Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activity Sheet 1: Ancient Period Primitive Education
Uploaded by
Charmaine Rose Laynes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views7 pagespre historic to new society
Original Title
Fundamentals of Education
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentpre historic to new society
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views7 pagesActivity Sheet 1: Ancient Period Primitive Education
Uploaded by
Charmaine Rose Laynespre historic to new society
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
FACULTY OF EDUCATION SCIENCES
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION 1
TEACHING PROFESSION
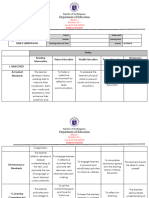
Activity Sheet 1
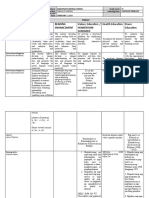
Historical Objectives of Methods of Content of Agencies of Educational Other information
Period Education Teaching Education Education Materials used
To conform All the Practice Home- center Word of Agents of Education
To teach instructions hunting for practical mouth (the providing
ANCIENT Primitive survival were done Fishing training education)
PERIOD Education
skills informally Songs Environment- Parents
Poems
To teach Simple telling good place for Tribal leaders
Dances
group Children learning Religious leaders
harmony imitate and Primitive education
To preserve observe Characteristics
and adults Life was very simple
transmit Participation- It is the process of
tradition children culture transmission
participated called enculturation
in the work Their means of
of their livelihood were
parents and hunting and gathering
they learned There is no reading
and writing
Types of Education
Vocational
Domestic training
Religious
(animistic)
SUMERIAN SUMERIAN Agencies of SUMERIAN
Oriental SUMERIAN Imitation and Content to be education are: SUMERIAN Types of education are :
Education Training of copying what studied are : home, school ( Cuneiform script writing, mathematical,
scribes- trained the teacher reading consist of walls 8- language, vocational,
to do had written writing, little 9 ft.) , temple professional, and art
ecclesiastical and followed arithmetic, school ( more education.
work in temple by minimal astronomy, elaborate),
mostly writing. explanation astrology, apprentice
Training of book Preparation of medicine, schools.
keepers- to tablets- the surgery,
record their main works of architecture
multifarious the learners agriculture,
business that dealt with hydraulics,
transactions their lessons jewelry,
Training of carpentry,
teachers ship building,
Training the smithing, law.
learners to be
good and to do
good things
especially to
their god and to CHINESE CHINESE
humanity called Sticks made of Students are males of
CHINESE upper class
namlulu CHINESE Curriculum is
woods and
CHINESE Memorization bamboo scrolls Curriculum is the
the Confucian classics
Prepare elite to and recitation Temples joined together
Confucian Beginning of written
govern empire
classics examinations ( civil
according to
Confucian INDIAN service examination)
INDIAN Agencies of
principles. Memorizing
INDIAN
education are: INDIAN INDIAN
and Content to be
To learn
home, outdoor ( Sanskrit (Vedas) First who set goal in
interpreting studied are: under large education on setting
behavior and texts literature for trees), behavior not only to
rituals based on
brahmans, monasteries survive.
the vedas
astronomy, Religion played a realm in
Intellectual – for
history, the field of education
excellent
grammar, law Types of education are:
intellectual
, medicine, religious education,
development
mathematics, intellectual education,
through
contemporary vocational, domestic, and
knowledge and
arithmetical military education
contemplation of
philosophical notation
truth including the
Cultural – to symbol “O”,
preserve the algebra,
caste system dancing,
through the use wrestling,
of precedent, archery, yoga,
history ,and linguistics,
strict observance philosophy,
of customs and theology, and
traditions the use of
horse,
elephant, and
chariot for
war.
EGYPTIAN EGYPTIAN
EGYPTIAN EGYPTIAN EGYPTIAN Agencies of Hieroglyphics EGYPTIAN
To prepare Memorization Content to be education are: They were polytheistic
priests according and copying studied are : home, temple Agencies of education
to scribes for the texts reading schools, military are: home, temple
empire Observation writing and schools, court schools, military
Religious- and language, school , and schools, court school ,
inculcate proper participation religious and vocational and vocational schools
respect for the secular schools Flogging was used to
gods and literature, penalized failure to
pharaoh artistry in learn.
Utilitarian- the metal and The pupils or students
father and lapidary, had to pay a certain
mother wanted mathematics, amount of school fees
to transfer their astronomy, even in the lower
skills in his engineering,, schools. Hence,
occupation and architecture, education was not
her skills in physics, universal.
keeping house. medicine,
Preservation of embalming,
cultural patterns dentistry, law,
music,
dancing,
playing the
harp, cymbals,
drum, lyre,
guitar,
tambourine,
and clapping
to rhythm,
sports, games,
physical
education
with
swimming,
wrestling,
archery, and
hunting and
fishing, and
training in the
use of bow,
arrow, axe,
mace and
shield
EARLY HEBREW EARLY HEBREW
EARLY HEBREW EARLY EARLY Agencies of Torah , EARLY HEBREW
Moral – to HEBREW HEBREW education are: home, Decalogue Types of education
develop faithful Compulsory- Content to temple are: religious and civic
and obedient the boys were be studied education, domestic,
servants to God, taught in the are: history
to assure school and the of Hebrews
harmony and girls at home and God’s
glorious future Oral – spoken relationship
for God’s chosen word was with them,
people used for lack the jewish
Preparation for of writing law or
destiny – instruct materials Mosaic law,
each succeeding Expositions – psalms and
generation to followed by proverbs,
perform its task questions Explanation
faithfully of festivities,
Holiness- to music,
attain holiness reading and
before the eyes writing
of the Lord
Observance of
religion – to
keep stylized
observance of
institutionalized
religion under
the Torah (body
of rules and
regulations) and
the Decalogue (
the ten
commandments)
Greek To cultivate civic Memorization Sparta Sparta
responsibility and recitation Content to Agencies of
Types of education are:
Lectures be studied Education physical education,
Discussions and are: are : Home- military education, moral
dialogs intensive center for training, very little
gymnastics intellectual training,
and
practical
music education,
paramilitary training and
gymnastics education
exercises, Environment- At birth weak children
practice in good place were disposed of,
moral and for learning abandoned, or exposed
social habits Educational to the elements
such as materials At early stage children
controlling used were taught habits of
the
appetite,
Environment silence and obedience
At 17-18 , the boys
modesty, Wax and undertook professional
obedience, tablets war training
and respect At 20- 30, took oath of
and allegiance and dispersed
listening to military posts for war
Athens maneuvers.
Agencies of
Content to The girls stayed at home
be studied
education are:
but they were also
are: reading private schools
organized into packs to
by the ( 1st schools for
develop group spirit,
Alphabet boys), home ( courage and loyalty.
method, for girls) , state Curriculum : drill,
writing, ( supervised by military, songs, and
arithmetic the state but tactics
for market not Types of Education are:
use, Homeric compulsory), Vocational, Domestic
and other training , Religious
palestra (
poems,
where (animistic)
music, lyre,
and flute gymnastics,
playing, sports, and
gymnastics games were
exercises, taught), Athens
physical didascaleum ( Curriculum :Writing,
education school for reading, arithmetic,
exercises, literature), drama, poetry, music
and military Types of education are:
gymnasium (
training civic training (desire to
subjects.
academic
serve the state), moral
secondary training (virtues of
school) Homeric heroes),
physical education ( to
develop grace and
harmony in the
body),intellectual
Education, and art
Can be assumed that
students paid for
tuition fees
Develop civic Methods of
ROMANS responsibility for teaching Content to be Agencies of
the empire, Direct imitation – studied are:
education are: Educational Types of education are:
administrative, boys imitate their ballads and materials physical and military
and military skills. songs, the law home, shop trainings, civic training,
fathers and girls used
Utilitarian – for imitate their of the twelve and farm, moral training, religious
practical tables, military camp, Wax and training, and vocational
mothers
purposes, to Memorization- religious forum, private tablets trainings
produce men who memorized the ceremonies
schools
would be active laws of the 12 and usages, Learners did not pay any
and efficient in tables, ballads, physical and fees. But when they
daily lives and religious military entered private schools
Moral- to produce songs exercises, they had to pay.
citizen who knew Discipline – there
domestic At the age of 7- 10 boys
how to exercise chores, and girls entered the
was corporal
their rights , fulfill vocations ( litterator
punishment and
their duties, and even death
craft and skills At the age of 10 – 16 boys
obligations and learned by entered secondary schools
Recitation in
acquire virtues males.) At 16 or older, boys
ludus
Religious – to train entered the school of the
Declamation in
men to have rhetor for 2 – 3 years
rhetorical schools
reverence for the Those who hurdled the
gods. school of the rhetor went
to Athenaeum for a
professional course.
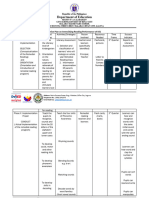
MEDIEVAL Monasticism Objectives of Methods of Content to Agents of Educational Other
EDUCATION education teaching be studied useful/unique/interesting
Spiritual – to obtain
Education (the materials
Catechetical are information
the salvation of The seven
providing used There are 2 types of
method
individual souls
Dictation – due to liberal arts education) Word of monasticism, the eremitic (
Moral – to attain
the ideals of the scarcity of composed Monasteries mouth a hermit lifestyle) and the
chastity, poverty books of: Texts cenobitic ( a communual
and obedience Discipline – a) The Trivium lifestyle)
Environment Monasticism became quite
Spiritual knowledge teachers used the composed of
– to attain the rod to punish Grammar- popular in the middle ages
highest spiritual erring pupils language and with religion being the
knowledge and the Language- Latin literature most important force in
purest spiritual Dialectic – Europe.
was the only
satisfaction through logic or right At age of 10, boys were
meditation, language for
learning reasoning admitted into the monastic
contemplation,
inspiration, and Meditation and Rhetoric – schools
asceticism. contemplation – law and At the age of 18, after
they believed that composition training for 8 years, they
the deepest b) The were admitted to the
spiritual Quadrivium monastic order.
experience could composed of Later in the middle ages ,
be gained only Geometry many monastic schools
through divine Arithmetic admitted boys and girls
inspiration Music who did not intended to
Astronomy become monks and nuns
Greek and Pupils paid some fees and
Roman the state shouldered some
classical expenses
culture and
literature
You might also like
- Meeting The World's EndDocument10 pagesMeeting The World's Endanon_860117019No ratings yet
- Catch-Up Fridays - Feb.2Document13 pagesCatch-Up Fridays - Feb.2Jim Cesar G. BaylonNo ratings yet
- Dark Green Leaves Pattern Bubble Map ChartDocument2 pagesDark Green Leaves Pattern Bubble Map ChartBetsy RiveraNo ratings yet
- Matrix Presentation of Curriculum History in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesMatrix Presentation of Curriculum History in The PhilippinesJanine CerradaNo ratings yet
- Methologi ES Proponen TS Approach Design ProcedureDocument6 pagesMethologi ES Proponen TS Approach Design ProcedureG-yan Dungan MamuyacNo ratings yet
- GUILARAN - Lesson 4. Historical Foundation MatrixDocument6 pagesGUILARAN - Lesson 4. Historical Foundation MatrixDiane GuilaranNo ratings yet
- Task No. 3Document6 pagesTask No. 3Jesryl Remerata OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Output History of EducationDocument4 pagesOutput History of EducationDominic NoblezaNo ratings yet
- Catch Up Fridays Feb.9Document9 pagesCatch Up Fridays Feb.9CARMINA VALENZUELANo ratings yet
- Community Culture and CurriculumDocument43 pagesCommunity Culture and CurriculumMahendra Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundations of EducationDocument4 pagesHistorical Foundations of EducationAthena Kiesha TornoNo ratings yet
- Catch-Up-Fridays-February 2, 2024Document18 pagesCatch-Up-Fridays-February 2, 2024DAHLIA BACHONo ratings yet
- Dll Catch Up Friday Week 3.Document18 pagesDll Catch Up Friday Week 3.Lorgin nunialaNo ratings yet
- Catch Up Fridays Feb Catch Up Friday Lesson PlanDocument15 pagesCatch Up Fridays Feb Catch Up Friday Lesson PlanedelynunayNo ratings yet
- Philippine Educational System TimelineDocument4 pagesPhilippine Educational System TimelineSeo Soojin100% (1)
- RISR Action Plan for Struggling ReadersDocument3 pagesRISR Action Plan for Struggling ReadersJenny Canoneo Getizo100% (1)
- OLIVAR, ERIKA JANE O. HISTORICAL FOUNDATIONS OF EDUCATIONDocument5 pagesOLIVAR, ERIKA JANE O. HISTORICAL FOUNDATIONS OF EDUCATIONFranchesca ValerioNo ratings yet
- 7goESREADING RECOVERY PLAN 2022 2023Document4 pages7goESREADING RECOVERY PLAN 2022 2023Kevin Ryan AbeledaNo ratings yet
- Catch Up Fridays Feb.23 1Document10 pagesCatch Up Fridays Feb.23 1DAHLIA BACHONo ratings yet
- Dll Catch Up Friday Week 7aDocument10 pagesDll Catch Up Friday Week 7aLorgin nunialaNo ratings yet
- Catch Up Fridays Feb.2Document9 pagesCatch Up Fridays Feb.2carlkevinval.ybanez029No ratings yet
- Action Plan On The Reading Remediation For Struggling ReadersDocument3 pagesAction Plan On The Reading Remediation For Struggling ReadersGILBERT DE VERA100% (2)
- Catch Up Fridays Feb Catch Up Friday Lesson PlanDocument15 pagesCatch Up Fridays Feb Catch Up Friday Lesson PlanCelestine MirandaNo ratings yet
- La Familia: Identifying Family Members in SpanishDocument8 pagesLa Familia: Identifying Family Members in SpanishHaimwantie PersaudNo ratings yet
- Catch Up FridaysDocument7 pagesCatch Up FridaysGenely Cascajo100% (1)
- Methods Historical Context Teacher's Role Student's Role Ability Class Advantages Disadvantages Brown's Principles Grammar TranslationDocument5 pagesMethods Historical Context Teacher's Role Student's Role Ability Class Advantages Disadvantages Brown's Principles Grammar TranslationLuigi OliNo ratings yet
- DLL Catch Up Friday Grade 4 Feb 2Document9 pagesDLL Catch Up Friday Grade 4 Feb 2A-jaye Celesena100% (3)
- Week1 EnglishDocument6 pagesWeek1 EnglishDioselle CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Sumerian and Primitive Education InsightsDocument22 pagesSumerian and Primitive Education InsightsWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- DLL-CATCH-UP-FRIDAY-lpDocument6 pagesDLL-CATCH-UP-FRIDAY-lpLiza ACNo ratings yet
- Comparative AnalysisDocument3 pagesComparative AnalysisRiRiNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 1 - Q1 - W8Document5 pagesDLL - Mapeh 1 - Q1 - W8Mary Anne PabloNo ratings yet
- 5 DLL - English 2 - Q1 - W1Document5 pages5 DLL - English 2 - Q1 - W1Eda Concepcion PalenNo ratings yet
- DLL Mapeh-1 Q1 W6Document2 pagesDLL Mapeh-1 Q1 W6Ranjell Allain Bayona TorresNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 2 - Q1 - W1Document4 pagesDLL - English 2 - Q1 - W1Carino ArleneNo ratings yet
- Ecec FPDDocument17 pagesEcec FPDapi-451063936No ratings yet
- Dll-Catch-Up-Friday-Week 8Document11 pagesDll-Catch-Up-Friday-Week 8ruthsingedas23100% (1)
- Kinder Catch Up Friday Action PlanDocument4 pagesKinder Catch Up Friday Action PlanAriane PimentelNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 1 - Q4 - W6Document7 pagesDLL - English 1 - Q4 - W6Arcon ArnocoNo ratings yet
- Mapeh Q1W4Document3 pagesMapeh Q1W4Nikki Galindez AragonNo ratings yet
- English III New_081400Document7 pagesEnglish III New_081400jacksonmartinus195No ratings yet
- Describing Learning and TeachingDocument11 pagesDescribing Learning and TeachingByron ValdiviesoNo ratings yet
- Action Plan On Reading Intervention ForDocument5 pagesAction Plan On Reading Intervention ForPamela Camille Plata Breton100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - BillonesDocument25 pagesChapter 3 - BillonesKim Layda BillonesNo ratings yet
- CATCH-UP-FRIDAY-GRADE-4.ddocxWEEK-4-DLL March 1Document6 pagesCATCH-UP-FRIDAY-GRADE-4.ddocxWEEK-4-DLL March 1AIZA EUNICE AUREADANo ratings yet
- Hawanay Elementary School: Action Plan On Reading Intervention For Struggling Readers (Risr) S.Y. 2019-2020Document5 pagesHawanay Elementary School: Action Plan On Reading Intervention For Struggling Readers (Risr) S.Y. 2019-2020Juliet Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Lunes Martes Miyerkules Huwebes Biyernes: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument5 pagesLunes Martes Miyerkules Huwebes Biyernes: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogJames B. AbucayNo ratings yet
- Dll Catch Up Friday Week 8Document11 pagesDll Catch Up Friday Week 8Lorgin nunialaNo ratings yet
- Pamela Camille - Project InnovationDocument7 pagesPamela Camille - Project InnovationPamela Camille Plata BretonNo ratings yet
- Reading Remediation Action PlanDocument2 pagesReading Remediation Action PlanJemarie Quiacusan100% (7)
- Action Plan Reading ProgramsDocument5 pagesAction Plan Reading ProgramsMA ASTERIA AGUSTINA CENALNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Activities & Skills: Cce / EeDocument6 pages21st Century Activities & Skills: Cce / EeHazimah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Catch-Up Fridays - Jan 19Document7 pagesCatch-Up Fridays - Jan 19Jim Cesar G. BaylonNo ratings yet
- Improvisation As Ability, CUlture, And, ExperieneDocument8 pagesImprovisation As Ability, CUlture, And, ExperieneAfriza Bin Yuana ArifinNo ratings yet
- LEANERSDocument1 pageLEANERSMarú Tranquilino Andrea SabinaNo ratings yet
- PerseveranceDocument3 pagesPerseveranceJonnah Lizz DagoyoNo ratings yet
- catch-up-fridays-jan-catch-up-friday-planDocument8 pagescatch-up-fridays-jan-catch-up-friday-planGlend AvenidoNo ratings yet
- Ge4 - Group5 - Chapter 1.2 ActivityDocument3 pagesGe4 - Group5 - Chapter 1.2 ActivityJohnkelvin MacadangdangNo ratings yet
- Staff Meeting YarralinDocument2 pagesStaff Meeting Yarralinapi-452829143No ratings yet
- Literacy Activities for Circle Time: Rhythm and Rhyme, Ages 3 - 6From EverandLiteracy Activities for Circle Time: Rhythm and Rhyme, Ages 3 - 6No ratings yet
- FlowerDocument1 pageFlowerCharmaine Rose LaynesNo ratings yet
- FruityDocument1 pageFruityCharmaine Rose LaynesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1 Natural HazardsDocument44 pagesLesson 2.1 Natural HazardsCharmaine Rose LaynesNo ratings yet
- The Elements ofDocument2 pagesThe Elements ofCharmaine Rose LaynesNo ratings yet
- The Elements ofDocument2 pagesThe Elements ofCharmaine Rose LaynesNo ratings yet
- Shenoute and The Women of The WH PDFDocument261 pagesShenoute and The Women of The WH PDFMóni SzuhaiNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundations of EducationDocument64 pagesHistorical Foundations of EducationMa Zhaira Grace CastroNo ratings yet
- Francis Tiso - Evagrius of Pontus and Buddhist AbhidharmaDocument32 pagesFrancis Tiso - Evagrius of Pontus and Buddhist AbhidharmaChris Schelin100% (1)
- The Egyptian Copts and Their Ancient Music TraditionDocument17 pagesThe Egyptian Copts and Their Ancient Music TraditionLinaNo ratings yet
- St. Benedict's Contribution To World Culture 1. The DialoguesDocument4 pagesSt. Benedict's Contribution To World Culture 1. The DialoguesEli SNo ratings yet
- Ionel Florentin MICU, Sfântul Paisie Velicikovski Revigorator Al Monahismului Și Părinte Al Rugaciunii Lui IisusDocument12 pagesIonel Florentin MICU, Sfântul Paisie Velicikovski Revigorator Al Monahismului Și Părinte Al Rugaciunii Lui IisusPaul GherasimNo ratings yet
- Pierre Pourrat - Christian Spirituality - Vol 1Document330 pagesPierre Pourrat - Christian Spirituality - Vol 1Clei De Jesus Santos100% (1)
- Great Compline: "The Day Being Past... "Document3 pagesGreat Compline: "The Day Being Past... "Adela UrcanNo ratings yet
- Carthusian NunsDocument28 pagesCarthusian Nunsbryan73No ratings yet
- DokumenDocument20 pagesDokumengitaNo ratings yet
- Oxford Early Christian Studies on St John CassianDocument318 pagesOxford Early Christian Studies on St John CassianRobert Manole100% (3)
- John Cassian and The Reading of Egyptian Monastic CultureDocument167 pagesJohn Cassian and The Reading of Egyptian Monastic CultureCosmin Maftei100% (1)
- Delatte On VocationDocument3 pagesDelatte On VocationSancrucensisNo ratings yet
- Cyril de Scythopolis Et Les Monasteries Du Desert PDFDocument290 pagesCyril de Scythopolis Et Les Monasteries Du Desert PDFJuan José Fuentes UbillaNo ratings yet
- Mount Athos - Microcosm of The Christian East PDFDocument228 pagesMount Athos - Microcosm of The Christian East PDFChristian WandriNo ratings yet
- Monastery LifeDocument4 pagesMonastery Lifeapi-439280190No ratings yet
- Unchained MonkDocument19 pagesUnchained Monk678ojyhiop100% (2)
- St. Basil The GreatDocument6 pagesSt. Basil The GreatAgnes SalaNo ratings yet
- The Monastic TonsureDocument3 pagesThe Monastic TonsureLockdown MaxhinNo ratings yet
- History of Monasticism 2Document37 pagesHistory of Monasticism 2Caitlin Anne OlayvarNo ratings yet
- 0520222059Document235 pages0520222059Szte Ehök100% (2)
- Western Civilization Beyond Boundaries 7th Edition Noble Test Bank DownloadDocument11 pagesWestern Civilization Beyond Boundaries 7th Edition Noble Test Bank DownloadClara Rodas100% (20)
- G. R. Evans - The I.B.tauris History of Monasticism The Western TraditionDocument336 pagesG. R. Evans - The I.B.tauris History of Monasticism The Western TraditionheresnemoNo ratings yet
- Impact of Monasticism on Medieval EducationDocument6 pagesImpact of Monasticism on Medieval EducationHarlene ArabiaNo ratings yet
- Franciscan Resources Book ListDocument15 pagesFranciscan Resources Book Listjjpuliken100% (1)
- Jiabs 17-2Document220 pagesJiabs 17-2JIABSonline100% (1)
- Introduction To Monasticism: Instructor: Jessica WhittemoreDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Monasticism: Instructor: Jessica WhittemorecharleneNo ratings yet
- Antiphonale Monasticum (1934)Document1,333 pagesAntiphonale Monasticum (1934)rarty100% (10)
- Spiritual Life of Monks in a Pluralistic AgeDocument16 pagesSpiritual Life of Monks in a Pluralistic AgeBarbieru MariusNo ratings yet
- Desert MothersDocument4 pagesDesert MothersAnonymous g5wqERNo ratings yet