Professional Documents
Culture Documents
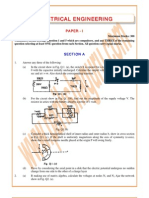
Experiment No. 1: AIM: To Observe Sine Wave, Square Wave, Triangular Wave and Ramp
Uploaded by
Anand SinghOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment No. 1: AIM: To Observe Sine Wave, Square Wave, Triangular Wave and Ramp
Uploaded by
Anand SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
EXPERIMENT NO.
1
AIM: To observe sine wave, square wave, triangular wave and ramp
waveforms on the C.R.O. and to measure amplitude and frequency of the
waveforms.
Introduction:
C.R.O. (Cathode Ray Oscilloscope) is the instrument which is used to
observe signal waveforms. Signals are displayed in time domain i.e.
variation in amplitude of the signal with respect to time is plotted on the
CRO screen. X-axis represents time and Y-axis represents amplitude. It is
used to measure amplitude, frequency and phase of the waveforms. It is
also used to observe shape of the waveform. C.R.O. is useful for
troubleshooting purpose. It helps us to find out gain of amplifier, test
oscillator circuits. We can measure amplitude and frequency of the
waveforms at the different test points in our circuit. Thus, it helps us for
fault finding procedure. In dual channel C.R.O. X-Y mode is available
which is used to create Lissajous patterns
Latest digital storage oscilloscope display voltage and frequency directly
on the LCD and does not require any calculations. It can also store
waveform for further analysis. More detailed study on C.R.O. will be
covered in EMI laboratory (SEM-V). In this practical, we will measure
amplitude and frequency of the different waveforms like sine wave, square
wave, triangular wave and ramp wave.
Procedure:
1. Connect function generator output at the input of C.R.O. at channel 1
or at channel 2
2. Select proper channel i.e. if signal is connected to channel 1 select
CH1 and if signal is connected to channel 2 select CH2
3. Adjust Time /Div knob to get sufficient time period displacement of
the wave on the CRO screen.
4. With fine tuning of time/Div make the waveform steady on screen.
5. Use triggering controls if waveform is not stable
6. Keep volt/div knob such that waveform is visible on the screen
without clipping
7. Measure P-P reading along y-axis. This reading multiplied with
volt/div gives peak to peak amplitude of the ac i/p wave.
8. Measure horizontal division of one complete cycle. This division
multiplied by time/div gives time period of the i/p wave.
9. Calculate frequency using formula f = 1/T.
E.C. DEPARTMENT, GOVERNMENT ENGINEERING COLLEGE,
RAJKOT
10. Note down your readings in the observation table.
EXPERIMENT NO.
22
BASIC ELECTRONICS LABORATORY MANUAL
You might also like
- Thyristor ReportDocument9 pagesThyristor ReportDhaval GamiNo ratings yet
- Multistage AmplifierDocument18 pagesMultistage AmplifierSai SadiqNo ratings yet
- S1S2122 KE37503 Chapter 4Document100 pagesS1S2122 KE37503 Chapter 4PenziiNo ratings yet
- EE1000 Problem Single Phase AC CircuitsDocument4 pagesEE1000 Problem Single Phase AC CircuitsAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2 Spectral Analysis of Signal HarmonicsDocument13 pagesExperiment No. 2 Spectral Analysis of Signal HarmonicsJoyce MalabananNo ratings yet
- ABB 36kV SF6 RMUDocument69 pagesABB 36kV SF6 RMURR_ramyNo ratings yet
- Communication Engineering Cycle Test 1 AnDocument2 pagesCommunication Engineering Cycle Test 1 AnsamNo ratings yet
- 2015 Distance Relay ExampleDocument2 pages2015 Distance Relay ExampleAmanNo ratings yet
- Measurement of High Voltages and High CurrentsDocument43 pagesMeasurement of High Voltages and High Currentssaikarthick023No ratings yet
- Example 8.27Document4 pagesExample 8.27Babasrinivas Guduru100% (1)
- Civil Services - Electrical Main Paper I & II - 1992-2012 - 7.6MBDocument253 pagesCivil Services - Electrical Main Paper I & II - 1992-2012 - 7.6MBAnika DixitNo ratings yet
- Emf Equation of AlternatorDocument2 pagesEmf Equation of AlternatorThe Engineers EDGE, CoimbatoreNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods Two MarksDocument29 pagesNumerical Methods Two MarksMürlî MünnâNo ratings yet
- 192 - EE8301, EE6401 Electrical Machines I - Question Bank 3Document15 pages192 - EE8301, EE6401 Electrical Machines I - Question Bank 3Kaleeswari SaraswathiNo ratings yet
- EE 370 Electronic Instrument Assignment 3Document1 pageEE 370 Electronic Instrument Assignment 3vineet mishraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power Systems (Eceg-3176) : Addis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology (Aait)Document38 pagesIntroduction To Power Systems (Eceg-3176) : Addis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology (Aait)DANIEL ABERANo ratings yet
- Conduction and Breakdown in Liquid DielectricsDocument6 pagesConduction and Breakdown in Liquid DielectricsSanjid ElahiNo ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesDocument18 pagesGovernment Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesVK DNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.5-Determination of XD and XQ of Synchronous Machine by Slip TestDocument3 pagesExperiment No.5-Determination of XD and XQ of Synchronous Machine by Slip Test61EEPrabhat PalNo ratings yet
- ADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFDocument21 pagesADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFJk RinkuNo ratings yet
- EEL2026-LabsheetDocument23 pagesEEL2026-LabsheetchandraNo ratings yet
- Power SystemsDocument21 pagesPower Systemssamg27100% (1)
- Question Bank Ac MachinesDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank Ac Machinesashwin paulNo ratings yet
- AVG and RMS Values of Periodic Waveforms 2012Document5 pagesAVG and RMS Values of Periodic Waveforms 2012Ang Yu LongNo ratings yet
- Image ImpedanceDocument16 pagesImage ImpedanceErick Wangila WanyonyiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Laboratory V Course Code: Epo662: Simulation of Three-Phase Inverter With A PWM Control EPO662Document5 pagesElectrical Engineering Laboratory V Course Code: Epo662: Simulation of Three-Phase Inverter With A PWM Control EPO662Danial AkramNo ratings yet
- BSNL JTO Exam 2006 Question PaperDocument17 pagesBSNL JTO Exam 2006 Question PaperROHITCHOURASIYANo ratings yet
- EME Tutorial - 2 To 5Document5 pagesEME Tutorial - 2 To 5Aditya Gadgil100% (1)
- Asynchronous and Synchronous Machines (EL-208) (IV SEM EL Session 2017-18) Tutorial Sheet 1 (Dated 08.01.2018) (3 Phase Induction MotorsDocument10 pagesAsynchronous and Synchronous Machines (EL-208) (IV SEM EL Session 2017-18) Tutorial Sheet 1 (Dated 08.01.2018) (3 Phase Induction MotorsKushagra BhatiaNo ratings yet
- 47-Wavelet Based Power Quality Disturbances Analysis of BLDC Motor Drive PDFDocument10 pages47-Wavelet Based Power Quality Disturbances Analysis of BLDC Motor Drive PDFveerannaNo ratings yet
- System ModelingDocument64 pagesSystem ModelingShuvo ShahedNo ratings yet
- M Systems: ScilloscopesDocument6 pagesM Systems: ScilloscopesAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Practical ExamDocument2 pagesPractical ExamIrfan AliNo ratings yet
- Module3 Numericals ADocument11 pagesModule3 Numericals ASomil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Services Design Midsem - Docx AbDocument5 pagesServices Design Midsem - Docx AbMichael Adu-boahenNo ratings yet
- What Is The Use of Choke in Florescent TubesDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Use of Choke in Florescent Tubessumanta1981100% (2)
- Lab 13-Under Voltage and Over Voltage Monitoring Numerical RelayDocument5 pagesLab 13-Under Voltage and Over Voltage Monitoring Numerical RelayAliza Sharif100% (1)
- Unit 1 - How To Access The Portal: Assignment0Document4 pagesUnit 1 - How To Access The Portal: Assignment0Prasenjit DeyNo ratings yet
- Assignment Problems HVDCDocument2 pagesAssignment Problems HVDCSelva KumarNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics 2 MarkDocument5 pagesPower Electronics 2 MarkPrakash Mahendran100% (2)
- A Report On The "3-Phase Line Fault Detector" Ee344 Minor Project - IDocument34 pagesA Report On The "3-Phase Line Fault Detector" Ee344 Minor Project - IDhruv PatelNo ratings yet
- Assignment TX LineDocument3 pagesAssignment TX LineMynam Meghana0% (1)
- ExamAut LWD2022BDocument6 pagesExamAut LWD2022BAyman100% (1)
- Ec8361-Adc Lab ManualDocument118 pagesEc8361-Adc Lab ManualmuminthajNo ratings yet
- 6.question Bank: Unit-I Part A QuestionsDocument10 pages6.question Bank: Unit-I Part A Questionsbashyam88No ratings yet
- Electrical Machines I Lab Twisted QuestionsDocument4 pagesElectrical Machines I Lab Twisted QuestionsPranav MenonNo ratings yet
- Feedback Amplifiers-EDC PDFDocument45 pagesFeedback Amplifiers-EDC PDFanjanaNo ratings yet
- Experiment# 10: Measure The Power and Power Factor by Three Ammeter MethodDocument10 pagesExperiment# 10: Measure The Power and Power Factor by Three Ammeter MethodFarwa MunirNo ratings yet
- Part - 3Document9 pagesPart - 3Keerthee MadhuriNo ratings yet
- RACTIFIERDocument19 pagesRACTIFIERDhananjay Aghara100% (1)
- Sheet 3Document3 pagesSheet 3geo_bi100% (1)
- Exp No. 1 Translines and AntennasDocument10 pagesExp No. 1 Translines and AntennasShairelle Anne Nunez FebrerNo ratings yet
- Lec # 021 Thermal Time ConstantDocument16 pagesLec # 021 Thermal Time ConstantAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Lab Div. B Tryout Test PDFDocument6 pagesCircuit Lab Div. B Tryout Test PDFMadhavi VangipurapuNo ratings yet
- ECE 424 - Assign3Document2 pagesECE 424 - Assign3Amos Atandi0% (1)
- MCQs Question Bank Basic Electrical Engineering AKTUDocument13 pagesMCQs Question Bank Basic Electrical Engineering AKTURaj ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Publication 1 19208 6043Document13 pagesPublication 1 19208 6043Stephen Velasco Villaruz0% (1)
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsFrom EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 1Document3 pagesExperiment No 1Mohsin Iqbal Department of Electrical Engineering100% (1)
- 3 EXPERIMENtDocument2 pages3 EXPERIMENtSumithNo ratings yet
- Ieee C57.12.30 - 2020Document28 pagesIeee C57.12.30 - 2020Anand SinghNo ratings yet
- Cables and WiresDocument124 pagesCables and WiresAlbertNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document28 pagesUnit 4Anand SinghNo ratings yet
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument30 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationAnand Singh100% (1)
- Soil Thermal Resistivity PaperDocument15 pagesSoil Thermal Resistivity PaperAnand SinghNo ratings yet
- IEEE STD 1277-2020Document90 pagesIEEE STD 1277-2020Anand SinghNo ratings yet
- Ieee C57.12.31 - 2020Document24 pagesIeee C57.12.31 - 2020Anand SinghNo ratings yet
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument30 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationAnand Singh100% (1)
- Al59 ConductorsDocument1 pageAl59 ConductorsAnand SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document28 pagesUnit 4Anand SinghNo ratings yet
- 08ABB860 Glossary 2010 EngDocument52 pages08ABB860 Glossary 2010 EngKuldip SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document28 pagesUnit 4Anand SinghNo ratings yet
- Bhel Haridwar Vocational Training ReportDocument35 pagesBhel Haridwar Vocational Training ReportPalak AriwalaNo ratings yet
- Measurement of The DC Current WithDocument2 pagesMeasurement of The DC Current WithAnand SinghNo ratings yet
- ABB Scheda - Tecnica - PVS980 - 0 - INVERTER 2MW PDFDocument6 pagesABB Scheda - Tecnica - PVS980 - 0 - INVERTER 2MW PDFbacuoc.nguyen356No ratings yet
- Accreditation DAkkS 2015-10-30Document9 pagesAccreditation DAkkS 2015-10-30Anand SinghNo ratings yet
- ANSI Codes PDFDocument3 pagesANSI Codes PDFelectrical_1012000100% (2)
- Unloading, Handling, Storage of Cables (Compatibility Mode)Document31 pagesUnloading, Handling, Storage of Cables (Compatibility Mode)Anand SinghNo ratings yet
- CRN 1915187151Document3 pagesCRN 1915187151Anand SinghNo ratings yet
- A Report On Design Estimation of 1MW Sol PDFDocument34 pagesA Report On Design Estimation of 1MW Sol PDFAnand SinghNo ratings yet
- Protecciones Contenidas Transformadores de PotenciaDocument45 pagesProtecciones Contenidas Transformadores de PotenciaRoh OJNo ratings yet
- Ola Share 1024662243Document3 pagesOla Share 1024662243Anand SinghNo ratings yet
- Is 1554 1 1988Document26 pagesIs 1554 1 1988karthikraja21No ratings yet
- Economic Survey 2016 - Volume IDocument162 pagesEconomic Survey 2016 - Volume Iaveshansari786No ratings yet
- Cable Laying SpecificationDocument16 pagesCable Laying SpecificationdavidgarciavazquezNo ratings yet
- Ferro ResonanceDocument67 pagesFerro ResonanceAnand SinghNo ratings yet
- ANSI Device NumbersDocument7 pagesANSI Device Numbersrajpre1213No ratings yet
- DTC Bus Pass Form PDFDocument2 pagesDTC Bus Pass Form PDF5No ratings yet
- Feb 2017 CA EnglishDocument86 pagesFeb 2017 CA EnglishGeethu RaviNo ratings yet