Professional Documents
Culture Documents
P Cell and e Cell
Uploaded by
seenu mohapatra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views12 pagesThis document outlines the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotes are the simplest type of cell, lacking membrane-bound organelles and having circular DNA within a nucleoid region. Eukaryotes are generally more complex, having membrane-bound organelles including a nucleus that contains linear DNA. While both have cell membranes and ribosomes, prokaryotes differ from eukaryotes in their lack of a nucleus and organelles as well as having circular DNA and generally being unicellular.
Original Description:
prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Original Title
p cell and e cell
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotes are the simplest type of cell, lacking membrane-bound organelles and having circular DNA within a nucleoid region. Eukaryotes are generally more complex, having membrane-bound organelles including a nucleus that contains linear DNA. While both have cell membranes and ribosomes, prokaryotes differ from eukaryotes in their lack of a nucleus and organelles as well as having circular DNA and generally being unicellular.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views12 pagesP Cell and e Cell
Uploaded by
seenu mohapatraThis document outlines the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotes are the simplest type of cell, lacking membrane-bound organelles and having circular DNA within a nucleoid region. Eukaryotes are generally more complex, having membrane-bound organelles including a nucleus that contains linear DNA. While both have cell membranes and ribosomes, prokaryotes differ from eukaryotes in their lack of a nucleus and organelles as well as having circular DNA and generally being unicellular.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Understanding the fundamental differences
Content
• Cell structure
• Prokaryotes
• Characteristic of prokaryotes
• Prokaryotic cell structure
• Prokaryotic cell parts
• Eukaryotes
• Characteristic of eukaryotes
• Eukaryotic cell parts
• Similarity between prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
• Difference between prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
• Conclusion
Cell structure
• All livings organisms can be sorted into one of two groups.
• Prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
• Prokaryotes (pro : primitive ; karyon –nuclei ).
• Eukaryotes (Eu : true ;karyon: nuclei ).
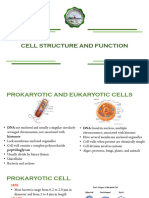
Characteristic of prokaryotes
• Prokaryotes are the simplest type of cell .
• Prokaryotes are the largest group of organisms .
• Prokaryotes mostly found in unicellular organisms .Like:Bacteria,
archaea and lower fungi.
• Mode of nutrition : Heterotroph or autotroph .
• Generally found in individuals or colony form or filamentous form .
• Reproduction happens through the process of binary fission .
• It doesn’t possess membrane bound cell organelles such as nuclei.
• It has simpler internal structure.
• They are smaller in size as compared to eukaryotes.
PROKARYOTIC CELL PARTS
• Cell Plasmid:All the membrane surrounding and protecting the cell.
• Cytoplasm:All of the material inside a cell except the nucleus .
• Flagella and pili:Protein-based, filaments found on the outside of some prokaryotic cells .
• Nucleoid : Nucleus like region of the cell where genetic material is kept a small molecule
of DNA that can reproduce independently .
• Ribosomes: particles that synthesize proteins.
• Cell wall: made of peptidoglycan, comprised of sugars and amino acids, and many have a
polysaccharide capsule.
• An extra layer of protection, helps the cell maintain its shape, and prevents dehydration.
Capsule: enables the cell to attach to surfaces in its environment. Some prokaryotes have
flagella, pili, or fimbriae.
• Flagella are used for locomotion,
• Pili are used to exchange genetic material during a type of reproduction called conjugation.
Characteristics EUKARYOTES
• Appeared approximately one billion years ago .
• Generally more advanced than prokaryotes .
More complex internal structure .
• Nuclear membrane surrounds linear genetic
material
• (DNA) .
• several different parts .
• Coverings known as cell membranes.
• Larger than prokaryotes in size.
Eukaryotic cell parts
• Cell membrane: Outer covering
• Nucleus: membrane-bound nucleus contains Genetic material .
• Chromosomes: Structure of nucleic acids and protein which carry genetic information in
the form of genes.
• Mitochondria: powerhouse of the cell.
• Endoplasmic reticulum :
• may be smooth :builds lipids and carbohydrates
• may be rough: stores proteins made by attached
ribosomes
• Golgi Complex:
• takes in sacs of raw material from RR
• sends out sacs containing finished cell products
• Lysosomes:
• sacs filled with digestive enzymes
• digest worn out cell parts
• digest food absorbed by cell
SIMILARITIES BETWEEN
PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC
• Both the cells have cell membrane .
• Both types of cells have ribosome .
• Both types of cells have DNA.
• Both types of cells have a liquid environment known as the
cytoplasm.
Difference between prokaryotic and
eukaryotic
Prokaryotes Eukaryotes
• Unicellular • Either unicellular or multicellular
• Cell wall is generally present • Cell wall can be present or
• DNA is circular absent
• Nucleus is absent • Nucleus is always present
• Mitochondria are absent • DNA is linear
• Mitochondria are generally
present
You might also like
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument56 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellKENT GARCIA100% (1)
- Test Bank For Human Anatomy 9th Edition by MartiniDocument31 pagesTest Bank For Human Anatomy 9th Edition by MartiniAnthony Cohen100% (38)
- Mitosis PPT EdittedDocument21 pagesMitosis PPT EdittedabdNo ratings yet
- 2nd Q CEellDocument30 pages2nd Q CEellDeserie ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Its Function DLLDocument62 pagesCell Parts and Its Function DLLRovelyn AlejoNo ratings yet
- Cell Types & Cell ModificationDocument41 pagesCell Types & Cell ModificationShane Marcande Calicdan78% (18)
- Cells As The Basis of Life 1Document40 pagesCells As The Basis of Life 1Singh Gurleen100% (1)
- Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Section II. Introduction To MicroorganismsDocument48 pagesMicrobiology For The Health Sciences: Section II. Introduction To MicroorganismsHashim Ghazo100% (1)
- Biology 2nd Lab Report (Onion Cell)Document4 pagesBiology 2nd Lab Report (Onion Cell)Johanna Haludilu88% (16)
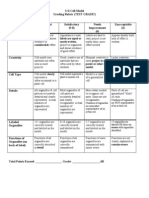
- Cell Model RubricDocument2 pagesCell Model RubricAkash Deep100% (3)
- Lecture Differences Between Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument16 pagesLecture Differences Between Prokaryotes and EukaryotesAyesha MasoodNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Unit 1.6 QuestionsDocument4 pagesIB Biology Unit 1.6 QuestionsLaura WNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Meiosis ComparedDocument1 pageMitosis Meiosis ComparedDURU ALTINKAYA100% (1)
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument21 pagesProkaryotes and EukaryotesJeff Hambre100% (2)
- Cell - Structure - Function Chapter 2Document42 pagesCell - Structure - Function Chapter 2ErizaNo ratings yet
- 5$0vjk Omqrg) T, V) ZDocument40 pages5$0vjk Omqrg) T, V) ZKristel AnneNo ratings yet
- Lesson-3-Prokaryotes-and-Eukaryotes CellsDocument14 pagesLesson-3-Prokaryotes-and-Eukaryotes CellsKivo ZoshikoroNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & FunctionDocument76 pagesCell Structure & Functionuday xeroxNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function (JIGSAW)Document15 pagesCell Structure and Function (JIGSAW)Milimo JingsawNo ratings yet
- Cell Unit of Life Class NoteDocument36 pagesCell Unit of Life Class NoteKavana SNo ratings yet
- Cell TypesDocument16 pagesCell TypesyvetteNo ratings yet
- The Building Blocks of LifeDocument105 pagesThe Building Blocks of LifePradhees BtechNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic/Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Dan FreemanDocument15 pagesProkaryotic/Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Dan FreemananneNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument3 pagesCell Parts and FunctionsKyle OwenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Cell TypesDocument16 pagesLesson 3 - Cell TypesArvin Jay LamberteNo ratings yet
- Cell and It's FunctionDocument13 pagesCell and It's FunctionPlayed By SphinxNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument55 pagesWeek 2 - Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellsz4g4v7gkzjNo ratings yet
- CEll Structures and Functions - SHSDocument42 pagesCEll Structures and Functions - SHSGABRIEL LOUIS GUANONo ratings yet
- 2 - Lec - MicroPara - Cell Structure and FunctionDocument94 pages2 - Lec - MicroPara - Cell Structure and FunctionFeona IgoroteNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument2 pagesThe Cellrosana f.rodriguezNo ratings yet
- CellDocument34 pagesCellSadaf JavedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document39 pagesLecture 1Mohammed SindiNo ratings yet
- Cell, Microscopy, EpitheliumDocument14 pagesCell, Microscopy, EpitheliumNICOLE JADE PINEDANo ratings yet
- Classification of MicroorganismsDocument23 pagesClassification of MicroorganismsEsai Kanaga YadavNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Lec 6Document25 pagesCell Biology Lec 6Mushtaq HassanNo ratings yet
- L1.3 - Cell Structures Note PackageDocument4 pagesL1.3 - Cell Structures Note Package中华雅思王No ratings yet
- Prokaryotes & EukaryotesDocument10 pagesProkaryotes & EukaryotesJogie De GuiaNo ratings yet
- A Tour of The CellDocument11 pagesA Tour of The CellJEVRIX RAMOSNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure FunctionDocument26 pagesCell Structure FunctionCharishma MadhaviNo ratings yet
- 03 The Nature of CellDocument45 pages03 The Nature of CellClarisse Apresurado SapidaNo ratings yet
- اشعة - بايو- م1Document25 pagesاشعة - بايو- م1sara so888No ratings yet
- Animal Cells and Bacterial CellsDocument40 pagesAnimal Cells and Bacterial CellsClarence CaparasNo ratings yet
- Microbial Structures and Functions MoicroorganismsDocument390 pagesMicrobial Structures and Functions MoicroorganismssamsoatsNo ratings yet
- Biology Basic ConceptsDocument6 pagesBiology Basic ConceptsAhsni128No ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument6 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYEllyn De chavezNo ratings yet
- Lec 3,4,5-Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument57 pagesLec 3,4,5-Cell and Cell OrganellesSatyam Arya100% (1)
- Lecture 2 - Cell StructureDocument54 pagesLecture 2 - Cell Structurekaslana kianaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Science 11Document7 pagesReviewer For Science 11Bea Hannah FarrenNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1. ADocument24 pages1.1.1. Ayishan.miao427No ratings yet
- EARTHSCI L7 Cell Theory and TimelineDocument31 pagesEARTHSCI L7 Cell Theory and Timeline2023200285No ratings yet
- Cell Biology Lec 4Document19 pagesCell Biology Lec 4Mushtaq HassanNo ratings yet
- Physiology ةجلسفلا cell composition ةيلخلا بيكرتDocument18 pagesPhysiology ةجلسفلا cell composition ةيلخلا بيكرتyasir mohammedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 GeneticsDocument12 pagesLesson 3 GeneticsAndrie PelarioNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Eukaryotic Cel Structure and OrganizationDocument47 pages1.3 Eukaryotic Cel Structure and Organizationjumbergy01No ratings yet
- Lecture 3.Document11 pagesLecture 3.rahaf.khalid226No ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument11 pagesFundamental Unit of Lifeyogeshks1985No ratings yet
- 4 Cell and TissuesDocument44 pages4 Cell and TissuesAmbreen RiazNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure FunctionDocument30 pagesCell Structure FunctionAngelo GabrielNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument78 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsLandon GlascockNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cell?: Basics of CytologyDocument22 pagesWhat Is A Cell?: Basics of Cytologyaybs solamoNo ratings yet
- CellDocument28 pagesCellرقية معتز محمودNo ratings yet
- Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Section II. Introduction To MicroorganismsDocument48 pagesMicrobiology For The Health Sciences: Section II. Introduction To MicroorganismsHiba Abu-jumahNo ratings yet
- Unit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HidupDocument56 pagesUnit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HidupYahya RhamadanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure FunctionDocument114 pagesCell Structure FunctionsolanaNo ratings yet
- BMB 1112 Biochemistry Iii (Cell Biology)Document124 pagesBMB 1112 Biochemistry Iii (Cell Biology)Bpharm weekend MkuNo ratings yet
- NCERT Science Solutions Class8 - Cell Structure & FunctionDocument3 pagesNCERT Science Solutions Class8 - Cell Structure & FunctionHarshit KumarNo ratings yet
- Burton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 3. Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument25 pagesBurton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 3. Cell Structure and TaxonomyLindsay SwanepeolNo ratings yet
- Heredity AND Variation: Cell DivisionDocument21 pagesHeredity AND Variation: Cell Divisionshahadah_rahimNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - PT1 Gr09 - June 2022Document2 pagesSyllabus - PT1 Gr09 - June 2022Talented world of Miya and fabiNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 5Document10 pagesBio Chapter 5Rosfaizzati MarnunNo ratings yet
- Cell 1Document2 pagesCell 1Trilochan TripathyNo ratings yet
- 10 Cell Cycle N Cell Division-NotesDocument4 pages10 Cell Cycle N Cell Division-NotesAnanth Dharanidharan100% (1)
- Human Biology: Dr. Safa Amer AliDocument20 pagesHuman Biology: Dr. Safa Amer AlikmoNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Dan Meiosis: DR I G K Nyoman Arijana, M.Si - MedDocument16 pagesMitosis Dan Meiosis: DR I G K Nyoman Arijana, M.Si - MedRisma SintyaNo ratings yet
- LESSON - 2 and 3Document26 pagesLESSON - 2 and 3Kerberos DelabosNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument36 pagesMeiosisPhia ViaNo ratings yet
- Cyto Unit 4Document2 pagesCyto Unit 4Vince CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Cell - Unit of Life BiohackDocument14 pagesCell - Unit of Life BiohackArghya PaulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Cell Structure & Functions-1 PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 3 - Cell Structure & Functions-1 PDFSTEM 8 PRODUCTIONSNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Meiosis PuzzleDocument4 pagesMitosis Meiosis PuzzleSheila Marie CortadoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument44 pagesCell Structure and FunctionPedro SuyuNo ratings yet
- Parts of A CellDocument16 pagesParts of A CellThomas417No ratings yet
- Happ Week 2 TransesDocument7 pagesHapp Week 2 TransesJohn TacordaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Division SB015Document59 pagesChapter 3 Cell Division SB015Muhammad IzuanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure 2Document5 pagesCell Structure 2slombez 150% (1)
- Cell Division Mitosis Biology Lecture PowerPoint VCBCCTDocument32 pagesCell Division Mitosis Biology Lecture PowerPoint VCBCCTIbrahim Adel zaidNo ratings yet
- Bio 221 Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesBio 221 Lecture NotesMuhammad LawalNo ratings yet
- Golgi ComplexDocument8 pagesGolgi ComplexvmshanesNo ratings yet
- The Cell: By: Kinza ChaudhariDocument16 pagesThe Cell: By: Kinza ChaudhariChris GayleNo ratings yet