Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 3: Chemical Formulae and Equations: A1: Relative Atomic Mass, A
Chapter 3: Chemical Formulae and Equations: A1: Relative Atomic Mass, A
Uploaded by
Eric ChewOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 3: Chemical Formulae and Equations: A1: Relative Atomic Mass, A
Chapter 3: Chemical Formulae and Equations: A1: Relative Atomic Mass, A
Uploaded by
Eric ChewCopyright:
Available Formats
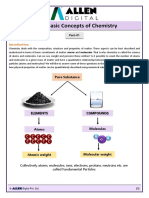
4541 CHEMISTRY
Chapter 3
CHAPTER 3 : CHEMICAL FORMULAE AND EQUATIONS
A1 :
Relative Atomic Mass, Ar
1.
2.
3.
The mass of an atom is very small. We cannot weigh a single atom.
We can determine the mass of one atom relative to a standard atom.
The atomic mass of an atom found comparing it with a standard atom is called Relative Atomic
Mass, RAM, Ar.
For the first, chemist using hydrogen atom as the standard atom for comparison because
hydrogen is the lightest atom.
4.
Hydrogen as
standard atom
Helium atom
A Helium atom is 4 times heavier compare to a hydrogen atom.
Relative atomic mass of Helium is 4.
5.
Oxygen was then used as a standard to compare the masses of atoms. However, this also posed
some problem when three isotopes of oxygen was discovered.
1961 : the International Unions of Chemists and Physicists agreed on a single the carbon -12
(C-12) atom used as a standard to compare the masses of atom. C-12 is choosen because :
it is solid at room conditions
can be easily handed.
6.
The relative atomic mass of an element is the average mass of one atom of the element when
1
compared with
of the mass of an atom of carbon 12.
12
Relative atomic mass of an element =
the average mass of one atom of an element
1
the mass of one atom of carbon - 12
12
of one atom carbon-12
How many helium
atoms are here?
Example :
Relative atomic mass of sodium is 23. [*Relative atomic mass does not have any unit]
1
This means that the average mass of a sodium atom is 23 times larger than
of the
12
mass of a carbon-12 atom.
23
Sodium
atom
Chapter 3
Chemical Formulae and Equations
4541 CHEMISTRY
Chapter 3
Activity 1:1. How many times is a copper atom heavier than two helium atoms?
[Relative atomic mass: He = 4; Cu = 64 ]
Solution :
Mass of a copper atom
Mass of two helium atoms
1 Ar of copper
2 Ar of helium
64
2x4
a copper atom is 8 times heavier than two helium atoms
2. How many times is one atom of silicon heavier than one atom of lithium?
[Relative atomic mass: Li = 7; Si = 28 ]
Mass of a silicon atom
Mass of a lithium atom
3. How many times is one atom of nitrogen heavier than one atom of lithium.
[Relative atomic mass: Li = 7; N = 14 ]
4. How many magnesium atoms have the same mass as two silver atoms?
[Relative atomic mass: Mg = 24; Ag = 108]
Solution :
Chapter 3
Chemical Formulae and Equations
4541 CHEMISTRY
Chapter 3
5. Calculate the number of atoms of lithium that have the same mass as two atoms of nitrogen.
[Relative atomic mass: Li = 7 ; N = 14 ]
6. The mass of one Y atom is 4 times larger than the mass of one nitrogen atom.
Calculate the relative atomic mass of Y.
[Relative atomic mass: N = 14 ]
7. The mass of an atom of element Y is ten times greater than the mass of an atom of element X.
What is the relative atomic mass of Y?
[Relative atomic mass: X = 9 ]
Chapter 3
Chemical Formulae and Equations
4541 CHEMISTRY
A2 :
Chapter 3
Relative Molecular Mass, Mr
The relative molecular mass of a molecule is the average mass of the molecule when compared
1
with
of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
12
the average mass of the molecule
1
the mass of one atom of carbon-12
12
Relative Molecular Mass of a molecule =
Example :
Relative molecular mass of water is 18.
This means that the average mass of one molecule of water is 18 times larger than
1
12
of the mass of carbon-12 atom.
Water molecule
18
1
12
Carbon-12 atom
Relative molecular mass of carbon dioxide is 44.
This means that the average mass of one molecule of carbon dioxide is 44 times larger
1
than
of the mass of carbon-12 atom.
12
The relative molecular mass of a substance can be calculated by adding up the relative atomic
masses of all the atoms that are present in one molecule of the substance.
Example :
1. Calculate the relative molecular mass of water, H 2O
[Relative atomic mass: H = 1; O = 16]
Mr of H2O
= 2(Ar of H) + 1(Ar of O)
= 2(1) + 2(16)
= 18
2. Calculate the relative molecular mass of carbon dioxide, CO 2
[Relative atomic mass: C = 12 ; O = 16 ]
Mr of CO2
= 1(Ar of C) + 2 (Ar of O)
= 1(12) + 2(16)
= 44
3. Calculate the relative molecular mass of ammonia, NH 3
[Relative atomic mass: H = 1; N = 14]
Mr of NH3
Chapter 3
= 1(Ar of N) + 3 (Ar of H)
= 1(14) + 3(1)
= 17
Chemical Formulae and Equations
4541 CHEMISTRY
Chapter 3
Activity 2 :Calculate the relative molecular mass, Mr for the following substances :
[ Relative atomic mass : H = 1 ; C = 12 ; N = 14 ; O = 16 ; Cl = 35.5 ]
Substance
Molecular formula
Relative molecular mass, Mr
(a)
Oxygen gas
O2
2(16) = 32
(b)
Butane gas
C4H10
4(12) + 10(1) = 58
(c)
Napthalene
C10H8
10(12) + 8(1) = 128
(d)
Nitrogen dioxide gas
NO2
1(14) + 2(16) = 46
(e)
Trichloromethane
CHCl3
1(12) + 1(1) + 3(35.5) = 119.5
(f)
Propanol
C3H7OH
3(12) + 8(1) + 1(16) = 60
(g)
Glucose
C6H12O6
6(12) + 12(1) + 6(16) = 180
(h)
Ethanoic acid
CH3COOH
2(12) + 4(1) + 2(16) = 60
Notes :
Relative molecular mass can only be used for substances that are made up of molecules.
(Covalent compound).
For ionic compound, we use relative formula mass, Fr
Activity 3 :Calculate the relative formula mass, Fr of the following ionic compounds :
[Relative atomic mass: H = 1 ; C = 12 ; N = 14 ; O = 16 ; Al = 27 ; Mg = 24 ; P = 31 ; S = 32 ; K = 37 ; Fe
= 56 ; Cu = 64 ; I = 127 ]
Name of ionic
compound
Formula
Relative formula mass, Fr
(a)
Potassium iodide
KI
37 + 127 = 164
(b)
Aluminium oxide
Al2O3
102
(c)
Copper(II) sulphate
CuSO4
160
(d)
Iron(III) nitrate
Fe(NO3)3
56 + 3[14 + 3(16)] = 242
56 + 3(14) + 9(16) = 242
Ammonium
carbonate
Magnesium
phosphate
Magnesium
sulphate
hepthahydrated
(NH4)2CO3
96
Mg3(PO4)2
262
MgSO4.7H2O
24 + 32 + 4(16) + 7 [2(1) +16] = 246
Cu(NO3)2.5H2O
278
(e)
(f)
(g)
(h)
Chapter 3
Copper(II) nitrate
penthahydrated
Chemical Formulae and Equations
4541 CHEMISTRY
CONCEPT OF MOLE
Chapter 3
[ Refer to Clinic Module 3 and 4 ]
The word pair and dozen represent a fixed number of objects.
A pair of shoe = 2 shoes
B1
One dozen of egg = 12 eggs
The Mole and the Number of Particles
Refer to CLINIC MODULE 3
In chemistry, we use the unit mole to measure the amount of substances.
The symbol of mole is mol.
One mol of substance
= the number of particles in 12 g of carbon-12
= 6 .02 1023 particles
The value of 6.02 x 1023
is called as the Avogadro Constant // Avogadros Number.
The number of particles in one mol of substance
One mol of substance contains 6.02 1023 particles. [atoms, molecules or ions]
1 mol of atomic substance contains 6 .02 1023 atoms.
Example :
(i) 1 mol of sodium, Na contains 6.02 1023 sodium atoms.
(ii) 1 mol of copper, Cu contains 6.02 1023 copper atoms.
(iii) 1 mol of iron atom contains 6.02 1023 iron atoms.
1 mol of molecular substance contains 6.02 1023 molecules.
Example :
1 mol of water, H2O contains 6.02 1023 H2O molecules.
1 mol of carbon dioxide, CO2 contains 6.02 1023 CO2 molecules
1 mol of hydrogen gas, H2 contains 6.02 x 1023 hydrogen molecules
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
Activity 4 :-
1.
Define a mole?
..
2.
(i)
(ii)
Chapter 3
A closed glass bottle contains 0.5 mol of oxygen gas, O2.
How many oxygen molecules, O2 are there in the bottle?
How many oxygen atoms are there in the bottle?
Chemical Formulae and Equations
4541 CHEMISTRY
Chapter 3
Solution :
3.
Find the number of moles of molecules in a sample containing 9.03 10 23
molecules of carbon dioxide, CO2.
Solution :
4.
Calculate the number of atoms in 2 mol carbon.
Solution :
5.
How many ions are there in 1.5 mol sodium chloride, NaCl?
Solution :
6.
Calculate the number of moles of bromine molecules, Br2 which consists 1.50
1022 of bromine molecules.
Solution :
7.
How many atoms are there in 2 mol of ammonia, NH3?
Solution :
Chapter 3
Chemical Formulae and Equations
4541 CHEMISTRY
Chapter 3
Activity 5 :1
Calculate the number of atoms contains in :
(a) 0.5 mol of argon, Ar
(b) 0.25 mol of ferum, Fe
How many moles of copper, Cu which contains 3.01 1022 copper atoms?
Calculate the number of molecules that contains in 0.01 mol of ammonia, NH3
Calculate the number of each atom, that contains in :
(a) 1 mol of ammonia, NH3
(b) 0.25 mol of carbon dioxide, CO2
A balloon contains 0.5 mol of oxygen gas, O2.
(a) How many oxygen molecules, O2 are there in the balloon?
(b) How many oxygen atoms are the in the balloon?
Chapter 3
Chemical Formulae and Equations
4541 CHEMISTRY
Chapter 3
A container contains 1.806 1023 oxygen molecules. A sample of 0.5 mol of nitrogen gas is added
to the container. How many molecules are there all together in the container?
Container contains 1.806 1023 oxygen
molecules
+ 0.5 mol
N2 gas
[ SPM 2008 ; P2 : Q3 (b) ]
7
Diagran below shows two balloons containing oxygen gas and carbon dioxide gas respectively.
0.5 mol
0.5 mol
Carbon dioxide
gas, CO2
Oxygen gas, O2
Balloon B
Balloon A
Based on the given information :
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
Chapter 3
calculate the mass of oxygen gas in Balloon A.
calculate the volume of carbon dioxide gas in Balloon B.
compare the number of gas molecules in Balloon A and in Balloon B.
[ Relative atomic mass : C = 12 ; O = 16 ]
[ Molar volume of gas = 24 dm3 mol-1 at room temperature and pressure ]
Chemical Formulae and Equations
4541 CHEMISTRY
Chapter 3
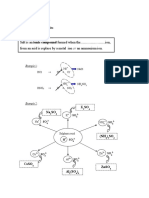
For IONIC substances
Example :
(i)
1 mol of sodium chloride contains 6.02 x 1023 formula units of sodium chloride.
NaCl
Na+
1 mol
1 mol
Cl-
1 mol
1 mol of sodium chloride, NaCl contains 1 mol of Na+ ion and 1 mol of Cl- ion
= 6 .02 10 23 of Na+ ion + 6.02 10 23 of Cl- ion
Total number of ions
(ii)
2 mol of aluminium oxide contains 2 6.02 x 1023 formula units of aluminium oxide.
Al2O3
2Al3+
1 mol
2 mol
3 mol
2 mol
4 mol
6 mol
3O2-
2 mol of aluminium oxide, Al2O3 contains 4 mol of Al3+ ion and 6 mol of O2- ion
= 4 [ 6.02 1023 ] of Al3+ ion + 6 [ 6 .02 10 23 ] of O2- ion
Total number of ions
We can convert the number of mole to the number of particles and vise versa by using the
following relationship :
NA
Number of particles
Number of mole
Number of particles
NA
NA
Activity 5 :Complete these equations :
Number of mole
.
Avogandro constant
Number of particles =
Chapter 3
10
Chemical Formulae and Equations
4541 CHEMISTRY
Chapter 3
Activity 6 :
Identify the ions that exist in the following ionic compound.
Calculate the number of moles and the number of each ion that contains in the compound.
Ions
(a)
0.10 mol copper(II) sulphate, CuSO4
CuSO4 Cu2+ + SO421 mol
(b)
1 mol
1mol
0.05 mol aluminium oxide, Al2O3
Al2O3
1 mol
2Al3+ + 3O22 mol
3 mol
(c)
2.5 mol of iron(III) nitrate, Fe(NO3)3
(d)
2.5 mol of magnesium chloride, MgCl2
(e)
0.05 mol of sodium sulphate, Na2SO4
(f)
0.25 mol of zinc nitrate, Zn(NO3)2
(g)
0.05 mol of ammonium sulphate, (NH4)2SO4
(h)
1.5 mol of ammonium chloride, NH4Cl
(i)
0.005 mol of nitric acid, HNO3
(j)
1.0 mol of hydrochloric acid, HCl
(k)
0.15 mol of sulphuric acid, H2SO4
Chapter 3
11
Number
of moles
( mol)
Number of ions
(ions)
Cu2+
0.01
0.01 6.02 1023
SO42-
0.01
0.01 6.02 1023
Al3+
2 0.05
2 0.05 6.02 1023
O2-
3 0.05
3 0.05 6.02 1023
Chemical Formulae and Equations
4541 CHEMISTRY
B2
Chapter 3
The Mole and the Mass of Substances
Refer to CLINIC MODULE 3
The molar mass of substances is the mass of 1 mol of the substances. It has a unit g mol-1
That means,
The molar mass of substances is the mass of 6.02 10 23 particles of substances.
The molar mass of any substances is numerically equal to its relative atomic mass, relative
molecular mass or relative formula mass.
Example :
Relative mass
Molar mass ( g mol-1)
Sodium, Na
23
23
Calcium, Ca
40
Substances
Oxygen gas, O2
2(16)
Methane, CH4
12 + 4(1)
16
Sodium oxide, Na2O
Zinc chloride, ZnCl2
Ammonia, NH3
[Relative atomic mass: H = 1; C = 12; N = 14; O =16; Na = 23; Cl = 35.5; Ca = 40; Zn = 65 ]
We can convert the number of moles to the mass of substance and vise versa by using the
following relationship :
Ar or Mr
Number of mole
Mass
Mass (g)
Ar @ Mr
Ar or Mr
Activity 7 :Complete these equations :
Number of mole
.
Relative atomic mass
Mass
Chapter 3
12
Chemical Formulae and Equations
4541 CHEMISTRY
Chapter 3
Activity 8 :[Relative atomic mass: H = 1; N = 14; O =16; Cl = 35.5; Ca = 40; Zn = 65 ]
1
Calculate the number of mole of :
(a) 2.0 g calcium, Ca
(b) 3.2 g oxygen gas, O2
What is the mass of :
(a) 0.1 mol ammonia, NH3 ?
(b) 0.25 mol zinc chloride, ZnCl 2 ?
Equal number of moles of substances contains the same number of particles.
Example:
1 mol of aluminium, Al contains the same number of atoms as 1 mol of iron, Fe.
0.5 mol of water, H2O contains the same number of molecules as 0.5 mol of carbon dioxide, CO2
Activity 9 :[Relative atomic mass: O =16; Mg = 24; Cl = 35.5; Ar = 40 ]
(i)
What is the mass of magnesium that has the same number of atoms as in 4 g of argon?
(ii)
What is the mass of oxygen gas that has twice the number of molecules as in 1.42 g of chlorine gas?
Chapter 3
13
Chemical Formulae and Equations
4541 CHEMISTRY
Chapter 3
STP :
B3
Room conditions :
T = 0 oC
P = 1 atm
The Mole and the Volume of Gas
T = 25 oC
P = 1 atm
1. The molar volume of a gas (Vmg) is defined as the volume occupied by one mol of the gas.
2. One mole of any gas always has the same volume under the same temperature and pressure.
3. The molar volume of any gas is 22.4 dm3 at STP or 24 dm3 at room conditions.
We can convert the number of moles to the volume of gas and vise versa by using the following
relationship :
Vmg
Vg
Number of moles
Volume of gas (dm3)
Vmg
Vmg
Activity 8 :Complete these equations :
Number of mole
.
Molar volume of gas
Volume of gas
Example :
1 mol of oxygen gas, O2 occupies 22.4 dm3 at STP.
0.5 mol of oxygen gas, O2 occupies 0.5 22.4 dm3 at STP.
2 mol of nitrogen gas, N2 occupies 2 24 dm3 at room conditions.
3 mol of chlorine gas, Cl2 occupies 3 24 dm3 at room conditions.
0.1 mol of oxygen gas, O2 occupies .... dm3 at STP.
0.25 mol of oxygen gas, O2 occupies ... cm3 at STP.
12 mol of nitrogen gas, N2 occupies . dm3 at room conditions.
Chapter 3
14
Chemical Formulae and Equations
4541 CHEMISTRY
Chapter 3
3 mol of chlorine gas, Cl2 occupies .. cm3 at room conditions.
Activity 9 :1. Calculate the volume of 0.01 mol hydrogen gas at STP.
2. What is the volume of 1.2 mol of ammonia gas at STP?
3. How many moles of nitrogen gas are present in 600 cm3 of the gas measured at room conditions?
4. Diagram below shows three balloons filled with different gas at room conditions.
Hydrogen, H2
24.0 dm3
Oxygen, O2
gas
6.02 1023
molecules
gas
32.0 g
Carbon dioxide,
CO2 gas
(a) Complete the table below :
Type of gas
Volume of gas / dm3
Hydrogen, H2
Oxygen, O2
Carbon dioxide, CO2
24.0
Mass / g
32.0
Number of molecules /
molecules
6.02 1023
Number of moles / mol
Chapter 3
15
Chemical Formulae and Equations
4541 CHEMISTRY
Chapter 3
(b) State the relationship between :
(i)
the volume of gas and the number of moles
(ii)
the volume of gas and the number of molecules
(iii)
the number of molecules and the number of moles
(c) State the relationship between :
(i)
the molar volume of gas, Vmg and the number of moles, n
(ii)
the molar volume of gas Vmg and Avogadro constant, NA
(iii) the number of moles, n and Avogadro constant, NA
Chapter 3
16
Chemical Formulae and Equations
You might also like
- Nanyang JC Atoms, Molecules and Stoichiometry PDFDocument26 pagesNanyang JC Atoms, Molecules and Stoichiometry PDFVarshLokNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument121 pagesCHAPTER 3 Chemical Formulae and EquationnorNo ratings yet
- A1951-194df-F4-Kimia-Chapter-3-Note - (Bi) - Edited - Compressed StudentDocument15 pagesA1951-194df-F4-Kimia-Chapter-3-Note - (Bi) - Edited - Compressed Studentforyourhonour wongNo ratings yet
- Mole ConceptDocument49 pagesMole Conceptd anjilappa100% (3)
- Aspire Mole Concept (17!4!21)Document44 pagesAspire Mole Concept (17!4!21)sourav gargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3:chemical Formulae and EquationsDocument7 pagesChapter 3:chemical Formulae and EquationsirisNo ratings yet
- (2095) Lecture Notes Mole Concept eDocument49 pages(2095) Lecture Notes Mole Concept eRamJiPandeyNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept & StoichiometryDocument58 pagesMole Concept & StoichiometryMuhammad Sahil KhanNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept & StoichiometryDocument58 pagesMole Concept & StoichiometryMuhammad Sahil KhanNo ratings yet
- Ijso Chemistry PDFDocument62 pagesIjso Chemistry PDFkumarkvNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionDocument52 pagesRedox ReactionChauhan DharmendraNo ratings yet
- Topical Test 3: Chemical Formulae and Equations: Ujian Topikal 3: Formula Dan Persamaan KimiaDocument6 pagesTopical Test 3: Chemical Formulae and Equations: Ujian Topikal 3: Formula Dan Persamaan KimiaameermxNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4: Chapter 3: Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocument12 pagesChemistry Form 4: Chapter 3: Chemical Formulae and EquationsNazatul Firdaus ZainonNo ratings yet
- AmsDocument13 pagesAmsMsMalik_XDNo ratings yet
- Relative Atomic/molecular Mass & Mole ConceptDocument18 pagesRelative Atomic/molecular Mass & Mole Conceptcikgu aisyahNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept 1Document6 pagesMole Concept 1vinitjadhav727No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Relative Masses and Mole CalculationsDocument9 pagesChapter 7 - Relative Masses and Mole CalculationsAdrawa NorwelNo ratings yet
- 2 Ar, MR and MolesDocument11 pages2 Ar, MR and MoleslfcluishoughtonNo ratings yet
- List Definition ChemistryDocument9 pagesList Definition Chemistryrandi saputraNo ratings yet
- SGCH 03Document25 pagesSGCH 03kalloliNo ratings yet
- Ne Ne Ne: (Fractional Abundance X Mass of Isotope)Document5 pagesNe Ne Ne: (Fractional Abundance X Mass of Isotope)Yvonne SipalayNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form4 Chapter3 SPMDocument11 pagesChemistry Form4 Chapter3 SPMkaiqianNo ratings yet
- 02.stoichiometry TheoryDocument27 pages02.stoichiometry Theoryshreyas bulbuleNo ratings yet
- Excel Chemistry TextbookDocument72 pagesExcel Chemistry TextbookLivis EyoreNo ratings yet
- s1.4 The MoleDocument88 pagess1.4 The Molelettybadran2007No ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry: Chapter - IDocument16 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry: Chapter - IMukul MathurNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Mole Concept TheoryDocument25 pagesTopic 3 Mole Concept TheoryMr. XNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Introduction in Water Desalination:: Dr. Adnan O. Alhathal Fall 2021/2022Document25 pagesChapter One Introduction in Water Desalination:: Dr. Adnan O. Alhathal Fall 2021/2022Hydar MohammedNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and StoichiometryDocument19 pagesAtoms, Molecules and StoichiometryMohammed ZakeeNo ratings yet
- Day: Wednesday Date: 10 MarchDocument16 pagesDay: Wednesday Date: 10 MarchKiTTyNo ratings yet
- Eat 131/4 Environmental Chemistry: Basic Concepts From General ChemistryDocument54 pagesEat 131/4 Environmental Chemistry: Basic Concepts From General ChemistryHafiz ShahrilNo ratings yet
- l8 Atomic Mass Molecular Formula MassDocument27 pagesl8 Atomic Mass Molecular Formula Massdevendra singhNo ratings yet
- 3 Chemical Formulae and Equations: 3.1 Relative Atomic Mass and Relative Molecular MassDocument60 pages3 Chemical Formulae and Equations: 3.1 Relative Atomic Mass and Relative Molecular MassSiva GuruNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Atomic StructureDocument32 pagesLecture 2 Atomic StructureAhmed FouadNo ratings yet
- Edited Mole ConceptDocument22 pagesEdited Mole Conceptd anjilappaNo ratings yet
- Nota KimiaDocument18 pagesNota KimiaAzmi Bin A Matali100% (1)
- Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocument25 pagesChemical Formulae and EquationsirisNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument31 pagesBasic Concepts of ChemistryMohammadHussainKhan100% (1)
- 3.1 Jar, JMRDocument16 pages3.1 Jar, JMRNurImanNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument11 pagesSome Basic Concepts of ChemistryKunalKumarSinghNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and Chemical Arithmetic: Paper - 1Document12 pagesAtoms, Molecules and Chemical Arithmetic: Paper - 1Rezin ChNo ratings yet
- Chem Chap 1 9097Document24 pagesChem Chap 1 9097biccyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and StoichiometryDocument9 pagesChemical Reactions and StoichiometryNathaniel Jay Rogador SumalinogNo ratings yet
- Ne Ne Ne: (Fractional Abundance X Mass of Isotope)Document9 pagesNe Ne Ne: (Fractional Abundance X Mass of Isotope)Nathaniel Jay Rogador SumalinogNo ratings yet
- c3 Chemical Formula (S)Document59 pagesc3 Chemical Formula (S)Wan nur Damia batrisyaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry With Physics Reviewer PDFDocument69 pagesChemistry With Physics Reviewer PDFRJ JRNo ratings yet
- 01 Formulae, Equations and Amount of SubstanceDocument40 pages01 Formulae, Equations and Amount of SubstanceM BNo ratings yet
- Chemguide Atom, MoleculeDocument28 pagesChemguide Atom, MoleculeSabina SabaNo ratings yet
- Chap 7 - Quantification of Elements - CompressedDocument16 pagesChap 7 - Quantification of Elements - Compressednoway snirfyNo ratings yet
- 5 Early Atomic TheoryDocument55 pages5 Early Atomic TheoryGlen Mangali100% (1)
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument11 pagesAtoms and Moleculesprakul varshneyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document12 pagesChapter 3HING LEE NA MoeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocument12 pagesChemical Formulae and EquationsJelitaAnisaNo ratings yet
- Chemisty Grade 11Document5 pagesChemisty Grade 11Krizzel LuayonNo ratings yet
- Glossary Avogadro's Number (N) : Protons and NeutronsDocument2 pagesGlossary Avogadro's Number (N) : Protons and NeutronsNash PanimbangNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept Stoichiometry (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)Document5 pagesMole Concept Stoichiometry (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)the lillyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Abul FazalDocument51 pagesChemistry: Abul FazalRania ZahidNo ratings yet
- 3.3 (B) Mole N MassDocument20 pages3.3 (B) Mole N MassFidree AzizNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- C12 - Notes (S) RedoxDocument43 pagesC12 - Notes (S) RedoxFarah Aisyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry, Chapter 10, Rate of ReactionDocument23 pagesChemistry, Chapter 10, Rate of ReactionFarah Aisyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry, C8A - Aanotes (S)Document26 pagesChemistry, C8A - Aanotes (S)Farah Aisyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 C8B SDocument10 pagesChemistry Form 4 C8B SFarah Aisyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry, C6A Electrolysis (S)Document30 pagesChemistry, C6A Electrolysis (S)Farah Aisyah Ahmad100% (1)
- Chemistry, C6C - Electrochemical Series (S)Document11 pagesChemistry, C6C - Electrochemical Series (S)Farah Aisyah Ahmad100% (1)
- Chemistry, Chapt 3, FormulaeDocument18 pagesChemistry, Chapt 3, FormulaeFarah Aisyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: The Periodic Table of ElementsDocument14 pagesChapter 4: The Periodic Table of ElementsFarah Aisyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Latih Tubi Menjelang SPM 2010Document15 pagesLatih Tubi Menjelang SPM 2010Farah Aisyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Latih Tubi Menjelang SPM Answer)Document15 pagesLatih Tubi Menjelang SPM Answer)Farah Aisyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 SolutionsDocument40 pagesChapter 17 Solutionseongl39No ratings yet
- Methanol To Ole Fins (MTO) : From Fundamentals To CommercializationDocument17 pagesMethanol To Ole Fins (MTO) : From Fundamentals To Commercializationsrijangupta1996No ratings yet
- Case Studies For Evaluating Hydrodynamic Motion Responses Using MOSESDocument26 pagesCase Studies For Evaluating Hydrodynamic Motion Responses Using MOSESATLURI SATYA SRINIVAS oe13m002No ratings yet
- Monte LevoDocument44 pagesMonte LevopremoshinNo ratings yet
- MasterTop 1200 EngDocument3 pagesMasterTop 1200 EngMohiuddin MuhinNo ratings yet
- List of NGSP Certified MethodsDocument17 pagesList of NGSP Certified MethodsTisha Patricia OedoyNo ratings yet
- AtomDocument15 pagesAtomdewi murtasimaNo ratings yet
- Hasil Pengamatan Waktu (Menit) Temperature (°C) Keterangan Cloud Point Cold Point Pour Point Cloud Point Cold Point Pour PointDocument4 pagesHasil Pengamatan Waktu (Menit) Temperature (°C) Keterangan Cloud Point Cold Point Pour Point Cloud Point Cold Point Pour PointIlham SaputraNo ratings yet
- QCVN - Nuoc - Thai - Cong - Nghiep (English Version) PDFDocument7 pagesQCVN - Nuoc - Thai - Cong - Nghiep (English Version) PDFHNmaichoiNo ratings yet
- All Units - Soil - 2 MarksDocument19 pagesAll Units - Soil - 2 Markscvsmithronn100% (1)
- Effect of System Parameters and of Inorganic Salts On The Decolorization and Degradation of Procion H-Exl Dyes. ..Document16 pagesEffect of System Parameters and of Inorganic Salts On The Decolorization and Degradation of Procion H-Exl Dyes. ..Nicholas YeohNo ratings yet
- ADM Specs GRP Enclosures and KiosksDocument3 pagesADM Specs GRP Enclosures and KiosksMahiBoumNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Flux Consumption and Metal Transfer For Tandem Submerged Arc Welding Process Under Iso Heat Input ConditionsDocument6 pagesAnalysis of The Flux Consumption and Metal Transfer For Tandem Submerged Arc Welding Process Under Iso Heat Input ConditionsShivam SinghNo ratings yet
- Evaporation: DKK3433 Unit Operation Dr. Syed Mohd Saufi 2012/2013-IDocument43 pagesEvaporation: DKK3433 Unit Operation Dr. Syed Mohd Saufi 2012/2013-IAzmiHafifiNo ratings yet
- Floating Matrix Tablets Based On Low Density Form Powder Effects of Formulation and Processing Parameters On Drug ReleaseDocument9 pagesFloating Matrix Tablets Based On Low Density Form Powder Effects of Formulation and Processing Parameters On Drug ReleaseCesar Rodolfo Angulo DelgadoNo ratings yet
- IMPATT Diode: Name:-Tuhin Dutta Stream: - ECE Roll: 1011Document16 pagesIMPATT Diode: Name:-Tuhin Dutta Stream: - ECE Roll: 1011Nava KrishnanNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Toxicology 1985 Articles 65 121Document58 pagesInternational Journal of Toxicology 1985 Articles 65 121Holman SanabriaNo ratings yet
- Zoology M.SC Sem.-Ii Radio-Immunoassay AMDocument3 pagesZoology M.SC Sem.-Ii Radio-Immunoassay AMJagatheeswari SelviNo ratings yet
- Design of Surface Irrigation SystemsDocument20 pagesDesign of Surface Irrigation SystemsEmha DwiNo ratings yet
- 846 Physics Definitions by Sajid Ali TalpurDocument15 pages846 Physics Definitions by Sajid Ali TalpurMuneer KaleriNo ratings yet
- History of The Discovery of DnaDocument15 pagesHistory of The Discovery of DnaEko SujatmikoNo ratings yet
- Process Monitoring in GrindingDocument47 pagesProcess Monitoring in GrindingBhargav ParsaNo ratings yet
- Arabian Journal of Chemistry Volume 7 Issue 1 2014 (Doi 10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.10.007) Rahman, Md. Mukhlesu PDFDocument17 pagesArabian Journal of Chemistry Volume 7 Issue 1 2014 (Doi 10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.10.007) Rahman, Md. Mukhlesu PDFDesiana NurulhNo ratings yet
- 3 - M. Sc. Microbiology Part I & IIDocument43 pages3 - M. Sc. Microbiology Part I & IIsnehsmileNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectra of Elements: Kms TarakkyDocument1 pageMass Spectra of Elements: Kms TarakkyKhondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Mol 2Document54 pagesMol 2Trung Tin NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lift Irrigation SchemesDocument154 pagesLift Irrigation SchemesAlapati Lakshmi Kumar100% (1)
- LTS Catalyst DesignDocument16 pagesLTS Catalyst Designkamranarif4161No ratings yet
- Analysis of Microwave Radiation For HeatingDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Microwave Radiation For HeatingSediki ZakariaNo ratings yet
- 300 TR WC Screw VFDDocument3 pages300 TR WC Screw VFDmanjunath hrNo ratings yet