Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circuit Theory 2 Activity 1
Uploaded by
John Mark CarpioOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circuit Theory 2 Activity 1
Uploaded by
John Mark CarpioCopyright:
Available Formats
Circuit Theory 2 Activity 1
Circuit Theory 2
1 SINOSOIDS AND PHASORS
Activities:
1. Discuss and Explain the following:
a. Instantaneous value
b. Peak amplitude
c. Period (T)
d. Cycle
e. Frequency
f. Why do we use sinosoids in representing alternating current?
g. Sinosoids
h. Parts of a sinosoids
i. Periodic Function
j. How to compare sinosoids?
k. Impedance
l. Admittance
m. Why Inductor is SHORT CIRCUIT at DC and OPEN CIRCUIT at high frequencies?
n. Why Capacitor is OPEN CIRCUIT at DC and SHORT CIRCUIT at high frequencies?
2. Answer the following:
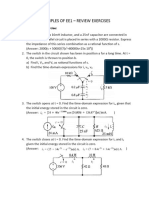
a. Find the amplitude, phase, period, and frequency of the sinusoid :v(t) = 12 cos(50t +
10)
b. Given the sinusoid 5 sin(4t 60), calculate its amplitude, phase, angular frequency,
period, and frequency.
c. Calculate the phase angle between v1 = 10 cos(t + 50) and v2 = 12 sin(t 10).
State which sinusoid is leading.
d. Find the phase angle between i1 = 4 sin(377t + 25) and i2 = 5 cos(377t 40) . Does
i1 lead or lag i2?
e. Evaluate:
i.
ii.
f. Transform to phasor:
i.
ii.
g. Transfor the following phasors to its corresponding sinusoids in time domain/frequency
domain
i.
ii.
h.
CIRCUIT THEORY 2 ACTIVITY 1 | Midterm
Circuit Theory 2 Activity 1
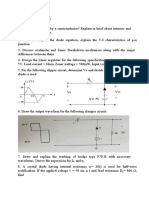
3. Find the voltage v(t) in a circuit described by the integrodifferential equation using the phasor
approach.
4. If voltage v = 6 cos(100t -30o) is applied to a 50 F capacitor, calculate the current through the
capacitor.
5. Determine v(t) and i(t).
6. Determine the input impedance of the circuit at = 10 rad/s.
7. Calculate vo in the circuit.
8. Find I in the circuit
9. What value of will cause the forced response vo in the circuit to be zero?
CIRCUIT THEORY 2 ACTIVITY 1 | Midterm
Circuit Theory 2 Activity 1
10. If is = 5 cos (10t + 40) A in the circuit in the circuit, find io.
11. Find Z in the network, given that Vo = 40 V
12. For the circuit, calculate ZT and Vab.
13. (a) Calculate the phase shift of the circuit.
(b) State whether the phase shift is leading or lagging.
(c) Determine the magnitude of the output when the input is 120 V.
14. An industrial coil is modeled as a series combination of an inductance L and resistance R, as
shown in Figure below. Since an ac voltmeter measures only the magnitude of a sinusoid, the
following measurements are taken at 60 Hz when the circuit operates in the steady state:
Vs 145V,
V1 50V,
Vo 110V
Use these measurements to determine the values of L and R.
Deliverables:
1. Answer sheets
Timeline:
1. 3 hours only
CIRCUIT THEORY 2 ACTIVITY 1 | Midterm
You might also like
- AC CircuitsDocument15 pagesAC CircuitsAlbert Tuazon92% (38)
- Ustp Student Handbook 28nov2018 FinalDocument76 pagesUstp Student Handbook 28nov2018 FinalJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit AnalysisDocument12 pagesElectric Circuit AnalysisMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- GSD 2241 Planting Systems Lecture Michael Flynn XuevxiDocument159 pagesGSD 2241 Planting Systems Lecture Michael Flynn XuevxiJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- PDC Assignment IDocument4 pagesPDC Assignment IathomeNo ratings yet
- Electronics RefresherDocument2 pagesElectronics RefresherPaolo Steven PolintanNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits and Electron Devices Unit I Circuit Analysis Techniques Part-ADocument8 pagesElectric Circuits and Electron Devices Unit I Circuit Analysis Techniques Part-ASalai Kishwar JahanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument12 pagesElectronic Devices and CircuitsAnandhi SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Unit: 4 (Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents)Document16 pagesUnit: 4 (Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents)Tuition MasterNo ratings yet
- Satyam College of Engineering and Technology, Aralvoimozhi Ece Iv-Semester Revision Questions Electronic Circuits Ii 2 Mark Questions Revision IDocument4 pagesSatyam College of Engineering and Technology, Aralvoimozhi Ece Iv-Semester Revision Questions Electronic Circuits Ii 2 Mark Questions Revision ISaranya MohanNo ratings yet
- PDC 1Document3 pagesPDC 1Sravya LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 QuestionsDocument5 pagesTutorial 4 QuestionsRobert Jackson100% (1)
- Lecture 5 and 6 Mist SpecialDocument26 pagesLecture 5 and 6 Mist SpecialGaffar KhanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet Analog ElectronicsDocument7 pagesTutorial Sheet Analog ElectronicsPraney KalraNo ratings yet
- A 2Document2 pagesA 2Rohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitsDocument26 pagesAC Circuitskaushik247No ratings yet
- 4 Ece - 15.4.13 (Mod)Document2 pages4 Ece - 15.4.13 (Mod)BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Kee-101 TutDocument2 pagesKee-101 TutsanidhyaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Problems 2012Document10 pagesCircuit Problems 2012Jamie HeredgeNo ratings yet
- 4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetDocument19 pages4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetmntykrNo ratings yet
- Assign Single Phase Ac-2 (Unit-2)Document4 pagesAssign Single Phase Ac-2 (Unit-2)Sunil JainNo ratings yet
- EE1 Review ExercisesDocument3 pagesEE1 Review ExercisesThanh TongNo ratings yet
- CircuitsII SH1Document4 pagesCircuitsII SH1aymanabuzNo ratings yet
- Ec Lab ExperimentDocument10 pagesEc Lab ExperimentMarhmello PadriqueNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Practice QuestionsDocument19 pagesAnalog Electronics Practice Questionssharma_rockstarNo ratings yet
- Short Answer Questions2 Pluse and Digital CircuitsDocument13 pagesShort Answer Questions2 Pluse and Digital CircuitsRAJNo ratings yet
- ECA CAT SolutionsDocument21 pagesECA CAT SolutionsAdan BagajaNo ratings yet
- Ec IiDocument1 pageEc IisramkmNo ratings yet
- AP Physc em Inductance Free Response Problems 2015-04-09Document12 pagesAP Physc em Inductance Free Response Problems 2015-04-09Alex2345660No ratings yet
- Ch7-Response of First-Order RL and RC CircuitsDocument34 pagesCh7-Response of First-Order RL and RC CircuitsFakrul HanifNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitsDocument48 pagesAC Circuitswocaja8645No ratings yet
- Astable Multivibrator: Non Linear Applications:-A) Astable Multivibrator B) Mono Stable MultivibratorDocument15 pagesAstable Multivibrator: Non Linear Applications:-A) Astable Multivibrator B) Mono Stable MultivibratorFarhan AkhterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Exercise AnswersDocument14 pagesChapter 3 Exercise AnswersHenok DerejeNo ratings yet
- Lab #2 CNET219: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesLab #2 CNET219: Objectivesliam butlerNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 2Document7 pagesExperiment No 2Mohsin TariqNo ratings yet
- Electric NoteDocument6 pagesElectric NoteKucing GemukNo ratings yet
- 120EI0884 - SamyakHinge CSL Lab RecordDocument51 pages120EI0884 - SamyakHinge CSL Lab Recordpappu singhNo ratings yet
- Pulse and Digital Circuits QuestionsDocument14 pagesPulse and Digital Circuits QuestionsKunal BatraNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis and Synthesis QBDocument11 pagesNetwork Analysis and Synthesis QBGowthamNo ratings yet
- Electronics AssignmentsDocument7 pagesElectronics AssignmentsSoumyaranjan PandaNo ratings yet
- Series RLC Circuits: Learning ObjectiveDocument18 pagesSeries RLC Circuits: Learning Objectiveandrew smithNo ratings yet
- Analog 01 Lab Exp 08 FullDocument6 pagesAnalog 01 Lab Exp 08 FullShuvro Sankar SenNo ratings yet
- Principle of Electronics EnggDocument47 pagesPrinciple of Electronics EnggNilabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis ManualDocument68 pagesNetwork Analysis ManualRana Zeeshan AfzalNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Module 1Document2 pagesAssignment-Module 1الجيش اليمنى الالكترونى YemenNo ratings yet
- Module-Wise Eln QBDocument5 pagesModule-Wise Eln QBRashmi SamantNo ratings yet
- Electronic Instrument atDocument8 pagesElectronic Instrument atkushalchandel0% (1)
- Practice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits: Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pagesPractice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits: Multiple Choiceapi-127299018No ratings yet
- Online Course Analog CircuitsDocument4 pagesOnline Course Analog CircuitsJoyce GeorgeNo ratings yet
- 電子學 (一) 許恒壽Document12 pages電子學 (一) 許恒壽qw3rtytr3wqNo ratings yet
- Part B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisDocument4 pagesPart B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisAnonymous Ndsvh2soNo ratings yet
- Question Bank AECDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank AECChandra SekharNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Ac XiiDocument4 pagesWorksheet Ac XiiYug GandhiNo ratings yet
- Ecx3210 Tma2 2010 PDFDocument2 pagesEcx3210 Tma2 2010 PDFThamara Dananjaya GunarathnaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank of Network Analysis and Synthesis UNIT-1 and UNIT-2Document9 pagesQuestion Bank of Network Analysis and Synthesis UNIT-1 and UNIT-2PrakharGupta100% (1)
- Elec102P Part I: Problem Sheet 3: C V DT DV R DT V D LDocument2 pagesElec102P Part I: Problem Sheet 3: C V DT DV R DT V D Lprofitmaker_2No ratings yet
- Anallysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits QuestionsDocument5 pagesAnallysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits QuestionsshankarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document24 pagesChapter 15Beverly PamanNo ratings yet
- Eneral Eceptacle Pacing: 2016 California Electrical Code Sections 210.52 (A) & 210.60Document2 pagesEneral Eceptacle Pacing: 2016 California Electrical Code Sections 210.52 (A) & 210.60John Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- (Estrera Final Papers) YAHOODocument95 pages(Estrera Final Papers) YAHOOJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Summary PDFDocument5 pagesChapter 8 Summary PDFJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Vertical Wind Turbine at Gusa Coastal RoadDocument31 pagesDesign and Implementation of Vertical Wind Turbine at Gusa Coastal RoadJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- Schedule of LoadsDocument4 pagesSchedule of LoadsJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report Elections IIEE CSC USTPDocument1 pageAccomplishment Report Elections IIEE CSC USTPJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - EcosystemDocument28 pagesLesson 2 - EcosystemJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- Shyn Marie Mijares House Plan Schedule of LoadsDocument4 pagesShyn Marie Mijares House Plan Schedule of LoadsJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- K 12 Grade 11 Practical Research: Second Semester 80 Hours/semDocument40 pagesK 12 Grade 11 Practical Research: Second Semester 80 Hours/semJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- University of Science and Technology of Southern PhilippinesDocument2 pagesUniversity of Science and Technology of Southern PhilippinesJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- Enhancement of The Automatic Controls of A Stand-Alone Small Scale Indoor Hydroponics SystemDocument14 pagesEnhancement of The Automatic Controls of A Stand-Alone Small Scale Indoor Hydroponics SystemJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- Template 001 - Header & FooterDocument1 pageTemplate 001 - Header & FooterJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- Application Letter PDFDocument1 pageApplication Letter PDFJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- Institute of Integrated Electrical Engineers-Council of Student Chapters USTPDocument5 pagesInstitute of Integrated Electrical Engineers-Council of Student Chapters USTPJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- John Mark A. Carpio Industrial Electronics Bsee-4A JANUARY 9, 2018Document14 pagesJohn Mark A. Carpio Industrial Electronics Bsee-4A JANUARY 9, 2018John Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- The Philippines' Largest Vertically Integrated Geothermal CompanyDocument3 pagesThe Philippines' Largest Vertically Integrated Geothermal CompanyJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- Institute of Integrated Electrical Engineers-Council of Student Chapters USTPDocument5 pagesInstitute of Integrated Electrical Engineers-Council of Student Chapters USTPJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- Incident Report Form: Personal InformationDocument1 pageIncident Report Form: Personal InformationJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- Recomendation LetterDocument1 pageRecomendation LetterJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- I Nterested? Gusto KA?: +63 XXX XXX XXXXDocument1 pageI Nterested? Gusto KA?: +63 XXX XXX XXXXJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- Ieee Journal SolarDocument12 pagesIeee Journal SolarJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- Ieee Journal SolarDocument12 pagesIeee Journal SolarJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet
- For USTP VENUEDocument2 pagesFor USTP VENUEJohn Mark CarpioNo ratings yet