Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Metallic Bond
Uploaded by
digreelee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views8 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views8 pagesMetallic Bond
Uploaded by
digreeleeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
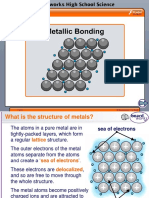
Metallic Bond
Metal atoms are held strongly to each other
by metallic bonding.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
How does metallic bond arise?
The atoms lose their valence
electrons and become
positively charged.
These electrons move freely
between the metal ions like
a cloud of negative charge.
The valence electrons no longer belong to any
metal atom and are said to be delocalised.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
How does metallic bond arise?
The lattice structure is
described as
a lattice of positive ions
surrounded by
a ‘sea of mobile electrons’.
We can therefore define a metallic bond as the force
of attraction between positive metal ions and the
‘sea of delocalised electrons’.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Properties of Metals
Malleability and ductility
Electrical conductivity
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Electrical conductivity
Metals are good conductors of electricity
because of the mobility of the delocalised
electrons within the metal lattice.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Malleability and ductility
Metals can be hammered into different
shapes (malleable) or drawn into wires
(ductile) without breaking.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Malleability and ductility
appliedforce is applied to the metal …
If sufficient
force
Layers of atoms can slide over another without
disrupting the lattice as there is metallic bonding
between the metal ions and sea of electrons.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
Malleability and ductility
Hence, metallic bonds are strong but flexible,
so metals are malleable and ductile.
Copyright © 2006-2011 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
You might also like
- Metallic BondingDocument5 pagesMetallic BondingsamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument16 pagesMetallic Bondingmathvin thummalaNo ratings yet
- تقرير محمدDocument8 pagesتقرير محمدm6czcv4mycNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument3 pagesMetallic BondingAli Issa OthmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Metallic Bonding InfoDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Metallic Bonding InfoShehbaaz SinghNo ratings yet
- Properties of Metals: Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesProperties of Metals: Metallic BondingNuan Ting NgNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsDocument4 pagesLecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsmartinNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document83 pagesUnit 5mtayyab zahidNo ratings yet
- RandomDocument12 pagesRandomDiego Mauricio Ayala SillerNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Document25 pagesInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Anonymous BW2VsFifi9No ratings yet
- My FileDocument12 pagesMy FileKeeben BadoyNo ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding Explained:-: NotesDocument2 pagesMetallic Bonding Explained:-: NotesAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- L05 (Bonding+Crystalline) 01Document14 pagesL05 (Bonding+Crystalline) 01amy.like.cooking.77No ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument12 pagesMetallic BondingilyasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project in Which My Group Didnt Help??Document9 pagesChemistry Project in Which My Group Didnt Help??muhammadumarlol10yrsNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondDocument10 pagesMetallic BondAbhishek NayakNo ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding - 1 - Free Electron ModelDocument21 pagesMetallic Bonding - 1 - Free Electron Modelsherin joyNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument6 pagesMetallic Bonding胡佳玲No ratings yet
- Band Theory 2016Document25 pagesBand Theory 2016Mohd Ridz Zul WanNo ratings yet
- 4 4 Metallic BondingDocument2 pages4 4 Metallic BondingNguyenHoangMinhDucNo ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding - Electron Sea ModelDocument13 pagesMetallic Bonding - Electron Sea ModelMirza MohammadNo ratings yet
- Atomic Bond: Valence ElectronDocument2 pagesAtomic Bond: Valence ElectronttitiNo ratings yet
- Summary of Chemistry Textbook - Section 2.2 Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesSummary of Chemistry Textbook - Section 2.2 Metallic BondingRachel JeffresonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10.2 The Solid StateDocument14 pagesLesson 10.2 The Solid StatefitriNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes STD Vii Chapter: Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesChemistry Notes STD Vii Chapter: Metallic BondingRafit BiswasNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument28 pagesMetallic BondingLysha Kana-an CarampatanaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 1st Quarter - Week Three Chemical Bonds and Lewis StructureDocument5 pagesGrade 12 1st Quarter - Week Three Chemical Bonds and Lewis Structurenicole MenesNo ratings yet
- Csec Chemistry Notes 5Document3 pagesCsec Chemistry Notes 5debestieNo ratings yet
- Sle DLP - Metallic BondingDocument5 pagesSle DLP - Metallic BondingRodney BarbaNo ratings yet
- 3.2.5. Metallic Bonding PDFDocument2 pages3.2.5. Metallic Bonding PDFClinton ChikengezhaNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument22 pagesMetallic BondingnkjkjkjNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Document25 pagesInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?lianghoo94No ratings yet
- 28.9.2022 4.5 Metallic BondingDocument17 pages28.9.2022 4.5 Metallic BondingJungun HwangNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Structure..Document6 pagesChemical Bonding Structure..rachelNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Solids Tanish, Rudar, Devansh, HarshDocument14 pagesBonding in Solids Tanish, Rudar, Devansh, HarshtanishbadyalsharmaNo ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding Activity Sheet Lower Ability-1Document1 pageMetallic Bonding Activity Sheet Lower Ability-1Yasmine ElmelegyNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument17 pagesMetallic Bondingaudrey.sengeNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Naming CompoundsDocument10 pagesBonding and Naming CompoundsDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding (Engineering Chemistry Lecture)Document13 pagesChemical Bonding (Engineering Chemistry Lecture)kiana Jessica MonroeNo ratings yet
- MME365 Glass and Ceramics Engineering: Bonding in Ceramic MaterialsDocument12 pagesMME365 Glass and Ceramics Engineering: Bonding in Ceramic MaterialsZahir Rayhan JhonNo ratings yet
- Summary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesDocument3 pagesSummary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesAnonymous L7ZuSkR100% (1)
- Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesMetallic Bondingonlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- Metalic BondingDocument1 pageMetalic Bondingmuhammad abdullahNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN-3-Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesLESSON PLAN-3-Metallic BondingHOWARD ZULUNo ratings yet
- Metallic Properties Report in Science 02Document6 pagesMetallic Properties Report in Science 02Jimwell SiegoNo ratings yet
- Tema 7 - Enlace MetalicoDocument39 pagesTema 7 - Enlace MetalicoLuchinPozo100% (2)
- Chapter 3 Chemical BondingDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Chemical BondingQutub KhanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Metallic Bonding: An Electrostatic Attraction Between A Lattice of Positive Ions and DelocalisedDocument1 pageChemical Bonding: Metallic Bonding: An Electrostatic Attraction Between A Lattice of Positive Ions and DelocalisedMatthew BongNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Metallic BondingDocument35 pagesIonic and Metallic BondingAULIA SAFIRA DWI OKTAVIANINo ratings yet
- Bonding A LevelDocument2 pagesBonding A LevelHamzah ArabicaNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Document36 pagesInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?aditya_2013No ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument1 pageMetallic BondingSoraya DeenNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesMetallic Bondingamarali11420222No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (9/13/2006) : Crystal Chemistry Bonding and Ionic RadiiDocument18 pagesLecture 3 (9/13/2006) : Crystal Chemistry Bonding and Ionic RadiiDhana Strata NNo ratings yet
- Bonding Revision GuidesDocument1 pageBonding Revision Guidesapi-255623302No ratings yet
- 1 MetalsDocument39 pages1 MetalsManuel Tutacha ™No ratings yet
- Metallic BondDocument2 pagesMetallic BondJulianne Marchela ParinNo ratings yet
- Properties of Metals and AlloysDocument19 pagesProperties of Metals and AlloysIlhamsidiqNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument16 pagesIntermolecular ForcesKatherine ToribioNo ratings yet
- Modern Semiconductor Devices For Integrated Circuits 1st Edition Hu Solutions ManualDocument19 pagesModern Semiconductor Devices For Integrated Circuits 1st Edition Hu Solutions ManualLaurenThompsonfpniz100% (16)
- How To Create A Time Crystal: ViewpointDocument2 pagesHow To Create A Time Crystal: Viewpointehtisham khanNo ratings yet
- Lectures 2-3 (v1.1) PDFDocument130 pagesLectures 2-3 (v1.1) PDFJordan ThomsonNo ratings yet
- Crystal Structure (21!10!2011)Document71 pagesCrystal Structure (21!10!2011)Swetha PrasadNo ratings yet
- Handout 10 ADocument7 pagesHandout 10 AMuhammad SohaibNo ratings yet
- Research 3 - LedDocument8 pagesResearch 3 - LedAlyssa Jane MagkalasNo ratings yet
- The Rheology Handbook: Thomas G. MezgerDocument6 pagesThe Rheology Handbook: Thomas G. MezgerCereliaNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors: Energy Level Diagram of A SemiconductorDocument30 pagesSemiconductors: Energy Level Diagram of A SemiconductorF2 - 57 Rahul Rajpurohit .MNo ratings yet
- Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids: SciencedirectDocument1 pageJournal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids: SciencedirectKumar AjeetNo ratings yet
- NNSE618 L8 Transport PhenomenologyDocument11 pagesNNSE618 L8 Transport PhenomenologyBayanjargal ErdeneeNo ratings yet
- Nchem2 PosttestDocument4 pagesNchem2 PosttestJessa GuerraNo ratings yet
- Abers Lee Gauge TheoriesDocument200 pagesAbers Lee Gauge TheoriesdheerajkmishraNo ratings yet
- Four Probe MethodDocument20 pagesFour Probe MethodSuresh Senanayake43% (7)
- Module 4 Chemical BondingDocument23 pagesModule 4 Chemical BondingJulie Anne Manggurit (Grade-10 Tesla)No ratings yet
- Physics Now de Jon OgbornDocument159 pagesPhysics Now de Jon OgbornFrancisco GurrolaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Questions and AnswersDocument20 pagesModule 2 Questions and Answerssiany adeNo ratings yet
- Unit-III Dielectrics, Magnetic & EnergymaterialsDocument26 pagesUnit-III Dielectrics, Magnetic & EnergymaterialsudayNo ratings yet
- Molecular GeometryDocument85 pagesMolecular GeometryKeri Gobin SamarooNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Test ReviewDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding Test ReviewAlakh Jagtap100% (1)
- 1991 - Bulk Conductivity and Defect Chemistry of Acceptor-Doped Strontium Titanate in The Quenched StateDocument7 pages1991 - Bulk Conductivity and Defect Chemistry of Acceptor-Doped Strontium Titanate in The Quenched StateBeh NaatNo ratings yet
- Textbook Ebook Spintronic 2D Materials Fundamentals and Applications Materials Today Wenqing Liu Editor All Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesTextbook Ebook Spintronic 2D Materials Fundamentals and Applications Materials Today Wenqing Liu Editor All Chapter PDFkathleen.white115100% (5)
- Picturing Quantum Processes SlideshowDocument258 pagesPicturing Quantum Processes Slideshowsaironwe100% (2)
- MSEnewDocument11 pagesMSEnewMIGUEL ANTONIO MACARAEGNo ratings yet
- Ijms 23 12652 v2Document12 pagesIjms 23 12652 v2Deym GómezNo ratings yet
- Gunti, Ayiriveetil, Sundarrajan - 2011 - Thermodynamic, Kinetic and Electrical Switching Studies On Si15Te85-xInxglasses Observation (2) - AnnotatedDocument8 pagesGunti, Ayiriveetil, Sundarrajan - 2011 - Thermodynamic, Kinetic and Electrical Switching Studies On Si15Te85-xInxglasses Observation (2) - AnnotatedJagan KbNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Sulfurisation Temperature On Structural Properties of Cuals Thin FilmsDocument6 pagesThe Effect of Sulfurisation Temperature On Structural Properties of Cuals Thin FilmsInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Epitaxial Growth and Study of 2D Se-Based Ultrathin Films: Bi Se, MoseDocument14 pagesEpitaxial Growth and Study of 2D Se-Based Ultrathin Films: Bi Se, MoseBandiyah Sri AprilliaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0925400514000859 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0925400514000859 Main1900066No ratings yet
- Chap 2 ModDocument16 pagesChap 2 ModM Zia DogarNo ratings yet