Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HW1
Uploaded by
priyadarshini2120070 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
122 views2 pagesProblem related to Electrical Engineering
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentProblem related to Electrical Engineering
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
122 views2 pagesHW1
Uploaded by
priyadarshini212007Problem related to Electrical Engineering
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
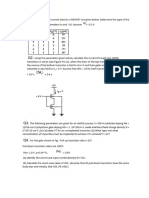
1.
Show that the current through two transistors in series is equal to the current
through a single transistor of twice the length if the transistors are well described
by the Chockley model. Specifically, show that IDS1 = IDS2 in Fig. 1 when the
transistors are in their linear region: VDS < VDD-Vt, VDD > Vt (this is also true in
saturation).
2. A 90 nm long transistor has a gate oxide thickness of 16 A. What is the gate
capacitance per micron of width?
3. Consider the nMOS transistor in a 0.6 um process with gate oxide thickness of
100 A. The doping level is NA = 2.10-3 cm-3 and the nominal threshold voltage is is
0.7 V. The body effect is tied to ground with a substrate contact. How much does
the threshold change at room temperature if the source is at 4 V instead of 0?
4. Find the threshold leakage current of an inverter at room temperature if the input
A = 0. Let n= 2 p = 1mA/V2, n = 1.0, and Vt = 0.4 V. Assume the body effect
and DIBL coefficients are = = 0.
5. An nMOS transistor has a threshold voltage of 0.4 V and a supply voltage of
VDD = 1.2 V. A circuit designer is evaluating a proposal to reduce Vt by 100 mV
to obtain faster transistors.
a) By what factor would the saturation current increase (at Vgs = Vds = VDD) if
the transistors were ideal?
b) By what factor would the subthreshold leakage current increase at room
temperature at Vgs = 0? Assume n = 1.4.
c) By what factor would the subthreshold leakage current increase at 120 C?
Assume the threshold voltage is independent of temperature.
You might also like
- Chapter 2 MOS Transistor TheoryDocument1 pageChapter 2 MOS Transistor TheoryCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Vlsi HW 3Document2 pagesVlsi HW 3Tâm LưuNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Mos Transistor: GS DSDocument2 pagesMos Transistor: GS DSHimanshu SahuNo ratings yet
- EC238 Electronics I: MOSFET DC and BiasingDocument9 pagesEC238 Electronics I: MOSFET DC and BiasingSara El-GendyNo ratings yet
- Electronic HomeworkDocument2 pagesElectronic HomeworkDeniz SummerNo ratings yet
- Elektronik OdevDocument2 pagesElektronik OdevMehmet YıldırımNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Questions-2Document8 pagesVlsi Questions-2Chinu SoodNo ratings yet
- Mosfet TheoreticalexerciseDocument3 pagesMosfet TheoreticalexercisebrettyNo ratings yet
- ExcersisesDocument19 pagesExcersisesLÊ QUANG BÁ LĨNHNo ratings yet
- ARF Current MirrorDocument11 pagesARF Current MirrorJk WorldNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Question Paper 2Document3 pagesVlsi Question Paper 2Chinu SoodNo ratings yet
- Sem 3 Module 1Document3 pagesSem 3 Module 1fczeroNo ratings yet
- Differential Amplifiers Problems of MOS - 1Document5 pagesDifferential Amplifiers Problems of MOS - 1lokeshwarrvrjcNo ratings yet
- Tut1 - KKM - EC 2001Document1 pageTut1 - KKM - EC 2001Gaurav Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- 博士班資格考 電子學題庫Document15 pages博士班資格考 電子學題庫Adil KhanNo ratings yet
- EE301-Fall 2016: Laboratory #6: MOS TRANSISTORSDocument3 pagesEE301-Fall 2016: Laboratory #6: MOS TRANSISTORSOrhunNo ratings yet
- VLSI DevicesDocument38 pagesVLSI DevicesPranav DarganNo ratings yet
- The Cmos Inverter: Slides Adapted From: N. Weste, D. Harris, CMOS VLSI Design,, 3/e, 2004Document40 pagesThe Cmos Inverter: Slides Adapted From: N. Weste, D. Harris, CMOS VLSI Design,, 3/e, 2004SrasVelNo ratings yet
- VLSI DESIGN: MOS TRANSISTORDocument162 pagesVLSI DESIGN: MOS TRANSISTORBasheer V.PNo ratings yet
- Edc MCQDocument5 pagesEdc MCQRajesh PathakNo ratings yet
- TalkDocument27 pagesTalksonsfhsdlfhsadhNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 5Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 5Shashank SinghNo ratings yet
- Mos Transistor TheoryDocument144 pagesMos Transistor TheorymailtolokiNo ratings yet
- Ec3058D-Vlsi Circuits and Systems Winter Semester-2020-21: DD Ton TopDocument2 pagesEc3058D-Vlsi Circuits and Systems Winter Semester-2020-21: DD Ton TopGamer AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet - 2Document1 pageTutorial Sheet - 2Akshay GoelNo ratings yet
- SheetDocument3 pagesSheetb5fc94cdd3No ratings yet
- Week1 VLSI Subsystems assignment answersDocument5 pagesWeek1 VLSI Subsystems assignment answersGPS INNOVATIVESNo ratings yet
- DE LA SALLE UNIVERSITY EXAM REVIEWDocument6 pagesDE LA SALLE UNIVERSITY EXAM REVIEWSahara MalabananNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Electronics Devices AssignmentDocument5 pagesMOSFET Electronics Devices AssignmentShaheer ShahzadNo ratings yet
- HW 5 S 22Document1 pageHW 5 S 22BobNo ratings yet
- EE 3313: Device Modelling Tutorial 7: N Ox - 4 2 BDocument1 pageEE 3313: Device Modelling Tutorial 7: N Ox - 4 2 BRahul VasanthNo ratings yet
- EC101 BECE - Question BankDocument21 pagesEC101 BECE - Question Bankdarkhuntert9No ratings yet
- Tut2 KKM EC2001Document2 pagesTut2 KKM EC2001Gaurav Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Transistor characteristics and exercisesDocument1 pageTransistor characteristics and exercisesCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Assignment 1 SolvedDocument17 pagesVlsi Assignment 1 SolvedNilesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 352 - 17385 - EC538 - 2013 - 4 - 1 - 1 - Problem Set 1 - V2Document3 pages352 - 17385 - EC538 - 2013 - 4 - 1 - 1 - Problem Set 1 - V2simoNo ratings yet
- PSE_9e_Ch_27Document7 pagesPSE_9e_Ch_27M ANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MOS Transistor TheoryDocument25 pagesChapter 2 MOS Transistor TheoryrasheeenNo ratings yet
- DiodeDocument6 pagesDiodepetrishia7_317164251No ratings yet
- No 2 Power DissipationDocument28 pagesNo 2 Power DissipationHasanAlBannaBhuiyanNo ratings yet
- ENGG*3450 Lab Manual MOSFET CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesENGG*3450 Lab Manual MOSFET Characteristicsdlat94No ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Tutorial 1Document3 pagesAnalog Electronics Tutorial 1mbathulaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Tutorial 2Document4 pagesBasic Electronics Tutorial 2Susheel SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document4 pagesSheet 1MohamedAlyNo ratings yet
- Cat 1 Review& e MosfetDocument43 pagesCat 1 Review& e Mosfetdocs miNo ratings yet
- Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetDocument2 pagesMicroelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetBobNo ratings yet
- CompreDocument8 pagesCompref20202001No ratings yet
- 08ece Ee331 Group 6 Le Van Hai Lab3Document19 pages08ece Ee331 Group 6 Le Van Hai Lab3Quốc HiếuNo ratings yet
- Irfb3306Pbf Irfs3306Pbf Irfsl3306Pbf: V 60V R Typ. 3.3M: Max. 4.2M: I 160ADocument11 pagesIrfb3306Pbf Irfs3306Pbf Irfsl3306Pbf: V 60V R Typ. 3.3M: Max. 4.2M: I 160AalvarezsilvaNo ratings yet
- Revisit: Resistance and Capacitance MOSFET Model For Digital CircuitsDocument33 pagesRevisit: Resistance and Capacitance MOSFET Model For Digital Circuitsdilshan singhNo ratings yet
- Mosfet Lab 1Document11 pagesMosfet Lab 1Pramod SnkrNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01Document6 pagesAssignment 01Z S PlaysNo ratings yet
- Mosfet Lab 2Document11 pagesMosfet Lab 2Jaime Aguilar100% (1)
- Fully Integrated Charge Pump Without Oxide BreakdownDocument4 pagesFully Integrated Charge Pump Without Oxide BreakdownJeffrey LiuNo ratings yet
- Power Analysis: Prof. Jagannadha Naidu KDocument23 pagesPower Analysis: Prof. Jagannadha Naidu KParth VijayNo ratings yet
- Experiment No1 Electronics and DevicesDocument6 pagesExperiment No1 Electronics and DevicesRosh SibalNo ratings yet
- Four-input NAND gate design using two-input NAND gatesDocument14 pagesFour-input NAND gate design using two-input NAND gatesarammartNo ratings yet
- Milletssiridhanya Book c2b7 Version 1Document29 pagesMilletssiridhanya Book c2b7 Version 1lakshmiescribd94% (36)
- Harur JM Court ComplexDocument2 pagesHarur JM Court Complexpriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- RDDocument11 pagesRDSundeep GargNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - HW4 ECE427 SolnDocument9 pagesMathcad - HW4 ECE427 Solnpriyadarshini21200733% (3)
- HK4Document2 pagesHK4priyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- Probability Distribution of a Random Variable ExplainedDocument38 pagesProbability Distribution of a Random Variable Explainedpriyadarshini2120070% (1)
- MIT3 024S13 2012lec17 PDFDocument10 pagesMIT3 024S13 2012lec17 PDFliaNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Home Work # 1: 3-14C Convection Heat Transfer Through The Wall Is Expressed AsDocument6 pagesSolutions To Home Work # 1: 3-14C Convection Heat Transfer Through The Wall Is Expressed Aspriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- Exercises Ch.33 Ch.34Document2 pagesExercises Ch.33 Ch.34priyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- Qip Ice 04 Operating ParametersDocument32 pagesQip Ice 04 Operating ParametersKuppu RajNo ratings yet
- Accounting Fraud: Learning from Past WrongsDocument4 pagesAccounting Fraud: Learning from Past Wrongspriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- 1 Evaluate The Potential of The Internet of Things Within Your Own DwellingDocument2 pages1 Evaluate The Potential of The Internet of Things Within Your Own Dwellingpriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- DSC Management Utility User ManualDocument22 pagesDSC Management Utility User ManualTomNo ratings yet
- Oscillator Types and CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesOscillator Types and Characteristicspriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- Probability Distribution of a Random Variable ExplainedDocument38 pagesProbability Distribution of a Random Variable Explainedpriyadarshini2120070% (1)
- CSC 125 Final Part I & IIDocument2 pagesCSC 125 Final Part I & IIpriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- A Typology of Actions To Tackle Social Inequalities in HealthDocument6 pagesA Typology of Actions To Tackle Social Inequalities in Healthpriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- 2 Os-Prob-SetDocument7 pages2 Os-Prob-Setpriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- 2 - MT - PSmarkup 374144 389528 1 TM TM MF Chapter 3 - Methodology RevisedDocument26 pages2 - MT - PSmarkup 374144 389528 1 TM TM MF Chapter 3 - Methodology Revisedpriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - SideheadingsDocument2 pagesChapter 3 - Sideheadingspriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- 345 S 02 P 4Document11 pages345 S 02 P 4khalidh2010No ratings yet
- L3 ED FBR Project Proposal Guidance and Template v2Document7 pagesL3 ED FBR Project Proposal Guidance and Template v2priyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- DesignDocument3 pagesDesignpriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- Chap 10.2 PracticeDocument2 pagesChap 10.2 Practicepriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- Case Study Edith Cowan University PDFDocument7 pagesCase Study Edith Cowan University PDFSher KhanNo ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis of Forced Harmonic OscillationDocument19 pagesVibration Analysis of Forced Harmonic OscillationRakesh BhaskerNo ratings yet
- Answers Units 6,7,8 Delmars Standard Textbook of ElectricityDocument3 pagesAnswers Units 6,7,8 Delmars Standard Textbook of ElectricityGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- Answers Units 6,7,8 Delmars Standard Textbook of ElectricityDocument3 pagesAnswers Units 6,7,8 Delmars Standard Textbook of ElectricityGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- BSc (Hons) Financial Services (General) Exam QuestionsDocument8 pagesBSc (Hons) Financial Services (General) Exam Questionspriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- Problem 1: CS 103 Homework 2 Solutions Spring 2013-14Document6 pagesProblem 1: CS 103 Homework 2 Solutions Spring 2013-14priyadarshini212007No ratings yet