Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment No. 6 Combustion Parameter Study of A Single Cylinder Four Stroke Diesel Engine
Uploaded by
Muket AgmasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment No. 6 Combustion Parameter Study of A Single Cylinder Four Stroke Diesel Engine
Uploaded by
Muket AgmasCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment No.
6
Combustion parameter study of a single cylinder four stroke diesel engine
Objectives:
1. To understand the different instrumentation used to study the combustion behavior of a single cylinder four stroke diesel
engine.
2. To understand the basic calculations to obtain different combustion parameters from in-cylinder pressure data.
Experimental Procedure:
Experiment would be conducted for three load conditions (no load, 2 kW and 4 kW) at a constant speed of 1350 rpm
Draw a neat sketch with all major dimensions of the test rig.
Measurement of rpm, load and fuel consumption.
Measurement of manometer reading to calculate air flow rates.
Measurement of temperatures.(inlet, exhaust, cylinder wall and lub oil)
Measurement of in-cylinder pressure date from the acquisition system.
Analysis of the results and report submission:
Each report should include the following
1 Neat sketch of the experimental test rig.
2 Calculate the start of combustion and plot the same with respect to load.
3 Calculate the pressure rise rate(PRR) and heat release rate (HRR) from pressure data.
4 Plot the followings for three different load conditions:
a) Crank angle vs pressure
b) Crank angle vs HRR
c) Crank angle vs PRR
5 Identify the crank angle at which peak pressure, peak PRR, peak HRR and SOC occurs. (for all 3 loads)
6 Make a plot of these four parameters (as in sl. No. 5) with their corresponding angle of occurrences. (for all three loads)
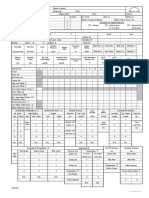
Observation table
Sl. RPM Fuel Load Mano T₁ T₂ T₃ T₄ CO CO₂ HC O₂ NOх Smoke
no Cons. (ppm)
Reading (°C) (°C) (°C) (°C) (%) (%) (%) (ppm ) (opacity)
Curr. Vol.
Mai(ml/m
in) (mm) Intake exhaust Lub oil Cyl. Wall
(Amp) (v)
temp.
Figure: Schematic diagram of experimental test rig.
Kirlosker single Cylinder
Type of engine NI Acquisition System
4-Stroke Diesel engine
Bore(mm)
Computer 102
Fuel
Stroke(mm) 116
tank
Length of connecting rod(mm) 230
Compression ratio Charge 17.5:1
Amplifier 2 1
Maximum power Air Drum 7.4kW@1500 rpm
PP
Table 1: detailed specifications of the engine re
ss
Dynamo
N.B. for calculations and analysis Engine
Loading Panel meter
Encoder Gas Analyzer
PP 1. Pressure Transducer 2. Fuel Injector
re
ss
The heat release rate is usually calculated by the following formula. [ Ref. J.B.Heywood]
Where=Rate of change of heat release w.r.t. crank angle,
Ө-crank angle in radian, = Rate of change of pressure w.r.t. crank angle,
=, V=Volume of cylinder at any position of crank angle,
Instantaneous volume (V) is given as,
Where,= clearance volume, B=Bore, l=Length of connecting rod, a= crank radius, =S/2 , s= stroke length
Air flow rate calculation:
ṁa= ρair×cd×A√ (2g×Δhw× ρw /ρair)
ρair=P/(R×T)……………………………………………………….…............................(4)
Where,
ṁa=mass flow rate of air in kg/sec
ρair=density of air at room temperature in kg/m3
P=atmospheric pressure in N/m2
R= specific gas constant in J/kg.K
T=absolute temperature
cd=coefficient of discharge of orifice (take 0.62 )
A=area of orifice in m2 (take 20 mm as diameter)
Δhw= meno metric head in meter
ρw=density of liquid used in U-tube manometer in kg/m3
Fuel properties: Density of diesel is 0.832 kg/ltr, CV of diesel is 43 MJ/kg
Density of petrol is 0.720 kg/ltr, CV of petrol is 46 MJ/kg
Take the value of as 1.32 for the calculation of HRR
You might also like
- Steam and Gas Tables with Computer EquationsFrom EverandSteam and Gas Tables with Computer EquationsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Experiment No. 6 Combustion Parameter Study of A Single Cylinder Four Stroke Diesel EngineDocument2 pagesExperiment No. 6 Combustion Parameter Study of A Single Cylinder Four Stroke Diesel EngineM RoyNo ratings yet
- Engine ParametersDocument27 pagesEngine ParametersMohsen Mubarak AlboqmiNo ratings yet
- I C EngineDocument3 pagesI C EngineAMIT PRAJAPATINo ratings yet
- Lec 3 - Engine ParametersDocument26 pagesLec 3 - Engine ParametersAneesh UNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 - Engine ParametersDocument26 pagesLec 3 - Engine ParametersGODNo ratings yet
- Trial On Reciprocating.Document12 pagesTrial On Reciprocating.zen tenNo ratings yet
- Engine ParametersDocument27 pagesEngine ParametersTrần Đại NamNo ratings yet
- Engine ParametersDocument27 pagesEngine ParametersAnas AlbasarhNo ratings yet
- Service Performance ME-BDocument2 pagesService Performance ME-BValeriy DomashenkoNo ratings yet
- Engine Nomenclature &performance ParametersDocument47 pagesEngine Nomenclature &performance Parametersahmed jemalNo ratings yet
- Test Data API 610Document4 pagesTest Data API 610Anton PaneNo ratings yet
- Service Performance ME-BDocument2 pagesService Performance ME-BThusitha DalpathaduNo ratings yet
- Refer This Lab Manual For Preparing Your Experimental Work.Document22 pagesRefer This Lab Manual For Preparing Your Experimental Work.Prem ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Expt. 2A - 4-Stroke Diesel Engine-Without DataDocument6 pagesExpt. 2A - 4-Stroke Diesel Engine-Without DataZen RuNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 Performance Parameter of Diesel EngineDocument7 pagesExp 2 Performance Parameter of Diesel EngineShashwat JainNo ratings yet
- MECH 435 - IC Engine Laboratory ExperimentDocument9 pagesMECH 435 - IC Engine Laboratory Experimentdesie yalewNo ratings yet
- Service Performance MEDocument2 pagesService Performance METhusitha DalpathaduNo ratings yet
- 7 PSERJ Volume 17 Issue 2 Pages 41-51Document13 pages7 PSERJ Volume 17 Issue 2 Pages 41-51Ali ElmaihyNo ratings yet
- Energy Auditing and Volumetric Efficiency of A C.I EngineDocument4 pagesEnergy Auditing and Volumetric Efficiency of A C.I EngineSIDDHARTH JAINNo ratings yet
- Investigation of The Prechamber Geometrical Configuration of A Natural Gas Spark Ignition Engine For Cogeneration: Part II. ExperimentationDocument15 pagesInvestigation of The Prechamber Geometrical Configuration of A Natural Gas Spark Ignition Engine For Cogeneration: Part II. ExperimentationEderNo ratings yet
- Test On Variable Speed Petrol EngineDocument7 pagesTest On Variable Speed Petrol EngineAbhishek KhatavkarNo ratings yet
- Knock Characteristics of Dual-Fuel Combustion in Diesel Engines Using Natural Gas As Primary FuelDocument8 pagesKnock Characteristics of Dual-Fuel Combustion in Diesel Engines Using Natural Gas As Primary FuelMohammad SafreedNo ratings yet
- Estimationof Automotive Engine ParametersDocument6 pagesEstimationof Automotive Engine ParametersSajjad MazdakNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 5 Full Load CI EngineDocument3 pagesExperiment No 5 Full Load CI EngineMohamad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Heat Balance Diesel Rope Brake-6Document3 pagesHeat Balance Diesel Rope Brake-6Arup NaskarNo ratings yet
- VCR EngineDocument6 pagesVCR EngineAbNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine Have Been Designed and Build To Deliver Power in The Range From 0.01 ToDocument33 pagesInternal Combustion Engine Have Been Designed and Build To Deliver Power in The Range From 0.01 ToRkd PadsNo ratings yet
- Meng470 ProjectDocument8 pagesMeng470 ProjectAmeer Hamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Data SheetDocument3 pagesTroubleshooting Data SheetRicardo La CruzNo ratings yet
- EngCalcPPC - User GuideDocument25 pagesEngCalcPPC - User GuideJavorsNo ratings yet
- Diesel EngineTestingDocument5 pagesDiesel EngineTestingGorilla GrooveNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic Design of A Single Stage Axi PDFDocument9 pagesAerodynamic Design of A Single Stage Axi PDFMuntather SalahNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic Design of A Single Stage Axi PDFDocument9 pagesAerodynamic Design of A Single Stage Axi PDFAnkur BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Unit IV: Testing of IC Engines & SuperchargingDocument101 pagesUnit IV: Testing of IC Engines & Superchargingsumit ChimkarNo ratings yet
- The Performance Characteristics of ICEDocument6 pagesThe Performance Characteristics of ICEKurdish AliNo ratings yet
- CHAP2Document21 pagesCHAP2Tran Lam PhatNo ratings yet
- DIESEL ENGINE SIMULATION HandoutsDocument12 pagesDIESEL ENGINE SIMULATION Handoutsakshair03No ratings yet
- 26-12 JanoskoDocument9 pages26-12 JanoskoivanNo ratings yet
- Specification Sheet of S6R2-T2MPTK Marine Diesel Engine: Item No. M0209-0012E Date April 2013Document4 pagesSpecification Sheet of S6R2-T2MPTK Marine Diesel Engine: Item No. M0209-0012E Date April 2013Nguyễn Văn CảnhNo ratings yet
- Hilux 2KD GeneralDocument20 pagesHilux 2KD GeneralGil Agostinho Boavida FreitasNo ratings yet
- 1 Cylinder Diesel EngineDocument3 pages1 Cylinder Diesel Engineramniwas123No ratings yet
- 3-Torque and Power Output and Engine EfficiencyDocument18 pages3-Torque and Power Output and Engine EfficiencyAHMADNo ratings yet
- Performance Testing of A Diesel Engine From No Load To Full Load (At Constant Speed) For A SiDocument3 pagesPerformance Testing of A Diesel Engine From No Load To Full Load (At Constant Speed) For A SiNavneet KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Cylinder Petrol Engine Test RigDocument2 pages1 Cylinder Petrol Engine Test Rigramniwas123No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Engine Performance and EfficiencyDocument38 pagesChapter 5 Engine Performance and EfficiencyPham Trung HuyNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual For ICEDocument21 pagesLab Manual For ICEAmey DNo ratings yet
- 2-S Petrol EngineDocument5 pages2-S Petrol EngineAbNo ratings yet
- Me Performance ReportDocument1 pageMe Performance ReportgioNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis and Dynamic Test of Single Cylinder Diesel Engine, Lihua Wang, Qi WangDocument7 pagesPerformance Analysis and Dynamic Test of Single Cylinder Diesel Engine, Lihua Wang, Qi Wangmr.htetwaiaung.mechNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: Title: Trial On Four Stroke Diesel Engine With Dynamometer. ObjectivesDocument10 pagesExperiment No: Title: Trial On Four Stroke Diesel Engine With Dynamometer. ObjectivesAl-hasanNo ratings yet
- IC Engine - EC LabDocument7 pagesIC Engine - EC LabvedNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Fuel Consumption of A Vehicle During European Certification CycleDocument4 pagesCalculation of Fuel Consumption of A Vehicle During European Certification CycleAnum YousafNo ratings yet
- Me6404 Te Even QBDocument32 pagesMe6404 Te Even QBBala NarayanasamyNo ratings yet
- Data Book: Automotive TechnicalDocument1 pageData Book: Automotive Technicalazzclown4uNo ratings yet
- Data Book: Automotive TechnicalDocument1 pageData Book: Automotive Technicalazzclown4uNo ratings yet
- ME23486DDocument1 pageME23486DriomaiorNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis Project 2Document24 pagesNumerical Analysis Project 2Muhammed AhnufNo ratings yet
- Engine Expt 4Document8 pagesEngine Expt 4aashiquear100% (3)
- Me 23219Document1 pageMe 23219riomaiorNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 MHEDocument149 pagesUnit 2 MHEMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- CH 1 River Eng (Desu)Document70 pagesCH 1 River Eng (Desu)Muket Agmas100% (1)
- Unit 2 MHEDocument149 pagesUnit 2 MHEMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-1Document153 pagesUnit 3-1Muket AgmasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4'Document74 pagesChapter 4'Muket AgmasNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Up 9 Probability Note-1 PDFDocument106 pagesCH 1 Up 9 Probability Note-1 PDFMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1Muket AgmasNo ratings yet
- Preface Acknowledgements General Notation 1 2 The Vibrations of Systems Having One Degree of FreedomDocument3 pagesPreface Acknowledgements General Notation 1 2 The Vibrations of Systems Having One Degree of FreedomhenryllecllishNo ratings yet
- Vibration: Fundamentals and PracticeDocument8 pagesVibration: Fundamentals and PracticeMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- 6 Robotics TechnologyDocument75 pages6 Robotics TechnologyMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- 1808 AnsDocument3 pages1808 AnsMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- 3183X IndxDocument4 pages3183X IndxdviryNo ratings yet
- Vibration: Fundamentals and PracticeDocument19 pagesVibration: Fundamentals and PracticeMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- 3183X 07Document91 pages3183X 07henryllecllishNo ratings yet
- 3183X PrefDocument2 pages3183X PrefdviryyNo ratings yet
- Mire VibrationDocument362 pagesMire VibrationMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- General Notation: (HZ), (HZ)Document4 pagesGeneral Notation: (HZ), (HZ)dviryNo ratings yet
- VibrationsDocument9 pagesVibrationsCalin CampeanNo ratings yet
- 3183X BibDocument3 pages3183X BibCalin CampeanNo ratings yet
- Engineering VibrationDocument3 pagesEngineering VibrationJorge PeraltaNo ratings yet
- VibrationDocument30 pagesVibrationRodriguez ArthursNo ratings yet
- Two Degree of Freedom SystemDocument62 pagesTwo Degree of Freedom SystemMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- Response To Harmonic Excitation Forced Vibration: Chapter ThreeDocument57 pagesResponse To Harmonic Excitation Forced Vibration: Chapter ThreeMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- University of Gondar School of Technology Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument184 pagesUniversity of Gondar School of Technology Department of Mechanical EngineeringMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of VibrationDocument91 pagesFundamentals of VibrationMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six Vibration Control: Defn: The Reduction of Unwanted Vibration in A Mechanical or Structural SystemDocument41 pagesChapter Six Vibration Control: Defn: The Reduction of Unwanted Vibration in A Mechanical or Structural SystemMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- Mode of Heat Transfer Due To Macro-Movements!!!Document24 pagesMode of Heat Transfer Due To Macro-Movements!!!Muket AgmasNo ratings yet
- Engineering of A Quick & Comprehensive Phenomenon ..Document17 pagesEngineering of A Quick & Comprehensive Phenomenon ..Muket AgmasNo ratings yet
- A Baby Care Engineering For A Quick & Comprehensive Phenomenon ..Document13 pagesA Baby Care Engineering For A Quick & Comprehensive Phenomenon ..Muket AgmasNo ratings yet
- mcl321 Pmvs 2Document20 pagesmcl321 Pmvs 2Muket AgmasNo ratings yet
- GDPDocument6 pagesGDPBenedetta NardiNo ratings yet
- CivilFEM GeotechnicaDocument107 pagesCivilFEM GeotechnicaRR886No ratings yet
- Operator PanelDocument11 pagesOperator PanelMostafa AlakhliNo ratings yet
- RCC BoxDocument85 pagesRCC Boxabhijeet sahuNo ratings yet
- Ma2 - Acca - Chapter 1Document24 pagesMa2 - Acca - Chapter 1leducNo ratings yet
- 10th PET POW EM 2023 24Document6 pages10th PET POW EM 2023 24rpradeepa160No ratings yet
- CalaDocument13 pagesCalaMorris KwangwareNo ratings yet
- Eagle: This Article Is About The Bird. For Other Uses, See - "Eagles" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument12 pagesEagle: This Article Is About The Bird. For Other Uses, See - "Eagles" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeMegaEkaSetiawanNo ratings yet
- 2011 33 MaintenanceDocument16 pages2011 33 MaintenanceKrishna Khandige100% (1)
- Seminar Report On Hydrogen As The Future FuelDocument63 pagesSeminar Report On Hydrogen As The Future FuelMOHIT MGMNo ratings yet
- Geo PDFDocument13 pagesGeo PDFTezera Mark TmhNo ratings yet
- PHontDawg Vol.2 2007Document8 pagesPHontDawg Vol.2 2007Tanczos AndrasNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Term Examination Cytogenetics 001Document16 pagesPreliminary Term Examination Cytogenetics 001MICHAEL JOHN AGUILARNo ratings yet
- Differential Release of Mast Cell Mediators and The Pathogenesis of InflammationDocument14 pagesDifferential Release of Mast Cell Mediators and The Pathogenesis of InflammationklaumrdNo ratings yet
- The Relationship of Language Development and Nutritional Status of The Child in The Region South of The City of Kediri Region Public HealthDocument12 pagesThe Relationship of Language Development and Nutritional Status of The Child in The Region South of The City of Kediri Region Public Healthdoddyk kurniawanNo ratings yet
- BOSCH FLEXIDOME Multi 7000 - DatasheetDocument8 pagesBOSCH FLEXIDOME Multi 7000 - DatasheetMarlon Cruz CruzNo ratings yet
- Asus Prime b250m Plus RGDocument13 pagesAsus Prime b250m Plus RGRenattech SilvaNo ratings yet
- Spek Dental Panoramic Rotograph EVODocument2 pagesSpek Dental Panoramic Rotograph EVOtekmed koesnadiNo ratings yet
- trivia questions 学生版Document9 pagestrivia questions 学生版YING YUNo ratings yet
- PSR-S700 S900 Lsi CDocument13 pagesPSR-S700 S900 Lsi CAdriano CamocardiNo ratings yet
- Soil Resources Inventory For Land Use PlanningDocument9 pagesSoil Resources Inventory For Land Use PlanningmehNo ratings yet
- Coumadin WarfarinDocument1 pageCoumadin WarfarinSheri490100% (1)
- Calvino - The Daughters of The MoonDocument11 pagesCalvino - The Daughters of The MoonMar BNo ratings yet
- NU632 Unit 4 Discussion CaseDocument2 pagesNU632 Unit 4 Discussion CaseMaria Ines OrtizNo ratings yet
- Dyneema Vs SteelDocument5 pagesDyneema Vs SteelSaurabh KumarNo ratings yet
- ID 7851 Стомат Англ Задачі 1540 English Sem 2Document237 pagesID 7851 Стомат Англ Задачі 1540 English Sem 2acerNo ratings yet
- Principle of Virtual Work and Its ApplicationDocument7 pagesPrinciple of Virtual Work and Its Applicationprem adhikari100% (1)
- (Ronald Weed, John Von Heyking (Eds.) ) Civil ReligiDocument375 pages(Ronald Weed, John Von Heyking (Eds.) ) Civil ReligiskaspeNo ratings yet
- Lab4 F15 Si DiodeDocument15 pagesLab4 F15 Si DiodeJohn MarkNo ratings yet
- Okuma GENOS M560R-V TECHNICAL SHEET (4th Edition)Document79 pagesOkuma GENOS M560R-V TECHNICAL SHEET (4th Edition)Ferenc Ungvári100% (1)