Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 4: Heat 4.1 Understanding Thermal Equilibrium ( . / 42 x100 )
Chapter 4: Heat 4.1 Understanding Thermal Equilibrium ( . / 42 x100 )
Uploaded by
aloydasweetOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4: Heat 4.1 Understanding Thermal Equilibrium ( . / 42 x100 )
Chapter 4: Heat 4.1 Understanding Thermal Equilibrium ( . / 42 x100 )
Uploaded by
aloydasweetCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 4 : HEAT
4.1 Understanding Thermal Equilibrium [. / 42 x100=]
A student is able to:
4.1.1 Explain thermal equilibrium
4.1.2 Explain ho a liquid!in!"lass thermometer or#s
$ %hoose the &orre&t ord in the bra&#et.
1. $' (eat ) *emperature + is the de"ree o, hotness o, a bod-.
2. $' (eat ) *emperature + is a ,orm o, ener"-.
.. A hot bod- has a temperature here as a &old bod- has a
temperature.
4. *he /0 unit ,or heat is .
1. *he /0 unit ,or temperature is
2. *emperature is a $' base ) deri3ed + quantit-.
4. (eat is a $' base ) deri3ed + quantit-.
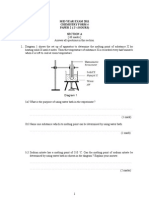
5. *he ,i"ure shos to metal blo&#s in thermal &onta&t.
'a+ Ener"- is trans,erred ,rom $' A ) 6 + to $' A ) 6 + at a ,aster rate.
'b+ Ener"- is trans,erred ,rom $' A ) 6 + to $' A ) 6 + at a sloer rate.
'&+ *emperature A ill $' in&rease ) de&rease +.
'd+ *emperature 6 ill $' in&rease ) de&rease +.
'e+ *he net heat ill ,lo ,rom $' A ) 6 + to $' A ) 6 + until the- are at the
same temperature.
7. *o bodies are said to be in thermal equilibrium hen :
'a+ the- are at the $' 8ero ) same + temperature.
'b+ the net rate o, heat ,lo beteen the to bodies is $' 8ero ) same +.
10. *emperature is measured b- a ..ith or#s ith the prin&iple o,
.
11. 9ame the ph-si&al propert- 'thermometri& propert-+ hi&h 3aries ith
temperature used in a liquid!in!"lass thermometer.
..
A
30C B
80C
1
12. *he liquids &ommonl- used in liquid!in!"lass thermometers are .
and .
1.. %omparison o, mer&ur- and al&ohol as a liquid!in!"lass thermometer.
Mercury Alchl
:ree8in" point :
6oilin" point :
:ree8in" point :
6oilin" point :
0t $'et) does not et+ the tube. 0t $'et) does not et+ the tube.
$';paque ) &olourless+
Eas- to read.
$';paque ) &olourless+
0t needs to be d-ed.
0t is $'poisonous) sa,e liquid+. 0t is $'poisonous) sa,e liquid+.
0t is $'&heap) expensi3e+. 0t is $'&heap) expensi3e+.
%ondu&ts heat ell) responds ,aster
to temperature &han"es.
<esponds more slol- then mer&ur-.
14. %omplete the ,olloin" table &on&ernin" a liquid!in!"lass thermometer.
:eatures Explanation
*he "lass bulb is thin.
*he bulb is made small.
*he bore o, the &apillar- tube is
narr! and uni"rm.
*he alls o, the lon" tube abo3e
the bulb are made thic#
2
11. *emperature o, liquid)
C
l l
l l
0
0 100
0
100
)
=here)
0
l
= len"th o, mer&ur- at .. point.
100
l
= len"th o, mer&ur- at .. point.
l
= len"th o, mer&ur- at point.
12. An un&alibrated thermometer is atta&hed to a &entimetre s&ale and reads
1.0 &m in pure meltin" i&e and .0.0 &m in steam. =hen the thermometer is
immersed in the liquid -) the len"th o, the mer&ur- &olumn is 11.0 &m. =hat
is temperature o, liquid ->
3
4.$ Understanding %&eci"ic Heat Ca&acity [. / 14 x100=]
A student is able to:
4.2.1 ?e,ine spe&i,i& heat &apa&it- 0
4.2.2 /tate that &= @
mA
4.2.. ?etermine the spe&i,i& heat &apa&it- o, a liquid
4.2.4 ?etermine the spe&i,i& heat &apa&it- o, a solid
4.2.1 ?es&ribe appli&ations o, spe&i,i& heat &apa&it-
4.2.2 /ol3e problems in3ol3in" spe&i,i& heat &apa&it-
1. *he o, a substan&e is the
quantit- o, heat needed to in&rease the temperature o, a mass o, 1 #" b-
1
0
% or 1 B.
2. /pe&i,i& heat &apa&it-) & =
m
Q
=here) m =
@ =
= .
.. *he unit o, spe&i,i& heat &apa&it- is .
4. *he quantit- o, heat absorbed or lost ,rom a bod- is "i3en b-) @ =
1. (o mu&h heat ener"- is required to raise the temperature o, 1.1 #" o, ater
,rom .0
0
% to its boilin" point > *he spe&i,i& heat &apa&it- o, ater is 4200 C
#"
1 0
%
1
.
2. %on3ersion o, ener"-
'a+ Electrical energy ,rom heater trans,ormed into heat ener"-.
= m &
'b+ Ptential energy o, a ,allin" obDe&t trans,ormed into heat ener"-.
= m &
'&+ 'inetic energy o, a mo3in" obDe&t is trans,ormed into heat ener"-
hen it is stopped due to ,ri&tion.
= m &
4
4. A 400 = ele&tri& heater is used to heat 2 #" o, ater ,or 10 minutes.
%al&ulate the temperature rise o, the ater. *he spe&i,i& heat &apa&it- o,
ater is 4200 C #"
1 0
%
1
.
5. A &opper blo&# ei"hin" 2 #" is dropped ,rom a hei"ht o, 20 m. =hat is the
rise in temperature o, the &opper blo&# a,ter it hits the ,loor. *he spe&i,i& heat
&apa&it- o, &opper is 400 C #"
1
0
%
1
.
7. A bullet tra3elin" at 20 m s
1
hit a sand ba". *he temperature o, the bullet
rises b- 4.1
0
%. %al&ulate the spe&i,i& heat &apa&it- o, the bullet.
10. 100 " o, hot ater at 70
0
% is mixed ith 200 " o, &old ater at .0
0
%.
Assumin" that no heat is lost) &al&ulate the ,inal temperature o, the mixture.
11. %omplete the ,olloin" table.
Material has a high s&eci"ic heat
ca&acity
Material has a l! s&eci"ic heat
ca&acity
0t ta#es a lon"er time to be heated.
0t lose heat easil-.
0t is a heat insulator.
4.( Understanding %&eci"ic )atent Heat [. / 21 x100=]
5
A student is able to:
4...1 /tate that trans,er o, heat durin" a &han"e o, phase does not &ause a &han"e
in temperature
4...2 ?e,ine spe&i,i& latent heat 'l+
4.... /tate that l = @
m
4...4 ?etermine the spe&i,i& latent heat o, ,usion
4...1 ?etermine the spe&i,i& latent heat o, 23apori8ation
4...2 /ol3e problems in3ol3in" spe&i,i& latent heat
1. Eatter exists in three states) that is solid) . and .. .
2. *he heat released or absorbed at &onstant temperature durin" a &han"e o,
state o, matter is #non as .. .
.. Fatent heat is released
Eeltin"
&ondensation
4. %&eci"ic latent heat " .. is the quantit- o, heat that is needed to
&han"e 1 #" o, a substan&e ,rom slid state to liquid state) ithout a &han"e
in temperature.
1. %&eci"ic latent heat " .. is the quantit- o, heat that is needed to
&han"e 1 #" o, a substan&e ,rom liquid state to *a&ur state) ithout a
&han"e in temperature.
2. /pe&i,i& latent heat) F =
m
Q
=here) @ = latent heat absorbed or released b- the substan&e
m = mass o, the substan&e.
4. *he /0 unit ,or spe&i,i& latent heat is . .
5. =hat is the quantit- o, heat required to melt 2 #" o, i&e at 0
0
% > /pe&i,i&
latent heat o, ,usion o, i&e = ..2000 C #"
1
.
7. *emperature /
0
%
6
Solid
Gas
:
70 ? E
6 %
40
.0 A
0 1 11 20 .1 *ime/minute
:i"ure shos the temperature! time "raph ,or a substan&e) / o, mass 2.0 #")
bein" heated usin" a 100 = heater.
'a+ 6ased on the "raph state the ph-si&al &ondition o, substan&e) / in
'i+ A6 : ..
'ii+ 6% : ..
'iii+ %? : ..
'i3+ ?E : ..
'b+ Eeltin" point : .
'&+ 6oilin" point :
'd+ 6- usin" #ineti& theor-) explain h- the temperature o, substan&e) /
in A6 is in&reasin".
7
'e+ 6- usin" #ineti& theor-) explain h- the temperature o, substan&e) /
is &onstant in 6% e3en thou"h heat is still been supplied to it.
',+ %al&ulate the spe&i,i& heat &apa&it- o, the substan&e in solid state.
'"+ %al&ulate the spe&i,i& latent heat o, 3apori8ation o, substan&e) /.
8
4.4 Understanding The +as )a!s [. / 24 x100=]
A student is able to:
4.4.1 Explain "as pressure) temperature and 3olume in terms o, the beha3ior o, "as
mole&ules
4.4.2 ?etermine the relationship beteen pressure and 3olume at &onstant
temperature ,or a ,ixed mass o, "as ie G3 = &onstant
4.4.. ?etermine the relationship beteen 3olume and temperature at &onstant
pressure ,or a ,ixed mass o, "as ie
H/* = &onstant
4.4.. ?etermine the relationship beteen pressure and temperature at &onstant
3olume ,or a ,ixed mass o, "as ie
p/* = &onstant
4.4.4 Explain about 8ero
4.4.1 Explain the absolute/Bel3in s&ale o, temperature
4.4.2 /ol3e problems in3ol3in" the pressure) temperature and 3olume o, a ,ixed
mass o, "as
1. %omplete the table belo about "as lasI
,yle-s )a! Charles- )a!
G
V
1
G *
Constant Variable :
1. Mass o !as
2.
Constant Variable :
1. Mass o !as
2. "ress#re o !as
Constant Variable :
1. Mass o !as
2.
Bo$le%s la& states t'at t'e
(ress#re o a i)ed *ass o
!as is in+ersel$
(ro(ortional to its +ol#*e
at ,onstant te*(erat#re.
C'arles% la& states t'at "ress#re la& states t'at
G
0 H
H
0 */
0
%
G
0 */
0
%
G
0
V
1
H
0 */B
G
0 */B
-
V
P
0 G
T
V
0 H
T
P
0 G
V
P
0 H
T
V
0 *
T
P
0 *
2. :i"ure 'a+ sho 15 &m o, air &olumn trapped in a &apillar- tube b- 4 &m o,
mer&ur-. 0, the "lass tube is in3erted) hat is the len"th) F) o, the air &olumn
trapped in the &apillar- tube>
'Atmospheri& pressure = 42 &m ("+
4 &m F air
15 &m air 4 &m
' a + ' b +
.. An air bubble released b- a di3er has a 3olume o, 4.0 &m
3
at depth o, 11 m.
=hat is the 3olume o, the bubble at a depth o, 10 m>
'Atmospheri& pressure = 10 m ater+
4. *he 3alue !24.
0
% is equi3alent to B. *his temperature is #non as the
10
1. %on3ert 24
0
% to its equi3alent temperature in Bel3in.
2. %on3ert ..0 B to its equi3alent temperature in de"rees %elsius.
4. *he 3olume o, a "as is 1 &m
3
at 24
0
%. *he "as is heated at ,ixed pressure
until the &olumn be&omes 2 &m
3
. %al&ulate the ,inal temperature o, the "as.
5. A "as o, 3olume 20 &m
3
at 44
0
% is heated until its temperature be&omes
54
0
% at &onstant pressure. =hat is the ,inal 3olume o, the "as>
7. 6e,ore a Dourne- ,rom Garit 6untar to 0poh) the air in a &ar t-re has a pressure
o, 200 #Ga and a temperature o, 24
0
%. A,ter the Dourne-) the air pressure in
the t-re is 220 #Ga. =hat is the temperature o, the air in the t-re a,ter the
Dourne->
10. *he pressure o, "as in a li"ht bulb is 10.1 #Ga at .0
0
%. %al&ulate the
pressure o, the "as hen the temperature inside the bulb rises to 54
0
% a,ter
the bulb is li"hted up.
11
You might also like
- Chapter-4-Heat (Answer) PDFDocument34 pagesChapter-4-Heat (Answer) PDFNadia Saidon100% (3)
- Physics Lesson Notes On Heat Capacity and Specific Heat CapacityDocument5 pagesPhysics Lesson Notes On Heat Capacity and Specific Heat CapacityAwajiiroijana Uriah OkpojoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Heat: 4.1: Understanding Thermal EquilibriumDocument34 pagesChapter 4: Heat: 4.1: Understanding Thermal EquilibriumYusfalina Mohd YusoffNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 4 - Teacher'sDocument9 pagesForm 4 Physics Chapter 4 - Teacher'sPavithiran50% (2)
- Design of Metal Anchors Used in Concrete To ACI318!08!4Document4 pagesDesign of Metal Anchors Used in Concrete To ACI318!08!4tamerragaaNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic and Logic InstructionsDocument83 pagesArithmetic and Logic InstructionsAkash PandaNo ratings yet
- Ulladu Narpadu - AnubandhamDocument18 pagesUlladu Narpadu - AnubandhamChris Bell100% (2)
- Food Processing IntroductionDocument45 pagesFood Processing IntroductionCarrylle Janne Noval100% (1)
- Cuckold - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesCuckold - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaputyeuesNo ratings yet
- Heat Physics SPMDocument33 pagesHeat Physics SPMJeffrey TehNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiDocument12 pagesChemistry Paper 2 Exam PremiSakinah Saad100% (3)
- Chapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideDocument32 pagesChapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuiderospazitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Heat StudentsDocument33 pagesChapter 4 Heat StudentsSyazwan AkidNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 4Document33 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 4Eric LengNo ratings yet
- Satisfied by Jeff Manion SamplerDocument28 pagesSatisfied by Jeff Manion SamplerZondervanNo ratings yet
- List of Core Electricals CompaniesDocument9 pagesList of Core Electricals CompaniesGp MishraNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics Extension QsDocument5 pagesThermal Physics Extension QsRamesh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Nota Padat HeatDocument10 pagesNota Padat Heatjesunathan44@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of Matter ImportantsDocument2 pagesThermal Properties of Matter Importantsommimishra0No ratings yet
- Remedial Topic 3Document3 pagesRemedial Topic 3FarzanaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of MatterDocument6 pagesThermal Properties of MatterranamalblogNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Temperature & Heat - Part 2Document4 pagesTutorial 2 Temperature & Heat - Part 2Yixiang TanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Teacher's GuideDocument33 pagesChapter 4 Teacher's GuideinezchewNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of MatterDocument24 pagesThermal Properties of MatterVansh AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Energetics AssignmentDocument5 pagesEnergetics AssignmentlisaNo ratings yet
- 0205 Heat EnergyDocument9 pages0205 Heat EnergyAhmed AdhamNo ratings yet
- Uace Physics Paper 1 2020Document4 pagesUace Physics Paper 1 2020benzjulius8No ratings yet
- Phy CHP 4 f4 Revision 1Document5 pagesPhy CHP 4 f4 Revision 1Alexandra ChiengNo ratings yet
- RevisionWsheet 5054 ThermalPropertiesofMatterDocument4 pagesRevisionWsheet 5054 ThermalPropertiesofMatterHem HemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Teacher S Guide 2009Document33 pagesChapter 4 Teacher S Guide 2009Chen ShyanNo ratings yet
- WAJA CHP.4 ThermochemistryDocument19 pagesWAJA CHP.4 ThermochemistrySafwan Mazlan100% (1)
- ThermalPhysicsExercise 4ADocument9 pagesThermalPhysicsExercise 4AHarsh SinhaNo ratings yet
- 7750 - Heat Capacity Latent HeatDocument11 pages7750 - Heat Capacity Latent Heatojo ayodeji johnsonNo ratings yet
- 9.1: Relationship Between Temperature and HeatDocument4 pages9.1: Relationship Between Temperature and HeatNor MasturaNo ratings yet
- Icse X Calorimetry Question BankDocument9 pagesIcse X Calorimetry Question BankanimeshtechnosNo ratings yet
- Termo ProblemsDocument9 pagesTermo ProblemsJohn StudentNo ratings yet
- Thermal Propeties of MatterDocument3 pagesThermal Propeties of MatterTanuNo ratings yet
- Maths IA IIDocument12 pagesMaths IA IIGRANDHE VENKAT SAI MANIKANTA 1923627No ratings yet
- 11G6 Topic - Thermal Properties and TemperatureDocument6 pages11G6 Topic - Thermal Properties and TemperatureAminaNo ratings yet
- Answer Homework 01Document2 pagesAnswer Homework 01Mohammed MNo ratings yet
- 11th NEET Part3 Test 6Document8 pages11th NEET Part3 Test 6Dev ShahNo ratings yet
- Study QuestionsDocument1 pageStudy Questionskiwandaemmanuel21No ratings yet
- 06-11-23 Thermal Properties of Matter Physics DPPDocument4 pages06-11-23 Thermal Properties of Matter Physics DPPZomatoswiggyNo ratings yet
- 3 6 2 1-Thermal-Energy-TransferDocument90 pages3 6 2 1-Thermal-Energy-TransferFrenzel Annie LapuzNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 (Heat and Gases) (Notes) (Empty)Document15 pagesTopic 3 (Heat and Gases) (Notes) (Empty)ethanl2028No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideDocument33 pagesChapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideRusnizaARNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 CalorimetryDocument5 pagesLesson 4 CalorimetryRamesh PatelNo ratings yet
- 10c Atp WorksheetDocument3 pages10c Atp WorksheetMohammad ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Heat Subjective, MCQ Google FormDocument1 pageHeat Subjective, MCQ Google FormNROCKSTARNo ratings yet
- CalorDocument4 pagesCalorcesar jimenezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Teachers Guide 2009Document34 pagesChapter 4 Teachers Guide 2009Devan KanesanNo ratings yet
- Quizz Chapter 2Document6 pagesQuizz Chapter 2torreblancacamilaNo ratings yet
- Heat ICSE Board QuestionsDocument5 pagesHeat ICSE Board QuestionsdebanivkashyapNo ratings yet
- Problems Sheet Physics (2) - EBA1104Document23 pagesProblems Sheet Physics (2) - EBA1104muhamedhamdy1No ratings yet
- Answer Homework 04Document3 pagesAnswer Homework 04Mohammed MNo ratings yet
- 2006 Form 3 Physics Half-Yearly Exam (Dec 2006)Document4 pages2006 Form 3 Physics Half-Yearly Exam (Dec 2006)Raistlin Chan Ching KitNo ratings yet
- Question Bank 170402: HEAT TRANSFER Unit IDocument7 pagesQuestion Bank 170402: HEAT TRANSFER Unit Iprakhar dubeyNo ratings yet
- CPP 05 26.04.21 Phy PMKDocument6 pagesCPP 05 26.04.21 Phy PMKSubhashNo ratings yet
- Physics XII / Chapter 1 (HEAT) With KeyDocument5 pagesPhysics XII / Chapter 1 (HEAT) With KeyShujat AbroNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- 3.6 Bernoulli's PrincipleDocument3 pages3.6 Bernoulli's PrinciplepedNo ratings yet
- Mock Test 2 - Questions For Paper 2-PerakDocument20 pagesMock Test 2 - Questions For Paper 2-PerakpedNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Understanding The Effects of ForceDocument3 pages2.5 Understanding The Effects of ForceShaZana JamilNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Pascal's PrincipleDocument2 pages3.4 Pascal's PrinciplepedNo ratings yet
- 2.12 Under Sanding ElasticityDocument3 pages2.12 Under Sanding ElasticitypedNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Understanding Gas PressureDocument4 pages3.3 Understanding Gas PressurepedNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Analising MomentumDocument3 pages2.4 Analising MomentumpedNo ratings yet
- Physics Module F5 (Electricity)Document15 pagesPhysics Module F5 (Electricity)pedNo ratings yet
- Physics Module F5 (Electromagnetism)Document16 pagesPhysics Module F5 (Electromagnetism)pedNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Understanding MeasurementsDocument6 pages1.4 Understanding MeasurementspedNo ratings yet
- Physics Module (Pressure)Document21 pagesPhysics Module (Pressure)ped50% (2)
- F4 CH 1 StudentDocument20 pagesF4 CH 1 StudentLechimi SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Physics Module F4 (Force and Motion 1)Document12 pagesPhysics Module F4 (Force and Motion 1)ped100% (1)
- Physics Module (Pressure)Document21 pagesPhysics Module (Pressure)ped50% (2)
- CHAPTER 1: Understanding Waves: The Nature of WavesDocument17 pagesCHAPTER 1: Understanding Waves: The Nature of WavespedNo ratings yet
- Answering Technique Paper 3 Physics SPMDocument1 pageAnswering Technique Paper 3 Physics SPMped88% (8)
- FM Module With Usb FunctionDocument3 pagesFM Module With Usb FunctionShruthi BhatNo ratings yet
- Written Report ON Ethical Issues IN Media CoverageDocument3 pagesWritten Report ON Ethical Issues IN Media CoverageEMMANo ratings yet
- Study The Book of Hebrew-Indonesia ClassDocument12 pagesStudy The Book of Hebrew-Indonesia ClassDimas Arsetyo GuntoroNo ratings yet
- CPS 4 Advanced ConceptsDocument312 pagesCPS 4 Advanced ConceptssudharaghavanNo ratings yet
- Physicochemical Properties and Sensory Attributes of New Formulations of Dry-Fermented SausagesDocument5 pagesPhysicochemical Properties and Sensory Attributes of New Formulations of Dry-Fermented SausagesShermsooddeen Asheer EvraheemNo ratings yet
- 8 Foundation: 8.1 Bearing CapacityDocument3 pages8 Foundation: 8.1 Bearing CapacityPiseth HengNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Special and Inclusive Education: Course OverviewDocument4 pagesFoundation of Special and Inclusive Education: Course OverviewDiane O. Barbarona-GudelosaoNo ratings yet
- 2 Grade Inquiry-Based Lesson South Africa vs. Slaton, TXDocument31 pages2 Grade Inquiry-Based Lesson South Africa vs. Slaton, TXSamantha MelvinNo ratings yet
- Problemas Circuitos Tema 1 SolucionarioDocument125 pagesProblemas Circuitos Tema 1 SolucionarioJosue GordilloNo ratings yet
- Guidelines and Strategy Bivalent Pfizer Vaccine 3Document31 pagesGuidelines and Strategy Bivalent Pfizer Vaccine 3Cristine Joy Jimenez SavellanoNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Short Story "Leaving" Exercise (Fill in The Blanks)Document1 pageForm 4 Short Story "Leaving" Exercise (Fill in The Blanks)syimamunira2012522588% (8)
- Essay Absence From SchoolDocument8 pagesEssay Absence From SchoolMarianaTaparíNo ratings yet
- C Chemical BondingDocument33 pagesC Chemical BondingMohitNo ratings yet
- Produced By:: PT Unijaya PratamaDocument8 pagesProduced By:: PT Unijaya PratamaNovalia Lorenta NapitupuluNo ratings yet
- Nischal NetworkingDocument140 pagesNischal NetworkingroodlesnepalNo ratings yet
- Paper TwoDocument8 pagesPaper Twoapi-666758658No ratings yet
- Za Total C HP en V9Document2 pagesZa Total C HP en V9Jose David BoteroNo ratings yet
- f1rc RCParts KyoshoDocument4 pagesf1rc RCParts KyoshoaascmdthlbaimpgtbiNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Projecs Class 12Document3 pagesPhysics Investigatory Projecs Class 12Rajarshi ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian Primary Health Care Clinical Guideline Implementation Manual - Nov 2019Document28 pagesEthiopian Primary Health Care Clinical Guideline Implementation Manual - Nov 2019Abebe Tilahun100% (6)
- IMO CLass 4Document4 pagesIMO CLass 4aruna270775% (4)
- Steps Involved in Questionnaire DesignDocument2 pagesSteps Involved in Questionnaire DesignHami KhaNNo ratings yet
- Community Nutrition Manual (AutoRecovered)Document77 pagesCommunity Nutrition Manual (AutoRecovered)Reen “Sudi” MuloliNo ratings yet