Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ch-7 Kinetic Model of Matter gd-8
Uploaded by
digamber0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views23 pagesThe kinetic model of matter states that particles that make up matter are always in random motion. In solids, molecules vibrate about fixed positions and are close together. In liquids, molecules are more spaced out but still have attraction, allowing liquids to flow freely but maintain a fixed volume. Gases have the most distance between molecules which are barely attracted to each other, allowing gases to expand freely to fill their containers.
Original Description:
Original Title
ch-7 kinetic model of matter gd-8
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe kinetic model of matter states that particles that make up matter are always in random motion. In solids, molecules vibrate about fixed positions and are close together. In liquids, molecules are more spaced out but still have attraction, allowing liquids to flow freely but maintain a fixed volume. Gases have the most distance between molecules which are barely attracted to each other, allowing gases to expand freely to fill their containers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views23 pagesch-7 Kinetic Model of Matter gd-8
Uploaded by
digamberThe kinetic model of matter states that particles that make up matter are always in random motion. In solids, molecules vibrate about fixed positions and are close together. In liquids, molecules are more spaced out but still have attraction, allowing liquids to flow freely but maintain a fixed volume. Gases have the most distance between molecules which are barely attracted to each other, allowing gases to expand freely to fill their containers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 23
Chapter -7
Kinetic Model of Matter
The kinetic model of matter states that the tiny
particles that make up matter are always in
continuous random motion that is moving all
the time.
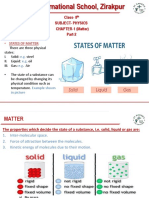
State of Matter
Properties of Solids, Liquids and Gases
Molecular Structure of Solids, Liquids and
Gases
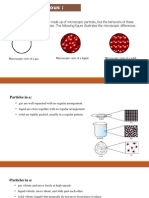
• Solids
• Distances between molecules
• Molecules arranged close together in regular
pattern
• Incompressible because molecules are close
together with little space between them
• Forces between molecules
• Balanced forces between molecules hold them
in fixed positions
• Molecules vibrate about fixed positions,
alternately attracting and repelling one another
• Attractive and repulsive forces explains why a
solid has fixed shape and fixed volume.
SOLID
• Motion of the molecules
• When a solid is heated, molecules gain energy
and vibrate more.
• Separation between molecules increase
slightly and the solid expands.
Liquid
• Distances between molecules
• Molecules not arranged in regular pattern
• Molecules slightly further apart than in solids
• Liquids cannot be easily compressed as
molecules are close together with little space
between them.
Liquid
• Forces between molecules and motion of the molecules
• Molecules vibrate to and fro, alternately attracting and
repelling one another.
• Molecules not held in fixed position by attractive forces.
• Molecules move among one another throughout the liquid.
• Explains why liquids flow and take the shape of container
• Forces between molecules and motion of the
molecules
• Attractive forces between molecules make it
difficult for molecules to leave the liquid.
• Thus liquids have fixed volume.
• When a liquid is heated, molecules vibrate and
move about more vigorously.
• Thus liquid expands, but only very slightly.
Gases
• Distances between molecules
• Molecules are far apart
• Mainly empty space between molecules
• That is why gas can be compressed easily.
Forces between molecules & motion of molecules
• Molecules move randomly at high speed
• Intermolecular repulsive forces act only when
molecules collide with one another and with
the walls of container.
• Molecules are so far apart that intermolecular
attractive forces are negligible in a gas.
• A gas is thus able to expand and fill a container
completely.
Work sheet 7A Pg- 69
• 1.(a) In a solids molecules vibrate about their
fixed position they are linked with strong
molecular bonds. In liquids the particles
randomly arranged. In gas particles are
randomly arranged and are very far apart from
one another.
• 1(b) - In a solid particles vibrate about fixed
positions they have strongest inter molecular
bond. In a liquid particles are free to move
with in the liquid inter molecular bond are
weaker than solid. In the gas particles the
inter molecular bond are very weak they move
at very high speed they don’t have fixed
simple shape nor volume.
• 2(b)- The particles in liquid mercury have
attractive forces holding them together hence
liquid mercury can not be compressed that’s
why liquid mercury has a fixed volume but not
fixed shape.
• 3(a)- The motion of the air molecule is
random
• b (i)- Air molecules move faster and more
vigorously
• (ii) The smoke particle move and change
directly faster and more vigorously . Because
the air molecules move faster and hit the
smoke particles more vigorously and faster.
Work sheet 7 B pg- 71
• Section A-
• 1- C
• 2- D
• Section B
• 1(a)- Oxygen molecule are further apart in gas
state then in solid and then liquid the number
of oxygen molecules per unit volume is lower
for gases than for solids and liquids.
• 1(b)- Oxygen molecules have weak attractive
force it has loose bonds they are far away
from one another to occupy space n shape.
• 2- (a) Air molecules will spread faster .
• (b) unchanged
• increases
• increases
• unchanged
• 3(a)-
You might also like
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Well Being Astrology 2016Document124 pagesWell Being Astrology 2016Marina RotaruNo ratings yet
- Design Your Ultimate Life With Lifebook OnlineDocument34 pagesDesign Your Ultimate Life With Lifebook OnlineJày Dēep43% (14)
- Plastic Surgery Without The SurgeryDocument155 pagesPlastic Surgery Without The SurgeryRohit Agrawal100% (1)
- Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument39 pagesKinetic Particle Theoryh8alfred100% (1)
- Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Solids and Their PropertiesDocument39 pagesIntermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Solids and Their PropertiesSTANNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of MatterDocument39 pagesParticulate Nature of MatterruqwNo ratings yet
- Hdev Canadian 2nd Edition Rathus Test BankDocument36 pagesHdev Canadian 2nd Edition Rathus Test BankJohnTaylortbios100% (11)
- Fault Isolation Manual Boeing PDFDocument1 pageFault Isolation Manual Boeing PDFbnmmauricioNo ratings yet
- AttitudeDocument29 pagesAttitudeAbhipsa SarkarNo ratings yet
- DLL English 10 Q1 - Module 1 - Lesson 1 - Daedalus and Icarus, Intensive and Reflexive Pronoun, Anti-Bullying ActDocument8 pagesDLL English 10 Q1 - Module 1 - Lesson 1 - Daedalus and Icarus, Intensive and Reflexive Pronoun, Anti-Bullying ActJennifer OestarNo ratings yet
- Matter and Phase Changes 2Document19 pagesMatter and Phase Changes 2vinujah100% (1)
- Assignment Money Cash Flow Inc Group 21,23,27,30Document3 pagesAssignment Money Cash Flow Inc Group 21,23,27,30Karan Vashee100% (3)
- Lesson Plan in General Chemistry Grade 12Document4 pagesLesson Plan in General Chemistry Grade 12Maren PendonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: The Science of Matter. The Composition of Substances and Their Properties and ReactionsDocument13 pagesChemistry: The Science of Matter. The Composition of Substances and Their Properties and ReactionstinevimboNo ratings yet
- Subject-Physics CHAPTER-1 (Matter) Class - 8Document8 pagesSubject-Physics CHAPTER-1 (Matter) Class - 8kamal_satnaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2Document23 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2St. DymphaMaralit, Joyce Anne L.No ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document5 pagesPresentation 4api-286027335No ratings yet
- 6resource 131602210601 53Document156 pages6resource 131602210601 53No ExcuseNo ratings yet
- ImfDocument92 pagesImfNeil Adrian MagnoNo ratings yet
- Particle Theory of MatterDocument23 pagesParticle Theory of MatterJennifer MagangoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - States of MatterDocument31 pagesChapter 10 - States of Matterjim tannerNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics States of Matter and Brownian MotionDocument27 pagesThermal Physics States of Matter and Brownian MotionSaad BBNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document14 pagesUnit 2musa shahidNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Chem Unit 3-5 FullDocument278 pagesGrade 11 Chem Unit 3-5 Fullbesufekadmaregu981No ratings yet
- Section 10.3 ReviewDocument1 pageSection 10.3 ReviewIsabelle GauthierNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 ModuleDocument6 pagesLesson 1 ModuleCrisanta GanadoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Module 1ADocument13 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Module 1ABenice GarciaNo ratings yet
- Phase ChangingDocument19 pagesPhase ChangingAnaa LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Midterm Week 1 Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument15 pagesMidterm Week 1 Kinetic Molecular TheoryLealyn OlunanNo ratings yet
- 4.3 The Particle ModelDocument10 pages4.3 The Particle ModelSarah ANo ratings yet
- 1 Kinetic Molecular ModelDocument28 pages1 Kinetic Molecular Modelmaryjoymarinduque13No ratings yet
- G9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2Document35 pagesG9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2hk6sd6cf7vNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Week 1Document4 pagesWorksheet Week 1Leyana Katriel T BeltranNo ratings yet
- KMT ImfaDocument44 pagesKMT Imfaellajazelle75No ratings yet
- Module On KMT of Liquids and Solids-RevisedDocument1 pageModule On KMT of Liquids and Solids-RevisedKuruko Tetsuya100% (1)
- States of MatterDocument13 pagesStates of MatternicoleNo ratings yet
- Particle Theory Q&aDocument2 pagesParticle Theory Q&aNancy MohamedNo ratings yet
- C07 Kinetic Model of Matter (Teacher)Document22 pagesC07 Kinetic Model of Matter (Teacher)a m i rNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Particulate Nature of MatterDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Particulate Nature of MatterShyam BudhwarNo ratings yet
- States of Matter: Advanced Secondary 1Document29 pagesStates of Matter: Advanced Secondary 1David JonesNo ratings yet
- AS Chemistry - States of MatterDocument25 pagesAS Chemistry - States of MatterwilsonconcepcionNo ratings yet
- I. The Kinetic Molecular Theory of MatterDocument5 pagesI. The Kinetic Molecular Theory of MatterKwon NieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Intermolecular Forces Lecture Outline 11.1 A Molecular Comparison of Gases, Liquids and SolidsDocument9 pagesChapter 11: Intermolecular Forces Lecture Outline 11.1 A Molecular Comparison of Gases, Liquids and SolidsLOLONo ratings yet
- The Gaseous State of MatterDocument15 pagesThe Gaseous State of MatterdwijpadaliaNo ratings yet
- States of Matter PT 1Document10 pagesStates of Matter PT 1api-310503032No ratings yet
- Mid-Term Chemistry Project by Ahmed Yasser, 9b1Document14 pagesMid-Term Chemistry Project by Ahmed Yasser, 9b1ASMS officialNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of Matter NewDocument26 pagesParticulate Nature of Matter NewKeith BryceNo ratings yet
- MELC 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsDocument27 pagesMELC 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and Liquidsreemm pascualNo ratings yet
- Ebookneonclasseschemistryeng 2Document63 pagesEbookneonclasseschemistryeng 2rameshNo ratings yet
- Understanding Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument50 pagesUnderstanding Kinetic Particle TheoryozmanNo ratings yet
- 6.1 States of MatterDocument11 pages6.1 States of MatterHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument9 pagesMatterryienlucNo ratings yet
- Week 1: Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsDocument31 pagesWeek 1: Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsCrizza Mae CuregNo ratings yet
- Can You Find The Three States of MatterDocument19 pagesCan You Find The Three States of Matterapi-205655271No ratings yet
- Act 1 Genchem 2 CALIBODocument2 pagesAct 1 Genchem 2 CALIBOChristianzzz CalibsNo ratings yet
- Matter Elements Compounds MixturesDocument16 pagesMatter Elements Compounds Mixturesapi-264004571No ratings yet
- Solids, Liquids, and GasesDocument13 pagesSolids, Liquids, and GasesmochimochikoNo ratings yet
- Crystalline SolidsDocument10 pagesCrystalline SolidsoracleNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids: Lesson 1Document28 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids: Lesson 1Fern Baldonaza100% (1)
- ACTIVITY 1 - KINETIC MOLECULAR MODEL - IngallaDocument4 pagesACTIVITY 1 - KINETIC MOLECULAR MODEL - Ingallajet tolintinoNo ratings yet
- Blue and Yellow Textured 2D and 3D Behaviors of Particles in Solid, Liquid, Gas Presentation-2Document18 pagesBlue and Yellow Textured 2D and 3D Behaviors of Particles in Solid, Liquid, Gas Presentation-2Gerald RefilNo ratings yet
- Latest Copy of Class 8 Physics Question Bank 1Document101 pagesLatest Copy of Class 8 Physics Question Bank 1KAMLESH PATIDARNo ratings yet
- Study Guide KMTDocument6 pagesStudy Guide KMT9Wezen Jowelyn Mae G. TabuzoNo ratings yet
- Bcsci8 Topic2.3 KMTDocument58 pagesBcsci8 Topic2.3 KMTJeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- Unit I-C - Liquid CrystalsDocument35 pagesUnit I-C - Liquid Crystalsjyoti kumariNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 3 HandoutsDocument6 pagesLesson 1 3 HandoutsLJ Princess Mary MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of MatterDocument4 pagesParticulate Nature of MatterSandy ItabNo ratings yet
- Ch-13 Waves IxDocument30 pagesCh-13 Waves IxdigamberNo ratings yet
- CH 15 Sound IxDocument4 pagesCH 15 Sound IxdigamberNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 8 TempDocument18 pagesChapter - 8 TempdigamberNo ratings yet
- 9A Physice MomentumDocument29 pages9A Physice MomentumdigamberNo ratings yet
- CH 14 Electromagnetic Waves 9Document10 pagesCH 14 Electromagnetic Waves 9digamberNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 15 SoundDocument25 pagesChapter - 15 SounddigamberNo ratings yet
- Ch-4 9A Mass, Weight and DensityDocument44 pagesCh-4 9A Mass, Weight and DensitydigamberNo ratings yet
- ch7 PressureDocument26 pagesch7 PressuredigamberNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 American Government Flashcards - QuizletDocument7 pagesChapter 13 American Government Flashcards - QuizletbananadelreyNo ratings yet
- Press Release Hit and RunDocument2 pagesPress Release Hit and RunAnthony_Smith4792No ratings yet
- 08 - Chapter 2 PDFDocument64 pages08 - Chapter 2 PDFZeshan AzeemNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0098135497875771 Main PDFDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0098135497875771 Main PDFHusnain AliNo ratings yet
- Wenjun Herminado QuizzzzzDocument3 pagesWenjun Herminado QuizzzzzWenjunNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting ANS: Cholinergic AgonistsDocument25 pagesDrugs Affecting ANS: Cholinergic AgonistsAjay SinghNo ratings yet
- Sydney Boys 2022 3U Trials & SolutionsDocument36 pagesSydney Boys 2022 3U Trials & SolutionssaramafareNo ratings yet
- Saints Communing Songs VOL 3 SONG SHEETDocument29 pagesSaints Communing Songs VOL 3 SONG SHEETanthonyNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Involvement in SyphilisDocument6 pagesPulmonary Involvement in SyphilisVijayesh MokalNo ratings yet
- Wittgenstein Picture TheoryDocument4 pagesWittgenstein Picture TheoryAlladi Bhadra Rao DevangaNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Introducing Public Administration 8th Edition Shafritz Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Introducing Public Administration 8th Edition Shafritz Test Bank PDFdopemorpheanwlzyv100% (11)
- 5 L1 Aspen TutorialDocument28 pages5 L1 Aspen TutorialariefNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Intro To Crim & Institutional CorrecDocument22 pagesReviewer in Intro To Crim & Institutional CorrecRhodora A. BorjaNo ratings yet
- Tools of Persuasion in AdvertisingDocument2 pagesTools of Persuasion in AdvertisingJulieta amicoNo ratings yet
- U.S. vs. Ah ChongDocument4 pagesU.S. vs. Ah ChongGroot GrootNo ratings yet
- Warren, Shilyh - By, For, and About-The 'Real' Problem in The Feminist Film Movement.Document17 pagesWarren, Shilyh - By, For, and About-The 'Real' Problem in The Feminist Film Movement.JkopkutikNo ratings yet
- MGT301 Quiz - 2Document14 pagesMGT301 Quiz - 2BilalNo ratings yet
- Evidence Summary NotesDocument2 pagesEvidence Summary NotesMemai AvilaNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan (Hypertension)Document1 pageFamily Nursing Care Plan (Hypertension)octoberttwentythreeNo ratings yet
- WK 8 Conflict - Management - Skills LaptopDocument24 pagesWK 8 Conflict - Management - Skills LaptopAMEERA SHAFIQA MOHD RASHIDNo ratings yet
- 03 - 1 - Frameworks DrillsDocument12 pages03 - 1 - Frameworks DrillsThanh Phu TranNo ratings yet
- Rustamji Institute of Technology: Predictive Analytics On Health CareDocument12 pagesRustamji Institute of Technology: Predictive Analytics On Health CareOcean BluuNo ratings yet