Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science 8 Q1 Exam Reviewer
Uploaded by
Sarah Jane Casipong0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views16 pagesOriginal Title
SCIENCE 8 Q1 EXAM REVIEWER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views16 pagesScience 8 Q1 Exam Reviewer
Uploaded by
Sarah Jane CasipongCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
1.
What do you call the push and pull
applied on an object?
a. motion
b. distance
c. displacement
d. force
2. It is the vector sum of all individual
forces acting on a body.
a. balanced force
b. net force
c. motion
d. unbalanced force
3. It refers to the size or strength of the
force.
a. net force
b. magnitude
c. speed
d. motion
4. When forces applied on an object are
equal in magnitude, applied in opposite
directions, and are lying in the same line of
action, what type of force is present?
a. balanced force
b. unbalanced force
c. net force
d. kinetic force
5. If the sum of the forces equate to
zero, they are considered ____________.
a. balanced
b. unbalanced
c. imbalanced
d. equal
6. _______ is the unit used to measure
force.
a. Joules
b. Newton
c. meter/second
d. kilogram
7. Who was the physicist who authored
the Three Laws of Motion?
a. Aristotle
b. Galileo
c. Isaac Newton
d. Archimedes
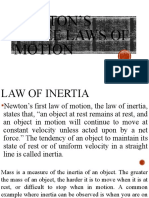
8. It is the tendency of the object to stay
at rest, if it is stationary, or to keep
moving once it is in motion.
a. inertia
b. power
c. work
d. potential energy
9. “A body will remain at rest or move at
constant speed/velocity unless acted upon
by an external net or unbalanced force”.
a. Law of Acceleration
b. Law of Inertia
c. Law of Interaction
d. Law of Conservation of Energy
10. “The acceleration of an object is directly
proportional to the magnitude of the net
force acting on it and is inversely
proportional to its mass”.
a. Law of Acceleration
b. Law of Inertia
c. Law of Interaction
d. Law of Conservation of Energy
11. The third law of motion which is also
known as _______ states that “For every
action, there is an equal and opposite
reaction.”
a. Law of Acceleration
b. Law of Inertia
c. Law of Interaction
d. Law of Conservation of Energy
12. Isaac Newton’s First law of Motion is
also known as the _________________.
a. Law of Acceleration
b. Law of Inertia
c. Law of Interaction
d. Law of Conservation of Energy
13. Isaac Newton’s Second law of Motion
is also known as the
___________________________.
a. Law of Acceleration
b. Law of Inertia
c. Law of Interaction
d. Law of Conservation of Energy
14. Isaac Newton’s Third law of Motion is
also known as the __________________.
a. Law of Acceleration
b. Law of Inertia
c. Law of Interaction
d. Law of Conservation of Energy
15. It is the unit measurement of work.
16. The unit, joule (J) was named after this English physicist.
17. It is the unit measurement of power.
18.______ = force x distance
19. The unit, watts (W) was named after this Scottish inventor.
20. It is the rate of doing work.
21. It is the capacity or ability to do work.
22. It is the unit measurement of force.
You might also like
- Lesson PlANDocument7 pagesLesson PlANJessica BarredoNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion QuizDocument1 pageForce and Motion QuizAvril Jade Esperanza100% (1)
- Science 8 Q1 Exam (22-23)Document3 pagesScience 8 Q1 Exam (22-23)Sarah Jane CasipongNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Test Science8 StrugglingDocument3 pages1st Periodical Test Science8 StrugglingtolisNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document43 pagesModule 2CHRYSTAL JANE ZARAGOZANo ratings yet
- Weekly Assessment Number 1Document1 pageWeekly Assessment Number 1Marissa FontanilNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE8 Newton's Three Laws of MotionDocument21 pagesSCIENCE8 Newton's Three Laws of Motiondiane kris del socorroNo ratings yet
- Phyiscs Act 8Document3 pagesPhyiscs Act 8Ires YuloNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 ScienceDocument2 pagesGrade 8 ScienceBart PorcadillaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Bio MechanicsDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Bio MechanicsAnushaFotedarNo ratings yet
- Weekly Assessment No. 1 Changes in The Motion of ObjectsDocument1 pageWeekly Assessment No. 1 Changes in The Motion of ObjectsAna Leika PasayloNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of Motion and Their ApplicationsDocument79 pagesNewton's Law of Motion and Their ApplicationsTalia JeonNo ratings yet
- 4TH QTR Exam Reviewer PhysciDocument5 pages4TH QTR Exam Reviewer PhysciJennelyn JacintoNo ratings yet
- PHY 1 - Module 4Document25 pagesPHY 1 - Module 4mtalquisola2002No ratings yet
- Class 9th Chapter Force and Laws of Motion Assertions - ReasonDocument6 pagesClass 9th Chapter Force and Laws of Motion Assertions - ReasonGarvitNo ratings yet
- Phy BWDocument14 pagesPhy BWsasasa785236No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesTOM RUIZNo ratings yet
- Science8 q1 Mod2 LawsOfMotion FINAL07282020Document21 pagesScience8 q1 Mod2 LawsOfMotion FINAL07282020Grayson RicardoNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: "Force, Type of Force and Free Body Diagram For Force"Document9 pagesStrength of Materials: "Force, Type of Force and Free Body Diagram For Force"Lulav BarwaryNo ratings yet
- Science-8 (1ST Quarterly)Document3 pagesScience-8 (1ST Quarterly)juliusvaldez07201996No ratings yet
- Forces and Newtons Law of MotionDocument20 pagesForces and Newtons Law of Motionjhunkelvin cusipagNo ratings yet
- Sci.8 1 2 Las by Arnold and Mam JennyDocument7 pagesSci.8 1 2 Las by Arnold and Mam JennyCherry Beth PagenteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Engineering MechanicsDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Engineering MechanicsghanshyamdassNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report4 PDFDocument9 pagesLaboratory Report4 PDFJuliana Mickaela MercadoNo ratings yet
- Newton'S Laws Newton's Laws of Motion Are Three: Philosophiae Naturalis Principia MathematicaDocument1 pageNewton'S Laws Newton's Laws of Motion Are Three: Philosophiae Naturalis Principia MathematicaKusuma MahadikaNo ratings yet
- Is P - 3 Laws ReviewDocument5 pagesIs P - 3 Laws Reviewapi-308247166No ratings yet
- Ch07 PPT NotesDocument75 pagesCh07 PPT NotesBeverly PamanNo ratings yet
- Robertson ForceDocument30 pagesRobertson ForceClubXSTemucoNo ratings yet
- Sample of Lesson Plan SciencexDocument8 pagesSample of Lesson Plan SciencexJochel AlingagNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Unit 9Document2 pagesPhysical Science Unit 9Bluematwo TwoNo ratings yet
- C ? (From Ancient Greek: IJȫıțȣ © "Nature") Is A Natural Science That InvolvesDocument9 pagesC ? (From Ancient Greek: IJȫıțȣ © "Nature") Is A Natural Science That InvolvesMelanie Vistal MarzonNo ratings yet
- Forces: Briefly Explained by Max de RooijDocument1 pageForces: Briefly Explained by Max de RooijMax De RooijNo ratings yet
- Dhruv Bhardwaj Physics 11 Law of Motion ProjectDocument30 pagesDhruv Bhardwaj Physics 11 Law of Motion ProjectComrade YTNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Frames of Reference, Forces and Newton's Laws of MotionDocument13 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Frames of Reference, Forces and Newton's Laws of MotionJacko LenoNo ratings yet
- nts112 4th Grading NotesDocument20 pagesnts112 4th Grading NotesMichelle AnnNo ratings yet
- Science 8-1st Quarter ModuleDocument59 pagesScience 8-1st Quarter ModuleAndrea Perez92% (24)
- Module 1 - Fundamental Concepts in Mechanics PDFDocument9 pagesModule 1 - Fundamental Concepts in Mechanics PDFRome Erwin Manalo FestinNo ratings yet
- Trusses 72 85Document91 pagesTrusses 72 85Carlorel AnteNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument91 pagesStatics of Rigid Bodies20-08702No ratings yet
- Newton'S Law: Prepared By: Mariane Gioiella Casem Cindy Claire BermudezDocument9 pagesNewton'S Law: Prepared By: Mariane Gioiella Casem Cindy Claire BermudezAngel Jimmyly EstanillaNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument3 pagesLab ReportJoseph Bernard Cantre DalusongNo ratings yet
- Studyofir Pixub ComDocument10 pagesStudyofir Pixub Comapi-353782053100% (1)
- 11-Woodpecker Science ReportDocument17 pages11-Woodpecker Science ReportrhaineNo ratings yet
- Engineering Short Answer QuestionsDocument31 pagesEngineering Short Answer Questionsmadhu35No ratings yet
- Notes-Laws of MotionDocument3 pagesNotes-Laws of MotionJocel BaquilarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1qmjcmarquezNo ratings yet
- BSC8 EDITEDPNSC8 Q1 New3RD LAW W2 W3Document9 pagesBSC8 EDITEDPNSC8 Q1 New3RD LAW W2 W3lance buenaNo ratings yet
- Tos Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesTos Multiple ChoiceVcra GenevieveNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Quarter 1 Module 5 Week 5 Newtons Law of MotionDocument16 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Quarter 1 Module 5 Week 5 Newtons Law of MotionRoniel VeluzNo ratings yet
- Experiment 101 - Phys101lDocument4 pagesExperiment 101 - Phys101lthomas melgarNo ratings yet
- Quiz - ForcesDocument2 pagesQuiz - ForcesmisterbrownerNo ratings yet
- Jaff Reflection PaperDocument2 pagesJaff Reflection PaperJeanette Heramiz ArnadoNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1 HELPDocument8 pagesAssignment No 1 HELPTooba KhanNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Grade 12 Q1 4 D e 28 31 32 33 34Document13 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Grade 12 Q1 4 D e 28 31 32 33 34Monica SolomonNo ratings yet
- Science 8 1st PrelimDocument2 pagesScience 8 1st PrelimChristeus Von SujeroNo ratings yet
- According To NewtonDocument19 pagesAccording To Newtonjaycey24No ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Module 11, Quarter 1, Week 4Document10 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Module 11, Quarter 1, Week 4xyxycalabiaNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument12 pagesPhysics Projectkaporkaran8523No ratings yet
- FORCEDocument1 pageFORCEJessie GainsanNo ratings yet
- Sephra Is An Extraterrestrial Whose Home Planet Is From Alpha CentauriDocument1 pageSephra Is An Extraterrestrial Whose Home Planet Is From Alpha CentauriSarah Jane CasipongNo ratings yet
- Mission Operations PhasesDocument3 pagesMission Operations PhasesSarah Jane CasipongNo ratings yet
- Lesson Photo RespDocument2 pagesLesson Photo RespSarah Jane CasipongNo ratings yet
- True True False (Pituitary Gland) True False (Dwarfism) False (28 Days) False True True False (Uterus)Document1 pageTrue True False (Pituitary Gland) True False (Dwarfism) False (28 Days) False True True False (Uterus)Sarah Jane CasipongNo ratings yet
- Detailed LPDocument3 pagesDetailed LPSarah Jane CasipongNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Q2 Exam (22-23)Document3 pagesScience 8 Q2 Exam (22-23)Sarah Jane CasipongNo ratings yet
- Detailed LP in Science 9Document9 pagesDetailed LP in Science 9Sarah Jane CasipongNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 7 and 8 Quarterly EXAMDocument9 pagesSCIENCE 7 and 8 Quarterly EXAMSarah Jane CasipongNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Q1 Exam (22-23)Document7 pagesScience 7 Q1 Exam (22-23)Sarah Jane Casipong100% (1)
- Asphalt Binder MSCR UpdatedDocument12 pagesAsphalt Binder MSCR Updatedjulio sierra0% (1)
- A) Standard Penetration Test (SPT) :: Permission)Document23 pagesA) Standard Penetration Test (SPT) :: Permission)Marcos NoronhaNo ratings yet
- M-Caps-04: Physics M-Caps-04: Physics M-Caps-04: Physics M-Caps-04: Physics M-Caps-04: PhysicsDocument5 pagesM-Caps-04: Physics M-Caps-04: Physics M-Caps-04: Physics M-Caps-04: Physics M-Caps-04: PhysicsJeel KadiaNo ratings yet
- Gear FatigueDocument12 pagesGear Fatigueismail_69No ratings yet
- Ujian 1Document16 pagesUjian 1cikgusyaNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Mortar and Early Age StrengthDocument24 pagesRelationship Between Mortar and Early Age StrengthMuhammadWazimAkramNo ratings yet
- L Ecture III Signoracci PDFDocument25 pagesL Ecture III Signoracci PDFArmagaddonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Internal WavesDocument207 pagesIntroduction To Internal WavesmailtoswaroopNo ratings yet
- Stability Checks: Analysis ApproachDocument9 pagesStability Checks: Analysis ApproachShahin VkNo ratings yet
- Work Power EnergyDocument72 pagesWork Power EnergyBuela, Lance GabrielNo ratings yet
- Gaussian ThermochemistryDocument19 pagesGaussian ThermochemistryMoslem DaneshNo ratings yet
- Notes in Che 324 Prepared: Engr. Brenda T. Domingo Coloma, CheDocument8 pagesNotes in Che 324 Prepared: Engr. Brenda T. Domingo Coloma, ChePaul Philip LabitoriaNo ratings yet
- Simulation Investigation - Youngs Double Slit ExpDocument4 pagesSimulation Investigation - Youngs Double Slit ExppixelhoboNo ratings yet
- Interpretation and Analysis of Hydraulic Fracture Pressures F. Guo N.R. Morgenstern J.D. ScottDocument6 pagesInterpretation and Analysis of Hydraulic Fracture Pressures F. Guo N.R. Morgenstern J.D. ScottEdwin TapiasNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of A Rubber BandDocument5 pagesThermodynamics of A Rubber BandAlejandra QuintinNo ratings yet
- Cohen-Tannoudji - Quantum Mechanics, Vol.1Document887 pagesCohen-Tannoudji - Quantum Mechanics, Vol.1elke_hk100% (15)
- Fundamentals of AerodynamicsDocument39 pagesFundamentals of AerodynamicsMarion Nori MarallagNo ratings yet
- Midterm Examination in Physics 101Document7 pagesMidterm Examination in Physics 101Ires YuloNo ratings yet
- Football SpeedDocument2 pagesFootball SpeedTom HochhalterNo ratings yet
- Fin Glass 6Document6 pagesFin Glass 6EIWAA100% (1)
- Chap17 SDocument90 pagesChap17 STest GgNo ratings yet
- Mechanical EngineeringDocument12 pagesMechanical Engineeringanjaiah_19945100% (1)
- 2007 Liu. Steric Effect A Quantitative Description From Density Functional TheoryDocument6 pages2007 Liu. Steric Effect A Quantitative Description From Density Functional TheoryKarlos Lds NvNo ratings yet
- ST Semi Exam No Answer PDFDocument5 pagesST Semi Exam No Answer PDFBrian UncianoNo ratings yet
- Enerpac - Multipliers Repair Parts SheetDocument12 pagesEnerpac - Multipliers Repair Parts SheetCruzCarrizalesNo ratings yet
- Find The Stress and Strain Diagram For Concrete and Timber.: Assgnment Reg 162Document16 pagesFind The Stress and Strain Diagram For Concrete and Timber.: Assgnment Reg 162SeLamah RahmanNo ratings yet
- Transport Phenomena and Unit Operations A Combined Approach by Richard G. GriskeyDocument5 pagesTransport Phenomena and Unit Operations A Combined Approach by Richard G. GriskeyRosaNo ratings yet
- Steel End/Base Plate & Anchor Bolts Analysis & DesignDocument6 pagesSteel End/Base Plate & Anchor Bolts Analysis & DesignRey GonzalesNo ratings yet
- An Application of HHT Method To Nearshore Sea Waves: Albena Dimitrova VeltchevaDocument23 pagesAn Application of HHT Method To Nearshore Sea Waves: Albena Dimitrova VeltchevaBekraoui KeltoumNo ratings yet
- NX Nastran 8 Rotor Dynamics User's GuideDocument333 pagesNX Nastran 8 Rotor Dynamics User's GuideMSC Nastran Beginner100% (1)