Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chem
Chem
Uploaded by
Crispy Chicken0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
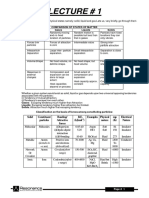
13 views2 pagesMatter can be classified into elements and compounds. Elements cannot be broken down further, while compounds are formed through chemical reactions combining elements. There are three main states of matter - solids have a fixed structure and low movement; liquids have a flowing structure and medium movement; gases have no fixed structure and high random movement. Matter can also be classified as pure substances or mixtures. Pure substances are uniform throughout while mixtures contain more than one substance mixed but not chemically combined.
Original Description:
Matter
Classifications of Matter
States of Matter
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMatter can be classified into elements and compounds. Elements cannot be broken down further, while compounds are formed through chemical reactions combining elements. There are three main states of matter - solids have a fixed structure and low movement; liquids have a flowing structure and medium movement; gases have no fixed structure and high random movement. Matter can also be classified as pure substances or mixtures. Pure substances are uniform throughout while mixtures contain more than one substance mixed but not chemically combined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesChem
Chem
Uploaded by
Crispy ChickenMatter can be classified into elements and compounds. Elements cannot be broken down further, while compounds are formed through chemical reactions combining elements. There are three main states of matter - solids have a fixed structure and low movement; liquids have a flowing structure and medium movement; gases have no fixed structure and high random movement. Matter can also be classified as pure substances or mixtures. Pure substances are uniform throughout while mixtures contain more than one substance mixed but not chemically combined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
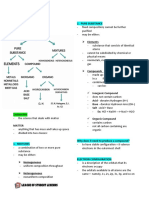
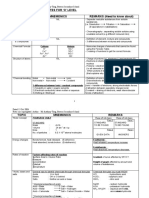
Matter - anything that has mass and Elements - form of substance that can’t be
occupies space (volume) broken down
● Stair-step Line (from Boron to
Polonium):
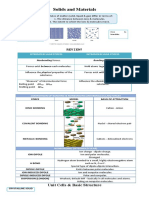
State of Matter and its Properties Left: Metals - conductors,
ductile, solid (except Hq)
State Particles Movement IMF Compressi Right: Nonmetals - brittle,
of bility
Matter
gain electrons
Metalloids - unique
Solid Compact VIbrates in High NO
conductivity (Si-most known)
🗸 S/V and tightly a fixed IMF
close to position Compounds - combined through chemical
one
another means (chemical reaction)
● Law of Definite Proportion (Joseph
Liquid Have Free Lower NO
XS spaces flowing; than Proust 1799)
🗸V between slips past solids - The observation and the
each other each other
elemental composition of a
Gas Are widely Constant, Low Highly compound is always the
X S/V separated rapid, IMF compressi
random ble same
motion Ex: Pure Water - 11%
Hydrogen; 89% Oxygen
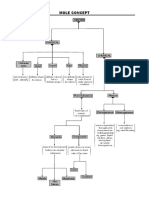
Classifications of Matter ● Law of Conservation of Mass
(Antoine Lavoiser 1787)
- Matter is neither created nor
Pure Substance Mixture
destroyed
Elements Compounds Homogene Heterogeneous Mixtures - combined and separated
ous
through physical means
Metals Ionic Coval Solution 1.Colloid 1. Homogeneous - uniform all
ent 2.Suspension throughout; 1 phase
Ex: brass, stainless steel
Nonmetal M- NM- 1. Alloy (S-
Solution - with solute and Solvent
s NM NM S)
(greater quantity)
2. Acid
Metalloid Cation(+) ● Water is the universal
s 3. Base
solvent.
4. Solution
Noble Anion
Gases (-) 2. Heterogeneous - not uniform; 2 or
more phases
Note: (*) means usually Ex: granite, halo-halo
Colloid - particles are mixed but not
Periodic Table - created by Dmitri dissolved and permanently
Mendelev in 1869 suspended
Monoatomic - one atom Suspension - large particles that
Diatomic (7) - H, N, O, F, Br, Cl, I have not settled
PHYSICAL SEPARATION TECHNIQUE
You might also like
- Chemistry Nmat ReviewerDocument8 pagesChemistry Nmat ReviewerAlec Jasper U. Villamayor100% (7)
- F. Reif - Fundamentals of Statistical and Thermal Physics PDFDocument333 pagesF. Reif - Fundamentals of Statistical and Thermal Physics PDFAllan SeeberNo ratings yet
- 1 - General Chemistry (MANOR 2017)Document13 pages1 - General Chemistry (MANOR 2017)Michaela Berndt100% (1)
- Von Mises TrescaDocument6 pagesVon Mises TrescaAlvin Garcia PalancaNo ratings yet
- TM 55 1520 228 10Document301 pagesTM 55 1520 228 10SlendreiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 General ChemistryDocument8 pages1.1 General ChemistryAzech Yam ÜNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes Full PDFDocument35 pagesChem Notes Full PDFVishal Kunnathur Senthilkumar100% (2)
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledAbigail OconNo ratings yet
- 1.1 General Chemistry PDFDocument8 pages1.1 General Chemistry PDFAzumi KleinNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-XII-Ch-1 - Solid State-MinhadDocument6 pagesHsslive-XII-Ch-1 - Solid State-MinhadZonicNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: I.E. H O H + O by ElectrolysisDocument7 pagesGeneral Chemistry: I.E. H O H + O by ElectrolysisSelena MoonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding One Day One Chapter Nitesh DevnaniDocument41 pagesChemical Bonding One Day One Chapter Nitesh Devnanivrinda11xxNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument6 pagesCHEMISTRYPrincess Diane AgripaNo ratings yet
- Solid State - PLPN MhtCetDocument42 pagesSolid State - PLPN MhtCetsiddheshmundlik6No ratings yet
- Organic and Inorganic Chemistry ReviewerDocument21 pagesOrganic and Inorganic Chemistry ReviewerArviNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument51 pagesChemistryj7mv5hskbvNo ratings yet
- Solid StateDocument22 pagesSolid State8446988233bwdNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: University of St. La Salle College of Engineering Engineering Sciences ReviewDocument5 pagesChemistry: University of St. La Salle College of Engineering Engineering Sciences ReviewJonas ParreñoNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon - Mind Map - Yakeen NEET English 2024Document1 pageHydrocarbon - Mind Map - Yakeen NEET English 2024suki.mumtazNo ratings yet
- Biochem Introduction PDFDocument5 pagesBiochem Introduction PDFJustin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Ionic, Covalent and Metallic BondingDocument1 pageIonic, Covalent and Metallic BondingJulia Garcia-LascurainNo ratings yet
- Midterm Chem86 NotesDocument9 pagesMidterm Chem86 NotessujzNo ratings yet
- Sunyzz - Unit 4 Chemistry TestDocument1 pageSunyzz - Unit 4 Chemistry TestAmiel DonqueNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Reviewer: DecompositionDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry Reviewer: DecompositionMariane Gayle CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Section 2 SummaryDocument6 pagesSection 2 SummarySean LamNo ratings yet
- Gen Chemistry 1: Same AsnDocument3 pagesGen Chemistry 1: Same Asnjames BernalNo ratings yet
- College Notes Unit-1 Solid StateDocument24 pagesCollege Notes Unit-1 Solid StateRamanujam JNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document3 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1Tricia BaltazarNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)Document11 pagesGeneral Chemistry Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)shieeesh.aNo ratings yet
- D and F YT UnacademyDocument29 pagesD and F YT Unacademynamansoni20032006No ratings yet
- Inbound 4695793937270644090Document6 pagesInbound 4695793937270644090joshuatimothylaoNo ratings yet
- Most Imp Chemistry Full Boards NotesDocument159 pagesMost Imp Chemistry Full Boards NotesAman KumarNo ratings yet
- Solid State Chemistry IPEDocument15 pagesSolid State Chemistry IPEAdiChemAdi100% (4)
- Chem 02 - Mod - WK1L3Document2 pagesChem 02 - Mod - WK1L32082862No ratings yet
- Bio - CO 4Document5 pagesBio - CO 4Jae Bert UbisoftNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMS - InOrgLec - Lesson 1Document4 pagesMIDTERMS - InOrgLec - Lesson 1Ayee Allyra Mocaram EspinosaNo ratings yet
- 2 Chemical Basis - AnaphysioDocument7 pages2 Chemical Basis - AnaphysioRayumaaaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry o Summary NotesDocument6 pagesChemistry o Summary Notesblankblank blankNo ratings yet
- Gen. Chem MATTER - NotesDocument4 pagesGen. Chem MATTER - NotesKrisha GatocNo ratings yet
- Unidad 61Document36 pagesUnidad 61Eloisa OvandoNo ratings yet
- Atoms and The Periodic: Classifying MatterDocument11 pagesAtoms and The Periodic: Classifying MattercharlieNo ratings yet
- AP Chem Cram Chart 2021Document1 pageAP Chem Cram Chart 2021Evangeline YaoNo ratings yet
- AP Chem Cram Chart 2021Document1 pageAP Chem Cram Chart 2021Evangeline YaoNo ratings yet
- 01 Theory6Document19 pages01 Theory6devli falduNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ChemistryDocument13 pagesChapter 2 Chemistryabbb25804No ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument2 pagesGeneral Chemistrysilentchase332No ratings yet
- Chemistry: Draw The Lewis Structure of Water H ODocument3 pagesChemistry: Draw The Lewis Structure of Water H OJulius CagampangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05Document3 pagesChapter 05Thabisile MoyoNo ratings yet
- Kimia Bab2Document17 pagesKimia Bab2idayu9779No ratings yet
- GENCHM2 Reviewer Week2&3Document2 pagesGENCHM2 Reviewer Week2&3Allysa Kim DumpNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision NotesDocument5 pagesChemistry Revision NotesShi Kai TengNo ratings yet
- Solid State 1Document10 pagesSolid State 1tinachaudhari132No ratings yet
- Solid State Theory PDFDocument28 pagesSolid State Theory PDFGOURISH AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- GENCHEM ReviewerDocument6 pagesGENCHEM ReviewerChricellFNo ratings yet
- States of Matter - Solids, Liquids, Gases & Plasma - ChemistryDocument8 pagesStates of Matter - Solids, Liquids, Gases & Plasma - Chemistryjerikbenito46No ratings yet
- LCs CH222Document92 pagesLCs CH222c68412639No ratings yet
- A. Lavoisier: History of Periodic TableDocument10 pagesA. Lavoisier: History of Periodic TableHaziraAzlyNo ratings yet
- Watermark Chemistry Igcse Notes 2 PDFDocument15 pagesWatermark Chemistry Igcse Notes 2 PDFMeerab ShahNo ratings yet
- Genchem1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenchem1 ReviewerCrystal Anne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet
- Ecofriendly Decolorisation of Textile Waste Water by Using Natural CoagulantsDocument5 pagesEcofriendly Decolorisation of Textile Waste Water by Using Natural Coagulantschumma pechukuNo ratings yet
- Connection: The Evidence of Evolution: Negor - Q3 - Science10 - Slkweek6 - V2 1 Negor - Q3 - Science10 - Slkweek6 - V2Document15 pagesConnection: The Evidence of Evolution: Negor - Q3 - Science10 - Slkweek6 - V2 1 Negor - Q3 - Science10 - Slkweek6 - V2Paul Anka UyNo ratings yet
- Book PDFDocument62 pagesBook PDFWafa BadullaNo ratings yet
- 2222Document5 pages2222Roberto UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- BL4S Results 2021Document2 pagesBL4S Results 2021Sadika AkhterNo ratings yet
- US5518537Document5 pagesUS5518537Marm246247 AlloyNo ratings yet
- AxaxxDocument19 pagesAxaxxkara_25No ratings yet
- 07e Annex3Document108 pages07e Annex3senpaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Atoms and MoleculesDocument34 pagesChapter 3 Atoms and MoleculesManushi ShahNo ratings yet
- WWW Erowid OrgDocument14 pagesWWW Erowid Orgtny6331100% (1)
- Kims CopiesDocument17 pagesKims Copieszafarchem_iqbalNo ratings yet
- SKF - Bearing Damage InvestigationDocument89 pagesSKF - Bearing Damage Investigationlalmimaj100% (2)
- Eled and SLDDocument15 pagesEled and SLDnikithaNo ratings yet
- AQWG-02 Legislation - South Korea PDFDocument13 pagesAQWG-02 Legislation - South Korea PDFAkulSenapatiNo ratings yet
- Din 2605 PDFDocument3 pagesDin 2605 PDFPedro Montes MarinNo ratings yet
- SDS Irganox 1076 Ex-BASF (Expiry 2024)Document14 pagesSDS Irganox 1076 Ex-BASF (Expiry 2024)Arista DianaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing ProcessDocument3 pagesManufacturing ProcessSatyam PatelNo ratings yet
- Advanced Manufacturing Processes (ALL SLIDES Gaurav Arora)Document259 pagesAdvanced Manufacturing Processes (ALL SLIDES Gaurav Arora)faizNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2213343722017419 MainDocument21 pages1 s2.0 S2213343722017419 MainIkram ADNANENo ratings yet
- FRP Catalogue NewDocument82 pagesFRP Catalogue Newamol ganvirNo ratings yet
- 1995 - Electrochemistry and Environment - The Role of ElectrocatalysisDocument10 pages1995 - Electrochemistry and Environment - The Role of ElectrocatalysisClaudio CastroNo ratings yet
- 2019 Chemical Engineering Plant Cost Index Annual Average: 68shareDocument8 pages2019 Chemical Engineering Plant Cost Index Annual Average: 68sharebNo ratings yet
- Form Qw-482 Suggested Format For Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS) (See QW-200.1, Section IX, ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code)Document2 pagesForm Qw-482 Suggested Format For Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS) (See QW-200.1, Section IX, ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code)Muhammad MunadiNo ratings yet
- 30-99!90!1826-Rev 0 Hardness Testing Procedure MPS IPS and MOTDocument9 pages30-99!90!1826-Rev 0 Hardness Testing Procedure MPS IPS and MOTSubrata PatraNo ratings yet
- Clarus 680 GC Specification SheetDocument8 pagesClarus 680 GC Specification SheetVarsha KankaniNo ratings yet
- Mix Design FormatDocument3 pagesMix Design FormatAkshay MitraNo ratings yet
- Performance Task #5: University of San AgustinDocument7 pagesPerformance Task #5: University of San AgustinMicole BrodethNo ratings yet