Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
Uploaded by
Sarah MCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
Uploaded by
Sarah MCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter D2 Circulation and Respiration
Table of Contents
Section 1 The Cardiovascular System
Section 2 Blood
Section 3 The Lymphatic System
Section 4 The Respiratory System
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 1 The Cardiovascular System
Chapter D2
Bellringer
In 2–3 minutes, list as many song titles and lyrics as
you can that contain the word heart. What ideas are
associated with the heart? Why do you think the heart
is part of so many songs?
Write your answers in your science journal.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 1 The Cardiovascular System
Chapter D2
Objectives
• List five main parts of the cardiovascular system,
and describe their functions.
• Describe the two types of circulation of blood in
the body.
• List four cardiovascular problems.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 1 The Cardiovascular System
Chapter D2
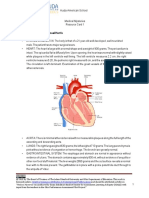
Your Cardiovascular System
• The cardiovascular system consists of the heart
and the three types of blood vessels that carry blood
throughout your body.
• The blood vessels—arteries, capillaries, and veins
—carry blood pumped by the heart.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 1 The Cardiovascular System
Chapter D2
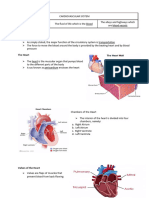
The Heart
• Cardiac Muscle
Your heart is an
organ made mostly of
cardiac muscle
tissue. It is about the
size of your fist and is
almost in the center
of your chest cavity.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 1 The Cardiovascular System
Chapter D2
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 1 The Cardiovascular System
Chapter D2
Blood Vessels
• Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood away
from the heart and to the body’s organs.
• Capillaries are tiny blood vessels that allow the
exchange between body cells and blood.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 1 The Cardiovascular System
Chapter D2
Blood Vessels, continued
• Veins are blood vessels that carry blood back to
the heart.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 1 The Cardiovascular System
Chapter D2
Two Types of Circulation
• Pulmonary circulation is the flow of blood from
the heart to the lungs and back to the heart through
the pulmonary arteries, capillaries, and veins.
• Systemic circulation is the flow of blood from the
heart to all parts of the body and back to the heart.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 1 The Cardiovascular System
Chapter D2
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 1 The Cardiovascular System
Chapter D2
Cardiovascular Problems
• Atherosclerosis
happens when
cholesterol builds up
inside of the blood
vessels.
Artherosclerosis is a
major cause of heart
diseases.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 1 The Cardiovascular System
Chapter D2
Cardiovascular Problems, continued
• High Blood Pressure Hypertension is abnormally
high blood pressure. The higher the blood pressure,
the greater the risk of a heart attack, heart failure,
kidney disease, and stroke.
• Heart Attacks and Heart Failure A heart attack
happens when heart muscle cells die and part of the
heart muscle is damaged. Heart failure happens when
the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the
body’s needs.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 2 Blood
Chapter D2
Bellringer
List three things that you know about blood, such as
the parts of blood, the places where blood forms, the
function of blood in the body, or the way in which
blood is donated.
Record your list in your science journal.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 2 Blood
Chapter D2
Objectives
• Identify the four main components of blood.
• Describe three functions of blood.
• Explain how blood pressure is measured.
• Explain what the ABO blood types are and why
they are important.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 2 Blood
Chapter D2
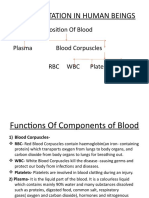
What Is Blood?
• Blood is a connective tissue that carries gases,
nutrients, and wastes through the body.
• Plasma is the fluid part of blood. It is a mixture of
water, minerals, nutrients, sugars, proteins, and
other substances.
• Red Blood Cells Most blood cells are red blood
cells (RBCs). RBCs take oxygen to every cell in your
body.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 2 Blood
Chapter D2
What Is Blood?, continued
• Platelets are pieces of larger cells found in bone
marrow. When you cut yourself, platelets help
blood clot.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 2 Blood
Chapter D2
What Is Blood?, continued
• White Blood Cells (WBCs) help keep you
healthy by destroying pathogens. WBCs also help
clean wounds.
• WBCs also keep you healthy by destroying body
cells that have died or been damaged.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 2 Blood
Chapter D2
Body Temperature Regulation
• Your blood does more than supply your cells with
oxygen and nutrients. It also helps regulate your body
temperature.
Blood Pressure
• The force exerted by blood on the inside walls of
arteries is called blood pressure.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 2 Blood
Chapter D2
Blood Types
• Every person has one of four
blood types: A, B, AB, or O.
Your blood type refers to the
type of antigens you have on
the surface of your RBCs.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 2 Blood
Chapter D2
Blood Types and Transfusions
• A transfusion is the injection of blood or blood
components into a person to replace blood that has
been lost. Blood type is an important consideration
of a blood transfusion.
Type Can receive Can donate to
A A, O A, AB
B B, O B, AB
AB all AB only
O O all
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 3 The Lymphatic System
Chapter D2
Bellringer
Do you know anyone who has had their tonsils
removed? Do you know what tonsils do or where they
are located in the body? If so, write a few sentences
explaining their function. If you don’t know what the
tonsils are for, make an educated guess about their
role in the body.
Write your response in your science journal.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 3 The Lymphatic System
Chapter D2
Objectives
• Describe the relationship between the lymphatic
system and the cardiovascular system.
• Identify six parts of the lymphatic system, and
describe their functions.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 3 The Lymphatic System
Chapter D2
Vessels of the
Lymphatic System
• The lymphatic
system is the
group of organs
and tissues that
collect excess fluid
and return it to
your blood.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 3 The Lymphatic System
Chapter D2
Vessels of the Lymphatic System, continued
• The smallest vessels of the lymphatic system are
lymph capillaries. The fluid and particles absorbed into
lymph capillaries are called lymph.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 3 The Lymphatic System
Chapter D2
Other Parts of the Lymphatic System
• Bone Marrow is the soft tissue inside of bones.
Bone marrow is where most red and white blood
cells, including lymphocytes, are produced.
• Lymph Nodes are small, bean-shaped masses of
tissue that remove pathogens and dead cells from
the lymph.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 3 The Lymphatic System
Chapter D2
Other Parts of the Lymphatic System,
continued
• The thymus is the gland that produces T cells that
are ready to fight infection.
• Your spleen is the largest lymphatic organ. The
spleen stores and produces lymphocytes.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 3 The Lymphatic System
Chapter D2
Other Parts of the Lymphatic System,
continued
• Tonsils are lymphatic
tissue in the nasal
cavity and at the back
of the mouth on either
side of the tongue.
Tonsils help defend the
body against infection.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 4 The Respiratory System
Chapter D2
Bellringer
Are breathing and respiration are the same thing?
Write your response in your science journal.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 4 The Respiratory System
Chapter D2
Objectives
• Describe the parts of the respiratory system and
their functions.
• Explain how breathing happens.
• Discuss the relationship between the respiratory
system and the cardiovascular system.
• Identify two respiratory disorders.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 4 The Respiratory System
Chapter D2
Respiration and the Respiratory System
• Respiration is the process by which a body gets
and uses oxygen and releases carbon dioxide and
water. Breathing is only one part of respiration.
• The second part of respiration is cellular respiration,
which involves chemical reactions that release energy
from food.
• The respiratory system is the group of organs that
take in oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 4 The Respiratory System
Chapter D2
Respiration and the Respiratory System,
continued
• Nose, Pharynx, and
Larynx Your nose is the
main passageway into
and out of the respiratory
system. From the nose,
air flows into the
pharynx, or throat. The
larynx is the part of the
throat that contains the
vocal chords.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 4 The Respiratory System
Chapter D2
Respiration and the Respiratory System,
continued
• Trachea The larynx guards the entrance to a large
tube called the trachea, or windpipe.
• Bronchi and Alveoli The trachea splits into two
branches called bronchi. One bronchus connects to
each lung. In the lungs, each bronchus branches into
bronchioles, which branch to form thousands of tiny
sacs that are called alveoli.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 4 The Respiratory System
Chapter D2
Respiration and the Respiratory System,
continued
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 4 The Respiratory System
Chapter D2
Breathing
• Breathing is done by the diaphragm and rib muscles.
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle beneath the
lungs.
Breathing and Cellular Respiration
• In cellular respiration, oxygen is used by cells to
release energy stored in molecules of glucose. When
you breathe, you take in oxygen, which diffuses into
red blood cells and is carried to tissue cells.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 4 The Respiratory System
Chapter D2
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter D2 Section 4 The Respiratory System
Respiratory Disorders
• Respiratory disorders include asthma, emphysema,
and severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS).
• Asthma causes the bronchioles to narrow. An
asthma attack may be triggered by irritants such as
dust or pollen.
• SARS is caused by a virus.
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Circulation and Respiration
Chapter D2
Concept Map
Use the terms below to complete the concept map on
the next slide.
arteries capillaries
cardiovascular system respiratory system
bronchi cellular respiration
alveoli blood
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Circulation and Respiration
Chapter D2
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Circulation and Respiration
Chapter D2
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 1 The Cardiovascular System
Chapter D2
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 1 The Cardiovascular System
Chapter D2
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 1 The Cardiovascular System
Chapter D2
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 2 Blood
Chapter D2
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 2 Blood
Chapter D2
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 3 The Lymphatic System
Chapter D2
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 3 The Lymphatic System
Chapter D2
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 3 The Lymphatic System
Chapter D2
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 4 The Respiratory System
Chapter D2
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Section 4 The Respiratory System
Chapter D2
Chapter menu Resources
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Pilates Flex and StretchDocument5 pagesPilates Flex and StretchEule100100% (1)
- The Skeletal SystemDocument24 pagesThe Skeletal SystemAlexa100% (1)
- Binder 50 Weight TrainingDocument3 pagesBinder 50 Weight TrainingmarkwsheppardNo ratings yet
- G9 Lesson 1 Circulation and Gas ExchangeDocument43 pagesG9 Lesson 1 Circulation and Gas ExchangeRyan Joshua RefuerzoNo ratings yet
- Biology November Circulatory System Arav Nair 8A ROLL NO - 11Document35 pagesBiology November Circulatory System Arav Nair 8A ROLL NO - 11aravnair2302No ratings yet
- 2023 - Handout - Cardiovascular System - STUDENT'SDocument17 pages2023 - Handout - Cardiovascular System - STUDENT'SmilifacultadfcmNo ratings yet
- U3circulatory SystemDocument50 pagesU3circulatory SystemraqduoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument63 pagesCirculatory Systemlezzaann delacuzNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 The Circulatory System 2015Document90 pagesTopic 1 The Circulatory System 2015Manpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Sci 9 Week 3Document25 pagesSci 9 Week 3Yael Ellie SumandiNo ratings yet
- Science 9 1.4 Circulation of Blood in The BodyDocument13 pagesScience 9 1.4 Circulation of Blood in The BodyChad Kirsten Mier LustreNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Cardiovascular SytemDocument37 pagesGroup 3 Cardiovascular Sytemsophiapelayo326No ratings yet
- ICSE-X Biology Chap 7-9Document40 pagesICSE-X Biology Chap 7-9krishnabhavith3No ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and HormonesDocument49 pagesCirculatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and HormonesChristopher EstevezNo ratings yet
- 15 Transport in The Body PDFDocument21 pages15 Transport in The Body PDFMarie MentorNo ratings yet
- CirculationDocument32 pagesCirculationhhhhhhhhhhhhhhNo ratings yet
- Complete BMIDocument384 pagesComplete BMISruti SinghNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and Hormones Chapter #32, Pg. 650 - 665Document38 pagesCirculatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and Hormones Chapter #32, Pg. 650 - 665Anggun Kharisma RaniNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 7 Revision Notes PDFDocument8 pagesClass 10 Biology Chapter 7 Revision Notes PDFNayla Masroor 9BNo ratings yet
- Class-12 (RBSE) Biology-Ch-24 Blood Circulatory System PDFDocument7 pagesClass-12 (RBSE) Biology-Ch-24 Blood Circulatory System PDFIshansi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Exchange and Transport Heart and CirculationDocument37 pagesExchange and Transport Heart and Circulationhannahangella5949No ratings yet
- L-1C TransportationDocument37 pagesL-1C Transportationdangishita28No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesCardiovascular Systemjamielsomera120No ratings yet
- Heart Grade 10Document18 pagesHeart Grade 10amulyajadhav119No ratings yet
- L-1C TransportationDocument37 pagesL-1C Transportationdangishita28No ratings yet
- Purple Illustrative The Human Body PresentationDocument24 pagesPurple Illustrative The Human Body PresentationNETHRA ESWARE A/P KAMALANATHAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Sulthan Circulatory System RevisedDocument12 pagesSulthan Circulatory System RevisedSonny BudimanNo ratings yet
- Human Performance For ATPL Class: Blood CirculationDocument41 pagesHuman Performance For ATPL Class: Blood CirculationListiyani IsmailNo ratings yet
- Biology C - Lesson 1 - Circulatory SystemDocument58 pagesBiology C - Lesson 1 - Circulatory SystemmemmotilalNo ratings yet
- Thecirculatorysystem 130618021608 Phpapp01Document70 pagesThecirculatorysystem 130618021608 Phpapp01Mikel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORTATIONDocument9 pagesTRANSPORTATIONAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Circulatory SystemDocument39 pagesUnit 3 Circulatory SystemSebastian IbañezNo ratings yet
- HEARTDocument10 pagesHEARTbgmiytNo ratings yet
- Bhs Class 6 Biology August PDFDocument7 pagesBhs Class 6 Biology August PDFgamerround2No ratings yet
- 11TH - BIOLOGY - BODY - FUIDS - CIR - 15 - 04 - 2024 - 22-Apr-2024 - SolutionDocument5 pages11TH - BIOLOGY - BODY - FUIDS - CIR - 15 - 04 - 2024 - 22-Apr-2024 - Solutionkeshavkhaneja7No ratings yet
- Y10 Heart & CirculationDocument11 pagesY10 Heart & CirculationTri MariyantiNo ratings yet
- Science 6 DLP 1 - Parts of The Circulatory System RepairedDocument11 pagesScience 6 DLP 1 - Parts of The Circulatory System RepairedMARIFE T. BAUINo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The HeartDocument18 pagesStructure and Function of The HeartVaradharajan SNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5 2ND QUARTERT Science 6 EDITDocument8 pagesMODULE 5 2ND QUARTERT Science 6 EDITEmie PonceNo ratings yet
- The Transport System in HumansDocument8 pagesThe Transport System in HumansazuraNo ratings yet
- Heart: How The Blood Gets Around The Body: by (Azia Houston) (Ms. Watts) (Yearbook) (March 1, 2011)Document8 pagesHeart: How The Blood Gets Around The Body: by (Azia Houston) (Ms. Watts) (Yearbook) (March 1, 2011)azia1011085No ratings yet
- Transport System in AnimalsDocument15 pagesTransport System in AnimalschiomasingsNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System LabDocument44 pagesCirculatory System LabMarileth CoNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Chapter 32 - Circulatory SystemDocument35 pagesLecture - Chapter 32 - Circulatory SystemKaseylene CabansagNo ratings yet
- Science 9 1.3 LessonDocument31 pagesScience 9 1.3 LessonHdisbdbd NfjdnbdncNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Cardiovascular System and ECG Performance, Troubleshooting, and InterpretationDocument47 pagesA Review of The Cardiovascular System and ECG Performance, Troubleshooting, and InterpretationRetroPilotNo ratings yet
- Rehab After Surgery BookletDocument60 pagesRehab After Surgery BookletscoopyNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Sistem KardiovaskularDocument28 pagesFisiologi Sistem Kardiovaskularpriesha aprilia03No ratings yet
- Animal TransportDocument20 pagesAnimal TransportFeranmi AkinboboyeNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - Week 3 - 2nd QuarterDocument4 pagesScience 6 - Week 3 - 2nd QuarterHoneylet Alberto Castro ArilloNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesBlood Circulatory Systemmenaga ilangkovanNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Lab Exercise - Cvs & Bood Vessels AnsDocument4 pagesWeek 10 Lab Exercise - Cvs & Bood Vessels AnsG4 AMOYO ANGELICA NICOLENo ratings yet
- Transport SystemDocument2 pagesTransport Systemgnana87No ratings yet
- Alwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 9. Transport in Animals NotesDocument62 pagesAlwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 9. Transport in Animals NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesCirculatory SystemIan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Life Processes, Class XDocument31 pagesLife Processes, Class XPiyushNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 Page 63Document3 pagesExercise 4 Page 63rnmrtdzht5No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument33 pagesCardiovascular SystemJay Anne CorrianoNo ratings yet
- Ap50 HW11Document3 pagesAp50 HW11wendyalvarez321No ratings yet
- Blood and Circulation Bridge LessonDocument12 pagesBlood and Circulation Bridge LessonManan PatelNo ratings yet
- Heart, Blood Tissue Blood Vessels: The Circulatory System Includes The and TheDocument44 pagesHeart, Blood Tissue Blood Vessels: The Circulatory System Includes The and TheAnnah JeanNo ratings yet
- Biology - Circulatory SystemDocument13 pagesBiology - Circulatory SystemEnkoujo KairiNo ratings yet
- Strengths and Weakness of The Articles of Confederation 1Document10 pagesStrengths and Weakness of The Articles of Confederation 1Sarah MNo ratings yet
- CA Lesson 04 Effects of Drugs PowerpointDocument18 pagesCA Lesson 04 Effects of Drugs PowerpointSarah MNo ratings yet
- Mexican American WarDocument21 pagesMexican American WarSarah MNo ratings yet
- Mexican American War - Online NotesDocument26 pagesMexican American War - Online NotesSarah MNo ratings yet
- Medical Mystery Resource CardDocument2 pagesMedical Mystery Resource CardSarah MNo ratings yet
- Medical Mystery Resource Card 1Document5 pagesMedical Mystery Resource Card 1Sarah MNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 The SensesDocument3 pagesLesson 4 The SensesSarah MNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Diversity of ProtistsDocument6 pagesLesson 2 Diversity of ProtistsSarah MNo ratings yet
- Neer Classification - How Do We Use It and Why Is It Important?Document46 pagesNeer Classification - How Do We Use It and Why Is It Important?endy ahmaruzamryNo ratings yet
- Keplan Q BankDocument385 pagesKeplan Q BankManisanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Bujinkan Takagi Yoshin Ryu DenshoDocument25 pagesBujinkan Takagi Yoshin Ryu Denshomoon100% (3)
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesMale Reproductive SystemRalph CelesteNo ratings yet
- 2 The Development of OcclusionDocument13 pages2 The Development of OcclusionbhargaviNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Interaction: Colegio Marista CastillaDocument1 pageUNIT 1 Interaction: Colegio Marista CastillamarcNo ratings yet
- Ripped Workout BreakdownDocument6 pagesRipped Workout BreakdownaprilfoolingNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity - Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesLaboratory Activity - Integumentary SystemJaw LastNo ratings yet
- Upper Extremities Rad PosiDocument12 pagesUpper Extremities Rad PosiJoan GemotoNo ratings yet
- Weight Bench Exerciser User's Manual: CautionDocument24 pagesWeight Bench Exerciser User's Manual: CautionmehralsmenschNo ratings yet
- Sarvangasana (All Member's Pose) : TechniqueDocument1 pageSarvangasana (All Member's Pose) : TechniqueKarisma SenapatiNo ratings yet
- Foot PronationDocument4 pagesFoot Pronationsalamz1100% (1)
- Musculoskeletal QuestionsDocument4 pagesMusculoskeletal QuestionsJen Del Mundo100% (1)
- 2-Meninges and SinusesDocument62 pages2-Meninges and SinusesMajd HallakNo ratings yet
- Class 1 Malocclusion TreatmentDocument11 pagesClass 1 Malocclusion TreatmenthanyNo ratings yet
- Short Note Biology Form 5-Chapter 3 Coordination and ResponseDocument6 pagesShort Note Biology Form 5-Chapter 3 Coordination and Responsesalamah_sabri75% (4)
- Brain Tumors غﺎﻣﺪﻟا ماروا Definition Brain Tumor ﻒﯾﺮﻌﺘﻟاDocument7 pagesBrain Tumors غﺎﻣﺪﻟا ماروا Definition Brain Tumor ﻒﯾﺮﻌﺘﻟامحمد سعد طه احمدNo ratings yet
- Overuse Injuries of UpperDocument55 pagesOveruse Injuries of UpperNicu Tanase-RaduNo ratings yet
- David Butler Neural Tissue Mobilisation-1Document11 pagesDavid Butler Neural Tissue Mobilisation-1Himani BhondgeNo ratings yet
- Idiopathic Toe Walking A Kinematic and Kinetic ProfileDocument8 pagesIdiopathic Toe Walking A Kinematic and Kinetic Profileyarimar hoyosNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Head, Face & NeckDocument134 pagesMuscles of Head, Face & NeckDMNo ratings yet
- Neurological SheetDocument70 pagesNeurological SheetKlb ElbnatNo ratings yet
- Lips Gateway To EstheticsDocument97 pagesLips Gateway To EstheticsSagar KhatriNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of ArmDocument22 pagesAnatomy of Armromaisa akhtarNo ratings yet
- Workout Plan: ScheduleDocument4 pagesWorkout Plan: ScheduleSarthak KapoorNo ratings yet
- MD 1st Year Rachna Sharir Shariropkrama 18-05-2020Document42 pagesMD 1st Year Rachna Sharir Shariropkrama 18-05-2020Dr.Mahesh kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Humeral Shaft Fractures in Adults: SciencedirectDocument9 pagesAcute and Chronic Humeral Shaft Fractures in Adults: SciencedirectAshish AgrawalNo ratings yet