methodology PDFSekar Ayu ParamitaNo ratings yet
- Mindfulness: Presented by Joshua Green, M.S. Doctoral Intern at Umaine Counseling CenterDocument12 pagesMindfulness: Presented by Joshua Green, M.S. Doctoral Intern at Umaine Counseling CenterLawrence MbahNo ratings yet
- What If The Class Is Very BigDocument2 pagesWhat If The Class Is Very BigCamilo CarantónNo ratings yet
- AL Applied Mathematics 1989 Paper1+2 (E)Document7 pagesAL Applied Mathematics 1989 Paper1+2 (E)eltytanNo ratings yet
- 50 Life Secrets and Tips - High ExistenceDocument12 pages50 Life Secrets and Tips - High Existencesoapyfish100% (1)
- DR LukeDocument126 pagesDR Lukegabryelbarretto7No ratings yet
- List of Naruto Char.Document40 pagesList of Naruto Char.Keziah MecarteNo ratings yet
- CPARDocument9 pagesCPARPearl Richmond LayugNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Effectiveness of Heat Exchanger Shell and Tube Type One Shell Two Tube Pass As Cooling OilDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Effectiveness of Heat Exchanger Shell and Tube Type One Shell Two Tube Pass As Cooling OilHendrik V SihombingNo ratings yet
- An Objective of Dress Code PolicyDocument4 pagesAn Objective of Dress Code PolicySiddhraj Singh KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Florida Firearm Bill of SaleDocument4 pagesFlorida Firearm Bill of SaleGeemoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Waiting Line ModelsDocument46 pagesChapter 11 Waiting Line ModelsLara FloresNo ratings yet
- Energizing Your ScalesDocument3 pagesEnergizing Your ScalesjohnNo ratings yet
- Schemes and Tropes HandoutDocument6 pagesSchemes and Tropes HandoutJohn LukezicNo ratings yet
- Accenture 172199U SAP S4HANA Conversion Brochure US Web PDFDocument8 pagesAccenture 172199U SAP S4HANA Conversion Brochure US Web PDFrajesh2kakkasseryNo ratings yet
- John Dee - Sigillum Dei Aemeth or Seal of The Truth of God EnglishDocument2 pagesJohn Dee - Sigillum Dei Aemeth or Seal of The Truth of God Englishsatyr70286% (7)
- Brand Zara GAP Forever 21 Mango H&M: Brand Study of Zara Nancys Sharma FD Bdes Batch 2 Sem 8 Brand-ZaraDocument2 pagesBrand Zara GAP Forever 21 Mango H&M: Brand Study of Zara Nancys Sharma FD Bdes Batch 2 Sem 8 Brand-ZaraNancy SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Digital Communication and AnalogueDocument6 pages1.3 Digital Communication and AnaloguenvjnjNo ratings yet
- Resume - General Manager - Mohit - IIM BDocument3 pagesResume - General Manager - Mohit - IIM BBrexa ManagementNo ratings yet
- Physical Education 10 WEEK 2Document10 pagesPhysical Education 10 WEEK 2Israel MarquezNo ratings yet
- Meditation On God's WordDocument26 pagesMeditation On God's WordBeghin BoseNo ratings yet
- Creating The HardboiledDocument20 pagesCreating The HardboiledBen NallNo ratings yet
- Quality of Life After Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Patients With Chronic RhinosinusitisDocument15 pagesQuality of Life After Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Patients With Chronic RhinosinusitisNarendraNo ratings yet