Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TQMs 3 C
Uploaded by
Mostak TahmidOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TQMs 3 C
Uploaded by
Mostak TahmidCopyright:
Available Formats
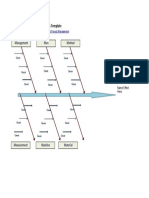
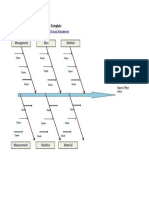
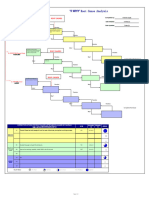
CAUSE EFFECT
Ishikawa diagrams (also called fishbone
diagrams, herringbone diagrams, cause-and-
effect diagrams, or Fishikawa) are causal
diagrams created by Kaoru Ishikawa (1968) that
show the causes of a specific event. Common uses
of the Ishikawa diagram are product design and
quality defect prevention, to identify potential
factors causing an overall effect. Each cause or
reason for imperfection is a source of variation.
Causes are usually grouped into major categories
to identify these sources of variation.
The categories typically include:
Man: Anyone involved with the process
Methods: How the process is performed and the
specific requirements for doing it, such as policies,
procedures, rules, regulations and laws
Machines: Any equipment, computers, tools etc.
required to accomplish the job
Materials: Raw materials, parts, pens, paper, etc. used
to produce the final product
Environment: The conditions, such as location, time,
temperature, and culture in which the process operates
Management: the attributes or point of view of
top management and people at other
managerial positions
Fishbone Diagram Guide
Cause and Effect Diagram
Category 1 Category 2 Category 3
Party A
Reason Reason Reason
Problem
Reason Reason Reason
Party B
Category 4 Category 5 Category 6
Ishkawa Diagram
Fishbone Diagram
Reason Reason
Reason
Reason
Reason Reason
Created by Edraw - all-in-one diagram software
Definition of Fishbone Diagram
The fishbone diagram, or the cause and effect diagram, is a
simple graphic display that shows all the possible causes of a
problem in a business process.
It is also called the Ishakawa diagram.
Created by Edraw - all-in-one diagram software
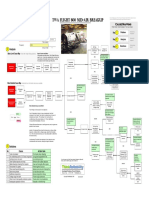
Measurements Materials Manpower
Specimen not sufficient Not enough ice Can't procure specimen
Analyzer out of calibration Plastic bag not up to standard Patients not in room
Lab Results
Delay
Order slip delays
Room too hot No centrifuge
Message delay
Courtesy visit
Room too cold Lack analyzer
Poor identification
Mother nature Methods Machines
Note: The 6M method is applied in this analysis, categorizing the reasons into Manpower, Materials, Measurements, Mother nature, Methods and Machines.
Created by Edraw - all-in-one diagram software
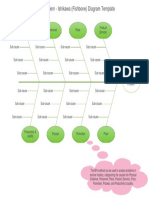
Service Problem - Ishikawa (Fishbone) Diagram Template
Product
Physical Evidence Personnel Place
(Service)
Sub-cause Sub-cause Sub-cause Sub-cause
Sub-cause Sub-cause Sub-cause Sub-cause
Sub-cause Sub-cause Sub-cause Sub-cause
Service
Problem
Sub-cause Sub-cause Sub-cause Sub-cause
Sub-cause Sub-cause Sub-cause Sub-cause
Sub-cause Sub-cause Sub-cause Sub-cause
Productivity &
Process Promotion Price
quality
The 8P method can be used to analyze problems in service
industry, categorizing the causes into Physical Evidence,
Personnel, Place, Product (Service), Price, Promotion,
Process, and Productivity & quality.
Created by Edraw - all-in-one diagram software
Relationship
Relationship Management
Management Workload
Workload Environment
Environment Welfare
Welfare Salary
Salary
with
with Co-workers
Co-workers
Different
Employer No incentive Demanding Location
concepts Control
Low welfare
low cost
Lack of Harsh High
Climate
communication management pressure
No welfare Low salary
No Too much Office
Misunderstanding
promotion work environment
Resign
Change profession Poor constitution Transportation Not confident
Find a job Conflict between
Illness Poor adaption ability
with higher pay. work and life
Employee Further studies Stressful Change of address Not qualified
Plan
Plan Health
Health Residence
Residence Self-confidence
Self-confidence
Change
Change
XXX: Important reasons
Created by Edraw - all-in-one diagram software
You might also like
- Fishbone Diagram Guide: Cause and Effect DiagramDocument12 pagesFishbone Diagram Guide: Cause and Effect DiagramyildirimonlineNo ratings yet
- Fishbone Diagram TemplateDocument1 pageFishbone Diagram TemplateNovi Y. PurbaNo ratings yet
- Fishbone DiagramDocument6 pagesFishbone DiagramGayathri VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson - 5.2 - Root Cause Analysis - Improve - PhaseDocument29 pagesLesson - 5.2 - Root Cause Analysis - Improve - Phaseطلال المطيريNo ratings yet
- Fishbone6M 2007Document1 pageFishbone6M 2007skullers99No ratings yet
- Fishbone6M 2007Document1 pageFishbone6M 2007Harris RabbasaNo ratings yet
- Fishbone6M 2007Document1 pageFishbone6M 2007zameer.a.j1877No ratings yet
- 8M5Y Root Cause Worksheet 5Document1 page8M5Y Root Cause Worksheet 5Masood KhanNo ratings yet
- Fishbone-Diagram v3.3 GoLeanSixSigma - ComDocument11 pagesFishbone-Diagram v3.3 GoLeanSixSigma - ComChalie HayesNo ratings yet
- Service Problem Ishikawa DiagramDocument1 pageService Problem Ishikawa DiagramYesus Antonio PerezNo ratings yet
- Service Problem - Ishikawa (Fishbone) Diagram TemplateDocument1 pageService Problem - Ishikawa (Fishbone) Diagram TemplateYesus Antonio PerezNo ratings yet
- Fishbone Diagram: Systems Process FormsDocument5 pagesFishbone Diagram: Systems Process Formstapera_mangeziNo ratings yet
- Fishbone Diagram: Systems Process FormsDocument5 pagesFishbone Diagram: Systems Process Formstapera_mangeziNo ratings yet
- Fishbone Diagram: Systems Process FormsDocument11 pagesFishbone Diagram: Systems Process FormslunaNo ratings yet
- 8D Report: A Step by Step Problem Solving ProcessDocument24 pages8D Report: A Step by Step Problem Solving Processsandeep devabhaktuniNo ratings yet
- Equipment Performance Improvement/ Analysis and Problem Solving Tools, SPCDocument32 pagesEquipment Performance Improvement/ Analysis and Problem Solving Tools, SPCCarlo AbillonarNo ratings yet
- Ishikawa DiagramDocument12 pagesIshikawa DiagramShaik HafeezNo ratings yet
- Fishbone Diagram TemplateDocument2 pagesFishbone Diagram TemplateEdgar FloresNo ratings yet
- 05 YBC3M3V3 Process MappingDocument2 pages05 YBC3M3V3 Process MappingMary OviedoNo ratings yet
- R. K. Life Services Private Limited (Department of Laboratory Medicine)Document1 pageR. K. Life Services Private Limited (Department of Laboratory Medicine)Aniruddha ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- FMEA Minus The Pain FiguresDocument3 pagesFMEA Minus The Pain FiguresMUNISNo ratings yet
- Fishbone - Training Course - EN - V01-R02 - 30082012Document16 pagesFishbone - Training Course - EN - V01-R02 - 30082012yildirimonlineNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Cause and Effect Diagram 2Document41 pagesLecture 2 - Cause and Effect Diagram 2n4ww85ftz7No ratings yet
- Fast Response Process: Standardized Rapid Reaction To Quality IssuesDocument162 pagesFast Response Process: Standardized Rapid Reaction To Quality IssuesSudhagarNo ratings yet
- 4.a Brainstorm Ideas: Template For Brainstorm and 5 WhysDocument2 pages4.a Brainstorm Ideas: Template For Brainstorm and 5 WhysKavinNo ratings yet
- Problem Analysis (Pa) A Systematic Approach: Dr. Yos SunitiyosoDocument36 pagesProblem Analysis (Pa) A Systematic Approach: Dr. Yos SunitiyosoChristian SuryadiNo ratings yet
- VI Semester Rubric For Second Presentation - 1582523257Document1 pageVI Semester Rubric For Second Presentation - 1582523257Anshul AliwalNo ratings yet
- Fmea (Failure Modes and Effects Analysis)Document11 pagesFmea (Failure Modes and Effects Analysis)Oswaldo VallesNo ratings yet
- BOM North West BankDocument25 pagesBOM North West Banknitish_735No ratings yet
- Gather Relevant Data and RCA No in ProcessDocument2 pagesGather Relevant Data and RCA No in ProcessTarun BhatejaNo ratings yet
- Root Cause Final AssignmentDocument8 pagesRoot Cause Final AssignmentsatexNo ratings yet
- Fishbone Diagram: Fish Out The Root of The ProblemDocument1 pageFishbone Diagram: Fish Out The Root of The ProblemAriadna SerranoNo ratings yet
- Fishbone Diagram TemplateDocument2 pagesFishbone Diagram TemplateRoger McnigNo ratings yet
- 06 5s Implementation Plan and Training Guide v20130618 PDFDocument16 pages06 5s Implementation Plan and Training Guide v20130618 PDFRamesh BabuNo ratings yet
- GMs Drill Deep WorkshopDocument47 pagesGMs Drill Deep WorkshopEduardo Magaña Gutierrez0% (1)
- 5 Why AnalysisDocument1 page5 Why AnalysisRAJESH SHARMANo ratings yet
- WhywhyDocument2 pagesWhywhyrakesh_nk9No ratings yet
- Potential Failure Mode and Effective Analysis (Process FMEA)Document1 pagePotential Failure Mode and Effective Analysis (Process FMEA)nainarmuthuramalingamNo ratings yet
- Single Machine - Multiple Parts (OEE Reporting)Document2 pagesSingle Machine - Multiple Parts (OEE Reporting)Vergence Business Associates100% (1)
- Benefits of Pencil Beam TechnologyDocument2 pagesBenefits of Pencil Beam TechnologySERP GERTE SPINo ratings yet
- Fishbone & 5-WhyDocument3 pagesFishbone & 5-WhyTheodore69No ratings yet
- April17 2120178thgradeadvDocument2 pagesApril17 2120178thgradeadvapi-327299670No ratings yet
- Twa Flight 800 Mid-Air Breakup: Cause MappingDocument1 pageTwa Flight 800 Mid-Air Breakup: Cause MappingAlejandroZappaNo ratings yet
- Tool Selector V2Document1 pageTool Selector V2Mohammed MuzakkirNo ratings yet
- Root Cause Techniques PresentationDocument17 pagesRoot Cause Techniques PresentationNaveed AkramNo ratings yet
- RCA SampleDocument2 pagesRCA Sampleedward tagarino100% (1)
- Digital Basic - 4Document4 pagesDigital Basic - 4Ilaiyaveni IyanduraiNo ratings yet
- Digital Basic - 4 PDFDocument4 pagesDigital Basic - 4 PDFIlaiyaveni IyanduraiNo ratings yet
- Why-Why Analysis 2013 - PPM (CAP)Document81 pagesWhy-Why Analysis 2013 - PPM (CAP)bimobimoprabowoNo ratings yet
- Materials Reliability Program: Tim Wells, ChairmanDocument23 pagesMaterials Reliability Program: Tim Wells, ChairmanLeonardo LimaNo ratings yet
- OAUX Wireframe Template Release 10 RDK V2Document32 pagesOAUX Wireframe Template Release 10 RDK V2dvartaNo ratings yet
- FMEA GuideDocument161 pagesFMEA GuideGyanesh_DBNo ratings yet
- 8D Systemic Problem SolvingDocument14 pages8D Systemic Problem Solvinghimanshumips20No ratings yet
- Hazard Identification (Hazid) NO YES: Checklist Analysis Hazop + Checklist AnalysisDocument7 pagesHazard Identification (Hazid) NO YES: Checklist Analysis Hazop + Checklist AnalysisZeroRecoNo ratings yet
- Fishbone Cause and Effect DiagramDocument2 pagesFishbone Cause and Effect DiagramHungNo ratings yet
- Inventor Object ModelDocument1 pageInventor Object ModelInventor APINo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document12 pagesAssignment 3Chennai RajaNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Budgets FCRDocument14 pagesNitrogen Budgets FCRMostak TahmidNo ratings yet
- TQMs 1Document23 pagesTQMs 1Mostak TahmidNo ratings yet
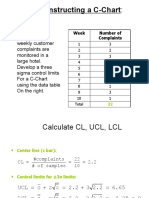
- Constructing A C-ChartDocument2 pagesConstructing A C-ChartMostak TahmidNo ratings yet
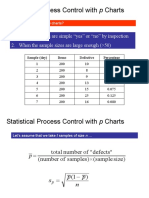
- Statistical Process Control With P ChartsDocument4 pagesStatistical Process Control With P ChartsMostak TahmidNo ratings yet
- TQMs 2Document13 pagesTQMs 2Mostak TahmidNo ratings yet
- Stages in TQM Implementation: First StageDocument7 pagesStages in TQM Implementation: First StageMostak TahmidNo ratings yet
- X-Bar and R Chart Example In-Class ExerciseDocument6 pagesX-Bar and R Chart Example In-Class ExerciseMostak TahmidNo ratings yet
- Legal Environment in BusinessDocument2 pagesLegal Environment in BusinessMostak TahmidNo ratings yet
- LEB Summer19 Lecture 2Document14 pagesLEB Summer19 Lecture 2Mostak TahmidNo ratings yet
- Module 02 (Making Decisions and Performing Iterations) : If StatementDocument6 pagesModule 02 (Making Decisions and Performing Iterations) : If StatementMostak TahmidNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Legal Environment in Business Summer 2019-20Document7 pagesCourse Outline Legal Environment in Business Summer 2019-20Mostak Tahmid0% (1)
- Intro Ecogeo (Revised) Topic-1Document25 pagesIntro Ecogeo (Revised) Topic-1Mostak TahmidNo ratings yet
- Variables, Data Types, and Arithmetic Expressions: Dept. of Computer Science Faculty of Science and TechnologyDocument19 pagesVariables, Data Types, and Arithmetic Expressions: Dept. of Computer Science Faculty of Science and TechnologyMostak TahmidNo ratings yet
- Data Types: Type Description Size (Bytes) RangeDocument8 pagesData Types: Type Description Size (Bytes) RangeMostak TahmidNo ratings yet
- Geo-Political Economy of Bangladesh Under Historical PerspectiveDocument40 pagesGeo-Political Economy of Bangladesh Under Historical PerspectiveAbid Hasan Jaid100% (1)
- Economic Geography (Chapter One)Document10 pagesEconomic Geography (Chapter One)Mostak TahmidNo ratings yet
- Food Safety For Food Security Relationship Between Global Megatrends and Developments in Food SafetyDocument16 pagesFood Safety For Food Security Relationship Between Global Megatrends and Developments in Food SafetyWayne0% (1)
- Learning Feedback Diary (LFD) : General ObjectiveDocument3 pagesLearning Feedback Diary (LFD) : General ObjectiveAlhadzra AlihNo ratings yet
- What Are Knock Knees?Document2 pagesWhat Are Knock Knees?thet waiNo ratings yet
- CDP ENR Management PlanDocument40 pagesCDP ENR Management PlanJacirJapsNo ratings yet
- Health Safety and Nutrition For The Young Child 9th Edition Marotz Test BankDocument21 pagesHealth Safety and Nutrition For The Young Child 9th Edition Marotz Test BankJosephWilliamsinaom100% (13)
- The Use of Isotretinoin in AcneDocument8 pagesThe Use of Isotretinoin in AcneMelisa Silvia SembiringNo ratings yet
- The 5 Minute Daily Stretch To Unlock Your Muscles (5 Exercises!)Document16 pagesThe 5 Minute Daily Stretch To Unlock Your Muscles (5 Exercises!)Nicolas Alonso100% (1)
- Preparation and Modification of High Dietary Fiber FlourDocument12 pagesPreparation and Modification of High Dietary Fiber FlourHuỳnh Như Đặng ThụyNo ratings yet
- GUDBARK Technical Details - RDocument12 pagesGUDBARK Technical Details - RMylanun100% (1)
- Winnicott ch1 PDFDocument18 pagesWinnicott ch1 PDFAlsabila NcisNo ratings yet
- DR - Hawary Revision TableDocument3 pagesDR - Hawary Revision TableAseel ALshareefNo ratings yet
- 에티오피아 제약 의료기기 인허가 절차 소개 - 영문Document39 pages에티오피아 제약 의료기기 인허가 절차 소개 - 영문Kidist TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Housing Colorado in Conjunction With University of Colorado Denver College of Architecture and PlanningDocument7 pagesHousing Colorado in Conjunction With University of Colorado Denver College of Architecture and PlanningAmy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Z-TRACK-METHOD ChecklistDocument5 pagesZ-TRACK-METHOD ChecklistDaniela Villanueva RosalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemguard PDFDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Chemguard PDFjoana ramirezNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Continuous Learning About MarketsDocument12 pagesChapter Five Continuous Learning About MarketsDr. Sahin SarkerNo ratings yet
- Tuckman's Theory of Team Development (Diagram)Document1 pageTuckman's Theory of Team Development (Diagram)Malcolm Payne100% (3)
- Internship ReportDocument39 pagesInternship ReportOdongo Isaac100% (4)
- DownloadDocument6 pagesDownloadDoraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Aral. Pan.Document3 pagesLesson Plan Aral. Pan.YrregRamSiclotArutnevNo ratings yet
- Ch8-Sekaran N BogieDocument61 pagesCh8-Sekaran N BogieSunardi NurcahyonoNo ratings yet
- BS Iso TR 05925-2-1997 (1999)Document16 pagesBS Iso TR 05925-2-1997 (1999)Олег СоловьевNo ratings yet
- Newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation 160410175058 PDFDocument37 pagesNewmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation 160410175058 PDFDevrathNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Important Questions PDFDocument12 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce Important Questions PDFSomik JainNo ratings yet
- Trainee's Record Book (TRB)Document10 pagesTrainee's Record Book (TRB)Shommer ShotsNo ratings yet
- Pearson's Correlation Coefficient: BMJ (Online) July 2012Document3 pagesPearson's Correlation Coefficient: BMJ (Online) July 2012Randy Rafael Asencio AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Write A Toefl Essay About If You Preffer Virtual Classes or PresencialDocument5 pagesWrite A Toefl Essay About If You Preffer Virtual Classes or PresencialCarlos RoldanNo ratings yet
- Review Related Literature Noise PollutionDocument8 pagesReview Related Literature Noise Pollutionafdtwbhyk100% (1)
- Health Teaching Plan: Age Group: Middle and Late ChildhoodDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching Plan: Age Group: Middle and Late ChildhoodHeinna Alyssa Garcia100% (1)
- G11 HOPE Module 6Document16 pagesG11 HOPE Module 6Unk NownNo ratings yet