Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math 4 Competencies
Uploaded by
Rey Almodiel SolitarioCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math 4 Competencies
Uploaded by
Rey Almodiel SolitarioCopyright:
Available Formats
Secondary Mathematics - Fourth Year Advanced Algebra, Trigonometry and Statistics
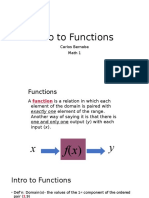
Functions
1: Functions Generally
• Demonstrate knowledge and skill related to functions in general
• Define a function.
• Differentiate a function from a mere relation.
• real life relationships
• set of ordered pairs
• graph of a given set of ordered pairs
• vertical line test
• given equation
• Illustrate the meaning of the functional notation f(x); determine the value of f(x) given a
value for x.
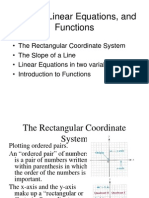
Linear Functions
2: Linear Functions and their Graphs
• Demonstrate knowledge and skill related to linear functions and apply in solving problems
• Define the linear function f(x) = mx + b.
• Given a linear function Ax + By = C, rewrite in the form f(x) = mx + b and vice versa.
• Draw the graph of a linear function, given:
• any two points
• x and y intercepts
• slope and one point
• slope and the y-intercept
• Given f(x) = mx + b, determine the following attributes of the function:
• slope
• trend: increasing or decreasing
• x and y intercepts
• some points
• Determine f(x) = mx + b given any two parameters.
• slope and y-intercept
• x and y intercepts
• slope and one point
• any two points
• Solve problems involving linear functions.
Quadratic Functions
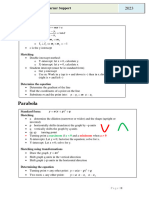
3: Quadratic Functions and their Graphs
• Quadratic functions - an introduction
2
• Identify quadratic functions f(x) = ax + bx + c
2 2
• Rewrite a quadratic function ax + bx + c in the form f(x) = a(x - h) + k and vice versa
• Given a quadratic function, determine the following characteristics of its graph.
• highest or lowest point (vertex)
• axis of symmetry
• direction of opening of the graph
• Given particular characteristics, draw the graph of a quadratic function, showing:
• vertex
• axis of symmetry
• direction of opening of the graph
• given points
• Analyze the effects on the graph of changes in a, h and k in f(x) = a(x-h)2 + k
4: Properties of Quadratic Functions
• Determine the 'zeros of a quadratic function' by relating this to 'roots of a quadratic equation'.
• Find the roots of a quadratic equation,
• by factoring
• using the quadratic formula
• by completing the square
• Derive a quadratic function from:
• zeros of the function
• table of values
• graph
• Solve problems involving quadratic functions and equations.
Polynomial Functions
5: Getting to know Polynomial Functions
• Identify a polynomial function from a given set of relations
• Determine the degree of a given polynomial function
• Find the quotient of polynomials
• by algorithm
• by synthetic division
6: Theorems, Zeros and Graphs
• Find by synthetic division the quotient and the remainder when p(x) is divided by (x-c)
• State and illustrate the Remainder Theorem
• Find the value of p(x) for x = k.
• synthetic division
• Remainder Theorem
• State and illustrate the Factor Theorem
• Find the zeros of polynomial functions of degree greater than 2
• Factor Theorem
• factoring
• synthetic division
• depressed equations
• Draw the graph of polynomial functions of degree greater than 2 (use graphing calculator if
available)
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
7: Exponential Functions and their Graphs
• Identify certain relationships in real life which are exponential (e.g. population growth over
time, growth of bacteria over time, etc.)
• Given a table of ordered pairs, state whether the trend is exponential or not
• Draw the graph of an exponential function
• Describe some properties of an exponential function from its graph
• f(x)=a
x
• for a > 1
• when 0 < a < 1
• Given the graph of an exponential function determine the domain, range, intercepts, trend and
asymptote
• Describe the behavior of the graph of an exponential function
8: Zeros and the Inverse
• Use the laws on exponents to find the zeros of exponential functions
• Define inverse functions
• Determine the inverse of a given function
9: Logarithmic Functions and their Graphs
• define the logarithmic function as the inverse of the exponential function
x
• f(x) = log x as the inverse of the exponential function f(x) = a
a
• draw the graph of a logarithmic function
• f(x) = log x
a
• Describe some properties of the logarithmic function from its graph
• State and apply the laws for logarithms
• Solve simple logarithmic equations
• solve problems involving exponential and logarithmic functions (e.g. - exponential growth or
decay)
Circular Functions and Trigonometry
10: The Unit Circle
• Define a unit circle; arc lengths; unit measures of an angle
• Convert from degree to radian and vice versa
• Illustrate angles in standard position (i.e. initial side coincident with the positive x-axis;
coterminal angles; reference angles
• Visualize rotations along the unit circle and relate these to angle measures (clockwise or
counterclockwise directions)
• length of an arc
o
• angles beyond 360 or 2â radians
• Given an angle in standard position in a unit circle, determine the coordinates of its terminal
side
• when one coordinate is given (apply the Pythagorean Theorem and the properties of
special right triangles)
• when the angle is of the form:
0
• 180 n ± 30
0
0 0
• 180 n ± 60
0
• 180 n ± 45
0
• 90 n
0
11: Circular Functions
• Define the six circular functions
• sine
• cosine
• tangent
• cotangent
• secant
• cosecant
• Find the six circular functions of angles with special values
• Draw the graph of the sine, cosine and tangent functions.
o o
• For the angles, - 2â<x<2â or - 360 <x<360
• Describe the properties of the graphs of the sine, cosine and tangent functions
12: Six Trigonometric Functions and Identities
• Define the six trigonometric functions of an angle in standard position
• Find the values of six trigonometric functions of an angle x, given some conditions
• Solve simple trigonometric equations
• State the fundamental trigonometric identities
13: Triangle Trigonometry
• Demonstrate ability to apply trigonometric functions, laws of sine and cosine to solve problems
• right triangles
• triangles using the Law of Sines
• triangles using the Law of Cosines
Statistics
14: Basic Statistics
• Define the terms statistics, sample, population
• Give the history and importance of the study of statistics
• Use the rules of summation to find sums
• State and explain the different sampling techniques
• Collect statistical data and organize in a table
• Construct frequency distribution tables
• Find the measures of central tendency using ungrouped data
• mean
• median
• mode
• Find the measures of central tendency using grouped data
• mean
• median
• mode
15: Measures of Variability
• Calculate the different measures of variability relative to a given set of data, grouped or
ungrouped
• Range
• Standard deviation
• Give the characteristics of a set of data using the measures of variability
• From a given statistical data, analyze, interpret, draw conclusions, make predictions and make
recommendations/decisions.
You might also like
- General and Specific Competencies in Mathematics IVDocument3 pagesGeneral and Specific Competencies in Mathematics IVCarlito Doringo100% (1)
- Calculus with Analytic Geometry: Rectangular Coordinates and Graphs of EquationsDocument52 pagesCalculus with Analytic Geometry: Rectangular Coordinates and Graphs of EquationsRolando MerleNo ratings yet
- FunctionDocument35 pagesFunctionDae DayNo ratings yet
- Polynomials and Other FunctionsDocument70 pagesPolynomials and Other FunctionsashNo ratings yet
- A Maths Syllabus 2012Document16 pagesA Maths Syllabus 2012utaminiumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PowerpointDocument97 pagesChapter 5 Powerpointapi-199670769No ratings yet
- Precalculus 01 Functions and GraphsDocument63 pagesPrecalculus 01 Functions and GraphssoniaNo ratings yet
- Calculus II Course Syllabus at University of GhanaDocument7 pagesCalculus II Course Syllabus at University of GhanaTennysonNo ratings yet
- Definition-and-Graph-of-Quadratic-FunctionsDocument23 pagesDefinition-and-Graph-of-Quadratic-FunctionsdaryllashleictevesNo ratings yet
- Math 10-4Document95 pagesMath 10-4James Philip GaddiNo ratings yet
- HSC 4 Unit Extension 2 Mathematics Dot Point OutlineDocument117 pagesHSC 4 Unit Extension 2 Mathematics Dot Point OutlineRey Rey100% (4)
- Chapter 1Document25 pagesChapter 1Florence UmlasNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Mathematical Economics and Economic ModelsDocument20 pagesThe Nature of Mathematical Economics and Economic ModelsHilmi KhuluqyNo ratings yet
- 4U Maths HSC SyllabusDocument75 pages4U Maths HSC SyllabusesiotrottersNo ratings yet
- Week003 PresentationDocument54 pagesWeek003 PresentationMikedaniel SalemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Quadratic FunctionsDocument44 pagesChapter 5 - Quadratic FunctionsashNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 FunctionsDocument94 pagesLecture3 FunctionsAmira Abdulshikur JemalNo ratings yet
- 3 Functions Part 2Document22 pages3 Functions Part 2Rabbin CaracasNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Math HL 2001Document6 pagesSyllabus - Math HL 2001Marek KossowskiNo ratings yet
- Lec2 FunctionsDocument75 pagesLec2 FunctionsTaetae ElyenNo ratings yet
- 10th GRADE Chapter-3 Sectıon-1 Quadratic FunctıonsDocument30 pages10th GRADE Chapter-3 Sectıon-1 Quadratic FunctıonssarwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1sidrajaffri72No ratings yet
- Grade 11 General MathematicsDocument5 pagesGrade 11 General Mathematicsjun del rosario78% (9)
- Lesson 4 Rational Function 2Document19 pagesLesson 4 Rational Function 2Geraldine ElisanNo ratings yet
- Quadratics: Prepared by Imani RichardsDocument35 pagesQuadratics: Prepared by Imani RichardsimaniNo ratings yet
- Exponential Functions and Logarithms Topic SummaryDocument3 pagesExponential Functions and Logarithms Topic SummaryPerson GainableNo ratings yet
- Mathematics GR 12 Learner Support - Inverse FunctionsDocument9 pagesMathematics GR 12 Learner Support - Inverse Functionsdonz69914No ratings yet
- Learning Competency DirectoryDocument3 pagesLearning Competency DirectoryRaymond Gorda88% (8)
- Exam Topics To Focus On Grade Ten 1793Document2 pagesExam Topics To Focus On Grade Ten 1793lerafi1309No ratings yet
- Core 1Document11 pagesCore 1Tasfia QuaderNo ratings yet
- 1.calculus I Math111 by DR - Biju V Week1Document68 pages1.calculus I Math111 by DR - Biju V Week1جعفر السلطانNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Functions AA StudentDocument112 pagesGrade 11 Functions AA StudentAnonymous EmjOwXNo ratings yet
- Ebe1133 Lu2 2022Document53 pagesEbe1133 Lu2 2022M.Musirah Abdul HamidNo ratings yet
- Physics - MathematicsDocument33 pagesPhysics - Mathematicsmd asad akhtarNo ratings yet
- Cartesian Product, Relations, GraphsDocument27 pagesCartesian Product, Relations, Graphssunshine1795No ratings yet
- 2023 2025 SyllabusDocument22 pages2023 2025 Syllabus15jirantanin TapNo ratings yet
- Teacher Notes. 304Document10 pagesTeacher Notes. 304Carlos BernabeNo ratings yet
- Topics Entry Test IBEB NonCD Version 2014Document5 pagesTopics Entry Test IBEB NonCD Version 2014YonYonNo ratings yet
- Even OddDocument45 pagesEven OddMohamad HaziqNo ratings yet
- Math 1 CompetenciesDocument3 pagesMath 1 CompetenciesRey Almodiel SolitarioNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument38 pagesReportEdward Raymund CuizonNo ratings yet
- Math - Topic Knowledge RequirementDocument21 pagesMath - Topic Knowledge Requirementrandomsites7No ratings yet
- Microproject PPT (MATHS)Document26 pagesMicroproject PPT (MATHS)BURHANUDDIN RATLAMWALANo ratings yet
- MHF4U Unit 1Document9 pagesMHF4U Unit 1Daniswara HafidzNo ratings yet
- Mat FungsiDocument36 pagesMat FungsimazayaNo ratings yet
- Math Fundamentals: Matrix Operations and Rigid TransformsDocument61 pagesMath Fundamentals: Matrix Operations and Rigid TransformsZaidKhanNo ratings yet
- Functions11 Sec1 1 PDFDocument12 pagesFunctions11 Sec1 1 PDFUS khanNo ratings yet
- Core Competencies - Math Iv Advanced Algebra, Trigonometry and Statistic First Quarter A. FunctionsDocument5 pagesCore Competencies - Math Iv Advanced Algebra, Trigonometry and Statistic First Quarter A. FunctionsFrederichNietszcheNo ratings yet
- Properties of Quadratic FunctionsDocument10 pagesProperties of Quadratic FunctionsCatalin BlesnocNo ratings yet
- 1009 Generalized Hough 1 (Autosaved)Document28 pages1009 Generalized Hough 1 (Autosaved)Robe SolomonNo ratings yet
- 2 1RelationsFunctionsDocument40 pages2 1RelationsFunctionsGehan FaroukNo ratings yet
- AS Maths Specifications 2024Document8 pagesAS Maths Specifications 2024Malik Ammad AnjumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document30 pagesChapter 1kassahun gebrieNo ratings yet
- Prob RV Opt BasicsDocument35 pagesProb RV Opt BasicsjfdweijNo ratings yet
- Graphs, Linear Equations, and FunctionsDocument46 pagesGraphs, Linear Equations, and FunctionsAmit BhararaNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics Graph of FunctionsDocument15 pagesGeneral Mathematics Graph of FunctionsMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- To Graph A Relation, We Need To Plot Each Given Ordered PairDocument11 pagesTo Graph A Relation, We Need To Plot Each Given Ordered PairSungmin KimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Calculus: Archimedes of Syracuse (Bhaskara II (1114 - 1185)Document63 pagesIntroduction To Calculus: Archimedes of Syracuse (Bhaskara II (1114 - 1185)Tai PhamNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Court Allows Reformation of Deed Due to Mistake in Lot NumberDocument1 pageCourt Allows Reformation of Deed Due to Mistake in Lot NumberRey Almodiel SolitarioNo ratings yet
- Daniel So vs. Food Fest Land Ruling on Rebus Sic StantibusDocument1 pageDaniel So vs. Food Fest Land Ruling on Rebus Sic StantibusRey Almodiel SolitarioNo ratings yet
- What Is This Module About?: An Empty Shell A Protist Once Lived inDocument42 pagesWhat Is This Module About?: An Empty Shell A Protist Once Lived inRey Almodiel SolitarioNo ratings yet
- Daniel So vs. Food Fest Land Ruling on Rebus Sic StantibusDocument1 pageDaniel So vs. Food Fest Land Ruling on Rebus Sic StantibusRey Almodiel SolitarioNo ratings yet
- Vertebrates Module: Animals with BackbonesDocument36 pagesVertebrates Module: Animals with BackbonesConnie LopicoNo ratings yet
- Di AdminDocument59 pagesDi AdminRey Almodiel SolitarioNo ratings yet
- Math 1 CompetenciesDocument3 pagesMath 1 CompetenciesRey Almodiel SolitarioNo ratings yet
- Secondary Math - GeometryDocument5 pagesSecondary Math - GeometryRey Almodiel SolitarioNo ratings yet
- Math 2 CompetenciesDocument4 pagesMath 2 CompetenciesRey Almodiel SolitarioNo ratings yet
- IPPD Form 1 PDFDocument2 pagesIPPD Form 1 PDFCHARINA SATONo ratings yet
- Division of Compostela ValleyDocument5 pagesDivision of Compostela ValleyRey Almodiel SolitarioNo ratings yet
- VAK Dominance Test ResultsDocument3 pagesVAK Dominance Test ResultsRey Almodiel SolitarioNo ratings yet
- 2007-2013 MERCANTILE Law Philippine Bar Examination Questions and Suggested Answers (JayArhSals)Document173 pages2007-2013 MERCANTILE Law Philippine Bar Examination Questions and Suggested Answers (JayArhSals)Jay-Arh97% (103)
- Orientation, Rotation, Velocity, and Acceleration and SRM CoordinatesDocument55 pagesOrientation, Rotation, Velocity, and Acceleration and SRM CoordinatesMic SchNo ratings yet
- 40 Enlargements PDFDocument7 pages40 Enlargements PDFAmaanahNo ratings yet
- Vector 3d Questions MathongoDocument3 pagesVector 3d Questions MathongoRutujaNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform Solves PDE ProblemsDocument11 pagesLaplace Transform Solves PDE ProblemsElliot KimNo ratings yet
- Automatic Control - ExercisesDocument140 pagesAutomatic Control - Exerciseshasan bishNo ratings yet
- Math Modern WorldDocument25 pagesMath Modern WorldZsef IryshNo ratings yet
- Satyan L. Devadoss, Rahul Shah, Xuancheng Shao and Ezra Winston - Visibility Graphs and Deformations of AssociahedraDocument18 pagesSatyan L. Devadoss, Rahul Shah, Xuancheng Shao and Ezra Winston - Visibility Graphs and Deformations of AssociahedraSwertyyNo ratings yet
- Integral Equations - 1Document13 pagesIntegral Equations - 1M S MostafaNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus: The Respondent's Email Address (1503438@ub - Edu.ph) Was Recorded On Submission of This FormDocument12 pagesDifferential Calculus: The Respondent's Email Address (1503438@ub - Edu.ph) Was Recorded On Submission of This FormJoseph LantoNo ratings yet
- Project Euler #11: Largest Product in A Grid: This Problem Is A Programming Version of FromDocument2 pagesProject Euler #11: Largest Product in A Grid: This Problem Is A Programming Version of Fromواسل عبد الرزاقNo ratings yet
- Dynamic and Progressive Filter Pruning For Compressing Convolutional Neural Networks From ScratchDocument9 pagesDynamic and Progressive Filter Pruning For Compressing Convolutional Neural Networks From ScratchisharkNo ratings yet
- VISHVESHDocument21 pagesVISHVESHsnowNo ratings yet
- NMOS 2021 Preliminary RoundDocument11 pagesNMOS 2021 Preliminary RoundLookdown Star0% (1)
- 024d06162d1f0-Topic Wise Circle, Function, Limit, Continuity - LR - 11Document9 pages024d06162d1f0-Topic Wise Circle, Function, Limit, Continuity - LR - 11Ravi Ranjan KumarNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Gaussian IntegralsDocument6 pagesEvaluation of Gaussian IntegralsBurakNo ratings yet
- Big O Notation in MathematicsDocument5 pagesBig O Notation in MathematicsrodwellheadNo ratings yet
- IB Mathematics Higher Level Sample QuestionsDocument77 pagesIB Mathematics Higher Level Sample QuestionsOmid Hossain91% (116)
- Unit-1 Real Numbers CoreDocument36 pagesUnit-1 Real Numbers CoreChandra SekharNo ratings yet
- What Information Does The Ability Profiler Provide?Document2 pagesWhat Information Does The Ability Profiler Provide?Mohynnie UsmanNo ratings yet
- ST NDDocument185 pagesST ND137 MOHAMMED SAQIB ANSARINo ratings yet
- A Simplified Derivation and Analysis of Fourth OrdDocument6 pagesA Simplified Derivation and Analysis of Fourth OrdKumaar RanjanNo ratings yet
- A Special Corollary of Zsigmondy S TheoremDocument8 pagesA Special Corollary of Zsigmondy S Theoremfreedom HDNo ratings yet
- 1 Statement and Notations 14 Jul 2020material I 14 Jul 2020 Day 1Document7 pages1 Statement and Notations 14 Jul 2020material I 14 Jul 2020 Day 1khushboo kanwar rajawatNo ratings yet
- Functions (1.1)Document2 pagesFunctions (1.1)teachopensourceNo ratings yet
- Advanced Algebra and Trigonometry Quarter 1: Self-Learning Module 9Document13 pagesAdvanced Algebra and Trigonometry Quarter 1: Self-Learning Module 9Dog GodNo ratings yet
- 2015 G5 ElimDocument7 pages2015 G5 ElimMelyn BustamanteNo ratings yet
- All 1314 Chap10-Grand Canonical EnsembleDocument9 pagesAll 1314 Chap10-Grand Canonical Ensemblegiovanny_francisNo ratings yet
- Differential and Integral Calculus - N Piskunov PDFDocument895 pagesDifferential and Integral Calculus - N Piskunov PDFallstarsamelo87% (30)
- Distribusi MultivariatDocument35 pagesDistribusi MultivariatGita HernawatiNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform Properties GuideDocument14 pagesLaplace Transform Properties GuideMohammed Al-OdatNo ratings yet