Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7 Dangerous Cargo
Uploaded by
Mamun0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views11 pagesOriginal Title
7_Dangerous_Cargo
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views11 pages7 Dangerous Cargo
Uploaded by
MamunCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
Learning Objectives 7
Dangerous Cargo
At the end of this lesson, you should be able to :
Describe the content of IMDG Code
Identify the classification of DG
Describe the packaging requirements for DG
Describe the marking, labelling and placarding of DG
List the documents required for the carriage of DG
Describe the stowage requirements for DG
State necessary precautions for loading and discharging
DG
KNR/01-2003 SP-SMA Slide 1
Introduction-Dangerous Cargo
The handling and carriage of dangerous goods must be carried out
in full compliance with the laws of the country :
from which the dangerous goods are being shipped,
in whose vehicle or ships it is moved,
through which the goods will transit,
to its final destination.
So the classification, packaging and stowage of dangerous goods
must be in accordance with any legislation which may be enforced
in
the country of origin
the country of destination
any country which it has entered
the country under whose flag the carrying vessel operates.
KNR/01-2003 SP-SMA Slide 2
IMDG Code
the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code
is based on the report of the United Nations Committee of
Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods , which also
forms the basis for legislation and recommendations for
transport of Dangerous Goods by other modes - road, rail
and air.
The IMDG code comes in 2 volumes and a Supplement.
The 2 volumes cover details of dangerous goods, all of
which are subdivided into:
9 classes.
KNR/01-2003 SP-SMA Slide 3
Contents of IMDG Code
Contents of the IMDG Code may be summarised as
follows:
a) General Provisions, Definitions and Training.
b) Classification
c) Dangerous Goods list and limited quantities
exceptions – Volume 2
d) Packing and Tank provisions
e) Consignment procedures
f) Construction and testing of packaging
g) Transport operations
h) Supplement covers, Ems, MFAG, Reporting
Procedure, Packing, Pesticides & Others.
KNR/01-2003 SP-SMA Slide 4
Contents of IMDG Code
Dangerous Goods shall be divided into the following classes:
Class 1 - Explosives
Class 2 - Gases: compressed, liquefied or dissolved under pressure.
Class 3 - Flammable liquids.
Class 4.1 - Flammable solids.
Class 4.2 - Substances liable to spontaneous combustion
Class 4.3 - Substances which, in contact with water, emit flammable
gases.
Class 5.1 - Oxidizing substances
Class 5.2 - Organic peroxides
Class 6.1 - Poisonous (toxic) substances
Class 6.2 - Infectious substances
Class 7 - Radioactive materials
Class 8 - Corrosives
Class 9 - Miscellaneous dangerous substances, that is any other
substance which experience has shown, or may show, to be
of such dangerous character that the provisions of this part
shall apply to it.
KNR/01-2003 SP-SMA Slide 5
Packaging
Well made and in good condition.
Interior not dangerously affected by contact with contents.
Strong enough to withstand normal handling- by sea.
Where absorbent or cushioning material is used, it shall be :
Capable of minimising the dangers to which the liquid may give rise.
So disposed as to prevent movement and that the receptacle remains surrounded.
Where reasonably possible, of sufficient quantity to absorb the liquid in the
event of breakage of the receptacle.
Receptacles to have an ullage (space) to allow for the highest
temperature during normal carriage.
Receptacles for gases under pressure shall be adequately constructed,
tested, maintained and correctly filled.
Empty receptacles used previously for carriage of dangerous goods, to
be treated as full, until thoroughly cleaned.
KNR/01-2003 SP-SMA Slide 6
Marking, Labelling and Placarding
Packages shall be durably marked with the correct technical name.
Trade name alone shall not be used.
Have distinctive labels or placards to indicate dangerous properties
Markings of technical name, labels or placards shall remains
identifiable on packages surviving at least three months' immersion
in the sea except the followings which may be exempted from
labelling requirements :
low degree of hazard or packed in limited quantity; and
When special circumstances permit, packages that are stowed and
handled in units that are identified by labels or placards
KNR/01-2003 SP-SMA Slide 7
Documents
the correct technical name and description of the goods
shall be used (trade names alone shall not be used)
a signed certificate or declaration that the shipment offered
for carriage is properly packaged and marked, labelled or
placarded, and in proper condition for carriage.
shall have a special list or manifest setting forth, in
accordance with the classification set out in the regulation,
the dangerous goods on board and the location thereof.
A detailed stowage plan which identifies by class and sets
out the location of all dangerous goods on board may be
used in place of such special list or manifest.
KNR/01-2003 SP-SMA Slide 8
Stowage Requirements
Stowed safely and appropriately according to the nature of goods.
Incompatible goods shall be segregated from one another.
Explosives (except ammunition) stowed in a magazine and segregated
from detonators. Electrical apparatus and cables in this
compartment designed and used so as to minimise the risk fire and
explosion.
Goods which give off dangerous vapours shall be stowed in a well
ventilated space or on deck.
Where inflammable liquids or gases are carried, special precautions
to be taken where necessary against fire or explosion.
Substances liable to spontaneous combustion or heating shall not be
carried unless adequate precautions have been taken to prevent
outbreak of fire.
KNR/01-2003 SP-SMA Slide 9
Precautions for Loading / Discharging
Dangerous Goods
Packages inspected for signs of damage, leakage prior to being stowed in the
compartment or container.
Keep combustible materials away from source of ignition.
Stow in places not liable to damage or heating
Segregate from substances liable to start or spread fire.
Ensure accessibility so that dangerous goods may be removed to safety.
Naked lights and smoking prohibited in or near DG areas at all times.
Safeguard electrical appliances against short circuit and sparking to avoid risk
of ignition.
Ensure fire-fighting appliances in constant state of readiness.
Protective clothing and self-contained breathing apparatus should be available
if cargo is liable of emitting dangerous fumes.
If loading explosives, avoid bunkering, hot work and working of radar and
radio.
KNR/01-2003 SP-SMA Slide 10
Precautions for Loading / Discharging
Dangerous Goods- cont...
Funnel and ventilators be fitted with "spark arrestor" if loading explosive.
DG cargo tightly stowed and well secured against movement- chafe.
Securing materials used should be compatible with the DG themselves.
Securing DG packages which have been wetted by rain, and received in a wet
condition with frost or snow adhering, should he effectively dried before
loading.
If possible, DG should be handled and stowed during daylight hours, if not,
adequate lighting must be provided during the operation.
Ambient temperatures in relation to the flash point should be taken into
account -particularly in hot weather/tropical climates.
If spillage occurs it should be carefully dealt with having regards to the
dangerous nature of the substances.
Loading and discharging of dangerous goods must be supervised by a
responsible officer. Establish communication with terminal.
KNR/01-2003 SP-SMA Slide 11
You might also like
- 7 Dangerous55 CargoDocument11 pages7 Dangerous55 CargoKhairudyIzwanNo ratings yet
- My Cargo WorkDocument168 pagesMy Cargo WorkRajeewa Wickramahewage100% (1)
- CH 08 Watch Keeping in PortDocument5 pagesCH 08 Watch Keeping in PortAmit Pandey100% (1)
- Chapter-32 Cargo EquipmentsDocument202 pagesChapter-32 Cargo EquipmentsdevmarineacademyNo ratings yet
- Imdg CodeDocument16 pagesImdg CodeAhmed AL BatalNo ratings yet
- IMDG Code Presentation1Document9 pagesIMDG Code Presentation1Prateek GandhiNo ratings yet
- Singapore Maritime Academy Class 1 & 2 (Deck) Certificate of Competency MA2024: Cargo Work IMDG: Tutorial SolutionsDocument10 pagesSingapore Maritime Academy Class 1 & 2 (Deck) Certificate of Competency MA2024: Cargo Work IMDG: Tutorial SolutionsS M HasanNo ratings yet
- CARGO HANDLING & STOWAGE V (6TH SEMESTER) UNIT 1 - Precautions for dangerous goods cargo operationsDocument11 pagesCARGO HANDLING & STOWAGE V (6TH SEMESTER) UNIT 1 - Precautions for dangerous goods cargo operationsXyrus Francisco MendozaNo ratings yet
- IMDG Code Cargo PlanDocument32 pagesIMDG Code Cargo PlanSushil Bhan100% (5)
- IMDGDocument12 pagesIMDGjejeNo ratings yet
- Dangerous GoodsDocument7 pagesDangerous GoodsTheoNo ratings yet
- IMDG Notes For AuditsDocument4 pagesIMDG Notes For AuditsNelum PereraNo ratings yet
- Bulk A Particular Class/type of Dangerous And/or Hazardous Cargoes or GoodsDocument5 pagesBulk A Particular Class/type of Dangerous And/or Hazardous Cargoes or GoodsMarixNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Dangerous Goods: Learning OutcomesDocument20 pagesLesson 3 Dangerous Goods: Learning Outcomesacharacharles970No ratings yet
- With Reference To The IMDG Code, List The Precautions To Be Observed When Loading and Discharging Dangerous GoodsDocument7 pagesWith Reference To The IMDG Code, List The Precautions To Be Observed When Loading and Discharging Dangerous GoodsKirtishbose ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Dangerous Goods in PackageDocument50 pagesChapter 7 - Dangerous Goods in PackagekaokieoeNo ratings yet
- Dangerous GoodsDocument18 pagesDangerous GoodsMahami M ProsperNo ratings yet
- CRMS Dangerous Goods - Study Pack PDFDocument17 pagesCRMS Dangerous Goods - Study Pack PDFPetra Stefanescu100% (1)
- Imdg CodeDocument17 pagesImdg CodeDeekshith raiNo ratings yet
- Packaged Cargoes Guidance for TankersDocument6 pagesPackaged Cargoes Guidance for TankersAntonio AntonioNo ratings yet
- Packing Marking and Shipping Instruction For Seaworthy Transport412 - 11576Document21 pagesPacking Marking and Shipping Instruction For Seaworthy Transport412 - 11576Lohith Kumar MenchuNo ratings yet
- Dangerous Cargo Documentation in Container ShipDocument11 pagesDangerous Cargo Documentation in Container ShipMin Soe100% (1)
- Shippers Declaration For Dangerous GoodsDocument14 pagesShippers Declaration For Dangerous GoodsPauline JaricottNo ratings yet
- 10.3.2 Keeping Hazardous Cargo WatchDocument3 pages10.3.2 Keeping Hazardous Cargo Watchnaveen zNo ratings yet
- Dangerous GoodsDocument10 pagesDangerous Goodsmoaid013No ratings yet
- Handling Hazardous Materials and Dangerous Goods SeminarDocument67 pagesHandling Hazardous Materials and Dangerous Goods SeminarEdwar Zulmi100% (3)
- Transport Packaged Dangerous Goods SafelyDocument11 pagesTransport Packaged Dangerous Goods SafelyJay KrishnaNo ratings yet
- IMDG IntroductionDocument9 pagesIMDG IntroductionMoș GerilăNo ratings yet
- Cargo and Ship HandlingDocument9 pagesCargo and Ship HandlingAdli dzil IkramNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Dangerous Goods in Packaged FormDocument17 pagesUnit 9 Dangerous Goods in Packaged Formnishant85408No ratings yet
- Imdg Code: Required Under Two Mandatory UN ConventionsDocument3 pagesImdg Code: Required Under Two Mandatory UN Conventionskameleon irisNo ratings yet
- DG Annex 111Document58 pagesDG Annex 111stabinmathewNo ratings yet
- Dangerous GoodsDocument13 pagesDangerous GoodsAmit Singla100% (2)
- Aluminium Ferrosilicon PowderDocument2 pagesAluminium Ferrosilicon PowderkemalaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Understand and Applies Internation Regulation For Dangerous CargoesDocument70 pagesChapter 6 - Understand and Applies Internation Regulation For Dangerous CargoeskaokieoeNo ratings yet
- CargoDocument38 pagesCargoAbhinand PNo ratings yet
- Aviation Dangerous Goods GuidanceDocument34 pagesAviation Dangerous Goods Guidancea320No ratings yet
- Dangerous Goods Awareness 2016Document58 pagesDangerous Goods Awareness 2016Cooter Looler100% (1)
- Klasse 7-Radioaktive Materialer-Uk PDFDocument6 pagesKlasse 7-Radioaktive Materialer-Uk PDFVianeyNo ratings yet
- Annex 3Document10 pagesAnnex 3jaiNo ratings yet
- Dangerous Goods Regulations OverviewDocument43 pagesDangerous Goods Regulations Overviewcelestetorino1No ratings yet
- Imdg CodeDocument26 pagesImdg CodeAnonimo weeeNo ratings yet
- Aviation Dangerous Goods GuidanceDocument34 pagesAviation Dangerous Goods Guidanceaeroagricola25580% (1)
- Guide to Transporting Dangerous GoodsDocument24 pagesGuide to Transporting Dangerous GoodsSammie Williams100% (1)
- Procedures and Precautions ImdgDocument4 pagesProcedures and Precautions ImdgAmit Pandey50% (2)
- Carriage of Dangerous Goods (Imdg) CodeDocument39 pagesCarriage of Dangerous Goods (Imdg) CodeParthasarathy Vasanth100% (4)
- Mormugao Port (Handling of Freight Container Containg Dangerous and Hazardous Cargo) Regulation 1988)Document24 pagesMormugao Port (Handling of Freight Container Containg Dangerous and Hazardous Cargo) Regulation 1988)Latest Laws TeamNo ratings yet
- Mormugao Port (Handling of Freight Container Containg Dangerous and Hazardous Cargo) Regulation 1988)Document24 pagesMormugao Port (Handling of Freight Container Containg Dangerous and Hazardous Cargo) Regulation 1988)Latest Laws TeamNo ratings yet
- 8 Things Deck Officers Must Know for IMDG CargoDocument11 pages8 Things Deck Officers Must Know for IMDG Cargorufo utom100% (1)
- Aviation Dangerous Goods PDFDocument34 pagesAviation Dangerous Goods PDFCristian Ciobanu0% (1)
- MAPANGHEDocument16 pagesMAPANGHEJohn Joseph Totanes ZantuaNo ratings yet
- Day 2Document224 pagesDay 2parasytemaxim30100% (1)
- 9 ClassesDocument26 pages9 Classesmvijayk3No ratings yet
- GelHandbook Part2 eDocument84 pagesGelHandbook Part2 etankimsinNo ratings yet
- DGR Recurrent 2020 Edition 61thDocument100 pagesDGR Recurrent 2020 Edition 61thSulistyoNo ratings yet
- AMMONIUM NITRATE UN 1942Document3 pagesAMMONIUM NITRATE UN 1942Harman SandhuNo ratings yet
- Loadline ConventionDocument161 pagesLoadline Conventionyogesh maneNo ratings yet
- Bombers' Training, and Application of Same in Trench WarfareFrom EverandBombers' Training, and Application of Same in Trench WarfareNo ratings yet
- Emergency Response GuidebookFrom EverandEmergency Response GuidebookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Shipbroker’s Working Knowledge: Dry Cargo Chartering in PracticeFrom EverandThe Shipbroker’s Working Knowledge: Dry Cargo Chartering in PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PAINT STOREDocument1 pagePAINT STOREMamunNo ratings yet
- 3.masterch - Off Standing OrderDocument1 page3.masterch - Off Standing OrderMamunNo ratings yet
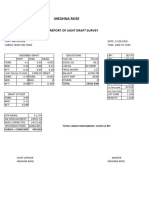
- Light Draft Survey Report BayuquanDocument1 pageLight Draft Survey Report BayuquanMamunNo ratings yet
- ROC-O Written QUESTION 2019-convertedDocument5 pagesROC-O Written QUESTION 2019-convertedMamunNo ratings yet
- ROC-O Written QUESTION 2019-convertedDocument5 pagesROC-O Written QUESTION 2019-convertedMamunNo ratings yet
- LSA & FFA LockerDocument10 pagesLSA & FFA LockerMamunNo ratings yet
- Gmdss Oral QuestionsDocument27 pagesGmdss Oral QuestionsMamunNo ratings yet
- Morning 11.09.20Document12 pagesMorning 11.09.20MamunNo ratings yet
- Light LoadDocument12 pagesLight LoadMamunNo ratings yet
- Morning 11.09.20Document12 pagesMorning 11.09.20MamunNo ratings yet
- Light LoadDocument12 pagesLight LoadMamunNo ratings yet
- Light LoadDocument12 pagesLight LoadMamunNo ratings yet
- Monthend Rob Aug 23Document6 pagesMonthend Rob Aug 23MamunNo ratings yet
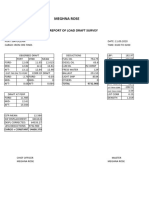
- Load Draft Survey Report BayuquanDocument1 pageLoad Draft Survey Report BayuquanMamunNo ratings yet
- Light LoadDocument12 pagesLight LoadMamunNo ratings yet
- Light LoadDocument12 pagesLight LoadMamunNo ratings yet
- Morning 11.09.20Document12 pagesMorning 11.09.20MamunNo ratings yet
- Light LoadDocument12 pagesLight LoadMamunNo ratings yet
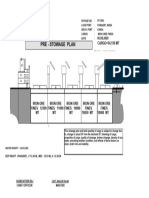
- 1 PRE Stowage Plan - v-12Document1 page1 PRE Stowage Plan - v-12MamunNo ratings yet
- Light LoadDocument12 pagesLight LoadMamunNo ratings yet
- Loading Seq - Cement Clinker3Document1 pageLoading Seq - Cement Clinker3MamunNo ratings yet
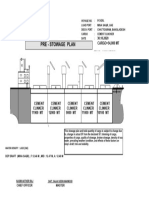
- PRE Stowage Plan - v-12Document1 pagePRE Stowage Plan - v-12MamunNo ratings yet
- DISCHARGE SEQ - Iron OreDocument1 pageDISCHARGE SEQ - Iron OreMamunNo ratings yet
- LOADING SEQ - Iron Ore 4Document1 pageLOADING SEQ - Iron Ore 4MamunNo ratings yet
- PRE Stowage Plan - v-11Document1 pagePRE Stowage Plan - v-11MamunNo ratings yet
- DISCHARGE SEQ - Iron OreDocument1 pageDISCHARGE SEQ - Iron OreMamunNo ratings yet
- PRE Stowage Plan - v-12Document1 pagePRE Stowage Plan - v-12MamunNo ratings yet
- IRON ORE Risk AssessmentDocument5 pagesIRON ORE Risk AssessmentMamunNo ratings yet
- Great Circle SailingDocument2 pagesGreat Circle SailingMamunNo ratings yet
- Bilge Condition ReportDocument2 pagesBilge Condition ReportMamunNo ratings yet
- Ecb Recovery PlanningDocument20 pagesEcb Recovery PlanningMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2 MNTDocument11 pagesCase Study 2 MNTapi-242547654No ratings yet
- 7e Lesson PlanDocument6 pages7e Lesson PlanDave Matthew LibiranNo ratings yet
- AppendicesDocument6 pagesAppendicesMark James Bugarin BarayugaNo ratings yet
- Final Duct Wraps Brochure 98-0213-4600-6rrDocument8 pagesFinal Duct Wraps Brochure 98-0213-4600-6rrDiego Armando Martinez GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Clear ViewDocument6 pagesClear ViewJamieNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Ansc 111Document6 pagesReviewer Ansc 111Jeric MadroñoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Fluids in Mobile Application Re98128 - 2015-06 - Online PDFDocument13 pagesHydraulic Fluids in Mobile Application Re98128 - 2015-06 - Online PDFDennis Huanuco CcamaNo ratings yet
- Student Admission FormDocument2 pagesStudent Admission FormOmmsai co2011No ratings yet
- JnaDocument34 pagesJnaDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- LEC 5 Elements of An Offence and Their QualificationsDocument27 pagesLEC 5 Elements of An Offence and Their QualificationsEliezer Charles Ngahyoma67% (3)
- Tm1tEMPLATES-SWBL-Forms 1.1-1.4 (1) (Back Up)Document17 pagesTm1tEMPLATES-SWBL-Forms 1.1-1.4 (1) (Back Up)Norrodin MangatongNo ratings yet
- Valtek Beta Positioners: For Control ValvesDocument8 pagesValtek Beta Positioners: For Control Valvesابزار دقیقNo ratings yet
- Class 8th syllabus overviewDocument1 pageClass 8th syllabus overviewMuhammad Abdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- 7.nuclear Chemistry and Environmental Chemistry ExerciseDocument38 pages7.nuclear Chemistry and Environmental Chemistry ExerciseYogy YNo ratings yet
- Learn English for Free at thichtienganh.comDocument30 pagesLearn English for Free at thichtienganh.comNhân Đăng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Egg Powder Manufacturing Plant Ecom Final Ppt1Document19 pagesEgg Powder Manufacturing Plant Ecom Final Ppt1brickses100% (2)
- STDs in Sangamon CountyDocument15 pagesSTDs in Sangamon CountyNewsTeam20No ratings yet
- BAslam - Kassimali Matrix - Analysis - of - StructureDocument123 pagesBAslam - Kassimali Matrix - Analysis - of - StructureAmitabha ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- CH 5 - Cyprus RestaurantDocument15 pagesCH 5 - Cyprus RestaurantmazenfarhatNo ratings yet
- HYDRO 2023 International: Nit Warangal, IndiaDocument2 pagesHYDRO 2023 International: Nit Warangal, IndiaBhargava ReddyNo ratings yet
- Brand New Milk Tea Market: Chinese Milk Tea Development and Brand AnalysisDocument9 pagesBrand New Milk Tea Market: Chinese Milk Tea Development and Brand AnalysisMariecel G. GuañoNo ratings yet
- Translation of The Original Operating Manual: Epg-Sprint XeDocument100 pagesTranslation of The Original Operating Manual: Epg-Sprint XePatricio Exequiel Silva ColileoNo ratings yet
- Đề Ôn Thi Tuyển Sinh Lớp 6 Môn Tiếng AnhDocument7 pagesĐề Ôn Thi Tuyển Sinh Lớp 6 Môn Tiếng AnhHoa TrònNo ratings yet
- Bảng Tính Cột Áp QuạtDocument4 pagesBảng Tính Cột Áp QuạtNguyen PhamNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa Inggris 7,8,9Document5 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris 7,8,9Jo windyNo ratings yet
- Flexible Ac Transmission Systems: BY:-Susmita PandaDocument32 pagesFlexible Ac Transmission Systems: BY:-Susmita Pandarahul kumarNo ratings yet
- What Is Newborn ScreeningDocument2 pagesWhat Is Newborn ScreeningroksanmiNo ratings yet
- Trail/Beaver Valley/Rossland Apr. 9, 2019Document39 pagesTrail/Beaver Valley/Rossland Apr. 9, 2019Pennywise PublishingNo ratings yet