Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Evaluation
Uploaded by
Yani Jane CosteloCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Evaluation
Uploaded by
Yani Jane CosteloCopyright:
Available Formats
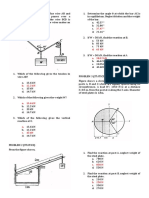
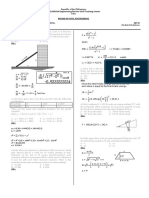
Situation 1: The homogeneous bar AB weighs 400 lb.
End B Situation 2: From the given figure, the mass of the block is 200
leans against a vertical wall and end A is supported by a ball- kg and the coefficient of static friction in all contact surfaces is
and-socket joint. 0.40.
200 kg
12˚
P
4. Determine the reaction between the wall and the block if it
is raised due to P.
A. 1794 N C. 1932 N *
B. 1036 N D. 1116 N
1. Determine the tension in Cable BC.
5. Determine the reaction between the wedge and the block.
A. 126.4 lb * C. 134.1 lb
A. 2994 N C. 3225 N *
B. 343.3 lb D. 829.8 lb
B. 1729 N D. 1862 N
2. Determine the wall reaction at B.
6. Determine the value of the horizontal force P.
A. 34.02 lb C. 164.2 lb *
A. 2866 N * C. 2680 N
B. 159.5 lb D. 257.9 lb
B. 1655 N D. 2886 N
3. Determine the total reaction at A.
Solution:
A. 390.4 lb * C. 376.4 lb
B. 387.0 lb D. 763.7 lb
0.40 N1 1962 N
Solution:
0.40 N2 (sin12º)
N1
TBC sin30º
TBC
0.40 N2
RB 0.40 N2 (cos12º)
N2 (sin12º)
12˚
TBC cos30º
N2 (cos12º) N2
E Using the Figure above:
AX
ΣFH = 0]
400 lb N1 – 0.40 N 2 ( cos12º ) - N 2 ( sin12º ) = 0
N1 – 0.599 N 2 = 0 → equation 1
AY
D
AZ ΣFV = 0]
Calculating for the value of TBC :
-0.40 N1 + N 2 ( cos12º ) – 0.40 N 2 ( sin12º ) – 1962 = 0
ΣM AE = 0] TBC sin30º ( 4 ) + TBC cos30º ( 5 ) – 400 ( 2 ) = 0
-0.40 N1 + 0.895 N 2 = 1962 → equation 2
TBC = 126.38 lb → answer
Solving the two equations:
Calculating for the value of R B :
N1 = 1,793.91 lb N 2 = 2,993.98 lb
ΣM AD = 0] (126.38 ) sin30º ( 6 ) + R B ( 5 ) – 400 ( 3) = 0
R B = 164.17 lb → answer Calculating for the reaction between the wall and the block:
R1 = 1793.912 + 0.4 (1793.91)
2
Calculating for the reaction at A
R1 = 1,932.10 N → answer
F x = 0: A x - 126.38 cos30o = 0 → A x = 109.45 lb
F y = 0: 164.17 - A y = 0 → A y = 164.17 lb
Calculating for the reaction between the wedge and the block:
F z = 0: 126.38 sin30o - 400 - A z = 0 → A z = 336.81 lb
R 2 = 2993.982 + 0.4 ( 2993.98 )
2
R A = 109.452 + 164.17 2 + 336.812
R 2 = 3,224.62 N → answer
R A = 390.35 lb → answer
N2 = 2,993.98 N 2,993.98 cos12º RB
2,993.98 sin12º
1,197.59 cos12º Cx
0.40 N2 = 1,197.59 N 12˚
P
1,197.59 sin12º Cy RD
0.40 N3
N3
Using the free body diagram:
Using the Figure above: ΣM D = 0] 300 ( 60 ) + C y ( 250 ) - 480 (150 ) = 0
ΣFV = 0] N 3 + 1197.59 sin12º – 2993.98 cos12º = 0 C y = 216 N
N 3 = 2,679.56 N
80
ΣFH = 0] ΣFy = 0] 216 - 480 + R D =0
170
0.40 ( 2679.56 ) + 1197.59 cos12º + 2993.98 sin12º - P = 0 R D = 561 N → answer
P = 2,865.73 N → answer
150
Situation 3: In the frame shown, members ACE and BCD are ΣFx = 0] - C x + 300 + 561 =0
170
connected by a pin at C and by the link DE. For the loading
C x = 795 N
shown:
R C = Cx 2 + C y 2 = 7952 + 2162 = 823.82 N → answer
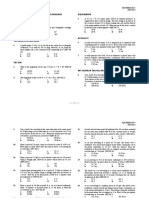
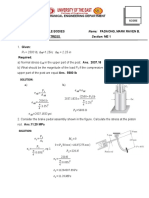
Situation 4: The force system shown consists of the couple C
and four forces. If the resultant of this system is a 500 lb-in.
counterclockwise couple, determine:
7. Determine the reaction at B.
A. 800 N C. 1200 N
B. 300 N * D. 480 N
8. Determine the force in link DE.
A. 264 N C. 495 N
B. 561 N * D. 216 N
9. Determine the reaction at C.
10. the value of P, in lb.
A. 216 N C. 824 N *
A. 200 * C. 260
B. 795 N D. 495 N
B. 130 D. 50
Solution:
11. the value of Q, in lb.
RAY A. 200 C. 260 *
B. 130 D. 50
RAX
12. The value of C, in lb-in.
A. 1440 * C. 852
B. 1944 D. 180
RB
Solution:
Using the given figure:
ΣM A = -500]
3 4
Using the free body diagram: -80 ( 4 ) + 20 ( 3) + C - P ( 6 ) - P ( 6 ) = -500
ΣM A = 0] 480 (100 ) - R B (160 ) = 0 5 5
42
R B = 300 N → answer C- P = -240 → equation 1
5
ΣM B = -500] 10000 lb
W
12 5
80 ( 2 ) - 20 ( 3) + C - Q ( 6 ) - Q ( 6 ) = -500
13 13 θB
B
102
C- Q = -600 → equation 2
13 H
To
ΣM O = -500]
12 3 x
80 ( 2 ) + 20 ( 3 ) + C - Q ( 6 ) - P ( 6 ) = -500
13 5
18 72 Using the free body diagram:
C- P- Q = -720 → equation 3
5 13 ΣFx = 0] 10000 cos ( 62.98 ) -T o =0
To = 4,542.84 lb → answer
Solving the three equations:
C = 1,440 lb-in → answer P = 200 lb → answer
Calculating for the value of x:
Q = 600 lb → answer
ΣFy = 0] 10000 sin ( 62.98 ) -W=0
Situation 5: The cable shown carries the uniformly distributed W = 8,908.57 lb
load w0 = 80 lb/ft, where the distance is measured along the W = w o ( x ) → 8,908.57 = 80 x
horizontal. If the cable tension does not exceed 10 000 lb, x = 111.36 ft 200 -x = 88.64 ft
Calculating for the value of H:
ΣM B = 0] 4,542.84 ( H ) - 8,908.57 ( 0.5 ) (111.36 ) = 0
H = 109.19 ft → answer
Calculating for the length of the cable:
2
w x
2
x2 111.36 80 x
S= 1 + o dx = 1 + dx
x1
To
-88.64
4542.84
S = 280.09 ft → answer
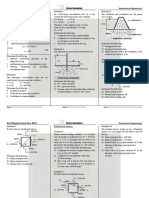
Situation 6: A truss is loaded as shown:
13. Determine the tension at the lowest point. `
A. 4543 lb * C. 7620 lb
B. 8909 lb D. 6476 lb
14. Determine the length of the shortest cable.
A. 253.1 ft C. 307.1 ft
B. 334.1 ft D. 280.1 ft *
15. Determine the corresponding vertical distance H.
A. 68.4 ft C. 109.2 ft *
B. 90.8 ft D. 131.6 ft
Solution:
10000 lb
80 (200)
θB
16. Determine the reaction at A.
A. 2000 lb C. 4472 lb *
B. 4000 lb D. 3236 lb
17. Determine the force in member FI.
A. 2500 lb (Compression) * C. 3610 lb (Compression)
B. 2500 lb (Tension) D. 3610 lb (Tension)
Using the free body diagram:
ΣM A = 0]
18. Determine the force in member JC.
10000 cosθ B ( 40 ) - 10000 sinθ B ( 200 ) + 80 ( 200 ) (100 ) = 0 A. 2500 lb (Compression) C. 3610 lb (Compression)
θ B = 62.98o B. 2500 lb (Tension) D. 3610 lb (Tension) *
Solution: Situation 7: As shown in the figure, a flexible cable which
supports the 100-kg load is passed over a fixed circular drum
and subjected to a force P to maintain equilibrium. The
coefficient of static friction μ between the cable and the fixed
drum is 0.30.
19. If α = 0, determine the maximum value which P may have
in order not to raise or lower the load.
Using the free body diagram: A. 2518 N C. 612 N
ΣM A = 0] 3000 ( 8 ) + 1000 (12) - PDE (18 ) = 0 B. 1572 N * D. 382 N
PDE = 2000 lb
20. If α = 0, determine the minimum value which P may have
in order not to raise or lower the load.
ΣFx = 0] A x - PDE = 0 → A x = PDE → A x = 2000 lb A. 2518 N C. 612 N *
B. 1572 N D. 382 N
ΣFy = 0] A y - 3000 - 1000 = 0 → A y = 4000 lb
21. For P = 500 N, determine the minimum value which the
angle α may have before the load begins to slip.
R A = A x 2 + A y 2 = 20002 + 40002 = 4,472.14 lb → answer A. 52.62º C. 128.72º
B. 38.72º * D. 142.62º
Solution:
Using the principle of belt friction:
T2
= eμsβ ; if α = 0, β = 90o = 0.5π
T1
Using section 1:
3 4
ΣM G = 0] -3000 ( 4 ) - PFI ( 4 ) - PFI ( 3) = 0
5 5 100 kg
PFI = -2500 lb = 2500 lb (compression) → answer Figure 1
Considering the 100 kg load will go down (Figure 1):
(100) (9.81)
= e(0.3) (0.5π) → P = 612.37 N
P
Using section 2: 100 kg
2 Figure 2
ΣFx = 0] 2000 - PJC =0
13 Considering the 100 kg load will go up (Figure 2):
PJC = 3610 lb (tension) → answer P
= e(0.3) (0.5π) → P = 1,571.54 N
(100) (9.81)
Based from the above calculations: Solution:
612.37 N P 1,571.54 N
Pmin = 612.37 N → answer 200 mm
Pmax = 1,571.54 N → answer
TU
α
α
300 mm
P = 500 N
90°
θ
540 N θ 540 N
100 kg TL 300 mm
Figure 3
Considering the 100 kg load will go down (Figure 3):
(100) (9.81)
= e(0.3) β → β = 2.247 radians Calculating for the angle:
500 300
180o tanθ = → θ = 56.31o
β = 2.247 radians = 128.72
o 200
π radians
α = 128.72o - 90o = 38.72o → answer Calculating the force exerted on the right arm:
FR = 540 N → answer
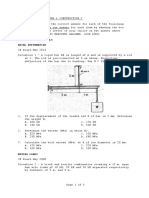
Situation 8: The figure below shows the archer aiming to
release the arrow. As the archer pulls the cord with his right
Considering the joint on the right hand:
arm, he applies a force of 540 N with his left arm.
F V = 0: TU sin(56.31o ) - TL sin(56.31o ) = 0
Given: a = 200 mm TU = TL
b = 300 mm
F H = 0: TU cos(56.31o ) + TL cos(56.31o ) - 540 = 0
c = 300 mm
but TU = TL :
a
TU cos(56.31o ) + TU cos(56.31o ) - 540 = 0
TU = TL = 486.75 N → answer
22. Calculate the resulting tension in the upper cord, in N.
A. 309 C. 270
B. 487 * D. 556
23. Calculate the resulting tension in the lower cord, in N.
A. 487 * C. 270
B. 556 D. 309
24. How much force (N) does the archer exert with his right
arm?
A. 540 * C. 270
B. 259 D. 518
You might also like
- Preboard 2 SECDocument14 pagesPreboard 2 SECJae Han100% (1)
- Engineering MechanicsDocument4 pagesEngineering MechanicsDonna MelgarNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument17 pagesProblemsMugiwara SparrowNo ratings yet
- Week 5 6 Problem SetDocument3 pagesWeek 5 6 Problem SetFidel LansanganNo ratings yet
- Preboard Problems FinalDocument5 pagesPreboard Problems FinalAngel MarkNo ratings yet
- Design PreboardDocument9 pagesDesign PreboardReinyl Angelo Cruz100% (1)
- CE Board Problems in PhysicsDocument4 pagesCE Board Problems in PhysicsGinto Aquino50% (4)
- CE Board Nov 2021 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 5Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2021 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 5Lemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Steel 3Document3 pagesSteel 3Mayya Bona100% (1)
- Final Preboard Design 2021Document2 pagesFinal Preboard Design 2021Vic NairaNo ratings yet
- Conc 1 - Nov 2020Document2 pagesConc 1 - Nov 2020Glenn CalingasanNo ratings yet
- Mata Deseree Plate 7Document9 pagesMata Deseree Plate 7Diecon Irish ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoMichael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems PDFDocument8 pagesPractice Problems PDFJea Clarie Mendioro EspinasNo ratings yet
- Statics OF Rigid Bodies ModuleDocument47 pagesStatics OF Rigid Bodies ModuleCj Llemos67% (3)
- StaticsDocument5 pagesStaticslakr lama100% (1)
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Restrained Beam AnalysisDocument11 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Restrained Beam AnalysisRizette Palogan100% (1)
- MEGAREVIEW PRE-BOARD EXAMDocument6 pagesMEGAREVIEW PRE-BOARD EXAMe100% (1)
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsDocument7 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsadrianNo ratings yet
- Concurrent Force Systems ChapterDocument212 pagesConcurrent Force Systems ChapterMeghan Opena100% (2)
- Chapter05 Probs44 61Document39 pagesChapter05 Probs44 61fang123100% (1)
- Design Examples for Structural Joints and Wood PanelsDocument24 pagesDesign Examples for Structural Joints and Wood PanelsAlan Peter100% (2)
- PS Statics 1Document9 pagesPS Statics 1Kenny SiludNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 StructuralDocument20 pagesExam 2 StructuralMs. Engr100% (1)
- Evals RCD 1 PDFDocument4 pagesEvals RCD 1 PDFRennekien MateoNo ratings yet
- Struc Const 1 1Document23 pagesStruc Const 1 1Marichu Davillo Garbiles100% (1)
- Seminar 3 4Document33 pagesSeminar 3 4Zwinky Manlai100% (1)
- May 2022 Refresher ReviewDocument3 pagesMay 2022 Refresher ReviewDan Edison RamosNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Problems SolvedDocument3 pagesSoil Mechanics Problems SolvedEj ApeloNo ratings yet
- Method of Members - Frames Containing Three-Force MembersDocument75 pagesMethod of Members - Frames Containing Three-Force MembersAna May DocotNo ratings yet
- Problem 431Document12 pagesProblem 431Cheska FernandezNo ratings yet
- Tos 1Document5 pagesTos 1Allyanna Elise Diam100% (1)
- Nov23 Design 01 06 Nov. 2023Document19 pagesNov23 Design 01 06 Nov. 2023Jayson MariNo ratings yet
- Design Seta (Latest)Document13 pagesDesign Seta (Latest)steven bianesNo ratings yet
- REVIEW INNOVATIONS CE BOARD EXAM MAY 2022 ALVAREZ 1Document3 pagesREVIEW INNOVATIONS CE BOARD EXAM MAY 2022 ALVAREZ 1Mayya BonaNo ratings yet
- Seac 2 - Strength of Materials (No Answers)Document6 pagesSeac 2 - Strength of Materials (No Answers)Joshua John Julio100% (1)
- Structural Design and Construction ProblemsDocument12 pagesStructural Design and Construction ProblemsCath100% (1)
- Board Exam Sample - Structural EngineeringDocument3 pagesBoard Exam Sample - Structural EngineeringEl Mer100% (3)
- VERTERA Preboard 2 ROMEL SolutionDocument4 pagesVERTERA Preboard 2 ROMEL SolutionRichie Juls BacalsoNo ratings yet
- Torsion of Circular ShaftsDocument7 pagesTorsion of Circular ShaftsJoshua John Julio100% (1)
- Engineering Economics QuizDocument10 pagesEngineering Economics QuizLarah PiencenavesNo ratings yet
- A Stone Is Projected Vertically Upward From The To...Document4 pagesA Stone Is Projected Vertically Upward From The To...KRISTINE JOY DE GUZMANNo ratings yet
- THEORY OF STRUCTURES REVIEW PROBLEMSDocument8 pagesTHEORY OF STRUCTURES REVIEW PROBLEMSChristine Verena SarteNo ratings yet
- Set ADocument12 pagesSet ADan Casurao0% (1)
- Tolentino and Associates Sample Construction and Design Preboard ExamDocument17 pagesTolentino and Associates Sample Construction and Design Preboard ExamDindo Mojica100% (7)
- STEEL DESIGN EVALUATIONDocument3 pagesSTEEL DESIGN EVALUATIONMichael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Besavilla Surveying TraverseDocument25 pagesBesavilla Surveying TraverseZaineNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Nce 520 Integration Course 2 Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Nce 520 Integration Course 2 Statics of Rigid BodiesAndrea Sochayseng SolijonNo ratings yet
- Engineering Achievement Exam ReviewDocument12 pagesEngineering Achievement Exam ReviewJade Paul D. BesanaNo ratings yet
- Review-Module 44 RC - Columns - Usd - Nov2020Document4 pagesReview-Module 44 RC - Columns - Usd - Nov2020Ma Ella Mae LogronioNo ratings yet
- Module 8 SolDocument10 pagesModule 8 SolMae Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document8 pagesAssignment 1Kenn Fabre100% (2)
- Mathematics - Quiz 28 Solutions - 8 Nov. 2021Document12 pagesMathematics - Quiz 28 Solutions - 8 Nov. 2021Mark Carlo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Kippap-Handout-Evaluation Exam 5Document6 pagesKippap-Handout-Evaluation Exam 5Michael MercadoNo ratings yet
- Ec 2 Problem SetDocument11 pagesEc 2 Problem SetNenia RosasNo ratings yet
- 2500 LB D 1.25in D 2.25 In: Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument5 pages2500 LB D 1.25in D 2.25 In: Mechanical Engineering DepartmentPHILIPANTHONY MASILANGNo ratings yet
- Example 1Document8 pagesExample 1jgolloberNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Ans. F = 1404.917 N; θ = 7.05ºDocument3 pagesExercises: Ans. F = 1404.917 N; θ = 7.05ºRhey LuceroNo ratings yet
- D T V T TDocument2 pagesD T V T TRachita Prakash SarafNo ratings yet
- M1a1 Attempt 1,2,3Document7 pagesM1a1 Attempt 1,2,3Ericka Mae RuizNo ratings yet
- Villanueva Poetry Analysis Template BSEE 35Document7 pagesVillanueva Poetry Analysis Template BSEE 35CHRISTIAN MAHINAYNo ratings yet
- MOW Procurement Management Plan - TemplateDocument7 pagesMOW Procurement Management Plan - TemplateDeepak RajanNo ratings yet
- 2019 Implementasie-SamsatdiBaliDocument10 pages2019 Implementasie-SamsatdiBaliDiannita SusantiNo ratings yet
- Business Judgment Rule and Directors' Duty to Inform in Smith v Van GorkomDocument1 pageBusiness Judgment Rule and Directors' Duty to Inform in Smith v Van GorkomDorothy ParkerNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Ain Shams 123 - Compress 1Document552 pagesPharmacology Ain Shams 123 - Compress 1ahmed hoty100% (1)
- Climate Change Survivor GameDocument22 pagesClimate Change Survivor Game许凉发No ratings yet
- Nelson Climate Change Plan UpdateDocument37 pagesNelson Climate Change Plan UpdateBillMetcalfeNo ratings yet
- 6 An Indian American Woman in Space 2Document11 pages6 An Indian American Woman in Space 2Manju YadavNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall DetailsDocument1 pageRetaining Wall DetailsWilbert ReuyanNo ratings yet
- 01 A Brief Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument25 pages01 A Brief Introduction To Cloud ComputingfirasibraheemNo ratings yet
- The Accidental AddictsDocument6 pagesThe Accidental AddictsnorthandsouthnzNo ratings yet
- Computer ViruesDocument19 pagesComputer ViruesMuhammad Adeel AnsariNo ratings yet
- Setup LogDocument77 pagesSetup Loganon-261766No ratings yet
- Shooting ScriptDocument12 pagesShooting Scriptapi-544851273No ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/preparation and of The Company/undertakingDocument4 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/preparation and of The Company/undertakingBalasubramanian AnanthNo ratings yet
- Creating Literacy Instruction For All Students ResourceDocument25 pagesCreating Literacy Instruction For All Students ResourceNicole RickettsNo ratings yet
- 2 Both Texts, and Then Answer Question 1 On The Question Paper. Text A: Esports in The Olympic Games?Document2 pages2 Both Texts, and Then Answer Question 1 On The Question Paper. Text A: Esports in The Olympic Games?...No ratings yet
- Ap4955 PDFDocument4 pagesAp4955 PDFGilvan HenriqueNo ratings yet
- Forecast Time Series-NotesDocument138 pagesForecast Time Series-NotesflorinNo ratings yet
- Psych 1xx3 Quiz AnswersDocument55 pagesPsych 1xx3 Quiz Answerscutinhawayne100% (4)
- cmc2 OiDocument147 pagescmc2 OiJesus Mack GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Orion C.M. HVAC Case Study-07.25.23Document25 pagesOrion C.M. HVAC Case Study-07.25.23ledmabaya23No ratings yet
- A Report On Kantajew MandirDocument21 pagesA Report On Kantajew MandirMariam Nazia 1831388030No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Water Treatment Ce3303Document18 pagesUnit 2 Water Treatment Ce3303shivaNo ratings yet
- CP302 Example 01 OKDocument5 pagesCP302 Example 01 OKAw Yeong Pei Yee100% (1)
- TM T70 BrochureDocument2 pagesTM T70 BrochureNikhil GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2iccas2005 Paper 377Document5 pages2iccas2005 Paper 377Cristian BandilaNo ratings yet
- Q3 Curriculum Map - Mathematics 10Document3 pagesQ3 Curriculum Map - Mathematics 10Manilyn BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Idler Sprockets: Poly Chain GT and Powergrip GTDocument2 pagesIdler Sprockets: Poly Chain GT and Powergrip GTVolodymуr VorobetsNo ratings yet
- Wolfgang KohlerDocument16 pagesWolfgang KohlerMaureen JavierNo ratings yet