Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sealers 2nd Yr Ug Class
Uploaded by
Shalini0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views12 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views12 pagesSealers 2nd Yr Ug Class
Uploaded by
ShaliniCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
SEALERS
Dr. Shalini Maria
DEFINITION
Root canal sealers are used
in conjunction with
biologically acceptable semisolid or solid
obturating materials
to establish an adequate seal of the root canal
system
GROSSMAN’S CRITERIA FOR AN
IDEAL ROOT CANAL SEALER
• Provide an excellent seal when set
• Produce adequate adhesion between itself, the canal walls and
the filling material
• Be radiopaque
• Be non staining
• Be dimensionally stable
• Be easily mixed and introduced into the canals
• Be easily removed if necessary
• Be insoluble in tissue fluids
• Be bactericidal or discourage bacterial growth
• Be non irritating to periradicular tissues
• Be slow setting to ensure sufficient working
CLASSIFICATION OF ROOT CANAL
SEALERS
• Grossman’s formula
I. Zinc oxide eugenol
• Roth’s 801
based sealers
• Tubliseal
II. Calcium hydroxide • Sealapex
based sealers • Apexit
III. Glass ionomer based
sealers
•AH plus
IV. Resin-based sealers •AH26
•Epiphany
•Diaket
GROSSMAN’S FORMULA OF A NON
STAINING SEALER
Powder
Parts
Liquid
Zinc oxide, reagent - 42
Staybelite resin - 27
Bismuth subcarbonate - 15
Barium sulfate - 15
Eugenol
Sodium borate, anhydrous -1
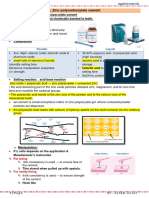
HOW TO MIX A SEALER?
• The sealer is mixed on a sterile glass slab with a sterile spatula.
• Depending on the number of canals to be filled, one uses two or three
drops of root canal cement liquid.
• Slowly, small increments of cement powder are added to the liquid while
one spatulates it to a smooth, creamy mix.
• The spatulation time depends on the number of drops of liquid used, a
minute per drop.
The completed mix can be tested for proper consistency by:
Raising the flat blade of the spatula up from the mixed mass.
The cement should “string out” for at least an inch before
breaking.
The suspended mix should cling to the inverted spatula blade
for 10–15 seconds before dropping from the spatula.
SEALAPEX
described as noneugenol,
calcium hydroxide polymeric resin root canal sealer
available in a base catalyst system
Base
Calcium Butyl Sulfonamide Zinc
Zinc oxide
hydroxide benzene and stearate
Catalyst
Isobutyl Barium Titanium
Resin Aerosol
salicylate sulfate dioxide
RESIN-BASED SEALERS
AH26 – Releases formaldehyde
AH Plus – Does not release formaldehyde
GLASS IONOMER BASED
SEALERS
Ex: Ketac Endo - not popular because of the difficulty in removing the
sealer from root canal walls
CONCLUSION
Zinc oxide eugenol type of cements are probably
irritating because of the eugenol, while epoxy resin
sealers are more biocompatible.
Fortunately, the irritation caused by overfilling is
generally mild for most filling materials.
Nevertheless, all filling materials should be confined
within the root canal.
You might also like
- Epoxy Resin Arts and Crafts for BeginnersFrom EverandEpoxy Resin Arts and Crafts for BeginnersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- Dental CementsDocument103 pagesDental Cementsaishwarya khareNo ratings yet
- S - 9 Bonding of Porcelain To MetalDocument34 pagesS - 9 Bonding of Porcelain To MetalShaliniNo ratings yet
- Root Canal Obturating Materials and SealersDocument45 pagesRoot Canal Obturating Materials and SealersasmaNo ratings yet
- Obturation MaterialDocument61 pagesObturation MaterialsaksheeNo ratings yet
- 15.1 Root Canal SealersDocument48 pages15.1 Root Canal SealersRevathy M NairNo ratings yet
- Ob Turati OnDocument55 pagesOb Turati OnyogeshNo ratings yet
- Lenin-Root Canal SealersDocument117 pagesLenin-Root Canal SealersVidya SagarNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Luting CementsDocument82 pagesRecent Advances in Luting CementsChaitrali Desai83% (6)
- Lecture 5 Root Canal SealersDocument32 pagesLecture 5 Root Canal SealersZakria Al-HadadNo ratings yet
- Dental Cements SectionDocument56 pagesDental Cements Sectionnehalabosamra91No ratings yet
- Silicate Cement 1Document13 pagesSilicate Cement 1Harish KhundrakpamNo ratings yet
- 20220619150419root Canal Filling Materials Theme 16 17 64814 1Document51 pages20220619150419root Canal Filling Materials Theme 16 17 64814 1Crimsonine SacredTranquilNo ratings yet
- Impression Materials: DR - Madhu Billa 2 Year PG SIBAR Institute of Dental SciencesDocument85 pagesImpression Materials: DR - Madhu Billa 2 Year PG SIBAR Institute of Dental SciencesMujthaba Admani100% (1)
- Ev Gyokertomo Anyagokangol HandoutDocument35 pagesEv Gyokertomo Anyagokangol HandoutNima DarabiNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Gypsum ProductsDocument17 pagesSeminar On Gypsum ProductsHarish Khundrakpam0% (1)
- Root Canal Filling Materials: EndodonticsDocument19 pagesRoot Canal Filling Materials: EndodonticsمحمدNo ratings yet
- Obturasi Saluran Akar: DRG Erma Sofiani, SP - KG Prodi KG UMYDocument18 pagesObturasi Saluran Akar: DRG Erma Sofiani, SP - KG Prodi KG UMYthiyaaNo ratings yet
- Dental Cements SectionDocument56 pagesDental Cements Sectionnehalabosamra91No ratings yet
- Die-Materials classEDITDocument45 pagesDie-Materials classEDITSatya AsatyaNo ratings yet
- Glass Ionomer Cement GICDocument25 pagesGlass Ionomer Cement GICsamar yousif mohamedNo ratings yet
- Cement Bases LinersDocument50 pagesCement Bases LinersNoura RihanNo ratings yet
- Root Canal Filling Materials. Chemical Structure. Physical-Chemical PropertiesDocument29 pagesRoot Canal Filling Materials. Chemical Structure. Physical-Chemical PropertiesShany SchwarzwaldNo ratings yet
- Sample Presentation - Denture Base MaterialsDocument99 pagesSample Presentation - Denture Base MaterialsDrnisanth100% (1)
- Fire Retardant Materials: Vishal. A .Gupta S.Y B.Voc 0102019011 Int - Materials & ProductsDocument10 pagesFire Retardant Materials: Vishal. A .Gupta S.Y B.Voc 0102019011 Int - Materials & ProductsVishal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Dental Cement 2Document5 pagesDental Cement 2eslamezzat21061990No ratings yet
- Die Materials: - Sachin ManturDocument55 pagesDie Materials: - Sachin ManturKashish ManghaniNo ratings yet
- Non Elastic ImpressionDocument65 pagesNon Elastic ImpressionAbdelruhman SobhyNo ratings yet
- F Impression Materials 1Document22 pagesF Impression Materials 1Jyoti TripathiNo ratings yet
- Endodontics: SealersDocument4 pagesEndodontics: SealersMustafa AliNo ratings yet
- By DR Rashid Hassan Head of Department Department of Science of Dental Materials W.M.D.C AbbottabadDocument55 pagesBy DR Rashid Hassan Head of Department Department of Science of Dental Materials W.M.D.C AbbottabadKrupali JainNo ratings yet
- Material Merged MergedDocument204 pagesMaterial Merged MergedBasma BasemNo ratings yet
- Gypsum 2023Document47 pagesGypsum 2023Syed Waqar HussainNo ratings yet
- DentalCements CopperOxideCementsDocument71 pagesDentalCements CopperOxideCementsfabrika100% (1)
- AcetalDocument20 pagesAcetalmanoNo ratings yet
- Glass Ionomer Cement: Presented By: 913-938 BDS, 2021Document24 pagesGlass Ionomer Cement: Presented By: 913-938 BDS, 2021kimt49370No ratings yet
- DENTMATCementsDocument3 pagesDENTMATCementsHannah RosalesNo ratings yet
- Elastomeric Impression MaterialsDocument121 pagesElastomeric Impression Materialskashyap sawantNo ratings yet
- Die Materials: Presented By:-Dr Manela Shill 2 Yr PGDocument63 pagesDie Materials: Presented By:-Dr Manela Shill 2 Yr PGAwani GuptaNo ratings yet
- Impression Mate ZZZDocument54 pagesImpression Mate ZZZsamar yousif mohamedNo ratings yet
- Operative Dentistry 2004Document269 pagesOperative Dentistry 2004dishakamath100% (5)
- Zinc Phosphate PolycarboxylateDocument67 pagesZinc Phosphate PolycarboxylateRajesh Rathod100% (1)
- Dental Cement FixDocument62 pagesDental Cement Fixmajumapanexpress.co.idNo ratings yet
- RPD ConstructionDocument7 pagesRPD ConstructionVivek ShankarNo ratings yet
- 0314 CompositesDocument9 pages0314 CompositesSoonki LeeNo ratings yet
- Basic Dental Materials: Factors Affecting SolubilityDocument9 pagesBasic Dental Materials: Factors Affecting SolubilityAlfina RizkaNo ratings yet
- Doc-20231127-Wa0026 (1)Document34 pagesDoc-20231127-Wa0026 (1)mechanicalengineering112No ratings yet
- Tooth Coloured Restorative MaterialsDocument66 pagesTooth Coloured Restorative MaterialsShabeel Pn100% (3)
- 4.4 Varnish and Liners 2023Document18 pages4.4 Varnish and Liners 2023Zahrani AssyifaNo ratings yet
- Elastic Impression MaterialsDocument119 pagesElastic Impression MaterialsSyed Noorani50% (2)
- Operative Dentistry Course RSTD 1100Document47 pagesOperative Dentistry Course RSTD 1100Anjana Ramroop-JogeeNo ratings yet
- Dental Luting Cements Objectives:: Course Date: 10/10 Expiration Date: 10/13Document14 pagesDental Luting Cements Objectives:: Course Date: 10/10 Expiration Date: 10/13Dampee ReturnNo ratings yet
- Gic Lecture SaturdayDocument117 pagesGic Lecture Saturdayaakriti100% (1)
- Root Canal Sealers - SeminarDocument49 pagesRoot Canal Sealers - Seminarkowmudimaddineni100% (2)
- Cavity LinersDocument18 pagesCavity LinersMaitreyi LimayeNo ratings yet
- Asphalt, Hollow Blocks, & SteelDocument48 pagesAsphalt, Hollow Blocks, & SteelNicholas Bonn SingNo ratings yet
- Elastic Impression Materials (Agar and Alginate)Document52 pagesElastic Impression Materials (Agar and Alginate)Saud Iqbal100% (1)
- Luting CementsDocument13 pagesLuting CementsPanah SalahiNo ratings yet
- Tooth Colored RestorationDocument98 pagesTooth Colored Restorationjamaica faith ramonNo ratings yet
- Periapical SurgeryDocument107 pagesPeriapical SurgeryShaliniNo ratings yet
- Pulp ProtectionDocument48 pagesPulp ProtectionShaliniNo ratings yet
- ObturationDocument35 pagesObturationShaliniNo ratings yet
- ARVIND SHENOY JConservDent11399-4568629 - 124126Document9 pagesARVIND SHENOY JConservDent11399-4568629 - 124126ShaliniNo ratings yet
- Amalgam War Mortensen1991Document6 pagesAmalgam War Mortensen1991ShaliniNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties Dental Materials2Document55 pagesPhysical Properties Dental Materials2ShaliniNo ratings yet
- Shaping TechniquesDocument50 pagesShaping TechniquesShaliniNo ratings yet
- Murray2012 ScaffoldDocument12 pagesMurray2012 ScaffoldShaliniNo ratings yet
- The Dental Amalgam Toxicity Fear: A Myth or Actuality: Review ArticleDocument9 pagesThe Dental Amalgam Toxicity Fear: A Myth or Actuality: Review ArticleShaliniNo ratings yet
- 2nd Gen Platelet Rich ScaffoldDocument8 pages2nd Gen Platelet Rich ScaffoldShaliniNo ratings yet
- Dental Amalgam: An Update: Invited ReviewDocument5 pagesDental Amalgam: An Update: Invited ReviewShaliniNo ratings yet
- Silver Amalgam: A Clinician's Perspective: Review ArticleDocument6 pagesSilver Amalgam: A Clinician's Perspective: Review ArticleShaliniNo ratings yet
- Clindamycin Drug DeliveryDocument8 pagesClindamycin Drug DeliveryShaliniNo ratings yet
- Radiograph Interpret Aug 2018Document33 pagesRadiograph Interpret Aug 2018ShaliniNo ratings yet
- S - 8 Composites Composition, Classification & PolymerisationDocument36 pagesS - 8 Composites Composition, Classification & PolymerisationShaliniNo ratings yet
- S - 6 Shaping Techniques 2019Document91 pagesS - 6 Shaping Techniques 2019ShaliniNo ratings yet
- S - 10 Direct Filling GoldDocument30 pagesS - 10 Direct Filling GoldShaliniNo ratings yet
- S - 8 Composites Composition, Classification & PolymerisationDocument36 pagesS - 8 Composites Composition, Classification & PolymerisationShaliniNo ratings yet
- S - 8 Composites Composition, Classification & PolymerisationDocument36 pagesS - 8 Composites Composition, Classification & PolymerisationShaliniNo ratings yet